Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Pneumonia Pathodiagram
Transféré par
Lester AbadCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Pneumonia Pathodiagram
Transféré par
Lester AbadDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
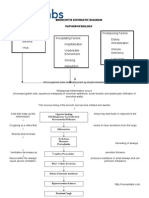
XII.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Modifiable Risk Factors: No history of pneumococcal vaccination No history of having received influenza vaccine Asthma Direct contact with infected person Alcohol Abuse Cigarette Smoking Chronic llnesses !C"D# emph$ema# DM% &ong term use if immunosuppressant drugs Non-modifiable Risk Factors: Contaminated Air
)ortal of ',it: Mouth and Nose 'tiologic Agent: Streptococcus pneumoniae "iral# (acterial# Fungal# )roto*oa Reser-oir: ./MAN
Mode of +ransmission: Airborne# droplet nuclie
)ortal of 'ntr$: Mouth and Nose
'ntr$ to the upper airwa$
nhaled to the lower airwa$ (acteria multiplies in al-eolar spaces
Hyperthermia S1S2: ncreased temperature 3454 6C !N73859-345: 6C% ncreased RR: ;8 bpm !N7:;-39 breaths per minute% ncreased .R <3= bpm !N7<>>-<3> beats per minute% Lab Test: CBC ncreased ?(C !N7 9-<>2<>@:1&%
Stimulation of defense mechanisms
Release of damaging to,ins b$ bacteria
Antigen-antigen bod$ combines with endoto,ins released b$ microorganisms
Mucociliar$ clearance Cough refle, )hagoc$tosis b$ al-eolar macrophages
Release of biochemical mediators b$ al-eolar mast cells .$perresponsi-eness of airwa$s
C$tokine 0 mediated inflammation !Neutrophils migrate to al-eoli%
Further damage to bronchial mucous membranes and al-eolocapillar$ membranes ncreased capillar$ permeabilit$ Al-eolar edema
',udate Formation
Impaired gas exchange S/SX: D RR: ;8 cpm!N7:;-39cpm% D .R: <3= bpm !N7<>><3>bpm% D$spnea ?eak appearance
Stimulation of goblet cells ncrease mucous production
CANB'S+ AN: Al-eoli and Respirator$ brionchioles fill with serous e,udates# blood cells# fibrins# bacteria CANSA& DA+ AN of lung tissue R'D .')A+ CA+ AN: e,udates coagulates resulting to red appearance of tissue with li-er tissue consistenc$
S/SX: Dullness upon percusion Rales upon auscultation
Rich medium for proliferation of bacteria
&ocal capillar$ leak
)artial occlusion of the al-eoli
CXR: Streak$ ha*ed infiltrates at both lungs M): )neumonia# bilateral
Ineffective Airway Clearance S/SX: ?hee*es on auscultation )roducti-e cough +hick purulent sputum ncreased RR: ;8bpm !N7:;-39 breaths per minute%
Spread infection to other areas of the lungs
Reduced surfactant
Stiffens the lung Reduced compliance Decreased -ital capacit$ ?ork of breathing
Ineffective breathing pattern S/SX: D RR: ;8 bpm !N7:;-39bpm% D$spnea /se of accessor$ muscle Nasal flaring
&eukoc$tes !Neutrophils and Macrophages% dominate and eliminate inEurious agents and dead cells BRAF .')A+ CA+ AN: fibrin deposition on pleural surfacesG phagoc$tes in al-eoli R'SA&/+ AN AF NF'C+ AN: ingestion of degenerated neutrophils# fibrin# bacteria b$ macrophages and remo-al b$ l$mphatic -essels Restoration of both structure and function of the lungs
Legend: Disease Process Signs and Symptoms
RED Blue
Mo-es into the bloodstream
Atelectasis !al-eolar collapse
Diagnostics Complications Factors
nfection spreads to other organs of the bod$ reduces the abilit$ of the lungs to o,$genate
h$po-entilation -entilation perfusion mismatch
Septicemia
Septic Shock h$po,emia h$po,ia
h$percapnia Respirator$ acidosis HussmaulIs respiration Respirator$ alkalosis Respirator$ failure Respirator$ arrest
DEAT H
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- CBT Midwifery Full Mock Test 3 Questions Answers Numerical OrderDocument31 pagesCBT Midwifery Full Mock Test 3 Questions Answers Numerical OrderMimi BoamahPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study Near DrowningDocument6 pagesCase Study Near DrowningNashwa Fathira0% (1)
- Aerosols and the Lung: Clinical and Experimental AspectsD'EverandAerosols and the Lung: Clinical and Experimental AspectsStewart W. ClarkePas encore d'évaluation
- Nephrology Notes For USMLEDocument2 pagesNephrology Notes For USMLEGrilled Crowe100% (1)
- Lesson Plan DepressionDocument7 pagesLesson Plan DepressionAnnapurna Dangeti0% (1)
- Acute & Chronic Bronchitis & COPDDocument49 pagesAcute & Chronic Bronchitis & COPDHendraDarmawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Discussion - CopdDocument63 pagesCase Discussion - CopdrajeshPas encore d'évaluation
- 6.pneumonia (New)Document104 pages6.pneumonia (New)sallykartikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pulmonary ConditionsDocument42 pagesPulmonary ConditionsMinettePas encore d'évaluation
- BronchiectasisDocument63 pagesBronchiectasisprabad dunusinghePas encore d'évaluation
- PneumoniaDocument24 pagesPneumoniaMuhammad HassanPas encore d'évaluation
- Morning Report Oct 10 2014Document27 pagesMorning Report Oct 10 2014davidchandra993Pas encore d'évaluation
- Radiological Features of PneumoniaDocument21 pagesRadiological Features of PneumoniaARUSHI ARVINDPas encore d'évaluation
- Physiology of Nose & P.N.S.: Dr. Vishal SharmaDocument54 pagesPhysiology of Nose & P.N.S.: Dr. Vishal SharmaE=MC2Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Lung AbscessDocument51 pages1 Lung AbscessЕвгений ХанькоPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory System DisorderDocument46 pagesRespiratory System DisorderYaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Pg36 37 of Pneumothorax Case StudyDocument2 pagesPg36 37 of Pneumothorax Case StudyCharles Dean Ugalde100% (2)
- ARDSDocument81 pagesARDSShanaz NovriandinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Retropharyngeal Space.Document18 pagesRetropharyngeal Space.Shraavya ShivanandaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument48 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseddallasPas encore d'évaluation
- Lung QuizDocument14 pagesLung QuizConcepcion R. AquinoPas encore d'évaluation
- COPDDocument73 pagesCOPDBroken OreosPas encore d'évaluation
- Suppurative Lung Diseases: DR Taher El Naggar Prof of Pulmonary Medicine Ain Shams UniversityDocument65 pagesSuppurative Lung Diseases: DR Taher El Naggar Prof of Pulmonary Medicine Ain Shams UniversitykingmedicPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Otitis MediaDocument18 pagesAcute Otitis MediaaliramzanPas encore d'évaluation
- Lung AbscessDocument41 pagesLung AbscessokaciaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 s2.0 S193004332100902X MainDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S193004332100902X MainFatimah AssagafPas encore d'évaluation
- By S F Hashmi Guided by DR D G Mhaisekar Sir 22TH FEB 2011Document57 pagesBy S F Hashmi Guided by DR D G Mhaisekar Sir 22TH FEB 2011Fazlullah Hashmi100% (1)
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: TH NDDocument22 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: TH NDSuhaila Naif NasserPas encore d'évaluation
- Emphysema 1Document7 pagesEmphysema 1ironPas encore d'évaluation
- Bronchitis PathophysiologyDocument23 pagesBronchitis PathophysiologyRama Setya Bagaskara100% (2)
- Materi Kelainan ParuDocument72 pagesMateri Kelainan ParuDebiNingtyasDwiKusumaWardaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Shamim Reza CPD Pneumonea Near FinalDocument50 pagesShamim Reza CPD Pneumonea Near FinalMinhajul IslamPas encore d'évaluation
- Scenario 5: Group 6Document51 pagesScenario 5: Group 6Gd SuarantaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ineffective Breathing PatternDocument3 pagesIneffective Breathing PatternErickson OcialPas encore d'évaluation
- The System: RespiDocument247 pagesThe System: RespiKatrina PoncePas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Doctor in Faculty of Medicine, University of Udayana, - Pulmonologist in Faculty of Medicine, University of Indonesia, JakartaDocument24 pagesMedical Doctor in Faculty of Medicine, University of Udayana, - Pulmonologist in Faculty of Medicine, University of Indonesia, Jakartazulfantri1983Pas encore d'évaluation
- RS 1 - Rhinosinusitis + AdenotonsilitisDocument30 pagesRS 1 - Rhinosinusitis + AdenotonsilitisPayung TeduhPas encore d'évaluation
- L 5 - Lungs PathologyDocument128 pagesL 5 - Lungs PathologyDiana Popovici100% (1)
- Left Bronchus SyndromeDocument3 pagesLeft Bronchus SyndromephobicmdPas encore d'évaluation
- Resp Lung Diseases eDocument24 pagesResp Lung Diseases eYudi Aryasena Radhitya PurnomoPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQDocument136 pagesMCQRahul Patil100% (1)
- Respiration CH 43.Dr SarahDocument59 pagesRespiration CH 43.Dr Sarahaiman siddiquiPas encore d'évaluation
- COPD Vs RLDDocument64 pagesCOPD Vs RLDXine DeePas encore d'évaluation
- Bronchitis, COPD, BA 2020Document31 pagesBronchitis, COPD, BA 2020Aditi JainPas encore d'évaluation
- DR Sumardi PPOK - Emfisema-UIIDocument22 pagesDR Sumardi PPOK - Emfisema-UIItrianaamaliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Concept MapDocument3 pagesConcept MapKevin T. KatadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Respirasi System ImagingDocument98 pagesRespirasi System ImagingRerePas encore d'évaluation
- ARDS (Dr. Edi Nurtjahja - SP.P)Document23 pagesARDS (Dr. Edi Nurtjahja - SP.P)Mirna Ayu Permata SariPas encore d'évaluation
- Nader Kamangar, MD, FACP, FCCP FCCM, FAASM, Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, UniversityDocument7 pagesNader Kamangar, MD, FACP, FCCP FCCM, FAASM, Associate Professor of Clinical Medicine, UniversitynurulfitriantisahPas encore d'évaluation
- SGL6 - CoughDocument63 pagesSGL6 - CoughDarawan MirzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Aspergillosis: Radiological DiagnosisDocument12 pagesAspergillosis: Radiological DiagnosisrajdiphazraPas encore d'évaluation
- Bronchopneumonia PP 2003Document31 pagesBronchopneumonia PP 2003Rizky FadhilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lung AbsesDocument48 pagesLung AbsesAvhindAvhindPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (Ards) : Muamar Aldalaeen, RN, Mba, HCRM, Cic, Ipm, MSN, Phd. Haneen Alnuaimi, MSNDocument59 pagesAcute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (Ards) : Muamar Aldalaeen, RN, Mba, HCRM, Cic, Ipm, MSN, Phd. Haneen Alnuaimi, MSNAboodsha ShPas encore d'évaluation
- PBQsDocument18 pagesPBQsShashanka PoudelPas encore d'évaluation
- Annoying New Surgery-1Document81 pagesAnnoying New Surgery-1HIMANSHU GUPTAPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Lung InjuryDocument18 pagesAcute Lung InjuryMariam AlavidzePas encore d'évaluation
- Lower Respiratory (Autosaved)Document58 pagesLower Respiratory (Autosaved)VIVEK DHADYANPas encore d'évaluation
- Quizlet LungsDocument20 pagesQuizlet LungsPrincePas encore d'évaluation
- Defense Mechanism (IB)Document60 pagesDefense Mechanism (IB)wirdahajaPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Mnemonic Sketches : Pulmonary DiseasesD'EverandMedical Mnemonic Sketches : Pulmonary DiseasesPas encore d'évaluation
- Civil Service Form N1Document2 pagesCivil Service Form N1Lester AbadPas encore d'évaluation
- Lord GodDocument1 pageLord GodLester AbadPas encore d'évaluation
- What Are Common Issues On WinS That You Wish To Address With Your Technical Assistance PlanDocument2 pagesWhat Are Common Issues On WinS That You Wish To Address With Your Technical Assistance PlanLester AbadPas encore d'évaluation
- Vaccination AlgorithmDocument2 pagesVaccination AlgorithmLester AbadPas encore d'évaluation
- The Potential Survival and Transmission of SARSDocument2 pagesThe Potential Survival and Transmission of SARSLester AbadPas encore d'évaluation
- Civil Service Form NoDocument1 pageCivil Service Form NoLester AbadPas encore d'évaluation
- Research OutputDocument11 pagesResearch OutputLester AbadPas encore d'évaluation
- Abad - Assignment No. 2Document2 pagesAbad - Assignment No. 2Lester AbadPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrition Month 2021Document2 pagesNutrition Month 2021Lester AbadPas encore d'évaluation
- Outbreak Investigation ReportDocument2 pagesOutbreak Investigation ReportLester AbadPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment of Learning: Prepared By: Loveria, Elsa ADocument14 pagesAssessment of Learning: Prepared By: Loveria, Elsa ALester AbadPas encore d'évaluation
- MudrasDocument2 pagesMudrasPopa MirceaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharm 415b - Antibiotics For Dummies Presentation FinalDocument40 pagesPharm 415b - Antibiotics For Dummies Presentation Finalapi-204163358Pas encore d'évaluation
- Casts N TractionDocument3 pagesCasts N Tractionkatmarie14344100% (1)
- Lecture Hemophilia and Thrombocytopenic PurpuraDocument55 pagesLecture Hemophilia and Thrombocytopenic PurpuraaymenPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid and Electrolyte Therapy During Vomiting and DiarrheaDocument22 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Therapy During Vomiting and Diarrheafernin96Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fitness Choices and First Aid Study NotesDocument11 pagesFitness Choices and First Aid Study NotesAlan VanPas encore d'évaluation
- Outline On Dengue Fever - EDITEDDocument2 pagesOutline On Dengue Fever - EDITEDDavid Skeat0% (1)
- Emmanuel A Etim 2017Document4 pagesEmmanuel A Etim 2017Shafici CqadirPas encore d'évaluation
- Chinese Herbal FormulasDocument8 pagesChinese Herbal Formulasryandakota100% (1)
- Pusponegoro HD. Standar Pelayanan Medis Kesehatan Anak Edisi 1. Jakarta: Badan Penerbit IDAI, 2004. Hal 149-153Document2 pagesPusponegoro HD. Standar Pelayanan Medis Kesehatan Anak Edisi 1. Jakarta: Badan Penerbit IDAI, 2004. Hal 149-153Nurrahmadani RambePas encore d'évaluation
- Electrocardiogram: Dr. PacnaDocument13 pagesElectrocardiogram: Dr. PacnaEcel AggasidPas encore d'évaluation
- Sas 15 MCN Lec 2Document3 pagesSas 15 MCN Lec 2Jhoanna Marie VillaverdePas encore d'évaluation
- Philippine CPG-2013-uti in Adults-Part1 PDFDocument82 pagesPhilippine CPG-2013-uti in Adults-Part1 PDFVirginia AbalosPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 1 6 A FinaldiagnosisDocument2 pages1 1 6 A Finaldiagnosisapi-327503253Pas encore d'évaluation
- 003 Pathology MCQ ACEM Primary CardiovascularDocument5 pages003 Pathology MCQ ACEM Primary Cardiovascularbmhsh100% (2)
- Folate (Vitamin B9) - Báo khoa họcDocument13 pagesFolate (Vitamin B9) - Báo khoa họcNam NguyenHoangPas encore d'évaluation
- Medicine - BhanuDocument469 pagesMedicine - BhanuHIMAVARADHAN UPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 - Case Disfagia DisfoniaDocument41 pages1 - Case Disfagia DisfoniaMegan ShanzuPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical SpecialistsDocument2 pagesMedical SpecialistsArvin Dela CrÜzPas encore d'évaluation
- All Questions To Be Answered. Each Question To Be Answered in A Separate Book (Or Books If More Than One Is Required For The One Answer)Document3 pagesAll Questions To Be Answered. Each Question To Be Answered in A Separate Book (Or Books If More Than One Is Required For The One Answer)matentenPas encore d'évaluation
- True PDFDocument459 pagesTrue PDFAmna MmfPas encore d'évaluation
- Backwell's 5 Min Veterinary ConsultDocument120 pagesBackwell's 5 Min Veterinary ConsultAndra Elena Pricop100% (2)
- Changes in Preventive Care Benefits Due To Health Care ReformDocument3 pagesChanges in Preventive Care Benefits Due To Health Care Reformv4meetPas encore d'évaluation
- Chronic Suppurative Otitis MediaDocument7 pagesChronic Suppurative Otitis MediaMeis MalirmaselePas encore d'évaluation
- Diseases of The Respiratory System and Circulatory SystemDocument7 pagesDiseases of The Respiratory System and Circulatory SystemMaria Teresa GimenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbiology Unit: Urine AnalysisDocument5 pagesMicrobiology Unit: Urine AnalysisSwissFm Cleaning CaptainsPas encore d'évaluation
- Stroke & Neurological Disease Conference: Ninth AnnualDocument2 pagesStroke & Neurological Disease Conference: Ninth Annualyos_peace86Pas encore d'évaluation