Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Problem 3: Risk For Fluid Volume Deficit Cues Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale Expected Outcomes Subjective Cues
Transféré par
Monchee YusonDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Problem 3: Risk For Fluid Volume Deficit Cues Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale Expected Outcomes Subjective Cues
Transféré par
Monchee YusonDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
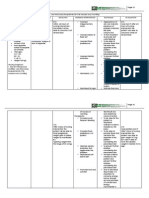
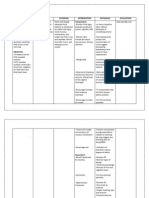
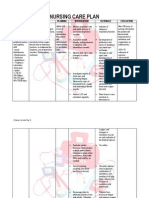
Problem 3: RISK FOR FLUID VOLUME DEFICIT Cues Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Vomiting is defined as the discharge of the
contents of the stomach up into the mouth by force. Vomiting can be an attempt removing toxins from the gastrointestinal tract such as diarrhea, lower gastrointestinal tract. These may lead to fluid volume deficit. Planning Maintain fluid volume at functional level as evidenced by stable vital signs,, good skin turgor and prompt capillary refill. Intervention
>Assess vital signs, noting low blood pressure, severe hypotension, rapid heartbeat, and thread peripheral pulses. >Administer IV fluids, as indicated. Replace blood products; administer plasma expanders, as ordered. >Provide frequent oral as well as eye care >Measure and record intake and output.
Rationale
Risk for fluid Subjective cues: volume deficit matas ne lagnat related to active at 3 days neng fluid loss as mamanyuka ya as associated with verbalized by the vomiting S.O. secondary to dengue fever. Objective cues: Upon assessment the client appeared : - Irritable and weak - Skin is dry and warm to touch - Lips is pale and dry With a temperature of 38.6C Low platelet count
Expected Outcomes >These changes in At the end of the vital signs are nursing care the associated with fluid objectives were volume loss and/or met and the client hypovolemia. achieved normal fluid volume as evidenced by stable vital signs,, > Maintaining the good skin turgor balance of fluid / and prompt electrolyte. capillary refill.
>To prevent injury from dryness
> Accurate documentation helps identify fluid losses/replacement needs and influences choice of interventions.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Problem 3: Deficient Fluid Volume Cues Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesProblem 3: Deficient Fluid Volume Cues Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationRica Licer Chantengco LacandolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ascites, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandAscites, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care PlanDocument28 pagesNursing Care PlanChristine Karen Ang Suarez67% (3)
- Planning (Nursing Care Plans)Document10 pagesPlanning (Nursing Care Plans)Kier Jucar de GuzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- A Simple Guide to Blood in Stools, Related Diseases and Use in Disease DiagnosisD'EverandA Simple Guide to Blood in Stools, Related Diseases and Use in Disease DiagnosisÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (1)
- DengueDocument14 pagesDengueKarenn Joy Concepcion OctubrePas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Mnemonics: The Ultimate Tips and Notes For NursesD'EverandNursing Mnemonics: The Ultimate Tips and Notes For NursesÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- AssessmentDocument2 pagesAssessmentWajiha Esmula TiuPas encore d'évaluation
- A Simple Guide to Celiac Disease and Malabsorption DiseasesD'EverandA Simple Guide to Celiac Disease and Malabsorption DiseasesPas encore d'évaluation
- Casestudy NCP LAURELDocument2 pagesCasestudy NCP LAURELMaria Karren Dela CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP For DehydrationDocument3 pagesNCP For Dehydrationpeter_degamo200025% (4)
- Nursing Care PlansDocument14 pagesNursing Care PlansTels Dela PeñaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP DMDocument21 pagesNCP DMKate ManalastasPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Nursing Care Plan Diabetes MellitusDocument5 pages3 Nursing Care Plan Diabetes MellitusAnnisa Silvera II50% (2)
- Nursing Diagnosis For Diarrhea: 1. Fluid Volume Deficit R / T Excessive DefecationDocument5 pagesNursing Diagnosis For Diarrhea: 1. Fluid Volume Deficit R / T Excessive DefecationJamesyPanilagCadeliña100% (1)
- EdemaDocument2 pagesEdemaVirus50% (2)
- NCPDocument14 pagesNCPclaidelynPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Diagnosis and Nursing Interventions For Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis and Nursing Interventions For Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverThirdy Aquino82% (28)
- NCP DengueDocument3 pagesNCP DengueRichmund Earl Geron100% (1)
- NCPINTRA1Document3 pagesNCPINTRA1Maria Rhodora PetajenPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Goal Intervention Rationale Expected Outcome SubjectiveDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Goal Intervention Rationale Expected Outcome SubjectiveKeith MirasolPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Volume Deficit (Dehydration) Nursing Care Plan - NurseslabsDocument17 pagesFluid Volume Deficit (Dehydration) Nursing Care Plan - NurseslabsA.Pas encore d'évaluation
- NCP DengueDocument4 pagesNCP DengueJanna Carrel Isabedra Rodio100% (2)
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Sto: StoDocument7 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objective Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Sto: StoclarheenaPas encore d'évaluation
- SAMPLE NCP For Diabetes InsipidusDocument3 pagesSAMPLE NCP For Diabetes InsipidusClancy Anne Garcia Naval50% (2)
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument23 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentWendy EscalantePas encore d'évaluation
- Patient's Name: Medical Diagnosis: LBM, Vomiting, Fever Age: 1year Old Gender: MaleDocument3 pagesPatient's Name: Medical Diagnosis: LBM, Vomiting, Fever Age: 1year Old Gender: MaleIsan LutzPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Chief Complaint: IndependentDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Chief Complaint: IndependentTed Cipriano VistaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plans With Nursing DiagnosisDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plans With Nursing DiagnosisLalaine RomeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objectives Interventions Rationale Expected OutcomeDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Objectives Interventions Rationale Expected OutcomeKimberlyLopezBautistaPas encore d'évaluation
- Neonatal Sepsis NCPDocument9 pagesNeonatal Sepsis NCPHollan Galicia100% (1)
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPyupipsjamPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Volume DeficitDocument3 pagesFluid Volume DeficitDan Gerald Alcido SalungaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Goal Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationVher SisonPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Fluid Volume DeficitXtinego89% (9)
- Sickle Cell Anemia Nursing Care PlanDocument6 pagesSickle Cell Anemia Nursing Care PlanArisa Vijungco100% (4)
- Sample NCP Table With Sample Priorotization and Justification of ProblemsDocument8 pagesSample NCP Table With Sample Priorotization and Justification of ProblemsCharm TanyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hypo Vole MiaDocument2 pagesHypo Vole MiaAladil TapsiPas encore d'évaluation
- Diarrhea NCPsDocument10 pagesDiarrhea NCPsJoia De LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument18 pagesCongestive Heart FailureAisha Rashed100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan3Document6 pagesNursing Care Plan3Kristine Artes AguilarPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care PlansDocument6 pagesNursing Care PlansTwobee Kriz LeghidPas encore d'évaluation
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument9 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputChinita Sangbaan75% (4)
- NCP FORM For TetralogyDocument3 pagesNCP FORM For TetralogyGraceMelendres100% (3)
- Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument1 pageDeficient Fluid VolumeSheila ErpeloPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesNCP Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitJeanineReyes44% (9)
- Drug StudyDocument17 pagesDrug Studyjlg513Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment NSG Diagnosis Goal Intervention Implementation EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment NSG Diagnosis Goal Intervention Implementation EvaluationMichelle ErikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetes Mellitus NCPDocument7 pagesDiabetes Mellitus NCPjfgnzls182892% (12)
- DM NCPDocument7 pagesDM NCPMichael Anthony Cardenas Macaballug67% (3)
- AGE NCPDocument4 pagesAGE NCPXane Tañada DiazPas encore d'évaluation
- Independent:: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument2 pagesIndependent:: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveMichelle Palacio-De la CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP PancreatitisDocument2 pagesNCP PancreatitisJeanelle Generoso100% (1)
- NCP Format 3 (CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus Nephropathy)Document4 pagesNCP Format 3 (CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus Nephropathy)John Christopher Celestino100% (10)
- Management of Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument7 pagesManagement of Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverjoycevillamorPas encore d'évaluation
- NCPDocument9 pagesNCPTracy Camille EscobarPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Acute PainDocument1 pageNCP Acute PainMonchee YusonPas encore d'évaluation
- Go DaddyDocument1 pageGo DaddyMonchee YusonPas encore d'évaluation
- Abruptio Placentae Case StudyDocument4 pagesAbruptio Placentae Case StudyMonchee YusonPas encore d'évaluation
- Case+Study AGN MINEDocument66 pagesCase+Study AGN MINEJm BernardoPas encore d'évaluation
- 9 PsychopathologyDocument2 pages9 PsychopathologyMonchee YusonPas encore d'évaluation
- Ineffective Health MaintenanceDocument2 pagesIneffective Health MaintenanceMonchee Yuson67% (6)
- Hands UpDocument2 pagesHands UpMonchee YusonPas encore d'évaluation