Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
AIEEE Minor Test #1
Transféré par
KAPIL SHARMADescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
AIEEE Minor Test #1
Transféré par
KAPIL SHARMADroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
AIEEE Minor Test #1
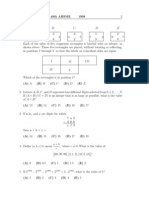
Q1. The triangle with vertices (1, 5); (3, 1) and (3, 5) is 1. isosceles 2. Equilateral 3. right angled 4. None of these Q2. If the points (4, 4), ( 4, 4) and (x, y) form an equilateral triangle then 1. 2. 3. 4. None of these Q3. If (4, 6), (2, 3) and (2, 5) are vertices of a triangle, then its incentre is 1. (1, 2) 2. (2, 1)3. (1, 2)4. (2, 1) Q4.Circumcentre of a triangle whose vertex are (0, 0), (4, 0) and (0, 6) is 1. 2. (0, 0) 3. (2, 3) 4. (4, 6) Q5.Orthocentre of a triangle whose vertex are (8, 2), (2, 2) and (8, 6) is 1. (8, 2) 2. (8, 6) 3. 4. (0, 0) Q6.The area of a triangle with vertices (3, 8); (4, 2) and (5, 1) is 1. 40.5 2. 36.5 3. 3.75 4. 37.5 Q7.If D, E, F are mid points of the sides AB, BC and CA of a triangle formed by the points A(5, 1) B(-7, 6) and C(1, 3), then area of DDEF is 1. 2/5 2. 5/2 3. 5 4. 10 Q8. The point (4, 1) undergoes two successive transformations (i) Reflection about the line y = x (ii) Translation through a distance 2 units along the positive direction of x axis The final position of the point is given by the coordinates 1. (4, 3) 2. (3, 4) 3. (7/2, 7/2) 4. (1, 4) Q9.If A(c, 0) and B( c, 0) are two points, then the locus of a point P which moves such that PA2+ PB2 = AB2 is 1. x2 y2 =c2 2. y2 = 4cx 3. x2 + y2 = c2 4. None of these Q10. Let A(2, 3) and B(4, 5) are two fixed points. A point P moves in such a way that DPAB = 12 sq. units, then its locus is 1. x2 + 6xy + 9y2 + 22 x + 66y 23 = 0 2. x2 + 6xy + 9y2 + 22 x + 66y + 23 = 0 3. x2 + 6xy + 9y2 22 x 66y 23 = 0 4. None of these Q11.If sum of square of distances of a point from axes is 4, then its locus is 1. x + y = 2 2. x2 + y2 = 16 3. x + y = 4 4. x2 + y2 = 4 Q12.The extremities of diagonal of a right-angled triangle are (2, 0) and (0, 2), then locus of its third vertex is 1. x2 + y2 2x 2y = 0 2. x2 + y2 + 2x 2y = 0 2 2 3. x + y 2x + 2y = 0 4. x2 + y2 + 2x + 2y = 0 Q13.Keeping coordinate axes parallel, the origin is shifted to a point (1, 2), then transformed equation of x2 + y2 = 2 is 1. x2 + y2 + 2x 4y + 3 = 0 2. x2 + y2 2x + 4y + 3 = 0 3. x2 + y2 2x 4y + 3 = 0 4. x2 + y2 2x + 4y + 3 = 0 Q14.To remove xy term from the second degree equation 5x2 + 8xy + 5y2 + 3x + 2y + 5 = 0, the coordinates axes are rotated through an angle q, then q equals 1. p/2 2. p/4 3. 3p/8 4. p/8 Q15.The ratio in which the line y x + 2 = 0 divides the line joining (3, 1) and (8, 9) is
1. 2 : 3 2. 3 : 2 3. 2 : 3 4. 3 : 2 Q16.The area of the triangle, formed by the straight lines 7x 2y + 10 = 0, 7x + 2y 10 = 0 and 9x + y + 2 = 0, is 1. 2. 3. 4. None of these Q17.Two vertices of a triangle are (3, 1) and ( 2, 3) and its orthocenter is origin, the coordinates of the third vertex are 1. 2. 3. 4. Q18. The equation of the internal bisector of BAC of DABC with vertices A(5, 2), B(2, 3) and C(6, 5) is 1. 2x + y + 12 = 0 2. x + 2y 12 = 0 3. 2x + y 12 = 0 4. None of these Q19.The equation of the straight line upon which the length of perpendicular from origin is units and this perpendicular makes an angle of 75 with the positive direction of x axis, is 1. 2. 3. 4. None of these Q20.The image of the point ( 8, 12) with respect to the line mirror 4x + 7y + 13 = 0 is 1. (16, 2) 2. ( 16, 2) 3. (16, 2) 4. ( 16, 2) Q21.The equation of the straight line passing through the point of intersection of lines3x4y7= 0 and 12x 5y 13 = 0 and perpendicular to the line 2x 3y + 5 = 0 is 1. 33x + 22y + 13 = 0 2. 33x + 22y 13 = 0 3. 33x 22y + 13 = 0 4. None of these Q22.If the family of lines x(a + 2b) + y(a + 3b) = a + b passes through the point for all values of a and b, then the coordinates of the points are 1. (2, 1) 2. (2, 1) 3. ( 2, 1) 4. None of these Q23.The value of k so that the lines 2x 3y + k = 0, 3x 4y 13 = 0 and 8x 11y 33 = 0 are concurrent, is 1. 7 2. 7 3. 5 4. 5 Q24.Let P be the image of the point ( 3, 2) with respect to x-axis. Keeping the origin as same, the coordinate axes are rotated through an angle 60 in the clockwise sense. The coordinates of point P with respect to the new axes are 12. 3. 4. None of these Q25.If for a variable line , the condition a2 + b2 = c2 (c is a constant) is satisfied, then the locus of foot of the perpendicular drawn from origin to this is 1. x2 + y2 = 2. x2 + y2 = 2c2 3. x2 + y2 = c2 Q26.If A and B are two sets, then A (A B) equals 1.A 2.B 3. 4. none of these Q27.Which of the following is an empty set ? (a)The set of prime numbers which are even (b)The solution set of the equation =0;x R (c)(A x B) (B x A), where A and B are disjoint (d)The set of real which satisfy x2 + ix + i 1 = 0 Q28.If sets A and B are defined as :A={(x, y) :y= 1. A B = A 2. A B = B 3. A B = 4. none of these 4. x2 y2 = c2
, x 0, x R},B = {(x, y) : y =-x, x R}, then
Q29.Let R be reflexive relation on a finite set A having n elements, and let there be m ordered pairs in R. Then 1. m n 2. m n 3. m = n 4. none of these Q30.f(x) = | sin x | has an inverse if its domain is : 1. [ 0, p ] 2. 3. 4.none of these Q31.Consider the following equations (1) A B = A (A B) (2) A = (A B) (A B) (2) A (B C) = (A B) (A - C) Which of these is / are correct 1. 1 and 3 2. 2 only 3. 2 and 3 4. 1 and 2 Q32.If a is the set of the divisors of the number 15, B is the set of prime numbers smaller than 10 and C is the set of even numbers smaller than 9, then (A C) B is the set 1. {1, 3, 5} 2. {1, 2, 3} 3. {2, 3, 5} 4. {2, 5} Q33.x, y and z are rational numbers. Consider the following statements in this regard A x+3=y+zx=y B. xz = yz x = y Which of the above statement(s) is / are correct ? 1. 1 alone 2. 2 alone 3. Both 1 and 2 4. Neither 1 nor 2 th Q34.If second term of an AP is 2 and 7 term is 22, then sum of 9 terms is 1. 126 2. 126 3. 90 4. 252 Q35.If Sn denotes the sum of the first n terms of an AP and S2n = 3Sn, then 1. 7 2. 6 3. 8 4. 10 Q36.The sum of r terms of an AP is denoted by Sr and , then the ratio of the 7th term and 5th term of the AP is 1. 2. 3. 4. Q37.A square is drawn by joining the mid points of the given square a third square in the same way and this process continues indefinitely. If a side of the first square is 16 cm, then the sum of the areas of all the squares 1. 128 sq cm 2. 256 sq cm 3. 512 sq cm 4. 1024 sq cm Q38.If the pth term of an AP is and qth term is then the sum of the first pq terms is 1. 0 2. (pq 1) 3. (pq + 1 )4. Q39.If the AM between pth and qth terms of an AP be equal to AM between rth and sth terms of the AP, then 1. p + s = q + r 2. p + q = r + s 3. p + r = q + s 4. p + q + r + s = 0 Q40.The value of 5 + 55 + 555 + to n terms is 1. 10n + 1 10 2. 3. [10n + 1 1 + 9n] 4. (10n + 1 10)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Families of CurvesDocument2 pagesFamilies of CurvesJoshua RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Lesson 1 - PT - Interior and Exterior Angles of PolygonsDocument32 pagesLesson 1 - PT - Interior and Exterior Angles of PolygonsDheeraj YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Volume and Surface Area of 3D Shapes: Key PointsDocument5 pagesVolume and Surface Area of 3D Shapes: Key PointsMohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- FOUNDATION - MATHS - STD7 - 8 - M92 - FLOW - PLANNER - SAMPLE - PAPERS of RAJESH SIR 2022-23Document23 pagesFOUNDATION - MATHS - STD7 - 8 - M92 - FLOW - PLANNER - SAMPLE - PAPERS of RAJESH SIR 2022-23Ramkumar SundaramPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Euclidean GeometryDocument146 pagesAdvanced Euclidean GeometryAltananyPas encore d'évaluation
- Summative Test in Math 5 by Sir Rei MarasiganDocument21 pagesSummative Test in Math 5 by Sir Rei MarasiganMarites James - LomibaoPas encore d'évaluation
- KR Classes Xi Sets Th+solved ExamplesDocument4 pagesKR Classes Xi Sets Th+solved ExamplesKAPIL SHARMAPas encore d'évaluation
- D Block Elements QBDocument8 pagesD Block Elements QBKAPIL SHARMAPas encore d'évaluation
- Binomial Theorum Question Bank PDFDocument17 pagesBinomial Theorum Question Bank PDFKAPIL SHARMAPas encore d'évaluation
- 01-05-16 SR - Iplco Ic Isb Liit Jee Adv (New Model-IV p1) Gta-8 Key & Sol'sDocument10 pages01-05-16 SR - Iplco Ic Isb Liit Jee Adv (New Model-IV p1) Gta-8 Key & Sol'sKAPIL SHARMAPas encore d'évaluation
- 01-05-16 SR - Iplco Ic Isb Liit Jee Adv (New Model-IV p1) Gta-8 Q'PDocument36 pages01-05-16 SR - Iplco Ic Isb Liit Jee Adv (New Model-IV p1) Gta-8 Q'PKAPIL SHARMA100% (1)
- The Real Number SystemDocument11 pagesThe Real Number SystemKAPIL SHARMAPas encore d'évaluation
- Baprog 2004Document170 pagesBaprog 2004Manish KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Suggested Problems On RelationDocument2 pagesSuggested Problems On RelationKAPIL SHARMAPas encore d'évaluation
- QUESTION BANK Multiple Choice6Document11 pagesQUESTION BANK Multiple Choice6KAPIL SHARMAPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Test Paper Trigonometry-03 Ace LevelDocument1 pagePractice Test Paper Trigonometry-03 Ace LevelKAPIL SHARMAPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Test Paper Inequation-02 Iit LevelDocument3 pagesPractice Test Paper Inequation-02 Iit LevelKAPIL SHARMAPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes: Chapter 9 Mensuration: CircleDocument4 pagesNotes: Chapter 9 Mensuration: CircleST Electrical & ConstructionPas encore d'évaluation
- 04 - Projection of SolidsDocument33 pages04 - Projection of SolidsCreative ThinkerPas encore d'évaluation
- Prmo SolutionDocument17 pagesPrmo SolutionBilly BlattPas encore d'évaluation
- IMO Paper (Class-X)Document7 pagesIMO Paper (Class-X)Hanuman ParsadPas encore d'évaluation
- 9th-IMO (Stage-II) (Class-8) 14-2-16 PDFDocument6 pages9th-IMO (Stage-II) (Class-8) 14-2-16 PDFMohnish JaiswalPas encore d'évaluation
- 3RD Grading Examination in Math9Document2 pages3RD Grading Examination in Math9earnestPas encore d'évaluation
- Geometry PracticeDocument8 pagesGeometry PracticeEddy R. VélezPas encore d'évaluation
- Analytic ReviewDocument9 pagesAnalytic ReviewpsittacosisPas encore d'évaluation
- AHSME 1998 ProblemsDocument5 pagesAHSME 1998 ProblemsjabagaweePas encore d'évaluation
- Aime OSN SMA 2024Document5 pagesAime OSN SMA 2024marvelrismawan43Pas encore d'évaluation
- 02-Aop (Adv) - Question Paper - 1-1Document7 pages02-Aop (Adv) - Question Paper - 1-1SUB MOH MAYA HAIPas encore d'évaluation
- MATHEMATICS1 To 101Document10 pagesMATHEMATICS1 To 101Adriane Patrick QuirosPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 6 Cbse Maths Question Paper Fa 2Document2 pagesClass 6 Cbse Maths Question Paper Fa 2Sunaina Rawat33% (3)
- SSC CHSL LDC DEO Numerical 2011 Paper PDFDocument5 pagesSSC CHSL LDC DEO Numerical 2011 Paper PDFyuvarajPas encore d'évaluation
- Arc Length & Circumference: Name: - DateDocument3 pagesArc Length & Circumference: Name: - DateKadiatou DialloPas encore d'évaluation
- Smarandache Curves and Spherical Indicatrices in The Galilean 3-SpaceDocument13 pagesSmarandache Curves and Spherical Indicatrices in The Galilean 3-SpaceDon HassPas encore d'évaluation
- ConstructionDocument9 pagesConstructionvedant singhPas encore d'évaluation
- Name: Teacher: Date: Score:: Triangle Angle SumDocument2 pagesName: Teacher: Date: Score:: Triangle Angle SumMohammadPas encore d'évaluation
- Circum RevDocument46 pagesCircum RevVroojak KhoshrooPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan Mathematics (3 Year High School)Document6 pagesLesson Plan Mathematics (3 Year High School)Marla Jean FabroPas encore d'évaluation
- Area & Perimeter - CRACK SSC PDFDocument10 pagesArea & Perimeter - CRACK SSC PDFSai Swaroop AttadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Colegio de San Juan de Letran: ND RDDocument5 pagesColegio de San Juan de Letran: ND RDELLAINE DE CLAROPas encore d'évaluation
- CirclDocument9 pagesCirclSantosh100% (1)