Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Charcoal Production Method
Transféré par
paulh1965Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Charcoal Production Method
Transféré par
paulh1965Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Charcoal production method
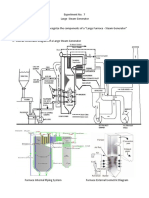
The decision as to the method of charcoal production was the subject of much research. Traditionally charcoal in the UK was made in earth covered mounds (clamps) which had a low conversion rate of approximately 2 ! and was very labour intensive. " lar#e proportion of the wood in the clamp was burnt to fuel the process. The predominant method used in the UK now is the rin# $iln% usin# the same basic method as the clamp% which has a conversion rate in the re#ion of & ! but has a number of drawbac$s includin# that it produces a 'dirty( charcoal contaminated with ash and earth from the #round below the $iln and it also produces hi#h levels of emissions. The contamination is very undesirable for many charcoal niche mar$ets . )etorts% which have been used since the *+ th century% produce charcoal in a fundamentally different process to the $iln or mound method they use an external heat source to brin# the wood up to carbonisation temperature at which point the #ases (syn#as) #enerated by carbonisation can then be burnt to fuel the process. ,n effect the wood is 'coo$ed( in an oven. This #ives very #ood conversion rates ( in excess of -2!) and much #reater control over the process allowin# very hi#h .uality charcoal to be produced. "lso the burnin# of the syn#as reduces air pollution to approx & ! of that produced by rin# $ilns. /e aim to tar#et niche mar$ets as they #ive hi#her returns for a much lower volume of production than barbe.ue charcoal so producin# the hi#hest .uality is paramount therefore we selected the retort as our production method. 0mall scale retorts are prohibitively expensive costin# in excess of 1*2 for the smallest units. This simply wouldn3t have been a reasonable choice for us so after a period of research we built a small retort usin# a 'batch continuous( process. This uses metal drums containin# the wood to be carbonised placed inside an 'oven( which uses waste softwood unsuitable for other uses as fuel to brin# the char#e up to carbonisation temperature whereupon the syn#as #enerated by the char#e is burnt to maintain the carbonisation. 4y usin# multiple metal drums and sta##erin# their insertion into the retort the process is lar#ely self maintainin# as lon# as the drums are removed and replaced at the correct intervals. 5nce the drums are removed they are sealed so that the charcoal can cool down with less ris$ of spontaneous combustion. The retort is ban$ed with earth to act as both insulation and a residual heat store. /e are also able to dry small batches of wood to produce $indlin# and the excess heat could be used for other purposes includin# dryin# lo#s and sawn timber.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- The WelfreughterDocument6 pagesThe Welfreughterpaulh1965Pas encore d'évaluation
- Oak Moss ExtractionDocument22 pagesOak Moss Extractionpaulh1965Pas encore d'évaluation
- Adam Kiln NotesDocument50 pagesAdam Kiln Notespaulh1965Pas encore d'évaluation
- The WelfreughterDocument6 pagesThe Welfreughterpaulh1965Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Anila Stove, Linking Agriculture To EnergyDocument39 pagesThe Anila Stove, Linking Agriculture To EnergyRaymond KatabaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Growing Native Trees From Seed Tree Nursery Production GuideDocument14 pagesGrowing Native Trees From Seed Tree Nursery Production Guidepaulh1965100% (1)
- Typical Charcoal Production TimetableDocument2 pagesTypical Charcoal Production Timetablepaulh1965Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tests For Metal OresDocument3 pagesTests For Metal Orespaulh1965Pas encore d'évaluation
- Oak Moss ExtractionDocument22 pagesOak Moss Extractionpaulh1965Pas encore d'évaluation
- Native Trees - Heights, Habitats and Growing ConditionsDocument1 pageNative Trees - Heights, Habitats and Growing Conditionspaulh1965Pas encore d'évaluation
- Monorail YardingDocument12 pagesMonorail Yardingpaulh1965Pas encore d'évaluation
- Beeswax SoapDocument1 pageBeeswax Soappaulh1965Pas encore d'évaluation
- Monorail YardingDocument12 pagesMonorail Yardingpaulh1965Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bandmill PlanDocument14 pagesBandmill Planpaulh1965100% (1)
- Low Cost Handpumps For Water Extraction From Below Ground Water Tanks - Rainwater HarvestingDocument28 pagesLow Cost Handpumps For Water Extraction From Below Ground Water Tanks - Rainwater HarvestingGreen Action Sustainable Technology GroupPas encore d'évaluation
- Bicycle Windlass Construction Manual (Use With BB-01 "Bailer Bucket")Document2 pagesBicycle Windlass Construction Manual (Use With BB-01 "Bailer Bucket")paulh1965Pas encore d'évaluation
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Catalog: Flanged Safety Relief Valves Series 526 CCDocument12 pagesCatalog: Flanged Safety Relief Valves Series 526 CCSuelen SobrinhoPas encore d'évaluation
- Effect of Torsional and Bending Stress On Machine PartsDocument6 pagesEffect of Torsional and Bending Stress On Machine PartsKartikeya Shukla100% (1)
- RajeshDocument4 pagesRajeshAjay PrajapatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Submission of PudloDocument82 pagesTechnical Submission of PudlotcthomasPas encore d'évaluation
- Dyplast Product InsulationDocument20 pagesDyplast Product InsulationbargezPas encore d'évaluation
- Running Head: Food Test Lab Report 1Document6 pagesRunning Head: Food Test Lab Report 1Jun Hong Tee100% (2)
- The Essential Ingredients in A PVC Formulation AreDocument7 pagesThe Essential Ingredients in A PVC Formulation AreRicky DavisPas encore d'évaluation
- Corrosion and Protection For Steel Pile: Yoshikazu Akira, Dr. EngDocument45 pagesCorrosion and Protection For Steel Pile: Yoshikazu Akira, Dr. EngAnand JadoenathmisierPas encore d'évaluation
- Sandwitched Fly Ash PanelDocument33 pagesSandwitched Fly Ash PanelEdeeksha Shekhawat100% (1)
- Chemistry: Pearson EdexcelDocument36 pagesChemistry: Pearson EdexcelSanti DiazPas encore d'évaluation
- The Analysis and Prevention of Failure in Railway AxlesDocument10 pagesThe Analysis and Prevention of Failure in Railway AxlesAnonymous PufNjgPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Purlins per IS800 and SP38Document2 pagesDesign of Purlins per IS800 and SP38MM93% (29)
- SSPC News Bulletin - July 2020Document26 pagesSSPC News Bulletin - July 2020JlkKumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Dilip Kumar Rajak PhD Research ProfileDocument4 pagesDilip Kumar Rajak PhD Research ProfileDilip RajakPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanical Properties of Engineered Materials Mechanical EngineeringDocument584 pagesMechanical Properties of Engineered Materials Mechanical EngineeringEnis Sevim100% (12)
- Basic Type Heat ExchangerDocument25 pagesBasic Type Heat ExchangerTaifurPas encore d'évaluation
- Heat Transfer: Conservation of EnergyDocument28 pagesHeat Transfer: Conservation of EnergyAhmadJaffarGulfarazPas encore d'évaluation
- Junction-Box-Para Instalaciones EléctricasDocument3 pagesJunction-Box-Para Instalaciones EléctricasOSCAR EDGARDO ARIAS CABEZAPas encore d'évaluation
- Cotton ListDocument22 pagesCotton ListL.N.CHEMICAL INDUSTRYPas encore d'évaluation
- Large Steam GeneratorDocument12 pagesLarge Steam GeneratorChe AguilarPas encore d'évaluation
- Insulating Flange Kits DatasheetDocument4 pagesInsulating Flange Kits DatasheetAndry RimanovPas encore d'évaluation
- Tribological Analysis of Thin Films by Pin-On-Disc Evaluation of Friction PDFDocument10 pagesTribological Analysis of Thin Films by Pin-On-Disc Evaluation of Friction PDFDavid Rafael RamírezPas encore d'évaluation
- DR. BABASAHEB AMBEDKAR TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY MID SEMESTER EXAMDocument2 pagesDR. BABASAHEB AMBEDKAR TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY MID SEMESTER EXAMdhiraj patilPas encore d'évaluation
- FFF SolutionsDocument152 pagesFFF SolutionsMohammedAL-AthariPas encore d'évaluation
- Ceilcote 180 Flakeline+ds+engDocument4 pagesCeilcote 180 Flakeline+ds+englivefreakPas encore d'évaluation
- TCE Babbitt 18391-2Document2 pagesTCE Babbitt 18391-2paulo cesar hernandez mijangosPas encore d'évaluation
- Rizvi New Unit Shed-3 - 68'X111'Document7 pagesRizvi New Unit Shed-3 - 68'X111'shohugPas encore d'évaluation
- Environmental Engineering QuizDocument4 pagesEnvironmental Engineering QuizmikeengineeringPas encore d'évaluation
- Allied Dyna-Flow PipeDocument1 pageAllied Dyna-Flow PipeMendoza Martinez GustaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fsci Assignment ADocument29 pagesFsci Assignment ARaj PrateekPas encore d'évaluation