Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
ChE 323 Prob Set 1 11 - 30-13
Transféré par
Stephanie JainarTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
ChE 323 Prob Set 1 11 - 30-13
Transféré par
Stephanie JainarDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
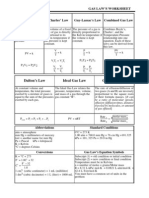
ChE 323 Physical Chemistry Compilation 1: PROPERTIES OF GASES Instructions: This assignment should be done individually. Read pp.
3-23 of the textbook Atkins Physical Chemistry (8th ed.) and answer the questions below. Write your answers on a long-size bondpaper. The answers should be hand-written. I. Concepts: 1. 2. 3. Explain why specifying the temperature, volume, and number of moles of a perfect gas fixes the pressure of that gas. Explain how the perfect gas equation of state arises by combination of Boyles law, Charless law, and Avogadros principle. A third year chemical engineering student relates the following story: I noticed my tires were a bit low and went to the gas station. As I was filling the tires I thought about the kinetic molecular theory (KMT), and I realized that I was increasing both the pressure and volume of the tires as I filled the tires with air. Hmmm, I thought, that goes against what I learned in chemistry, where I was told pressure and volume are inversely proportional. What is the fault of the logic of the student in this situation? Explain why we think pressure and volume to be inversely related (draw pictures and use the KMT). Consider two different containers, each filled with 2 moles of Ne(g). One of the containers is rigid and has constant volume. The other container is flexible (like a balloon) and is capable of changing its volume to keep the external pressure and internal pressure equal to each other. If you raise the temperature in both containers, what happens to the pressure and density of the gas inside each container? Assume a constant external pressure. Draw a qualitative graph to show how the first property varies with the second in each of the following (assume 1 mole of an ideal gas and T in Kelvins): i. PV versus V with constant T ii. P versus T with constant V iii. T versus V with constant P iv. P versus V with constant T v. P versus V with constant T vi. P versus 1/V with constant T vii. PV/T versus P Explain why Daltons law is a limiting law for partial pressures. Explain how the compression factor varies with pressure and temperature and describe how it reveals information about intermolecular interactions in real gases. Explain the significance of critical constants. Explain how the van der Waals equation accounts for critical behavior.
4.
5.
6. 7.
8. 9.
II. Problem-solving: 1. 2. Prove mathematically that the % mole is equal to % volume for ideal gases. State underlying laws and principles. If water is added to magnesium nitride, ammonia gas is produced when the mixture is heated. Mg3N2(s) + 3H2O(l) 3MgO(s) + 2NH3(g) If 10.3 g of magnesium nitride is treated with water, what volume of ammonia gas would be collected at 24 C and 752 mm Hg? Calculate the density of ammonia under these conditions. 3. Calculate the pressure and composition of air on top of Mt. Everest, assuming that the atmosphere has a temperature of 0oC independent of altitude (h = 29141 ft). Assume that air at sea level has a pressure of 1 bar and contains 20% O 2 and 80% N2. Hint: The difference in pressure drop dP between h and h + dh is equal to the mass of the gas between these two levels times g and divided by the area dP gdh . (Ans: 0.333 bar)
o
4.
A 5-ml container with a hole 10 m in diameter is filled with hydrogen. This container is placed in an evacuated chamber at 0oC. How long will it take for 90% of the hydrogen to effuse out? (Ans: 347 s) A compound contains only C, H, and N. A chemist analyzes it by doing the following experiments: Complete combustion of 35.0 mg of compound produced 33.5 mg CO 2 and 41.1 mg H2O. A 65.2-mg sample of the o compound was analyzed for nitrogen by the Dumas method, giving 35.6 mL N2 at 740.0 torr and 25 C. The effusion rate of the compound as a gas was measured and found to be 24.6 mL/min. The effusion rate of argon gas, under identical conditions, is 26.4 mL/min. a. b. What is the molecular mass of the compound? (Ans: 45.7 g/mol) What is the molecular formula of the compound? (Ans: CH6N2)
5.
6.
An impure 60.2 g sample of KNO3 was heated until al of the KNO3 had decomposed. 2 KNO3 (s) 2 KNO2 (s) + O2 (g) The oxygen produced occupied 4.22 L at STP. What was the percent purity of the KNO3 sample? Assume that KNO3 is the only source for the O2. (Ans: 63.3%)
7.
Hot air balloons gain their lift from the lowering of density of air that occurs when the air in the envelope is heated. To what temperature should you heat a sample of air, initially at 340 K, to increase its volume by 14%? (Ans: 373 K) A certain sample of a gas has a volume of 20.00 dm 3 at 0oC and 1.000 atm. A plot of the experimental data of its volume against the Celsius temperature, , at constant p, gives a straight line of slope of 0.0741 dm 3 (oC)-1. From these data alone (without making use of the perfect gas law), determine the absolute zero temperature in oC. Express the van der Waals equation of state as a virial expansion in powers of 1/V m and obtain expressions for B and C in terms of the parameters a and b. The expansion you will need is 1 x 1 1 x x 2 ... . Measurements on argon gave B = 21.7 cm3mol-1 and C = 1200 cm6mol-2 for the virial coefficients at 273 K. What are the values of a and b in the corresponding van der Waals equation of state?
8.
9.
10. A plastic bag is weighed and then filled successively with two gases, X and Y. The following data are gathered: Temperatu Pressure Mass of empty Mass of bag filled Mass of 1.12 L of Vol. of Molar vol. at re bag with gas X air @ conditions bag STP given 0.0oC 1.00 20.77 g 24.97 g 1.30 g 1.12 L 22.4L atm The mass of 1.12 L of gas Y is found to be 6.23 g. Calculate the density and molar mass of the gas. 11. The pressure in interplanetary space is estimated to be of the order of 10 -14 Pa. Assume that only hydrogen atoms are present and that the temperature is 1000K. Assume d = 0.2 nm. Calculate the following: a. b. c. The average number of molecules per cubic centimetre (Ans: 0.724 cm -3) The collision frequency (Ans: 5.92 x 10-10 s-1) The mean free path in miles (Ans: 4.83 x 109 mi)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 1.1 Introduction To Physical Chemistry QuestionsDocument2 pages1.1 Introduction To Physical Chemistry QuestionsWrl RossPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment - States of MatterDocument14 pagesAssignment - States of MatterYash KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Behavior of Pure Substances: Than One Phase, But Each Phase Must Have The Same Chemical CompositionDocument18 pagesBehavior of Pure Substances: Than One Phase, But Each Phase Must Have The Same Chemical CompositionDharmesh PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- LEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET-CHEM 1 q1 Week 4Document8 pagesLEARNING ACTIVITY SHEET-CHEM 1 q1 Week 4Jhude JosephPas encore d'évaluation
- Solucionario Maron Capítulo 1Document8 pagesSolucionario Maron Capítulo 1anon_788159847Pas encore d'évaluation
- Thermodynamics IntroductionDocument13 pagesThermodynamics IntroductionGissela BTPas encore d'évaluation
- UniversityPhysicsVolume2 Ch02Document9 pagesUniversityPhysicsVolume2 Ch02Dominador RomuloPas encore d'évaluation
- Exp 6 Determination of The Molar Volume of A Gas and The Universal Gas ConstantDocument5 pagesExp 6 Determination of The Molar Volume of A Gas and The Universal Gas ConstantMerrene Bright Divino JudanPas encore d'évaluation
- 03 - Ans To Gaseous State Supplemtary QN - 2012Document4 pages03 - Ans To Gaseous State Supplemtary QN - 2012caspersoongPas encore d'évaluation
- Combined Avogadros and Ideal Gas LawsDocument25 pagesCombined Avogadros and Ideal Gas Lawslevi0417Pas encore d'évaluation
- GasesDocument16 pagesGasesAnas MohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- CP Chemistry Unit 6 Gas Stoichiometry ReviewDocument4 pagesCP Chemistry Unit 6 Gas Stoichiometry ReviewRachel PascucciPas encore d'évaluation
- Gases & The Kinetic-Molecular TheoryDocument20 pagesGases & The Kinetic-Molecular TheoryAshley Marie ChildersPas encore d'évaluation
- GasesDocument3 pagesGasesソーダ エドゥアルドPas encore d'évaluation
- Kinetic Theory of Gas: Concept MapDocument7 pagesKinetic Theory of Gas: Concept MapSoham NagPas encore d'évaluation
- Cpp-Gaseous State - RGVDocument2 pagesCpp-Gaseous State - RGVGauri KabraPas encore d'évaluation
- Key Homework 3 11th Gas LawDocument5 pagesKey Homework 3 11th Gas LawTai PanPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Laws LecDocument43 pagesGas Laws LecJune Francis AngPas encore d'évaluation
- 10B KTGDocument16 pages10B KTGgourav gargPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Equations2Document43 pagesGas Equations2api-280572108Pas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet GasesDocument6 pagesWorksheet GasesakladffjaPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Questions For Ch. 5: Name: - Class: - Date: - Id: ADocument23 pagesPractice Questions For Ch. 5: Name: - Class: - Date: - Id: APrem MehrotraPas encore d'évaluation
- GASES Free Response WorksheetDocument4 pagesGASES Free Response WorksheetJJPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 1 - Stoichiometric Relationships - Part 2Document15 pagesTopic 1 - Stoichiometric Relationships - Part 2burcak gecPas encore d'évaluation
- States of Matter Subjective TypeDocument8 pagesStates of Matter Subjective TypePrajesh BiswasPas encore d'évaluation
- PHYCHEMDocument12 pagesPHYCHEM22-00248Pas encore d'évaluation
- AP Chemistry Fr3 Test BankDocument9 pagesAP Chemistry Fr3 Test BankzeustamPas encore d'évaluation
- Gases Practice Quest 2013 AnswersDocument5 pagesGases Practice Quest 2013 Answersethanwong3412Pas encore d'évaluation
- Kinetic Theory of Gases PresentationDocument13 pagesKinetic Theory of Gases PresentationF F ID KingPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermodynamics Practice Problems 3Document13 pagesThermodynamics Practice Problems 3Minh Trương PhúcPas encore d'évaluation
- CHEM 2820 Problem Set 1Document3 pagesCHEM 2820 Problem Set 1Vicente JonathanPas encore d'évaluation
- CHP 10Document4 pagesCHP 10aysekrzm07Pas encore d'évaluation
- Behaviour of Perfect Gas Class XIDocument12 pagesBehaviour of Perfect Gas Class XIKAMAL KANT KUSHWAHAPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical behavior of gases explained by kinetic theory and gas lawsDocument12 pagesPhysical behavior of gases explained by kinetic theory and gas lawsPAUL KOLEREPas encore d'évaluation
- 1Document2 pages1Bình TĩnhPas encore d'évaluation
- Gaseous State Iit NumericalsDocument5 pagesGaseous State Iit NumericalssamareshcmondalPas encore d'évaluation
- ThermodynamicDocument12 pagesThermodynamicWanMardziyyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise GasesDocument4 pagesExercise GasesAri AdiantariPas encore d'évaluation
- Date Planned: - / - / - Daily Tutorial Sheet Expected Duration: 90 Min Actual Date of Attempt: - / - / - Level-0 Exact DurationDocument55 pagesDate Planned: - / - / - Daily Tutorial Sheet Expected Duration: 90 Min Actual Date of Attempt: - / - / - Level-0 Exact DurationSickdanPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Exam H Rev QudsDocument18 pagesFinal Exam H Rev QudsItchyBallsPas encore d'évaluation
- Ejercicios de La Primera Ley de TermodinámicaDocument12 pagesEjercicios de La Primera Ley de TermodinámicaGissela BTPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 9Document9 pagesUnit 9sabirdxb107Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Laws 201314 Review Sheet W Answers 2Document4 pagesGas Laws 201314 Review Sheet W Answers 2Leighton RowlandPas encore d'évaluation
- States of MatterDocument5 pagesStates of MatterVipul GoelPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem 181 Chemistry of GasesDocument15 pagesChem 181 Chemistry of GasesJoey PoolePas encore d'évaluation
- C2740 Tutorial 1Document6 pagesC2740 Tutorial 1LitebohoPas encore d'évaluation
- Question PART 2 (2023)Document6 pagesQuestion PART 2 (2023)01khanh26Pas encore d'évaluation
- GLWS9Document6 pagesGLWS9Vince HernándezPas encore d'évaluation
- IDEAL GAS LAWS AND EQUATIONSDocument6 pagesIDEAL GAS LAWS AND EQUATIONSRica ChavezPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Laws Practice SheetDocument4 pagesGas Laws Practice SheetJensen Ryan LimPas encore d'évaluation
- GASEOUS STATE EXAMDocument8 pagesGASEOUS STATE EXAMGadde Gopala KrishnaPas encore d'évaluation
- 5.states of Matter AK 2018-19Document12 pages5.states of Matter AK 2018-19XXXPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Laws I SP 1617 (PreAP)Document3 pagesGas Laws I SP 1617 (PreAP)Nikhil Singh100% (1)
- CH 5 Practice ProblemsDocument16 pagesCH 5 Practice Problemsjaskaran singhPas encore d'évaluation
- Kinetic Theory of GasesDocument15 pagesKinetic Theory of Gasesmuddu00007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Chemistry Course for EngineersDocument78 pagesPhysical Chemistry Course for EngineersAbinow SPas encore d'évaluation
- Molecular Physics, Thermodynamics, Atomic and Nuclear Physics: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsD'EverandMolecular Physics, Thermodynamics, Atomic and Nuclear Physics: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (4)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterD'EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Time Spent Trading 1-2 Hours/DayDocument10 pagesTime Spent Trading 1-2 Hours/DayStephanie JainarPas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Freedom Through ForexDocument143 pagesFinancial Freedom Through Forexhulupat100% (5)
- Financial Freedom Through ForexDocument143 pagesFinancial Freedom Through Forexhulupat100% (5)
- Powerpoint Slides For Incident at MoralesDocument29 pagesPowerpoint Slides For Incident at MoralesShaun Menezes0% (1)
- Ethical TheoriesDocument30 pagesEthical TheoriesKommisetty MurthyrajuPas encore d'évaluation
- Demo TradeDocument1 pageDemo TradeStephanie JainarPas encore d'évaluation
- GATE Chemical Question Paper 2013 PDFDocument16 pagesGATE Chemical Question Paper 2013 PDFAayush AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Article2.Sections 13-14-15Document10 pagesArticle2.Sections 13-14-15Stephanie JainarPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes On Engineering EthicsDocument15 pagesNotes On Engineering Ethicsjunaidkhattak10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Adsorption of Natural Org Matter by Carbon Nanotubes (Liu, Et Al)Document7 pagesAdsorption of Natural Org Matter by Carbon Nanotubes (Liu, Et Al)Stephanie JainarPas encore d'évaluation
- Process Control FundamentalsDocument294 pagesProcess Control FundamentalsSana KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- CASE 7 Case Study On Process Safety - Ammonia Plant (CDLT)Document6 pagesCASE 7 Case Study On Process Safety - Ammonia Plant (CDLT)Stephanie JainarPas encore d'évaluation
- Study Guide On PolymersDocument6 pagesStudy Guide On PolymersStephanie JainarPas encore d'évaluation
- Network Analysis Tutorial Answers and Formulas GuideDocument6 pagesNetwork Analysis Tutorial Answers and Formulas GuideStephanie JainarPas encore d'évaluation
- ChE 428 Slide 3 - ToxicologyDocument35 pagesChE 428 Slide 3 - ToxicologyStephanie JainarPas encore d'évaluation
- AldehydesDocument3 pagesAldehydesStephanie JainarPas encore d'évaluation
- NSCPDocument53 pagesNSCPZaela EfronPas encore d'évaluation
- AGA8Document6 pagesAGA8Bled GegaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electro Magnetic Induction: 1 Mark QuestionsDocument6 pagesElectro Magnetic Induction: 1 Mark QuestionsRSPas encore d'évaluation
- Kelompok 4 Proses Transfer 2019Document7 pagesKelompok 4 Proses Transfer 2019Retnaning Setyo RiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Stability of ColumnsDocument45 pagesStability of ColumnsjemnesPas encore d'évaluation
- I Structural Terminologies: Architectural Preboard ExaminationDocument41 pagesI Structural Terminologies: Architectural Preboard ExaminationAr Agner O. BatuigasPas encore d'évaluation
- Symmetry and Group Theory For Computational Chemistry ApplicationsDocument12 pagesSymmetry and Group Theory For Computational Chemistry ApplicationsHocine el khaoudi enyouryPas encore d'évaluation
- A Comparative Study of MHD Flow Analysis in A Porous Medium by Using Differential Transformation Method and Variational Iteration MethodDocument15 pagesA Comparative Study of MHD Flow Analysis in A Porous Medium by Using Differential Transformation Method and Variational Iteration MethodRoberticoZeaPas encore d'évaluation
- Beam NotchingDocument3 pagesBeam NotchingMary Graçe ÇanoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Maxwell Indonesia 2Document20 pagesMaxwell Indonesia 2arrowzyPas encore d'évaluation
- MARITIME GEOTECHNICS I HOMEWORK #2 TOPICS: SHALLOW FOUNDATIONSDocument5 pagesMARITIME GEOTECHNICS I HOMEWORK #2 TOPICS: SHALLOW FOUNDATIONSWilliams AnthonyPas encore d'évaluation
- Solutions at Axis of SymmetryDocument48 pagesSolutions at Axis of SymmetryAhmedMahirPas encore d'évaluation
- EtoosDocument3 pagesEtoosmail2sgarg_841221144Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dislocations in Materials: An IntroductionDocument94 pagesDislocations in Materials: An IntroductionManjeet SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Pushover Analysis of BridgeDocument10 pagesPushover Analysis of BridgeDjordje LadjinovicPas encore d'évaluation
- MothballDocument1 pageMothballKristine Ann100% (1)
- Strength of Materials: D. K. SinghDocument923 pagesStrength of Materials: D. K. SinghAyoub75% (4)
- Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument9 pagesMultiple Choice QuestionsAniruddh RaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Composite Structures Roeder 1999Document8 pagesComposite Structures Roeder 1999BrunoAmorimPas encore d'évaluation
- Major Project Eco Air Clooer System PDFDocument14 pagesMajor Project Eco Air Clooer System PDFVinayPas encore d'évaluation
- Concrete Structure Design Conference AgendaDocument5 pagesConcrete Structure Design Conference AgendaSophia VarshiniPas encore d'évaluation
- Applied Partial Differential Equations: January 2003Document129 pagesApplied Partial Differential Equations: January 2003BryanAngamarcaPas encore d'évaluation
- Subject CSE40418: Advanced Structural Analysis: Phase I: Structural DynamicsDocument13 pagesSubject CSE40418: Advanced Structural Analysis: Phase I: Structural DynamicsEngibearPas encore d'évaluation
- Mit S1Document29 pagesMit S1maps1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Calculate Degree of Static and Kinematic Indeterminacy for Beams and FramesDocument6 pagesCalculate Degree of Static and Kinematic Indeterminacy for Beams and Framesvipin soniPas encore d'évaluation
- Are Tier Building Column SplicesDocument2 pagesAre Tier Building Column SplicesKarthi SriPas encore d'évaluation
- FEM - Solid - Mechanics - 2022-2023Document52 pagesFEM - Solid - Mechanics - 2022-2023houda houbanPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 1 Dorb001 Bsce3aDocument16 pagesGroup 1 Dorb001 Bsce3aJan TheGamerPas encore d'évaluation
- Structural Dynamics Spring Mass SystemDocument57 pagesStructural Dynamics Spring Mass Systemrobliutpg.com.auPas encore d'évaluation
- Module-3: G Madegowda Institute of Technology (Gmit), Bharathinagara Page 1Document10 pagesModule-3: G Madegowda Institute of Technology (Gmit), Bharathinagara Page 12BA19CV059 Rakshita SarangmathPas encore d'évaluation