Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Josefina E Florendo, RN, MAN
Transféré par
adnep1991Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Josefina E Florendo, RN, MAN
Transféré par
adnep1991Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Josefina E.
Florendo, RN, MAN
Insulin Injection Certification Workshop:Insulin Injection Techniques
INSULIN TECHNIQUES Objectives
At the end of the presentation, the participants will be able
to:
1 . State ways to administer insulin safely;
2. Identify interventions to prevent problems associated with
insulin administration;
3. Demonstrate the competencies expected in the
administration of insulin.
Josefina E. Florendo, RN, MAN
INSULIN Insulin Preparations
Most powerful and effective pharmacologic tool available Class Agents
to treat diabetes.
Human insulin Regular, NPH, lente
Its potential to lower plasma glucose levels is limited only
by hypoglycemia. Insulin analogues Aspart, Glulisine, Lispro,
Glargine, Detemir
Sustained near-normal blood sugar to prevent the onset
Premixed insulin Human 70/30, 50/50
and progression of long-term complications is the major
Humalog mix 75/25
treatment goal of insulin therapy. Novomix 70/30
INSULIN ADMINISTRATION Insulin Administration Devices
Insulin therapy is used to achieve
and sustain target-level glycemic
Delivered using various devices
Josefina E. Florendo, RN, MAN
Insulin Injection Certification Workshop:Insulin Injection Techniques
Insulin Administration Devices Insulin Pen
Insulin pens
reusable pen
Faster and easier
than syringes
Improve patient attitude
and adherence
Have accurate dosing
mechanisms, but
inadequate mixing may
Hides needle to reduce anxiety
be a problem
disposable pens
Insulin Pump Insulin Pump
Continuous
subcutaneous insulin
infusion (CSII)
External, programmable
pump connected to an
indwelling subcutaneous
catheter to deliver rapid- External, programmable
acting insulin pump connected to an
indwelling subcutaneous
catheter to deliver rapid-
acting insulin
Insulin Administration Devices INSULIN ADMINISTRATION
Inhaler
Technique employed in administration
may affect absorption rate and
eventually the blood glucose levels.
Designed for people with:
Poor eyesight No longer available
Dexterity problems
Learning difficulties
Josefina E. Florendo, RN, MAN
Insulin Injection Certification Workshop:Insulin Injection Techniques
Injection Tips Insulin Tips
Do NOT wipe the needle with alcohol Absorption differs in various areas of the human
as it removes the protective coating. body.
The coating makes injection easier The new shot can be given in the area with the
and less painful distance of 1 to 2 fingers from the site where
the last shot was given.
Site Selection/ Rotation Insulin Tips
Injecting any insulin at the same site
repeatedly over time or blunting a needle
with re-use can cause a lipodystrophy:
either lipoatrophy or lipohypertrophy.
Either makes absorption unreliable.
Varying the injection site can cause variability
in action profile.
Lipodystrophy Insulin Tips
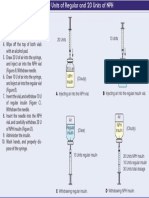
Eliminate bubbles
Keep vial upright
Draw insulin slowly
Re-inject insulin into vial when air bubble
get into the syringe
Tap the syringe with a finger or two to remove
air bubbles while holding it upright
Josefina E. Florendo, RN, MAN
Insulin Injection Certification Workshop:Insulin Injection Techniques
Insulin Tips Insulin Tips
In mixing clear and cloudy insulin, bubbles can be removed Cold Insulin
from the clear insulin, which is drawn first. but can't remove
bubbles after both insulins are in the syringe. Bring to room temperature to prevent sting
* Remove from fridge before administration
Insulin can’ t be pushed back into the bottle of cloudy insulin, * Warm capped syringe with hands
from the syringe which already contains clear insulin. This would
* Do not warm insulin using stove or
cause two problems:
* Y ou won't get the full amount of clear insulin microwave
that you need
* It will change the insulin in the cloudy insulin bottle
(because some clear insulin has been mixed into it)
Insulin Tips Injection Tips
Do Not Use Insulin If:
Injection leakage
bottle appear to be frosted
clear insulin that looks discolored, turned
Cause holding pinch too long when shot is given
cloudy, or hazy Pinch forces some of the insulin back from the newly
cloudy insulin that is appears yellowish or created hole in the
remains lumpy or clotted after mixing Short needle can cause insulin leakage
Bleeding at Site of Injection
usually caused when the syringe
Preventing leakage punctures a tiny blood vessel
Release pinch or can be stopped by putting pressure on the injection site
squeeze with finger or a cotton ball.
Count to 10 before Be sure that you:
removing the needle Don't rub the spot.
Maintain light pressure with your finger to prevent bruising.
If a bruise does appear, don't use that injection site again
until the bruise is gone.
Josefina E. Florendo, RN, MAN
Insulin Injection Certification Workshop:Insulin Injection Techniques
To keep your blood glucose on target follow Insulin Absorption
these two rules for proper site rotation: Insulin is absorbed fastest when injected into the subcutaneous tissue in the
abdomen (stomach), and somewhat less quickly in the upper arms, thighs, and
buttocks/hips.
Same general location at the same time
The difference in absorption rates can be used to plan where to inject insulin.
each day. For example:
Rapid-onset insulin can be injected into the abdomen just before or right after
Rotate within each injection site. you eat a meal to take advantage of the abdomen's fast absorption rate.
NPH insulin can be injected into a different site (arms, thighs, or buttocks), to
take advantage of the slower absorption rate while you sleep.
Injection Site Insulin Absorption
Do not inject close to the belly button. Do not inject close to moles or Inject breakfast and lunch bolus doses into the abdomen
scars. The tissue there is tougher insulin absorption will not be as because Insulin is absorbed fastest when injected into this
consistent.
area.
Injecting in the upper arm, use only the outer back area (where the most
fat is). It is hard to pinch the upper arm when doing self injection. Try Fast absorption is needed at mealtimes to cover the
pressing upper arm against a wall or door. carbohydrates you are about to eat.
When injecting in the thigh, stay away from the inner thighs. If thighs
rub together when walking, if might make the injection site sore.
Do not inject in an area that will be exercised soon. Exercising The supper or bedtime dose of long-acting insulin could
increases blood flow, which causes long-acting insulin to be absorbed be injected into the thigh, buttocks, or upper arm so the
at a rate that’ s faster needed. long-acting insulin can take effect gradually and cover
needs throughout the night.
Insulin Absorption
Exercise can affect
the absorption rate
Fastest from the abdomen
A little slower from the arms playing basketball after injecting choose a site other
Even slower from the legs than the shooting/dribbling arm, since injecting there can
increase the absorption rate.
Slowest from the buttocks
If it is preferred to inject near a part of body used when
exercising wait at least 45 minutes after injecting
before starting activity.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Insulin: Pancreatic Hormones and Antidiabetic DrugsDocument5 pagesInsulin: Pancreatic Hormones and Antidiabetic DrugsEric James ManuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Insulin Therapy Is A Critical Part of Treatment For People Who Have Type 1 Diabetes and For Many Who Have Type 2 DiabetesDocument3 pagesInsulin Therapy Is A Critical Part of Treatment For People Who Have Type 1 Diabetes and For Many Who Have Type 2 DiabetesRebeccah Abrazaldo100% (1)
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument2 pagesNew Microsoft Word Documenteslambasuony98Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology of Insulin and It'S AnaloguesDocument31 pagesPharmacology of Insulin and It'S AnaloguesVikas VikiPas encore d'évaluation
- Insulin Lispro Sanofi Epar Product Information - en PDFDocument63 pagesInsulin Lispro Sanofi Epar Product Information - en PDFAndreea Claudia NegrilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Insulin Injection How To AadeDocument8 pagesInsulin Injection How To AadeRamzi DkhiliPas encore d'évaluation
- Recent Trends in Insulin Drug Delivery SystemDocument39 pagesRecent Trends in Insulin Drug Delivery Systemandry natanel tonyPas encore d'évaluation
- Alternative Devices Insulin 508Document4 pagesAlternative Devices Insulin 508Aaron Wallace100% (1)
- EC3-3 - Kang Hee SimDocument50 pagesEC3-3 - Kang Hee SimerikaoktavianipurbaPas encore d'évaluation
- DiabetesDocument9 pagesDiabetesMsPocketbook HoarderPas encore d'évaluation
- TX Insulina IncretinasDocument5 pagesTX Insulina IncretinasFabiola Pantoja ViorPas encore d'évaluation
- InsulinDocument2 pagesInsulinKristine YoungPas encore d'évaluation
- Insulin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesInsulin Drug StudyAziil Liiza100% (2)
- Universitatea "Ovidius" Din Constanta Facultatea de Farmacie Program de Studii FarmacieDocument12 pagesUniversitatea "Ovidius" Din Constanta Facultatea de Farmacie Program de Studii FarmacieAnamaria AvramPas encore d'évaluation
- Insulin AdministrationDocument15 pagesInsulin Administrationmec17Pas encore d'évaluation
- Insulin and Its Preparation: DR C.Sadhana Final Year MD Pharmacology Department of Pharmacology SBMCHDocument62 pagesInsulin and Its Preparation: DR C.Sadhana Final Year MD Pharmacology Department of Pharmacology SBMCHP Vinod KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Gestational Starting Insulin - FINAL - July 20Document4 pagesGestational Starting Insulin - FINAL - July 20ThaísPas encore d'évaluation
- StudyDocument2 pagesStudyit4728Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing - CS - Comparison Chart of Different Insulins - 04Document1 pageNursing - CS - Comparison Chart of Different Insulins - 04Jazzmine GuraPas encore d'évaluation
- Insulin Therapies Current and Future Trends at DawDocument8 pagesInsulin Therapies Current and Future Trends at DawHardhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Insulin AdministrationDocument13 pagesInsulin AdministrationMuhammad Aji SantosoPas encore d'évaluation
- Insulin PharmDocument21 pagesInsulin PharmMeredith Barb0% (1)
- Insulin - Injection - How - To - Aade 564446545Document8 pagesInsulin - Injection - How - To - Aade 564446545Hassan kamalPas encore d'évaluation
- Health Teaching Plan: PreventDocument7 pagesHealth Teaching Plan: PreventGia ConconPas encore d'évaluation
- Insulin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesInsulin Drug Studykuro hanabusaPas encore d'évaluation
- Materi Apt. Christina Fix-The Role of Pharmacist EducationDocument35 pagesMateri Apt. Christina Fix-The Role of Pharmacist Educationrani widiastutiPas encore d'évaluation
- Insulin Injection Pro Tips AadeDocument6 pagesInsulin Injection Pro Tips Aaderavenska ramschiePas encore d'évaluation
- Insulin AnaloguesDocument10 pagesInsulin AnaloguesanthopivanPas encore d'évaluation
- Jaaha 1999 35 4Document83 pagesJaaha 1999 35 4A FMPas encore d'évaluation
- Diabetes MELLITUSDocument15 pagesDiabetes MELLITUSAshtua MandixPas encore d'évaluation
- Target Tahun 2019 Semester 1Document8 pagesTarget Tahun 2019 Semester 1Rero CitroPas encore d'évaluation
- Timely Intensification Using Bolus Insulin Therapy - HimawanDocument50 pagesTimely Intensification Using Bolus Insulin Therapy - HimawanVictoria BrandedBagPas encore d'évaluation
- Yguadiz TeachingDocument1 pageYguadiz TeachingYESSAMIN GUADIZPas encore d'évaluation
- Review of Efficacy and Safety of Insulin Agents 3Document14 pagesReview of Efficacy and Safety of Insulin Agents 3sendhilkumarPas encore d'évaluation
- P 174 Insulin TherapyDocument3 pagesP 174 Insulin TherapyJeane ClerkPas encore d'évaluation
- Mixing InsulinsDocument1 pageMixing InsulinsBloomPas encore d'évaluation
- Anti-Diabetic Drugs InsulinDocument26 pagesAnti-Diabetic Drugs Insulinwissam salimPas encore d'évaluation
- Insulin in DiabetesDocument9 pagesInsulin in DiabetesAbdul SamadPas encore d'évaluation
- Study Notes Notes Diabetes Insulin GuideDocument11 pagesStudy Notes Notes Diabetes Insulin GuideRaju Niraula100% (2)
- Insulin PreparationsDocument3 pagesInsulin PreparationsSiti Munirah OthmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparison Between Long Acting InsulinsDocument3 pagesComparison Between Long Acting InsulinsSiddiq MohammedPas encore d'évaluation
- InsulinDocument5 pagesInsulinAshan BopitiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Prepared By: Vijay Thapa Under Guidance of Uday Satone Shashank LamsalDocument13 pagesPrepared By: Vijay Thapa Under Guidance of Uday Satone Shashank LamsalTHAPA VIJAYPas encore d'évaluation
- 9 PropofolDocument2 pages9 PropofolAbdelhafiz Susmiran100% (3)
- Skills LabDocument107 pagesSkills LabskybluealiPas encore d'évaluation
- Nama: Mega Silvia Putri KELAS: 2.02 NIM: 430116065Document3 pagesNama: Mega Silvia Putri KELAS: 2.02 NIM: 430116065megaPas encore d'évaluation
- DC Your Guide To Diabetes Management PE enDocument9 pagesDC Your Guide To Diabetes Management PE enJimenez Renalyn M.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Pharmacology HandoutsDocument8 pagesNursing Pharmacology HandoutsDexie MaePas encore d'évaluation
- Drawing Up InsluinDocument4 pagesDrawing Up InsluinÀi ZìjǐPas encore d'évaluation
- Humulin 3070 Ca Pmi CartDocument5 pagesHumulin 3070 Ca Pmi CartJoshua DeonarinePas encore d'évaluation
- NCM 116a-DmDocument21 pagesNCM 116a-DmHanna BaddiriPas encore d'évaluation
- Readings (Insulin) - RetuyaDocument20 pagesReadings (Insulin) - RetuyaFionah RetuyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Product Monograph: HumulinDocument54 pagesProduct Monograph: HumulinpatgarettPas encore d'évaluation
- Insulin Therapy RevisedDocument17 pagesInsulin Therapy RevisedOluwatimilehin Olagunju100% (1)
- Subcutaneous Injection: Humalog U-100 or U-200: More CommonDocument2 pagesSubcutaneous Injection: Humalog U-100 or U-200: More Commonahmad ryanPas encore d'évaluation
- Novorapid Novomix Pi v8 2021Document19 pagesNovorapid Novomix Pi v8 2021Nazmul Hasan MahmudPas encore d'évaluation
- Insulin PharmacologyDocument1 pageInsulin PharmacologyzainabPas encore d'évaluation
- Insulin: BY Dental Student Mahmoud Kamal Mohammed SaeedDocument10 pagesInsulin: BY Dental Student Mahmoud Kamal Mohammed SaeedMahmood SaeedPas encore d'évaluation
- DM TreatmentDocument9 pagesDM TreatmentAshraf AbdullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Insulin Handbook: Understanding the Role and Effects of Insulin in Your BodyD'EverandInsulin Handbook: Understanding the Role and Effects of Insulin in Your BodyPas encore d'évaluation
- Myrissa Melinda L Alip, MDDocument5 pagesMyrissa Melinda L Alip, MDadnep1991Pas encore d'évaluation
- Exercise Leveling of Expectation 050611Document2 pagesExercise Leveling of Expectation 050611adnep1991Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cherian Varghese SlidesDocument8 pagesCherian Varghese Slidesadnep1991Pas encore d'évaluation
- DR Ronaldo M Toledo, MDDocument5 pagesDR Ronaldo M Toledo, MDadnep1991Pas encore d'évaluation
- Francis I Pasaporte, MD, MSDocument6 pagesFrancis I Pasaporte, MD, MSadnep1991Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nines P Bautista, MD, MSDocument12 pagesNines P Bautista, MD, MSadnep1991Pas encore d'évaluation
- Doh Circular On PADE ADNEP ConventionDocument1 pageDoh Circular On PADE ADNEP Conventionadnep1991Pas encore d'évaluation
- CPG THDocument335 pagesCPG THAhmad Syahmi YZPas encore d'évaluation
- The Scarecrow Queen (Excerpt)Document36 pagesThe Scarecrow Queen (Excerpt)I Read YA50% (2)
- Mitochondrial Respiratory ComplexesDocument30 pagesMitochondrial Respiratory ComplexesDouglas DíazPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug EduDrug Education and Vice Controlcation and Vice ControlDocument9 pagesDrug EduDrug Education and Vice Controlcation and Vice ControlChristian Dave Tad-awanPas encore d'évaluation
- Tonsillectomy TechniquesDocument11 pagesTonsillectomy TechniquesBrigita De VegaPas encore d'évaluation
- 4-6 SL PsychostimulantsDocument35 pages4-6 SL PsychostimulantsMichiko MeritasariPas encore d'évaluation
- UntitledDocument138 pagesUntitledDilşad Okan ÖzerkanPas encore d'évaluation
- CBC Reviewer Anaphy LabDocument9 pagesCBC Reviewer Anaphy LabARVINE JUSTINE CORPUZPas encore d'évaluation
- Aki 2018Document45 pagesAki 2018NURUL ROMADHONPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Burns ArticleDocument7 pagesTypes of Burns ArticleSeltri 'ceti' SeptianiPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathology+101 Complete)Document147 pagesPathology+101 Complete)Goh Kah Yong100% (2)
- Immunocal Tops Mount EverestDocument4 pagesImmunocal Tops Mount Everestapi-3714923Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dr. Vijetha Shenoy Belle Associate Professor & In-Charge Clinical Biochemistry Laboratory Department of Biochemistry KMC ManipalDocument53 pagesDr. Vijetha Shenoy Belle Associate Professor & In-Charge Clinical Biochemistry Laboratory Department of Biochemistry KMC ManipalKavya GaneshPas encore d'évaluation
- WBI11 01 Que 20220108Document28 pagesWBI11 01 Que 20220108Hammodshan 7Pas encore d'évaluation
- START Triage Training PresentationDocument85 pagesSTART Triage Training PresentationAnita Amanda100% (1)
- Total LaryngectomyDocument15 pagesTotal LaryngectomyKumaran Bagavathi RagavanPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes For Zoology - Page 5 - CSS ForumsDocument13 pagesNotes For Zoology - Page 5 - CSS ForumsTahirMobeen0% (1)
- Extroverts (Also Spelled Extraverts: ExtroversionDocument8 pagesExtroverts (Also Spelled Extraverts: Extroversionrams4u_001Pas encore d'évaluation
- Kingdom Animalia Pactical 1Document5 pagesKingdom Animalia Pactical 1Alexson UndiPas encore d'évaluation
- Phonetics & Phonology (Danial Nadeem, Areeba Hamid, Shahrose Shahzadi, Muhammad Dawood)Document9 pagesPhonetics & Phonology (Danial Nadeem, Areeba Hamid, Shahrose Shahzadi, Muhammad Dawood)Danial GujjarPas encore d'évaluation
- How Does Exercise Affect Heart Rate Alvin PDFDocument13 pagesHow Does Exercise Affect Heart Rate Alvin PDFapi-134712575Pas encore d'évaluation
- FrostbiteDocument19 pagesFrostbiteKhadim Hussain Shah100% (1)
- AnatomyDocument8 pagesAnatomyRobbie WoelkersPas encore d'évaluation
- Science Chapter 7Document6 pagesScience Chapter 7Deb Kumar SarkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Nano DentistryDocument6 pagesNano DentistryanugrasPas encore d'évaluation
- Thehumancerebellum: A Review of Physiologic NeuroanatomyDocument11 pagesThehumancerebellum: A Review of Physiologic NeuroanatomyCan EkerPas encore d'évaluation
- Impression Materials For Partial DentureDocument40 pagesImpression Materials For Partial Dentureyunie0959Pas encore d'évaluation
- Guide To AMA Manual of StyleDocument5 pagesGuide To AMA Manual of StyleAbo Ahmed TarekPas encore d'évaluation