Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Describing A Process - Exercise - 3
Transféré par
Yuliana PurnamasariTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Describing A Process - Exercise - 3
Transféré par
Yuliana PurnamasariDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Describing A Process Week 3 A. Use the passive to complete the text about Chocolate.
English for Biology Students
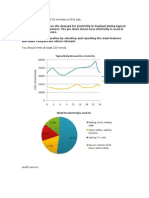
Chocolate 1 (make) from up to 12 different types of cocoa beans. First, the beans 2 (sort) by hand before being roasted. Each type of bean 3 (roast) separately, which is time consuming but important. Next, the beans 4 (load) into a machine called a winnower, which removes the hard outer shells of the beans. After this the beans 5 (mash) into a thick paste and sugar and vanilla 6 (add). This paste 7 (call) the chocolate liquor. Then the chocolate liquor 8 (heat) for up to 72 hours to make sure the liquid 9 (blend) evenly. Following this, the liquor 10 (temper) for several hours repeatedly heated and then cooled. Finally, the chocolate 11 (allow) to cool and harden before being packaged. B. How greenhouse gases trap energy from the sun. Complete the text with the words in the box. You may need to change the word form. Energy from the sun 1 the Earth as heat. Some of this heat energy is 2 radiated into space, while some of it is trapped by greenhouse gases in the atmosphere and reflected back to Earth. This is a natural process, but in recent 3 , human activities have 4 an increase in the 5 of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere which is now trapping too much heat. One of the main greenhouse gases is carbon dioxide, and extra quantities of this 6 into the atmosphere 7 burning fossil fuels as a source of energy in power stations, factories, and homes. Exhaust gases from cars and lorries 8 further emissions of carbon dioxide. Plants serve to remove some of the carbon dioxide from the atmosphere by absorbing it through their leaves. However, as large areas of forest 9 in the Amazon and elsewhere, 10 carbon dioxide is removed in this way. lead to reach release less result in decades subsequently amounts fell as a result of
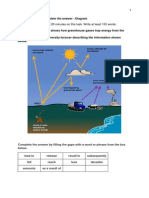
C. Complete the text with the words in the box. Use the verbs in passive or active forms, as appropriate. The heat of the sun 1 water to evaporate from seas, rivers, and lakes. In addition, water vapor 2 from the soil and from plants. As the water vapor then 3 into the atmosphere, it cools and condenses into clouds. The clouds 4 by winds until they 5 high ground. At this stage, the water droplets 6 back to earth as rain, hail, or snow. After the rain has fallen on land, it either evaporates into the air or it 7 by soils and plants. Some of it also 8 into rivers and lakes and eventually reaches the sea.
reach fall absorb rise
run cause release blow http://yasmeenshakoor.edublogs.org/
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Introduce The Diagram-BricksDocument4 pagesIntroduce The Diagram-BricksLenapsPas encore d'évaluation
- It Is Rather Nice Outside Interactive WorksheetDocument2 pagesIt Is Rather Nice Outside Interactive WorksheetHenry Vargas GamboaPas encore d'évaluation
- Talking About FashionDocument2 pagesTalking About FashionАйшат ДеккушеваPas encore d'évaluation
- Prepositions of Movement To Into in at British English Teacher Ver2 PDFDocument3 pagesPrepositions of Movement To Into in at British English Teacher Ver2 PDFtracy nguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- The Best Guide To IELTS Writing Task 1 - ModelsDocument17 pagesThe Best Guide To IELTS Writing Task 1 - ModelsBao HoangLuuPas encore d'évaluation
- Booklet Course 8 Chapter 4Document22 pagesBooklet Course 8 Chapter 4Mayis Monzón100% (1)
- ICAO ELP ApprovalDocument2 pagesICAO ELP ApprovalSayed MohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Task 1 - Flow ChartDocument18 pagesTask 1 - Flow Chartnavigator290679Pas encore d'évaluation
- Process - CheckedDocument4 pagesProcess - CheckedPhương VyPas encore d'évaluation
- IELT Sample Writing Task 1Document15 pagesIELT Sample Writing Task 1Silver DobellPas encore d'évaluation
- Astronomy 1Document5 pagesAstronomy 1nounaPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Simple WH Questions WorksheetDocument2 pagesPresent Simple WH Questions WorksheetВікторія KPas encore d'évaluation
- Speakout Pronunciation Extra Advanced Unit 7Document1 pageSpeakout Pronunciation Extra Advanced Unit 7hector18170% (1)
- Aviation and EnvironmentDocument10 pagesAviation and EnvironmentGiang Nguyễn TrườngPas encore d'évaluation
- Reported Speech: 1. When TheDocument11 pagesReported Speech: 1. When TheIvana Plenča100% (1)
- Nasa-Space-Toilet-Challenge-2001010718-Article Quiz and AnswersDocument4 pagesNasa-Space-Toilet-Challenge-2001010718-Article Quiz and Answersapi-302899266Pas encore d'évaluation
- Week 5 - Describing A Process PDFDocument9 pagesWeek 5 - Describing A Process PDFDhea Kirana FaihaPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 5 - Describing A ProcessDocument9 pagesWeek 5 - Describing A Process458 269 Cinta Alivia AthaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lessons 1 - 2: I. Supply The Correct Form of The Verbs in BracketsDocument3 pagesLessons 1 - 2: I. Supply The Correct Form of The Verbs in BracketsViệt AnhPas encore d'évaluation
- Writing Task 1Document3 pagesWriting Task 1Jaspreet SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Present Simple Vs ContinuousDocument5 pagesPresent Simple Vs ContinuousJavito GomezPas encore d'évaluation
- Diagram. Fill in The BlanksDocument3 pagesDiagram. Fill in The BlanksCraciun Andreea100% (1)
- B.1-2 Tense Revision1Document3 pagesB.1-2 Tense Revision1Heaven's DoorPas encore d'évaluation
- Theme 1: Sea Level Rise: Experiment 1: When Ice MeltsDocument7 pagesTheme 1: Sea Level Rise: Experiment 1: When Ice Meltsapi-292520116Pas encore d'évaluation
- Revision-English 9-2 Term School Year: 2017 - 2018Document20 pagesRevision-English 9-2 Term School Year: 2017 - 2018Quynh Ngan TranPas encore d'évaluation
- QuestionsDocument2 pagesQuestionsChi NguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- English Exercises For Grade 3. Kd.3.3 Explanation Text. 2022Document6 pagesEnglish Exercises For Grade 3. Kd.3.3 Explanation Text. 2022OncakPas encore d'évaluation
- Bài Tập Điền TừDocument2 pagesBài Tập Điền TừNguyễn NgọcPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive and Active Voice LessonDocument2 pagesPassive and Active Voice LessonFrida HrnPas encore d'évaluation
- Test 5Document4 pagesTest 5Marta ECPas encore d'évaluation
- ProcessDocument2 pagesProcessĐào Nguyễn Duy TùngPas encore d'évaluation
- لقطة شاشة 2023-12-13 في 5.34.56 مDocument8 pagesلقطة شاشة 2023-12-13 في 5.34.56 مmansourelgabry8Pas encore d'évaluation
- O Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions HomeostasisD'EverandO Level Biology Practice For Structured Questions HomeostasisÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- New Cpe - ExercisesDocument4 pagesNew Cpe - ExercisesBasil AngelisPas encore d'évaluation
- Year 9 June Exam NADocument8 pagesYear 9 June Exam NAAlejandro EspiPas encore d'évaluation
- ScienceDocument17 pagesSciencefolanelfolaniePas encore d'évaluation
- The Cooling Oceans: PFEC 2022-2023 Mock Test 01 Section: Word FormationDocument66 pagesThe Cooling Oceans: PFEC 2022-2023 Mock Test 01 Section: Word FormationDuy Anh TrầnPas encore d'évaluation
- English PDFDocument2 pagesEnglish PDFmootaz haddadPas encore d'évaluation
- The Exxon ValdezDocument2 pagesThe Exxon Valdezfcbalck29Pas encore d'évaluation
- Thermodynamics (SI Units) Sie 6E - CengelDocument157 pagesThermodynamics (SI Units) Sie 6E - CengelMatt HarrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Another Test For 9th FormersDocument3 pagesAnother Test For 9th FormersStarr BluePas encore d'évaluation
- IIP Final Year 9 March - EngDocument4 pagesIIP Final Year 9 March - EngHtoo Myat LinnPas encore d'évaluation
- PhotosynthesisDocument9 pagesPhotosynthesisbok24Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Rainmaker DesignDocument5 pagesThe Rainmaker DesignYến NhiPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiration Lab ADADocument7 pagesRespiration Lab ADAtimothy charlton0% (1)
- NCERT Dictation Magazine Part 1Document30 pagesNCERT Dictation Magazine Part 1googlitechindiaPas encore d'évaluation
- De Luyen Thi Vao Lop 10Document4 pagesDe Luyen Thi Vao Lop 10Bão SvPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 Lesson 1 Worksheet 1Document2 pagesUnit 1 Lesson 1 Worksheet 1Hazem OmarPas encore d'évaluation
- Burn Fossil Fuel Electricity ProducedDocument4 pagesBurn Fossil Fuel Electricity ProducedYear11RevisionPas encore d'évaluation
- Passive and Active Voice LessonDocument2 pagesPassive and Active Voice Lessonbensai sadenPas encore d'évaluation
- Cloze Test 12 Out of This World: Soup-MakingDocument4 pagesCloze Test 12 Out of This World: Soup-MakingGalina IlievaPas encore d'évaluation
- Science IGCSE Recap Tasks Paper 1Document9 pagesScience IGCSE Recap Tasks Paper 1Sami AachaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.8 Bio WS 21.03.23 MalakDocument3 pages2.8 Bio WS 21.03.23 MalakMalak APas encore d'évaluation
- Osmolarity ExptDocument2 pagesOsmolarity ExptBenjamin YeboahPas encore d'évaluation
- Photosynthesis WorksheetDocument47 pagesPhotosynthesis Worksheetsaba100% (1)
- Explanation Global WarmingDocument7 pagesExplanation Global WarmingWidyaMahardikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ahmed Kalim Niazi: Beaconhouse School SystemDocument7 pagesAhmed Kalim Niazi: Beaconhouse School SystemAhmed Kaleem Khan NiaziPas encore d'évaluation
- Renewable & Nonrenewable EnergyDocument1 pageRenewable & Nonrenewable Energybensai sadenPas encore d'évaluation
- Ielts Test 6Document23 pagesIelts Test 6Miguel Ruiz100% (1)
- Reading 1: Sentence Completion + Passage 1 Practice: Exercise 1Document14 pagesReading 1: Sentence Completion + Passage 1 Practice: Exercise 1Lanh PhuongPas encore d'évaluation
- Pearson Academic Collocation List PDFDocument42 pagesPearson Academic Collocation List PDFMuhammad Ashraf100% (8)
- 99 Top IELTS CollocationsDocument1 page99 Top IELTS Collocationsamirlove20667% (6)
- 99 Top IELTS CollocationsDocument1 page99 Top IELTS Collocationsamirlove20667% (6)
- Transpiration: Function of Water in LeavesDocument5 pagesTranspiration: Function of Water in LeavesYuliana PurnamasariPas encore d'évaluation
- Marine VisionDocument16 pagesMarine VisionYuliana PurnamasariPas encore d'évaluation
- Transpiration Importance: Are RootDocument7 pagesTranspiration Importance: Are RootYuliana PurnamasariPas encore d'évaluation
- 14-2002-Lucas-EXP-J-Stored-Prod-Res-Sitophilus-Biol+Mechan Control-Lphy-Lbio-ParaoDocument12 pages14-2002-Lucas-EXP-J-Stored-Prod-Res-Sitophilus-Biol+Mechan Control-Lphy-Lbio-ParaoYuliana PurnamasariPas encore d'évaluation
- 71 142 1 PBDocument5 pages71 142 1 PBYuliana PurnamasariPas encore d'évaluation
- Gleichenia Microphylla NotesheetDocument3 pagesGleichenia Microphylla NotesheetYuliana PurnamasariPas encore d'évaluation
- Fei World Dressage Challenge - Medium Test: CollectedDocument3 pagesFei World Dressage Challenge - Medium Test: CollectedYuliana PurnamasariPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOTECH Project, University of Arizona DNA Extraction From KiwifruitDocument2 pagesBIOTECH Project, University of Arizona DNA Extraction From KiwifruitYuliana PurnamasariPas encore d'évaluation
- Study Guide For Cell DivisionDocument2 pagesStudy Guide For Cell DivisionYuliana PurnamasariPas encore d'évaluation
- BIOTECH Project, University of Arizona DNA Extraction From KiwifruitDocument2 pagesBIOTECH Project, University of Arizona DNA Extraction From KiwifruitYuliana PurnamasariPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.2. Pembelahan Meiosis Dan FertilisasiDocument32 pages3.2. Pembelahan Meiosis Dan FertilisasiYuliana PurnamasariPas encore d'évaluation
- Onion Root Mitosis LabDocument6 pagesOnion Root Mitosis Labapi-2469736100% (1)
- 151F13 Mitosis3 PDFDocument4 pages151F13 Mitosis3 PDFYuliana PurnamasariPas encore d'évaluation
- Asia's Suffering Bears Exploited For BileDocument2 pagesAsia's Suffering Bears Exploited For BileYuliana PurnamasariPas encore d'évaluation
- Asia's Suffering Bears Exploited For BileDocument2 pagesAsia's Suffering Bears Exploited For BileYuliana PurnamasariPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Make A Pencil BoxDocument2 pagesHow To Make A Pencil BoxYuliana PurnamasariPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Make A Pencil BoxDocument2 pagesHow To Make A Pencil BoxYuliana PurnamasariPas encore d'évaluation
- Uenr Uenr: Flow Regimes in The ReservoirDocument12 pagesUenr Uenr: Flow Regimes in The ReservoirOdonkor NicholasPas encore d'évaluation
- MagnetosDocument339 pagesMagnetosrobertocadenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Dogde Nitro 2007 Exhaust and TurboDocument28 pagesDogde Nitro 2007 Exhaust and TurboMurat SahitiPas encore d'évaluation
- Changing Water - Different States of MatterDocument4 pagesChanging Water - Different States of Matterapi-422625647Pas encore d'évaluation
- Whrs ManualDocument41 pagesWhrs ManualAKHLESH JHALLAREPas encore d'évaluation
- SW 347 CoredDocument1 pageSW 347 CoredDanut RusPas encore d'évaluation
- Blow Out Prevention SystemDocument10 pagesBlow Out Prevention SystemABDULBASIT ALIPas encore d'évaluation
- Air Compressors NHP1500 T3 PDFDocument4 pagesAir Compressors NHP1500 T3 PDFpowermanagerPas encore d'évaluation
- Report On CGD Business in IndiaDocument24 pagesReport On CGD Business in IndiaKunal SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 22 Boundary Layer Analogies 2016IDocument59 pagesLecture 22 Boundary Layer Analogies 2016ICESAR AUGUSTO VASQUEZ RUIZPas encore d'évaluation
- Control Valve Straight TravelDocument5 pagesControl Valve Straight TravelSteven Y.MPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3 - Control Components in Hydraulic SystemDocument10 pagesUnit 3 - Control Components in Hydraulic SystemDagnachee TeguPas encore d'évaluation
- Capability Dl&tocument For Process Platforms PDFDocument72 pagesCapability Dl&tocument For Process Platforms PDFSunil SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Bill of Materials: Seal Support SystemsDocument1 pageBill of Materials: Seal Support SystemsBacano CapoeiraPas encore d'évaluation
- 24d03 EFI Diesel Common Rail PDFDocument16 pages24d03 EFI Diesel Common Rail PDFSurya Irawan100% (1)
- MHK Comp Spe Ep Ecp 0103Document56 pagesMHK Comp Spe Ep Ecp 0103roy bermanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Val AlivioSeguridad NPT - HydrosealDocument4 pagesVal AlivioSeguridad NPT - Hydrosealjnu6mnju6njPas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamentals of Gas Pipeline Metering StationDocument5 pagesFundamentals of Gas Pipeline Metering Stationsandeepsri9Pas encore d'évaluation
- HVAC DaikinDocument48 pagesHVAC DaikinSharon LambertPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter - 2 DistillationDocument75 pagesChapter - 2 DistillationJACOB DAVEPas encore d'évaluation
- Viscometer-Group 7Document25 pagesViscometer-Group 7Camille Millondaga100% (1)
- MaintenanceDocument34 pagesMaintenanceThiago SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Industrial Air ControlsDocument195 pagesIndustrial Air ControlsJShearer100% (1)
- First Law of Thermodynamics Applied To ProcessesDocument43 pagesFirst Law of Thermodynamics Applied To ProcessesDavid ChikusePas encore d'évaluation
- Accepted ManuscriptDocument33 pagesAccepted ManuscriptAbhishek Kumar SinhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Turbo Tutorial API 619 5thDocument33 pagesTurbo Tutorial API 619 5thmishraengg100% (2)
- After 4000 RH & 2000 RH After 1000 RHDocument2 pagesAfter 4000 RH & 2000 RH After 1000 RHadeel ghousePas encore d'évaluation
- Why Do We Need Air Compressor in Underground MiningDocument4 pagesWhy Do We Need Air Compressor in Underground MiningBikem BulakPas encore d'évaluation
- 222 34-10-7 Well Testing Report DST2Document62 pages222 34-10-7 Well Testing Report DST2evio guierrezPas encore d'évaluation