Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment
Transféré par
dasohamathDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Assignment
Transféré par
dasohamathDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Assignment for Engineering Mechanics
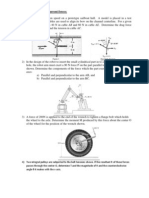
1) The hydraulic cylinder operates the toggle which closes the vertical gate against the pressure of fresh water on the opposite side. The gate is rectangular with a horizontal width of 2m perpendicular to the paper. For a depth h = 3m of water, calculate the required force exerted by the hydraulic cylinder to keep the gate just closed.
2) As shown in Fig, the uniform slender 10-lb rod AB is supported by a balland-socket joint at A and leans against both the rod CD and the vertical wall. Neglecting the effects of friction, determine (a) the force which rod CD exerts on AB, (b) the reactions at B.
3) For the given loading, determine the zero-force members in the truss shown.
4) Verify that the loaded truss is partially constrained and indicate an alternative way to properly constraint the truss by the addition of one or more members.
5) A light flexible cord DABC is passed around the circular disk of mass m and ends in a small mass-less, frictionless pulley at C that is free to find its equilibrium position on the cord. The coefficient of friction between the cord and the disk is = 0.5. Show that, for the position where the disk is on the verge of turning under the action of a couple M applied to the disk, the angle (BOA) between the normals (OB and OA) to the cord at the tangency points (B and A) is equal to = 87.3o. (8 marks)
6) For the mechanism shown, the spring of stiffness k has an un-stretched length of essentially zero, and the larger link has a mass m with mass center at B. The mass of the smaller link is negligible. Determine the equilibrium angle for a given downward force P. Use principle of minimum potential energy only.
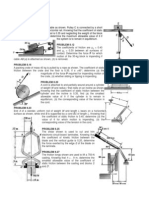
7) Consider a uniform square plate ABCD of mass M hinged about point A (shown in the figure). The plate is maintained in equilibrium in the position shown with the help of a spring EB of spring constant k. Obtain the frequency of vibration of the plate for small rotation about point A with respect to the equilibrium position. What is the maximum possible value
of M for which the plate with undergo a simple harmonic motion
8) For the pruning shears shown, determine the force Q applied to the circular branch of 15mm diameter for a gripping force P = 200 N. (Suggestion: First draw a free-body diagram of the isolated branch).
9) The three identical rollers are stacked on a horizontal surface as shown. If the coefficient of static friction s is the same for all pairs of contacting surfaces, find the minimum value of s for which the rollers will not slip.
10) The ball is released from position A with a velocity of 3 m/s and swings in a vertical plane. At the bottom position, the cord strikes the fixed bar at B, and the ball continues to swing in the dashed arc. Calculate the velocity vc of the ball as it passes position C.
11) Two barges, each with a mass of 500 Mg, are loosely moored in calm water. A stunt driver starts his 1500-kg car from rest at A, drives along the deck, and leaves the end of the 15 degrees ramp at a speed of 50 km/h relative to the barge and ramp. The driver successfully jumps the gap and brings his car to rest relative to barge 2 at B. Calculate the velocity v2 imparted to barge 2 just after the car has come to rest on the barge. Neglect the resistance of the water to motion at the low velocities involved.
12) Motion of the roller A against its restraining spring is controlled by the downward motion of the plunger E. For an interval of motion the velocity of E is v = 0.2m/s. Determine the velocity of A when becomes 90 degrees.
13) The uniform slender bar of mass m and length L with small end rollers is released from rest in the position shown with the lower roller in contact with the horizontal plane. Determine the normal force N under the lower roller and the angular acceleration of the bar immediately after release.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Assignment2ed PDFDocument4 pagesAssignment2ed PDFIza HamdanPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamics FULL Equation SheetDocument2 pagesDynamics FULL Equation SheetZachPas encore d'évaluation
- First Project ExamplesDocument49 pagesFirst Project ExamplesMeleti Meleti MeletiouPas encore d'évaluation
- Question Bank Engg. MechanicsDocument18 pagesQuestion Bank Engg. MechanicsSakendra Kumar0% (2)
- PhyDocument56 pagesPhyJohn Ray CuevasPas encore d'évaluation
- GNG 1105 Final Exam 2000Document3 pagesGNG 1105 Final Exam 2000Stefano MazzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Suspension A8Document5 pagesSuspension A8Bonny SidhuPas encore d'évaluation
- Practise Problems Set01Document7 pagesPractise Problems Set01rohit kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper 1 12889 997Document12 pagesPaper 1 12889 997Mohammad Keyhani75% (4)
- Correl 2 Until MidtermsDocument23 pagesCorrel 2 Until MidtermsKimberly TacaisanPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering MechanicsDocument8 pagesEngineering MechanicsNanna ShivuPas encore d'évaluation
- Me601 HW1Document6 pagesMe601 HW1chinmayPas encore d'évaluation
- 00 Sampe For Question S & AnsDocument5 pages00 Sampe For Question S & Ansmail2sgarg_841221144Pas encore d'évaluation
- BB 2.0 - Friction & Circular MotionDocument108 pagesBB 2.0 - Friction & Circular MotionSunil DahalePas encore d'évaluation
- Paper 1 12889 997Document12 pagesPaper 1 12889 997Madeley Yoselin ZPPas encore d'évaluation
- DPP Nlm-IiDocument8 pagesDPP Nlm-IiMohammed Aftab Ahmed0% (1)
- Physics Five PointsDocument16 pagesPhysics Five PointsMary Grace VelitarioPas encore d'évaluation
- Umay DesignDocument55 pagesUmay DesignMhel CenidozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pokhara University Applied Mechanics - I Question PapersDocument4 pagesPokhara University Applied Mechanics - I Question PapersBuddhisagar BastolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment-3 Last Date To Submit-12/05/2023Document9 pagesAssignment-3 Last Date To Submit-12/05/2023Parth PawarPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Questions For All UnitsDocument10 pagesAssignment Questions For All UnitsPiyush BhandariPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanics Tutorials 08 09Document14 pagesMechanics Tutorials 08 09Yun RamPas encore d'évaluation
- AP Physics 1 - Test 09 - Rotational Dynamics Score:: A B C D EDocument9 pagesAP Physics 1 - Test 09 - Rotational Dynamics Score:: A B C D ESTPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 ReviewDocument3 pagesChapter 2 ReviewFlora DongPas encore d'évaluation
- Problems On DynamicsDocument3 pagesProblems On DynamicsPablo AlejandroPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 8 PDFDocument16 pagesTutorial 8 PDFBharat SaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorials 1 5Document7 pagesTutorials 1 5faizankhan260690Pas encore d'évaluation
- Q. 1 - Q. 9 Carry One Mark Each.: D: Solid MechanicsDocument8 pagesQ. 1 - Q. 9 Carry One Mark Each.: D: Solid MechanicsSundarRajanPas encore d'évaluation
- Work Sheet On DynamicsDocument6 pagesWork Sheet On DynamicstorsrinivasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Solid MechanicsDocument25 pagesSolid MechanicstvkbhanuprakashPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 4Document4 pagesTutorial 4Rajkamal NayakPas encore d'évaluation
- 03 - Circular Motion - ExerciseDocument7 pages03 - Circular Motion - Exercisekenchan0810.kcPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 2-Equilibrium 1Document2 pagesTutorial 2-Equilibrium 1Sai KrishnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Question BankDocument9 pagesQuestion Bankpragash100% (1)
- Chapter 3 To 10Document22 pagesChapter 3 To 10Angelica Ecal Migriño67% (3)
- Candidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksDocument4 pagesCandidates Are Required To Give Their Answers in Their Own Words As Far As Practicable. The Figures in The Margin Indicate Full MarksManish Shrestha100% (1)
- BB 2.0 - NLMDocument142 pagesBB 2.0 - NLMParthMaluPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering MEchanics Part - BDocument38 pagesEngineering MEchanics Part - BPreethi SharmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Rigid Body 3DDocument6 pagesRigid Body 3DSyed ShaulPas encore d'évaluation
- Midterm Exam Answer KeyDocument6 pagesMidterm Exam Answer KeyFiel Ericson SolaresPas encore d'évaluation
- Rev2, ENGR 62, StanfordDocument40 pagesRev2, ENGR 62, StanfordsuudsfiinPas encore d'évaluation
- Practise Problems Set06Document3 pagesPractise Problems Set06rohit kumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Structural Mechanics Paper 2 Examples Paper 2Document6 pagesStructural Mechanics Paper 2 Examples Paper 2Michael BlairPas encore d'évaluation
- ME 601 - Stress Analysis Assignment 1 - Review of Strength of Materials Due Date: 27/07/2015, at The Beginning of The ClassDocument6 pagesME 601 - Stress Analysis Assignment 1 - Review of Strength of Materials Due Date: 27/07/2015, at The Beginning of The Classfatty acidPas encore d'évaluation
- Model QSTN Paper 1-Be100Document5 pagesModel QSTN Paper 1-Be100nanduPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Questions For Potential FlowsDocument3 pagesProblem Questions For Potential FlowsSnehal SinhaPas encore d'évaluation
- CENG198 CE Competency Appraisal IllDocument4 pagesCENG198 CE Competency Appraisal IllJeric DinglasanPas encore d'évaluation
- Ce 371 Homework 4 1) A Plug in The Bottom of A Pressurized TankDocument4 pagesCe 371 Homework 4 1) A Plug in The Bottom of A Pressurized TankSubhash KorumilliPas encore d'évaluation
- Tut1 Chapters 2to4Document14 pagesTut1 Chapters 2to4darkknightonePas encore d'évaluation
- NL CQ 6 SSPDocument4 pagesNL CQ 6 SSPGokul NathPas encore d'évaluation
- STPM 2014 p1 TrialDocument13 pagesSTPM 2014 p1 Trialshinichi_kesian6117Pas encore d'évaluation
- Er. Shravan Katiyar: Physics For Iit-Jee (Main & Advanced)Document4 pagesEr. Shravan Katiyar: Physics For Iit-Jee (Main & Advanced)ShreyanshPas encore d'évaluation
- HowDocument43 pagesHowAudrey Ruth V. SirunoPas encore d'évaluation
- 9A01101 Engineering MechanicsDocument8 pages9A01101 Engineering MechanicssivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- Motion in A Circle Updated 11Document3 pagesMotion in A Circle Updated 11Yahya Salman GamingPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanics DADocument5 pagesMechanics DAMihir AgarwalPas encore d'évaluation
- The Mechanics of Water-Wheels - A Guide to the Physics at Work in Water-Wheels with a Horizontal AxisD'EverandThe Mechanics of Water-Wheels - A Guide to the Physics at Work in Water-Wheels with a Horizontal AxisPas encore d'évaluation
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2D'EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Évaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Problem Solving P 3Document1 pageProblem Solving P 3dasohamathPas encore d'évaluation
- Kom MechanismDocument26 pagesKom MechanismShivalingappa AnnaraoPas encore d'évaluation
- Late Shri Vinod Kumar MittalDocument6 pagesLate Shri Vinod Kumar MittaldasohamathPas encore d'évaluation
- ASEE 2012 Watson Draft 2 PDFDocument22 pagesASEE 2012 Watson Draft 2 PDFdrpPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Solving P 2Document1 pageProblem Solving P 2dasohamathPas encore d'évaluation
- Yoga For Stress Management PDFDocument37 pagesYoga For Stress Management PDFdasohamathPas encore d'évaluation
- Policy DaDocument16 pagesPolicy DadasohamathPas encore d'évaluation
- The Karnataka State Co-Operative Apex Bank LimitedDocument6 pagesThe Karnataka State Co-Operative Apex Bank LimiteddasohamathPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem Solving P 1Document1 pageProblem Solving P 1dasohamathPas encore d'évaluation
- Savings Bank AccountDocument3 pagesSavings Bank AccountdasohamathPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 NotificationDocument6 pages01 NotificationdasohamathPas encore d'évaluation
- Biocompatibility of Stent Materials: Issel Anne L. LimDocument5 pagesBiocompatibility of Stent Materials: Issel Anne L. LimdasohamathPas encore d'évaluation
- ObjectivesDocument2 pagesObjectivesdasohamathPas encore d'évaluation
- Sl. No. CCR A/C No. Purpose of Loan Rate of Interest: Viii Working Capital Loan To State Level Coop. InstitutionsDocument1 pageSl. No. CCR A/C No. Purpose of Loan Rate of Interest: Viii Working Capital Loan To State Level Coop. InstitutionsdasohamathPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 4 - Bio - CompositeDocument40 pagesGroup 4 - Bio - Compositedasohamath100% (1)
- Bio MaterialsDocument28 pagesBio MaterialsGrace Jeba Rani CPas encore d'évaluation
- Institute Server InstallationDocument16 pagesInstitute Server InstallationdasohamathPas encore d'évaluation
- MenuCommands EDocument1 pageMenuCommands Eabby2007Pas encore d'évaluation
- AssignmentDocument5 pagesAssignmentdasohamathPas encore d'évaluation
- ArticleDocument4 pagesArticledasohamathPas encore d'évaluation
- PH D Notification Bub fINALDocument17 pagesPH D Notification Bub fINALdasohamathPas encore d'évaluation
- Visvesvaraya Technological University: RegistrarDocument3 pagesVisvesvaraya Technological University: RegistrarsarukalashettyPas encore d'évaluation
- Kinematics & Dynamics of Machines - Ultimate DefenderDocument196 pagesKinematics & Dynamics of Machines - Ultimate DefenderNaveen Krishna0% (2)
- Prediction of Wax Pattern Dimensions in Investment Casting: A. S. Sabau and S. ViswanathanDocument14 pagesPrediction of Wax Pattern Dimensions in Investment Casting: A. S. Sabau and S. ViswanathandasohamathPas encore d'évaluation
- 3D Static and Dynamic AnalysisDocument32 pages3D Static and Dynamic AnalysisvanmurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- TMA2 12 09 2021 UploadDocument3 pagesTMA2 12 09 2021 UploadG.G. PRABHATH CHINTHAKAPas encore d'évaluation
- 2002 KX250 Race TuningDocument4 pages2002 KX250 Race TuningKidKawie100% (1)
- Recommendation of RILEM TC 261-CCF Test Method ToDocument20 pagesRecommendation of RILEM TC 261-CCF Test Method ToManelPas encore d'évaluation
- 26 Type Brake EquipmentsDocument8 pages26 Type Brake EquipmentsRafael SchelbauerPas encore d'évaluation
- ProblemsDocument5 pagesProblemsJustine Roy PunzalanPas encore d'évaluation
- 3TF8 Reversing Contactors - Motor Starters - SiemensDocument2 pages3TF8 Reversing Contactors - Motor Starters - SiemensAlberto Morillo ParelladaPas encore d'évaluation
- Parker 2H CylindersDocument26 pagesParker 2H CylindersnitinjainmechPas encore d'évaluation
- Material Testing LaboratoryDocument13 pagesMaterial Testing Laboratorydantan187100% (1)
- Ot SluiceDocument3 pagesOt Sluicegurumurthy38Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cooling System MechanicallDocument23 pagesCooling System MechanicallStuart FerreiraPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 Tool Geometry: 3.1 Basic ConceptsDocument4 pages3 Tool Geometry: 3.1 Basic ConceptsHM DYPas encore d'évaluation
- Regolatore Aspirazione Rh38EDocument2 pagesRegolatore Aspirazione Rh38EДжон ДиллинджерPas encore d'évaluation
- Automobile Workshop PracticeDocument2 pagesAutomobile Workshop PracticeSachi MensiPas encore d'évaluation
- Staad Input FileDocument18 pagesStaad Input FileKP SahuPas encore d'évaluation
- 188 Lamborghini Gallardo 101 EngDocument4 pages188 Lamborghini Gallardo 101 EngVIET VehiclePas encore d'évaluation
- Section 3 Hydraulic SystemDocument3 pagesSection 3 Hydraulic SystemRafał DworakPas encore d'évaluation
- Cyclones ExerciseDocument4 pagesCyclones ExerciseValeria cPas encore d'évaluation
- Alfa Laval Separartor s937 Alarms & Fault FindingsDocument19 pagesAlfa Laval Separartor s937 Alarms & Fault FindingsIgors VrublevskisPas encore d'évaluation
- Zanotti DFZDocument44 pagesZanotti DFZHubert Von Süßer BusartzPas encore d'évaluation
- Exploded View of WEBER 32-36 DGV 5A GBPDocument3 pagesExploded View of WEBER 32-36 DGV 5A GBPJannie CoetzeePas encore d'évaluation
- Cmae Prop 3Document3 pagesCmae Prop 3Mithun Kumar SandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Duct Design For "Super" SupermarketDocument47 pagesDuct Design For "Super" Supermarketkevin_thian_1100% (4)
- Ymfe (24-60) Bnjmcmo(s) - X 14 Seer Solo FrioDocument4 pagesYmfe (24-60) Bnjmcmo(s) - X 14 Seer Solo FrioAb CaamañoPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT I Gas Power Cycles FinalDocument75 pagesUNIT I Gas Power Cycles FinalMAYUR BHOSALEPas encore d'évaluation
- Mapex AN0320SN PDFDocument1 pageMapex AN0320SN PDFDiegoTierradentroPas encore d'évaluation
- FGM Piston Liner Kit IndexDocument88 pagesFGM Piston Liner Kit IndexLuis Arturo Arevalo LeonPas encore d'évaluation
- Materials Today: Proceedings: Chirag D. Bhatt, Mukesh Nadarajan, R. Balaji, Isukapalli Rohith, Ashish SelokarDocument7 pagesMaterials Today: Proceedings: Chirag D. Bhatt, Mukesh Nadarajan, R. Balaji, Isukapalli Rohith, Ashish SelokarRahulJNairPas encore d'évaluation