Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Lesson 6 Egyptian Gods Cards
Transféré par
Brett Michael ChinchenCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Lesson 6 Egyptian Gods Cards
Transféré par
Brett Michael ChinchenDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
God: Amun Appearance: Man with a ram-head staff and wearing an ostrich plumed hat.
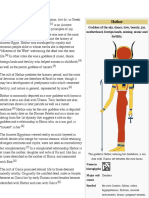
Goddess: Bastet Appearance: Woman with the head of a cat 17 Goddess: Hathor 'House of Horus' Appearance: Woman with the ears of a cow and a headdress of horns and a sun disk.
29 Amun was one of the most powerful gods in ancient Egypt. 28 At the height of Egyptian civilisation he was called the 'King of the Gods'. 24 Amun was important throughout the history of ancient Egypt. 30 When Amun was combined with the sun god Ra he was even more powerful. He was then called Amun-Ra. 16 A large and important temple was built at Thebes to honour Amun.
23 Bastet was a protective goddess. 24 Bastet was usually seen as a gentle protective goddess. However, she sometimes appeared with the head of a lioness to protect the Pharaoh in battle. 20 The cat was a symbol of Bastet. The ancient Egyptians made many statues of cats like this one to honour Bastet. 21 Bastet was one of the daughters of the sun god, Ra. 19 A great temple was built in her honour at Bubastis in the Delta.
27 Hathor was a protective goddess. She was also the goddess of love and joy. 23 Hathor was the wife of Horus, and was sometimes thought of as the mother of the pharaoh. 18 Hathor was connected with foreign places and materials. For instance, Hathor was the goddess of the desert and the turquoise mines in the Sinai. 14 A large temple was built to honour Hathor at Dendera.
God: Khnum Appearance: Man with the head of a curlyhorned ram
Goddess: Nut Appearance: Woman whose body arches across the sky, wearing a dress decorated with stars. 25 Nut was the sky-goddess, whose body created a vault or canopy over the earth. 16 Nut was the sister/wife of Geb, the god of the earth. She was also the mother of Isis, Osiris, Nepthys and Seth. 18 The ancient Egyptians believed that at the end of the day, Nut swallowed the sungod, Ra, and gave birth to him again the next morning.
17 God: Ra-Horakhty 'Horus in the Horizon' Appearance: Man with the head of a hawk, with a sun disk headdress. 29 Ra-Horakhty was a combination of the gods Horus and Ra. 27 Horus was a god of the sky, and Ra was the god of the sun. Thus, Ra-Horakhty was thought of as the god of the rising sun.
28 Khnum was a creator god, and a god of the innundation (The yearly flooding of the Nile River). 26 Khnum was a creator-god, moulding people on a potter's wheel. Since potters used Nile mud,
God: Thoth Appearance: A man with the head of an ibis holding a writing palette 27 Thoth was the god of writing and knowledge. 24 The ancient Egyptians believed that Thoth gave them the gift of hieroglyphic writing God: Anubis Appearance: Man with a jackal head 19 Anubis was the god of embalming and the dead. 10 Since jackals were often seen in cemeteries, the ancient Egyptians believed that Anubis watched over the dead.
God: Shu 'He Who Rises Up' Appearance: Man wearing a headdress with feathers.. 25 Shu was the god of the air. 17 Shu held up the figure of Nut so that the earth and the sky were separated.
28 Thoth served as a mediating power, especially between good and evil, making 9 Anubis was the god who helped to embalm sure neither had a decisive victory over Osiris after he was killed by Seth. Thus,
the other. 30 Without his words, the Egyptians believed, the gods would not exist. His power was unlimited in the Underworld and rivaled that of Ra and Osiris. 24 The Egyptians credited him as the author of all works of science, religion, philosophy, and magic. Anubis was the god who watched over the process of mummifying people when they died. 11 Priests often wore a mask of Anubis during mummification ceremonies.
God: Horus 'The One Far Above' God: Bes 12 Appearance: A Dwarf with lion and human features Appearance: Man with the head of a hawk 24 Horus was a god of the sky. 28 He is probably most wellknown as the protector of the ruler of Egypt. The Egyptians believed that the pharaoh was the 'living Horus'. 11 The ancient Egyptians had many different beliefs about the god Horus. One of the most common beliefs was that Horus was the son of Isis and Osiris. 6 After Osiris was murdered by his brother Seth, Horus fought with Seth for the throne of Egypt. In this battle, Horus lost one of his eyes. 28 The eye was restored to him and it became a symbol of protection. After this battle, Horus was chosen to be the ruler of the world of the living. Goddess: Ma'at Appearance:Woman with a feather on her head. 29 Ma'at was the goddess of truth, justice and harmony. She was associated with the balance of things on earth. 8 Ma'at was the daughter of the sun god Ra. 6 Pharaohs are frequently shown in wall reliefs making an offering of Ma'at to the gods-showing that they are preserving harmony and justice on earth. 5 The vizier who was in charge of the law courts was known as the 'priest of Ma'at'.
Bes was the protector of pregnant women, newborn babies and the family. 7 The ancient Egyptians also believed that Bes protected against snake and scorpion bites. 5 Amulets of Bes were popular at all levels of Egyptian society.
God: Osiris Appearance: A mummified man wearing a white cone-like headdress with feathers
17 Godess: Sekhmet 'The Powerful One' Appearance: Woman with the head of a lioness
God: Sobek Appearance: Man with the head of a crocodile and a headdress of feathers and a sun-disk.
28 Osiris was the god of the dead, and ruler of the underworld. 25 Osiris was the brother/husband of Isis, and the brother of Nepthys and Seth. He was also the father of Horus. 24 As well as being a god of the dead, Osiris was a god of resurrection and fertility. 26 In fact, the ancient Egyptians believed that Osiris gave them the gift of barley, one of their most important crops. 16 A large temple was built to honour Osiris at Abydos.
29 Sekhmet was the goddess of war. She was also a goddess of healing. 24 Sekhmet also is a sun goddess, sometimes called the daughter of the sun god Ra. 22 To pacify and calm Sekhmet, festivals were celebrated at the end of battle, so that the destruction would come to an end. 24 During an annual festival held at the beginning of the year, a festival of intoxication, the Egyptians danced and played music to soothe the wildness of the goddess and drank great quantities of wine.
28 Sobek was a Nile god. 27 Sobek was connected with the Nile, and protected the king. Live crocodiles were kept in pools at temples built to honour Sobek. When they died, they were mummified and buried in special animal cemeteries 18 Egyptians who worked or travelled on the Nile hoped that if they prayed to Sobek, the crocodile/Nile god, he would protect them from being attacked by crocodiles. 23 Sobek was considered the army's patron, as a representation of strength and power.
God: Aten God: Geb
Goddess: Isis Appearance: Woman with headdress in the shape of a throne A pair of cow horns with a sun disk.
Appearance: A sun disk with rays which end in hands. Aten is interesting as he is not normally shown with a human form but rather as rays of the sun. 28 Aten was a form of the sun god Ra.
Appearance: Man lying down below the arch of the sky goddess Nut. 15 Geb was the god of the earth.
29 During the reign of Akhenaten, the Aten 18 Geb was the husband and brother of the sky goddess Nut. He was also the father of was made the 'king' of the gods. Osiris, Isis, Nepthys and Seth. 29 In a way Aten replaced all the other gods as some Egyptians worshipped only him, (Monotheism one god like in Islam, Christianity and Judaism unlike most ancient Egyptians who believed in Polytheism many gods). 22 When Seth and Horus fought for the throne of Egypt, Geb made Horus the ruler of the living. 27 The ancient Egyptians believed that earthquakes were Geb's laughter.
23 Isis was a protective goddess. She used powerful magic spells to help people in need. 25 Isis was the wife of Osiris and the mother of Horus. Isis was very important. Since each pharaoh was considered the 'living Horus', 24 Isis is often shown holding Horus on her lap. Isis is associated with thrones because her lap was the first 'throne' that Horus sat upon. 8 A commonly worn amulet was the 'Isis knot' - a symbol of protection. 17 A temple was built to honour Isis at Philae.
Goddess: Nephthys 'Lady of the Mansion' Appearance: Woman with headdress showing her name in hieroglyphs.
God: Ptah Appearance: Man wrapped in a tight white cloak carrying a staff.
Goddess: Seshat Appearance: Woman wearing a panther skin dress and a star headdress
22 Nephthys was a protective goddess of the dead. 18 Nephthys was the sister of Isis and Osiris, and the sister/wife of Seth. Nephthys was also the mother of Anubis. 7 She is often shown on coffins, or in funerary scenes.
14 Ptah was the god of craftsmen. 28 In one creation myth Ptah was a creator god. He spoke the words and the world came into being. 15 He is the husband of Sekhmet and the father of Nefertum. 11 He was also regarded as the father of the sage Imhotep (a mortal). 23 Seshat was the goddess of wisdom, knowledge, and writing. 28 She was seen as a scribe and record keeper, and is credited with inventing writing. 22 She also became identified as the goddess of architecture, astronomy, astrology, building, mathematics, and surveying. These are all professions that relied upon expertise in her skills.
23 Goddess: Tawaret 'The Great One' Appearance: Head of a hippopotamus with the arms and legs of a lion, the back and tail of a crocodile, and the breasts and stomach of a pregnant woman. 27 Tawaret was a goddess who protected women during pregnancy and childbirth. 24 Many of the gods and goddesses in ancient Egypt had temples built to honour them. Other gods and goddesses like Tawaret and Bes were worshipped by people in their own homes. 6 Many women wore Tawaret amulets, or kept them in their homes.
God: Nefertum Appearance: Nefertem a man with a cluster of lotus flowers upon his head, but sometimes he has the head of a lion. He is also often shown standing upon the 29 God: Atum 'The All' or 'Perfection' Appearance: Man with the double crown
back of a lion.
21 An ancient Egyptian god identified with the lotus, but he also personified some form of the morning sun. He was often considered the most handsome and beautiful of all the gods. 18 He is a son of Ptah and Sakhmet or Bastet. He represents the sun-god in the legend which made him burst forth from a lotus. ? Ancient Egyptians often carried small statuettes of him as good-luck charms.
29Atum was a creator god. 30 The ancient Egyptians believed that Atum was the first god to exist on earth. 29 The ancient Egyptians believed that Atum rose from the waters of chaos (Nun) and created all the gods. Atum was therefore a very important god.
15 God: Hapy or Hapi Not to be confused with a god of the same name who was the son of Horus and had a baboon head as depicted on the canopic jar that lungs would be placed in during mummification. 17 Appearance: Man with a pot belly, shown with water plants, sometimes shown as a pair of blue genies holding up the upper and lower Nile. 27 Hapy was the god of the innundation (The yearly flooding of the Nile River). 29 Hapy was especially important to the ancient Egyptians because he brought the flood every year. 28 The flood deposited rich silt on the banks of the Nile, allowing the Egyptians to grow crops.
God: Khepri 'He Who is Coming into Being' Appearance: Man with the head of a scarab.
God: Nun
Appearance: Man carrying a bark (A boat (also spelled 'barque'). 29 According to an ancient Egyptian creation myth, Nun was the waters of chaos (The state of being without order or organization). 29 Nun was the only thing that existed on Earth before there was land. Then, the first land (in the form of a mound) rose out of Nun. 29 Nun was also associated with the chaos that existed at the edges of the universe.
26 Khepri was a god of creation, the movement of the sun, and rebirth. 23 The scarab beetle lays its eggs in a ball of dung. Then, it rolls the ball along the ground until the young beetles are ready to hatch. When the young beetles are ready, they crawl out of the ball. The ancient Egyptians believed that the beetles just appeared from nowhere- as they believed that their creator god had appeared from nowhere. Thus, they thought that the scarab beetle was special. 26 In certain creation stories, Khepri is connected with the god Atum. He is also connected with the sun god Ra who pushed the sun through the sky every day.
27 God: Ra 'Sun' Appearance: Man with hawk head and headdress with a sun disk. 30 Ra was the sun god. He was the most important god of the ancient Egyptians. 27 The ancient Egyptians believed that Ra was swallowed every night by the sky goddess Nut, and was reborn every morning. 25 The ancient Egyptians also believed that he travelled through the underworld at night. In the underworld, Ra appeared as a man with the head of a ram. 30 When Ra was combined with Amun, king of the gods he was even more powerful. He was then called Amun-Ra.
God: Seth Appearance: Man with the head of a 'Seth animal' (unidentifiable)
Goddess: Tefnut Appearance: Woman with the head of a lioness.
29 Seth was the god of chaos. 28 Seth represented everything that threatened harmony in Egypt. 18 He was the brother of Osiris and Isis, as well as the brother/husband of Nepthys. 28 He murdered his brother Osiris, then battled with his nephew Horus to be the ruler of the living. 14 At certain times in the history of ancient Egypt, Seth was associated with royalty.
23 Tefnut was the goddess of moisture. 22 She was the wife of Shu and the mother of Nut (the sky) and Geb (the earth). 22 When in a rage she would travel to Nubia.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Ancient Egyptian Doctrine of the Immortality of the SoulD'EverandThe Ancient Egyptian Doctrine of the Immortality of the SoulPas encore d'évaluation
- The Burden of Isis: Being the laments of Isis and NephthysD'EverandThe Burden of Isis: Being the laments of Isis and NephthysÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Egyptian Mythology: Deities, Sphinxes, and Stories from Ancient EgyptD'EverandEgyptian Mythology: Deities, Sphinxes, and Stories from Ancient EgyptÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Dhwty Aka THTH Aka YhvhDocument6 pagesDhwty Aka THTH Aka YhvhNanya Faatuh El100% (2)
- GodsDocument4 pagesGodsjamessonian100% (4)
- The Resurrection of King TutDocument33 pagesThe Resurrection of King TutBaalim HotepPas encore d'évaluation
- Hermopolis The Ennead of Heliopolis: Cult Center: LinksDocument18 pagesHermopolis The Ennead of Heliopolis: Cult Center: LinksSyed Adnan Hussain ZaidiPas encore d'évaluation
- Eye of HorusDocument4 pagesEye of HorusNabil RoufailPas encore d'évaluation
- NutDocument18 pagesNutmaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Women in Ancient KemetDocument11 pagesWomen in Ancient Kemetdarrell_nichols_4100% (2)
- Goddess MaatDocument12 pagesGoddess MaatTemple of the starsPas encore d'évaluation
- Amun RaDocument6 pagesAmun RarkamundimuPas encore d'évaluation
- An Introduction To Reproduction in Pharaonic EgyptDocument7 pagesAn Introduction To Reproduction in Pharaonic EgyptfloresmariPas encore d'évaluation
- Book of The GoddessDocument70 pagesBook of The Goddessshtaten100% (2)
- Het Heru in The Coffin TextDocument6 pagesHet Heru in The Coffin TextAankh Benu50% (2)
- Depictions of The Sky-Goddess NutDocument18 pagesDepictions of The Sky-Goddess NutRui PereiraPas encore d'évaluation
- Sobek: The Idolatrous God of Pharaoh Amenemhet IIIDocument7 pagesSobek: The Idolatrous God of Pharaoh Amenemhet IIImontag2100% (1)
- Why The Neteru of Ancient EgyptDocument25 pagesWhy The Neteru of Ancient EgyptNectanebusPas encore d'évaluation
- Egyptian Gods PDFDocument4 pagesEgyptian Gods PDFMaahes Cultural Library100% (1)
- 33 Year Diamond by Raah SirusDocument10 pages33 Year Diamond by Raah SirusG.n.o.d.e.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Het Heru (Hathor)Document8 pagesHet Heru (Hathor)Alison_VicarPas encore d'évaluation
- On The Heels of The Wandering Goddess THDocument34 pagesOn The Heels of The Wandering Goddess THAmal MohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- 88 Laws For Iron Level InitiatesDocument51 pages88 Laws For Iron Level InitiatesCheryl Anne Golden0% (1)
- Mandala of The Denderah ZodiacDocument18 pagesMandala of The Denderah ZodiacJohn Victor100% (4)
- The Celestial Cow Goddess Mehet-WeretDocument12 pagesThe Celestial Cow Goddess Mehet-Weretmai refaatPas encore d'évaluation
- The Zodiac of Dendara EgyptDocument81 pagesThe Zodiac of Dendara EgyptEce Ayvaz100% (1)
- Axioms of Kemet Instructions For Today From Ancient EgyptDocument63 pagesAxioms of Kemet Instructions For Today From Ancient Egyptch0zen_1100% (2)
- The Many Aspects of Hathor: A. A.1 The Cult of The Mother GoddessDocument48 pagesThe Many Aspects of Hathor: A. A.1 The Cult of The Mother GoddessMia Kristine100% (2)
- Priestesses of Hathor Their FunctionsDocument28 pagesPriestesses of Hathor Their FunctionsninzuPas encore d'évaluation
- Thoth Hermes Mercuri UsDocument3 pagesThoth Hermes Mercuri UsMihaita SprinceanaPas encore d'évaluation
- EGYPT LIST of GODS PDFDocument13 pagesEGYPT LIST of GODS PDFReubenPas encore d'évaluation
- Ancient Star MapsDocument18 pagesAncient Star MapsmaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Egyptian God of Emerging Land After Floodwaters RecedeDocument5 pagesEgyptian God of Emerging Land After Floodwaters RecedeKoop Da VillePas encore d'évaluation
- Angelish: The Language of Creation - AngelynxDocument21 pagesAngelish: The Language of Creation - AngelynxHennie Namløs ThornePas encore d'évaluation
- Instuctions of Ptah HoptepDocument10 pagesInstuctions of Ptah HoptepWalid Hesham GhareebPas encore d'évaluation
- Egyptian Amduat, Isis Raising The DjedDocument13 pagesEgyptian Amduat, Isis Raising The DjedDazzlestar100% (3)
- Auset-Ausar or Isis-Osiris PDFDocument5 pagesAuset-Ausar or Isis-Osiris PDFBrett Blanks100% (1)
- The Calendars of Ancient Egypt: BCE BCEDocument22 pagesThe Calendars of Ancient Egypt: BCE BCERobert DavisPas encore d'évaluation
- Ma'atDocument7 pagesMa'atres49293100% (1)
- The Book of GatesDocument60 pagesThe Book of GateskachenlaPas encore d'évaluation
- HathorDocument8 pagesHathorZoth BernsteinPas encore d'évaluation
- The 33 Year Persian Leap-Day Sequence V5.0Document5 pagesThe 33 Year Persian Leap-Day Sequence V5.0G.n.o.d.e.100% (1)
- The Egyptian Coffin Texts - Volume 8Document472 pagesThe Egyptian Coffin Texts - Volume 8Ona100% (3)
- Uraeus: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesUraeus: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaelgorrion98Pas encore d'évaluation
- Astronomy Ancient Egyptians and The Constellations Fletcher PDFDocument146 pagesAstronomy Ancient Egyptians and The Constellations Fletcher PDFHans SchauerPas encore d'évaluation
- Apollo and Lumina - Crystal Wind™ - ElohimDocument7 pagesApollo and Lumina - Crystal Wind™ - ElohimsnezanaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Gods of The Egyptians Vol1 - Chapter VIII - The History of The Creation of The Gods and of The World - Version ADocument4 pagesThe Gods of The Egyptians Vol1 - Chapter VIII - The History of The Creation of The Gods and of The World - Version AOrockjoPas encore d'évaluation
- HathorDocument9 pagesHathorSolomanTrismosin100% (1)
- Book of the Earth - Ancient Egyptian funerary text exploring the underworldDocument10 pagesBook of the Earth - Ancient Egyptian funerary text exploring the underworldBLK413Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ancient Egyptian Cippus Healing CharmDocument4 pagesAncient Egyptian Cippus Healing CharmAdina BadarauPas encore d'évaluation
- EnneadDocument13 pagesEnneadvstrohmePas encore d'évaluation
- Why The Neteru of Ancient EgyptDocument9 pagesWhy The Neteru of Ancient EgyptJacque Van Der BergPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharoah TarotDocument38 pagesPharoah TarotCristal Till Infinity100% (2)
- The Conception of OrionDocument7 pagesThe Conception of OrionDAVIDNSBENNETT100% (1)
- Lizla, the Daughter of Isis: The Birth of a Soul in a Crumbling EmpireD'EverandLizla, the Daughter of Isis: The Birth of a Soul in a Crumbling EmpirePas encore d'évaluation
- Egyptian Divinities: The All Who Are the OneD'EverandEgyptian Divinities: The All Who Are the OneÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5)
- Koolwheelz Eagle TransportDocument2 pagesKoolwheelz Eagle TransportBrett Michael ChinchenPas encore d'évaluation
- PT 1 Micro ArmourDocument69 pagesPT 1 Micro ArmourkispatkanyPas encore d'évaluation
- Robin Hood Game Aid by Liumas 2009-09Document2 pagesRobin Hood Game Aid by Liumas 2009-09Brett Michael ChinchenPas encore d'évaluation
- Event Card Almanac v3.0 (2018)Document30 pagesEvent Card Almanac v3.0 (2018)Brett Michael ChinchenPas encore d'évaluation
- Roman Army OrganisationDocument38 pagesRoman Army OrganisationBrett Michael Chinchen100% (2)
- Denizens of Robin's WoodDocument4 pagesDenizens of Robin's WoodBrett Michael ChinchenPas encore d'évaluation
- Legend of Robin HoodDocument12 pagesLegend of Robin HoodBrett Michael ChinchenPas encore d'évaluation
- Joust - Heroes of The Lists (2011) PDFDocument37 pagesJoust - Heroes of The Lists (2011) PDFmars100% (1)
- Blood Faith Genre Pack v1Document12 pagesBlood Faith Genre Pack v1Brett Michael ChinchenPas encore d'évaluation
- LoRH Map SplicesDocument10 pagesLoRH Map SplicesBrett Michael ChinchenPas encore d'évaluation
- S&T 062 - South AfricaDocument67 pagesS&T 062 - South AfricaBrett Michael Chinchen100% (1)
- Soviet Naval Battles During Civil WarDocument58 pagesSoviet Naval Battles During Civil WarBrett Michael ChinchenPas encore d'évaluation
- Counter ReduxDocument1 pageCounter ReduxBrett Michael Chinchen100% (1)
- S&T 033 - The Winter WarDocument62 pagesS&T 033 - The Winter WarBrett Michael Chinchen100% (3)
- Legend of Robin Hood Rules by Liumas 2007-08Document7 pagesLegend of Robin Hood Rules by Liumas 2007-08cybermichaelPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Hour WWI Naval Warfare V3Document1 page1 Hour WWI Naval Warfare V3Brett Michael ChinchenPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Hour WWI Naval Warfare V3Document1 page1 Hour WWI Naval Warfare V3Brett Michael ChinchenPas encore d'évaluation
- To The Strongest Army Lists - Cradle of CivilizationDocument46 pagesTo The Strongest Army Lists - Cradle of CivilizationBrett Michael ChinchenPas encore d'évaluation
- Velmad Age of Sail Naval Wargame Rules Book PDFDocument24 pagesVelmad Age of Sail Naval Wargame Rules Book PDFBrett Michael ChinchenPas encore d'évaluation
- War in HellDocument9 pagesWar in HellBrett Michael ChinchenPas encore d'évaluation
- Fear Naught - Quick Naval Wargaming (11833859)Document13 pagesFear Naught - Quick Naval Wargaming (11833859)Brett Michael Chinchen100% (1)
- 1 Hour WWI Naval Warfare V3Document1 page1 Hour WWI Naval Warfare V3Brett Michael ChinchenPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechs SenseDocument1 pageMechs SenseBrett Michael ChinchenPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Hour WWI Naval Warfare V3Document1 page1 Hour WWI Naval Warfare V3Brett Michael ChinchenPas encore d'évaluation
- SWR Qpc-Part-1Document1 pageSWR Qpc-Part-1Brett Michael ChinchenPas encore d'évaluation
- SWR Qpc-Part-2Document1 pageSWR Qpc-Part-2Brett Michael ChinchenPas encore d'évaluation
- SWR Appendix ADocument2 pagesSWR Appendix ABrett Michael ChinchenPas encore d'évaluation
- SWR Ancients 20130820aDocument25 pagesSWR Ancients 20130820aBrett Michael Chinchen100% (1)
- SWR Order CardsDocument1 pageSWR Order CardsBrett Michael ChinchenPas encore d'évaluation
- Phalanx ListDocument47 pagesPhalanx ListBrett Michael ChinchenPas encore d'évaluation
- The Orion MysteryDocument11 pagesThe Orion MysteryRazvan Geo86% (7)
- The-Sun-Within by Neb Heru Khaf-ReDocument31 pagesThe-Sun-Within by Neb Heru Khaf-ReSmoovAshlah100% (57)
- Hymns To The KingDocument9 pagesHymns To The Kingგვანცა ყრუაშვილიPas encore d'évaluation
- The Gods of The Egyptians, Studies in Egyptian Mythology Vol. 2Document552 pagesThe Gods of The Egyptians, Studies in Egyptian Mythology Vol. 2thislittleman100% (2)
- Scott-Moncrieff, McLean, King, Hall. Paganism and Christianity in Egypt. 1913.Document250 pagesScott-Moncrieff, McLean, King, Hall. Paganism and Christianity in Egypt. 1913.Patrologia Latina, Graeca et OrientalisPas encore d'évaluation
- Posteguillo The Semantic Structure of Computer Science Research ArticalsDocument22 pagesPosteguillo The Semantic Structure of Computer Science Research ArticalsRobin ThomasPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharaoh Expansion Cheat CodesDocument9 pagesPharaoh Expansion Cheat CodesalexnanlohyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Sun-Disc in Akhenaten's Program IDocument25 pagesThe Sun-Disc in Akhenaten's Program I田富Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sothis Is Aldebaran The Eye of Ra & The Red Sirius Is Ain The Eye of Horus - The Two Eyes of TaurusDocument27 pagesSothis Is Aldebaran The Eye of Ra & The Red Sirius Is Ain The Eye of Horus - The Two Eyes of TaurusEulalio EguiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Geography Assignment On EgyptDocument2 pagesGeography Assignment On EgyptYiheng8pPas encore d'évaluation
- The Tree of LightDocument21 pagesThe Tree of LightLeonel KongaPas encore d'évaluation
- HekaDocument211 pagesHekaNadia94% (16)
- Legends of The Gods The Egyptian Texts, Edited With Translations by Budge, E. A. Wallis, 1857-1934Document123 pagesLegends of The Gods The Egyptian Texts, Edited With Translations by Budge, E. A. Wallis, 1857-1934Gutenberg.orgPas encore d'évaluation
- The Book of GatesDocument120 pagesThe Book of GatesPierre Marcovicz Tarot100% (1)
- A Comparative List of Some Pre-Existing and Pre-Christian Data Which Were Christianized in The Canonical Gospels and The Book of RevelationDocument21 pagesA Comparative List of Some Pre-Existing and Pre-Christian Data Which Were Christianized in The Canonical Gospels and The Book of RevelationLifzParadisePas encore d'évaluation
- A Solar Litany From The Tomb of Ramesses PDFDocument6 pagesA Solar Litany From The Tomb of Ramesses PDFMohamed NassarPas encore d'évaluation
- HethertDocument43 pagesHethertDaymonDrakonPas encore d'évaluation
- Budge The Gods OfThe Egyptians 1904 Vol 2 CompleteDocument556 pagesBudge The Gods OfThe Egyptians 1904 Vol 2 CompleteJamie Vida100% (1)
- The Rise and Fall of an Ancient Necromantic EmpireDocument9 pagesThe Rise and Fall of an Ancient Necromantic EmpireJeeses RibeiroPas encore d'évaluation
- Anousen Leonte - Cat MagickDocument23 pagesAnousen Leonte - Cat MagickКлавдий100% (1)
- RAMESSES I-KV16 p.2Document6 pagesRAMESSES I-KV16 p.2Gohed BraunPas encore d'évaluation
- Zep TepiDocument4 pagesZep TepiNeb Nyansapo Noopooh100% (1)
- Who Is Anu in EgiptDocument6 pagesWho Is Anu in EgiptKhefri Tehuti Hotep-Ptah100% (1)
- Playing for Eternity: The Game-Box of TutankhamunDocument6 pagesPlaying for Eternity: The Game-Box of TutankhamunanikunifenixPas encore d'évaluation
- Leprohon - Use of Royal Titulary in 12 DynDocument8 pagesLeprohon - Use of Royal Titulary in 12 DynMarly Shibata100% (1)
- ETERNITY Book Anwar SheikhDocument231 pagesETERNITY Book Anwar Sheikhasadilife100% (1)
- 70 Ankh Gods of Egypt RulebookDocument32 pages70 Ankh Gods of Egypt RulebookBalam MendozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sky GodsDocument11 pagesSky GodsmehPas encore d'évaluation
- بطاقات متحف الحضارةDocument43 pagesبطاقات متحف الحضارةIbrahim SaidPas encore d'évaluation
- Signs Symbols of The World - DR McElroyDocument658 pagesSigns Symbols of The World - DR McElroyClip ClapsPas encore d'évaluation