Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Ques 39
Transféré par
Vijay PrakashCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Ques 39
Transféré par
Vijay PrakashDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
1. The force on a positive charge Q in an electric eld of intensity E is (a) E/q (b) 1/(qE) (c) q/E (d) qE 2.
An electron is accelerated through a potential dierence of V volts. Its nal velocity is (a) (b) (c) (d)
2e V m 2e 2 V m 2e V m 2e 3 V m
3. Current density is dened as (a) Charge per unit volume (b) Current per unit area (c) Current per unit volume (d) Charge per unit area 4. Force experienced by a particle in magnetic eld is (a) q/B (b) q/vB (c) q(vB) (d) qv/B 5. The Oscilloscope which is used to examine very fast signals is (a) sampling (b) dual beam (c) storage (d) dual trace 6. Time base circuit in CRO generates (a) sawtooth (b) triangular wave (c) square wave (d) sine wave 7. The sync control in CRO is used to (a) control the intensity of the beam (b) lock the input signal being viewed (c) focus the beam (d) control the width of the sweep signal 8. A point source of electrons is situated in mutually perpendicular uniform magnetic and electric elds. The magnetic ux density is 0.01 b/m2 and electrical eld strength is 104 v/m. Determine the minimum distance from the same at which an electron with zero velocity will again have zero velocity (a) 36 cm (b) 0.36 cm (c) 3.6 cm (d) 3 cm 9. In a CRT, a pair of deecting plates are 2.0 cm long and are spaced 0.5 cm apart. The distance from the center of the plates to the screen is 24 cm. The nal anode voltage is 1000v. Calculate the displacement produced by deecting voltage of 60 v. (a) 28.8 cm (b) 2.88 cm (c) 0.288 cm (d) 288 cm 10. The electrons emitted from the thermionic cathode of a cathode Ray tube gun are accelerated by a potential of 400 v. The essential dimensions are D = 19.4 cm, l = 1.27 cm and s =0.475 cm. determine SE (a) 65 m/v. (b) 6.5 m/v (c) 0.65 m/v (d) 650 m/v 11. Hole diusion current is proportional to (a) (b) (c) (d)
dp dx dp dt dp dn dn dx
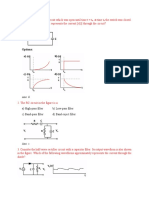
12. In the P-N junction diode the barrier potential VO is given by the relation (a) KT 1n (NA ND /n2 i) (b) KT e NA /nI (c) 1/VT 1n NA ND /n2 i (d) KT 1n n2 i / NA ND 13. The electron concentration in a semiconductor is shown in gure 13. Determine the potential between points x = (0) 0and x = w given nn = 103 . 0
Figure 13 (a) 175 mV (b) -170 mV (c) - 173 mV. (d) 160 mV 14. If A is the area of the junction and ND is donor concentration, the charge Q in the distance W is
D (a) Q= qN WA
(b) Q =
qND W A
(c) Q=qND WA WA (d) Q= NDq 15. The diusion capacitance related to volt equivalent temperature as (a) CD = (b) CD = (c) CD = (d) CD =
V T IO IO F VT IO VT V T IO
16. Each valance electron in an intrinsic semiconductor establishes a (a) metalic bond (b) Thermal energy (c) Coordinate covalent bond (d) covalent bond 17. In any PN junction, the transition capacitance CT varies with respect to W as (a) W2 (b) W (c) W (d) 1/W 18. The following diode is used as voltage regulator. (a) Varicap (b) Tunnel (c) Photo (d) Zener 19. Which of the following has a negative resistance region (a) tunnel diode (b) Schottky diode (c) Opto coupler (d) step-recovery diode 20. The fermilevel in intrinsic semiconductor EF = (a) (b) (c) (d)
Ev 2 Ec 2 Ec +Ev 2 Ec Ev 2
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Differential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksD'EverandDifferential Forms on Electromagnetic NetworksÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Ques 44Document1 pageQues 44Vijay PrakashPas encore d'évaluation
- Ques 30Document1 pageQues 30Vijay PrakashPas encore d'évaluation
- Ques 47Document1 pageQues 47Vijay PrakashPas encore d'évaluation
- Ques 38Document1 pageQues 38Vijay PrakashPas encore d'évaluation
- Edc Ques 4Document1 pageEdc Ques 4Vijay PrakashPas encore d'évaluation
- Ques 48Document1 pageQues 48Vijay PrakashPas encore d'évaluation
- QuesDocument13 pagesQuessanjujoshhi7550Pas encore d'évaluation
- Objective Ques - of 3EI04Document7 pagesObjective Ques - of 3EI04SanjayPas encore d'évaluation
- Elec Assign 2Document5 pagesElec Assign 2paulaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cmda Mock Exam Phy 124Document4 pagesCmda Mock Exam Phy 124tajudeenabdullahaPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 Copies Ncert Part-1 12th PhyDocument7 pages8 Copies Ncert Part-1 12th PhyAbin VarghesePas encore d'évaluation
- WBJEE 2014 Physics Question Paper With SolutionsDocument14 pagesWBJEE 2014 Physics Question Paper With SolutionsLokesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Question Bank For High School Science/Physics/DPMT2005: QuestionsDocument4 pagesQuestion Bank For High School Science/Physics/DPMT2005: QuestionsDhika PutraPas encore d'évaluation
- ch32 PDFDocument14 pagesch32 PDFRodrigo S QuirinoPas encore d'évaluation
- ISRO Electronics and Electrical Questions and Answers With Detailed ExplanationsDocument12 pagesISRO Electronics and Electrical Questions and Answers With Detailed ExplanationsGirdhar Gopal Gautam100% (1)
- ElectromagneticsDocument11 pagesElectromagneticsdhruv111Pas encore d'évaluation
- Model Question Paper Higher Secondary - Second Year - PhysicsDocument6 pagesModel Question Paper Higher Secondary - Second Year - Physicsbindum_9Pas encore d'évaluation
- Quest Tutorials Head Office: E-16/289, Sector-8, Rohini, New Delhi, Ph. 65395439Document6 pagesQuest Tutorials Head Office: E-16/289, Sector-8, Rohini, New Delhi, Ph. 65395439ChennaiSuperkingsPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics PaperDocument20 pagesPhysics Papermohamed sahilPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Practice Paper - 8 Term-1Document11 pagesPhysics Practice Paper - 8 Term-1JatinPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes On 2nd Physics by Asif RasheedDocument7 pagesNotes On 2nd Physics by Asif RasheedAsif Rasheed RajputPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Exam MCQsDocument12 pagesLab Exam MCQsShivansh LaadPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic Wave ExerciseDocument10 pagesElectromagnetic Wave ExerciseAnkit VatsaPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQ ElectrostaticsDocument4 pagesMCQ ElectrostaticsqesuzPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 Copies 3rd Sem 2k19Document7 pages8 Copies 3rd Sem 2k19Abin VarghesePas encore d'évaluation
- Wlxz3nlae9xdwvfrtnvmdvzv2pwr04yoa A Gp&Filename Diode+QueDocument4 pagesWlxz3nlae9xdwvfrtnvmdvzv2pwr04yoa A Gp&Filename Diode+QueerjayprakashpatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Em Waves JeeDocument14 pagesEm Waves JeeTobiramaPas encore d'évaluation
- Comedk 2019 Question Paper With Answer KeyDocument52 pagesComedk 2019 Question Paper With Answer Keyrishi reddyPas encore d'évaluation
- EDCDocument5 pagesEDCGiri KandePas encore d'évaluation
- Aieee 2002 QDocument18 pagesAieee 2002 Qvishal kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Phy Aipmt 2015 QuesDocument6 pagesPhy Aipmt 2015 QuesakalikarPas encore d'évaluation
- SKN Test XiiDocument10 pagesSKN Test XiiKamran AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Q. Mark The Correct AnswerDocument9 pagesQ. Mark The Correct AnswerSana RasulPas encore d'évaluation
- BEE Electrostatic MCQDocument5 pagesBEE Electrostatic MCQAnirud SomasePas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Exam 1Document7 pagesPractice Exam 1425Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mcqs Preparation For Engineering Competitive ExamsDocument17 pagesMcqs Preparation For Engineering Competitive ExamsAnnajan BalochPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment3 PDFDocument6 pagesAssignment3 PDFSuresh ThallapelliPas encore d'évaluation
- PCB - Gujcet 28 03 2024Document14 pagesPCB - Gujcet 28 03 2024Mayursinh rathodPas encore d'évaluation
- PCM - Gujcet 28 03 2024Document14 pagesPCM - Gujcet 28 03 2024Mayursinh rathodPas encore d'évaluation
- Phy 124Document18 pagesPhy 124hardebolzem12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment 6Document6 pagesAssignment 6Suresh ThallapelliPas encore d'évaluation
- Viteee Mock TestDocument24 pagesViteee Mock TestJanaki KrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics XII CH 12 and 13Document2 pagesPhysics XII CH 12 and 13Sahir HemnaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrostatics Practice ProblemsDocument4 pagesElectrostatics Practice ProblemsMohammed Aftab AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQ XII Physics Chapter 2Document31 pagesMCQ XII Physics Chapter 2Mayank ChoudharyPas encore d'évaluation
- BSNL JTO Exam 2006 Question PaperDocument17 pagesBSNL JTO Exam 2006 Question PaperROHITCHOURASIYAPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics 4Document5 pagesPhysics 4gayathri444Pas encore d'évaluation
- Prac FinaleDocument14 pagesPrac FinaleadadafasfasPas encore d'évaluation
- AIEEE Paper 2002 PDFDocument18 pagesAIEEE Paper 2002 PDFKiran Raj RPas encore d'évaluation
- BEE MCQ Unit IIIDocument10 pagesBEE MCQ Unit IIIUmesh PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- AIEEE 2002 Paper: Physics and ChemistryDocument36 pagesAIEEE 2002 Paper: Physics and ChemistryDiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Test For NeetDocument13 pagesPractice Test For NeetMohammed Aftab AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Iit Mains Exam Type Questions of Electrostatics PDFDocument13 pagesIit Mains Exam Type Questions of Electrostatics PDFRupinder Sidhu100% (2)
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyD'EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyPas encore d'évaluation
- Reviews in Computational ChemistryD'EverandReviews in Computational ChemistryAbby L. ParrillPas encore d'évaluation
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsD'EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsPas encore d'évaluation
- Meo Class IV Steam BitsDocument26 pagesMeo Class IV Steam BitsVijay Prakash100% (3)
- Marine Engineering PracticeDocument24 pagesMarine Engineering PracticeVijay PrakashPas encore d'évaluation
- Meo Class IV Steam BitsDocument26 pagesMeo Class IV Steam BitsVijay Prakash100% (3)
- Only Oral Qs Asked in MMDDocument78 pagesOnly Oral Qs Asked in MMDVijay Prakash100% (1)
- NR 10105 Engineering MechanicsDocument13 pagesNR 10105 Engineering MechanicsVijay PrakashPas encore d'évaluation
- Ques 25Document1 pageQues 25Vijay PrakashPas encore d'évaluation