Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Principles of Pervaporation
Transféré par
Nithya RamCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Principles of Pervaporation
Transféré par
Nithya RamDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
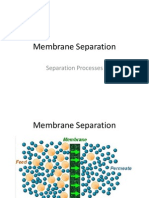
PERVAPORATION : It is a membrane technical method for the separation of mixtures of liquids by partial vaporization through a non-porous or porous membrane..
It is employed when distillation cannot be employed like for azeotropic mixtures.(EX: ethanol-water, isopropyl alcoholwater) Cos separation of close boiling mixtures usind distillation,liq-liq extraction is difficult as compounds have similar physico-chem properties.
PRINCIPLES OF PERVAPORATION: Is the only membrane process where phase transition occurs. Liq mixture is kept in direct contact with 1 side of membrane and permeated pdt(pervaporate)is removed in the form of vapor. At least the heat of vaporization have to be supply. The mass flux is achieved by maintaining the downstream pp lower than the saturation pressure on the permeate side by: gas carrier, vacuum or temperature difference. The driving force is the partial pressure difference of the permeate between the feed and permeate streams. The permeate pressure has to be lower than the saturation pressure of the permeant to achieve the separation.
ZXADWWD
Pervaporation involve a sequence of three steps: Selective sorption Selective diffusion through the membrane BY PERMEATION. Desorption into a vapor phase on the permeate side BY VAPORISATION.
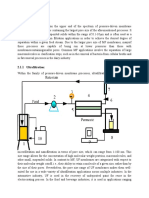
BASIC PRINCIPLE: It involves: 1)evaporation.- the temp of feed liqis elevated to pt wer sat vap comes in contact with membrane. 2)permeation.- the vapor diffuses from feed side,across membrane to permeate side.a condenser is installed on permeate side to create a pressure lower than feed side.mathemattically,second process is defined as ratio of components in te permeate vapor to ratio of components in feed vapor. The vapor permeate is at least partially condensed to produce a liq pdt.any uncondensable vapor is purged out. Mass flux is due to cont adsorption on one side and desorption on the other.
DESIGN FOR PERVAPORATION MODULE:
FACTORS AFFECTING PERVAPORATION: 1)FEED COMPOSITION AND CONCENTRATION:a change in the feed composition directly affects te sorption phenomena at the liq membrane interface.this can b proved by solution diffusion principle,and as diffusion of the components in the membrane is dependant on the conc of the components,the permeation characteristics are,hence dependant on the feed conc as well. 2)FEED AND PERMEATE PRESSURE: The driving force in pervaporation is the partial pressure ddiff of components which in turn is dependant on activity gradient of components.the permeate pressure is directly related to the activity of components at downstream side of membrane and strongly influences the pervaporation characteristics.the max gradient can b obtained for zero permeate presuure,n thus for higher permeate pressures,the feed pressure influences the pervaporation characteristics. 3)TEMPERATURE: As temp of feed increases,the permeation rate generaaly follows arrhenius type eqn.the selectivity is strongly dependant on temp,in most small cases a small dec in selectivity is observed with inc temp.
CONCENTRATION POLARIZATION: DESIGN OF PERVAPORATION MODULE: MEMBRANES FOR PERVAPORATION: The choice of the membrane material has direct bearing on the separation effect to be achieved. It depends on the feed solution.the performance of the membrane is determined by the degree ofseparation of fluid mixtures and permeation rate(flux).Two main kinds of polymers for pervaporation may be identified
1.COMPOSITE MEMBRANES: Tey consist of two layers. The first layer is porous,polymeric support coated with a second polymer,the active or permselective layer,which preferentially adsorbs the chemical species. EX :asymmetric composite hydrophilic membrane lik PVAPS[POLY(VINYL ALCHOL)-POLYSULPHONE] 2.HYDROPHILIC MEMBRANES: Tey r used to remove wter from organic solutions. Cos of hydrophilic charcter,tese membranes enable te extraction of wter with fluxes and selectivity depending upon chemical structure of te active layer and its mode of cross linking. Tey r made up of organic polymers having glass transition temp above room temp. EX: polyvinyl alcohol. 3.ELASTOMERIC(ORGANOPHILIC): Tey are used to recover organics from solutions. Tey r polymers with glass transition temperature below room temp. EX: butadiene rubber,styrene butadiene rubber. MEMBRANE MODULE: Hollow fiber module: This module is used with an insideout configuration to avoid increase in permeate pressure within the fibers, but the outsidein configuration can be used with short fibers. Another advantage of the inside-out configuration is that the thin top layer is better protected but higher membrane area can be achieved with the outside-in configuration Plate and Frame: This module is mainly used for dehydration of organic compounds. Spiral wound module: This module is very similar to the plate and frame system but has a greater packing density and offers hihg mem surface area per module
and allows for high feed flow rates. This type of module is used with organophilic membranes to achieved organic solutes frm dil .aq solns Tubular modules: Inorganic (ceramic) membranes are produced mainly as tubes, then the obvious module is the tube bundle for applications that used this kind of membranes. On the other hand, for sweep gas pervaporation, tubular membranes conducting the gas-permeate mixture are the only option. MASS TRANSFER IN PERVAPORATION: mass flux across the membrane can b described as a partial diff between feed saturated vapour pressure and permeate vapour pressure. As permeate pressure dec and approaches the feed pressure,the flux dec toz ero in a linear matter. Wen temp of feed is incd,sys is able to handle a high flux of wter.thats why the feed streams are heated before entering the membrane housing. The final sep of feed liq is the pdt of sep achieved by evaporation of liq and sep achieved by permeation thru membrane. It consists of following five steps: a) Transport of component from feed soln to surface of membrane. b) Selective sorption of component at memb surface. c) Diffusional transport of component thru the membrane. d) Desorption of component at permeate side of membrane e) Transfer of the component from the membrane surface to bulk of permeate. 1st n last steps are fast n takes placev at equim. Diffusion is kinetic and slow. Permeation is dependen ton sorption and diffusion process. Selectivity is controlled by relative sorption of components being separated.
Major parameters involved in sorption and diffusion steps are:temp,pressure,conc mt.wt.,size and shape of molecule,crystallinity of polymeric materials. Sorption involves thermo aspects while diffusion is related to kinetic factors. Due to low pressure on permeate side,desorption step is normally the fastest one and does nt contribute much to overall mass transfer resistance. APPLICATIONS:
ADVANTAGES: It minimizes thermal degradation of heat sensitive cmpds,such as flavor essences.
No entrainer required,no contamination. No adsorbents used which requires regeneration. Due to modular design,evn small units cn operate economically. Better selectivity without thermodynamic limitations. No process wastes. It is continous and offers immediate recovery of solvents in Indus.
Significantly reduced energy consumption for hybrid systems. With low temp and pressure involved,it often has cost and performance advantage for sep of azeotropic mixtures.
DRAWBACKS Scarce membrane market. Lack of information. Low permeate flows. Better selectivity without thermodynamic limitations. LIMITED APPLICATIONS: Organic substances dehydration. Recovery of volatile compounds at low concentrations. Separation of azeotropic mixtures.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Al-Muthanna University College of Engineering Department of Chemical EngineeringDocument11 pagesAl-Muthanna University College of Engineering Department of Chemical Engineeringسراء حيدر كاظمPas encore d'évaluation
- Membrane SeparationDocument13 pagesMembrane SeparationSharing Caring50% (2)
- MembranesDocument30 pagesMembranesInamullah MaitloPas encore d'évaluation
- Liquid Membranes: Principles and Applications in Chemical Separations and Wastewater TreatmentD'EverandLiquid Membranes: Principles and Applications in Chemical Separations and Wastewater TreatmentPas encore d'évaluation
- Millipore MicrofiltrationDocument8 pagesMillipore MicrofiltrationMichael McNeelyPas encore d'évaluation
- Membrane 1Document41 pagesMembrane 1Abhishek GadhwalPas encore d'évaluation
- AVP - Gas AbsorptionDocument33 pagesAVP - Gas AbsorptionrishikeshmandawadPas encore d'évaluation
- Humidification and DryingDocument36 pagesHumidification and Dryingnivedhitha100% (1)
- Methyl Acetate Project DesignDocument36 pagesMethyl Acetate Project Designdjona lokimaPas encore d'évaluation
- TareaDocument3 pagesTareaAydee GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Membrane ProcessesDocument49 pagesMembrane ProcessesNur AmaninaPas encore d'évaluation
- Membrane ReactorDocument36 pagesMembrane ReactorMax KopPas encore d'évaluation
- Leaching Notes PDFDocument14 pagesLeaching Notes PDFimmo50% (2)
- Chapter - 1Document9 pagesChapter - 1Sahil PatilPas encore d'évaluation
- CONTINUOUS DistillationDocument5 pagesCONTINUOUS DistillationNaseer SattarPas encore d'évaluation
- RD Column For Butyl Acetate ProductionDocument8 pagesRD Column For Butyl Acetate ProductionAbuBakar SaleemPas encore d'évaluation
- Filtration PDFDocument18 pagesFiltration PDFarno6antonio6spinaPas encore d'évaluation
- AgitationDocument10 pagesAgitationKenneth Jireh Taboco100% (2)
- Mass Transfer Operations 1: List of Books Information of CrystallizationDocument13 pagesMass Transfer Operations 1: List of Books Information of CrystallizationZaid MansuriPas encore d'évaluation
- 9 EvaporationDocument82 pages9 Evaporationsanjay YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit Operation: 2 Chemical EngineeringDocument3 pagesUnit Operation: 2 Chemical EngineeringMohammad Hosein KhanesazPas encore d'évaluation
- Rawr PDFDocument3 pagesRawr PDFGrazel MDPas encore d'évaluation
- 8 - Filtration Part 1Document35 pages8 - Filtration Part 1اشرفاللساميPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 1 - DiffusionDocument31 pagesExperiment 1 - DiffusionPatricia Ann Mae0% (1)
- Plumbing Design and InstallationsDocument2 pagesPlumbing Design and InstallationsGeorina LyconPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Problems On Gas AbsorptionDocument2 pagesSample Problems On Gas AbsorptionKevin Laganao67% (3)
- Screen 2Document3 pagesScreen 2Ramon Dela CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- AbsorptionDocument54 pagesAbsorptionBebo El MasryPas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Absorption and Gas StrippingDocument14 pagesGas Absorption and Gas StrippingEK63Pas encore d'évaluation
- Convective Mass TransferDocument46 pagesConvective Mass TransferSandra Enn BahintingPas encore d'évaluation
- Membrane 2Document51 pagesMembrane 2Abhishek GadhwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment No. 7 Measurement of Reaction ConversionDocument8 pagesExperiment No. 7 Measurement of Reaction ConversionHoneylet Recaña TayactacPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Reaction Engineering-II (2170501) : Semester - VII (CHEM) Chapter Name: Catalysis (Chapter 5)Document11 pagesChemical Reaction Engineering-II (2170501) : Semester - VII (CHEM) Chapter Name: Catalysis (Chapter 5)khushbu100% (2)
- Membrane SeparationDocument41 pagesMembrane SeparationAriadne ChuaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 Psychomentry, Humidification and DehumidificationDocument14 pagesChapter 4 Psychomentry, Humidification and DehumidificationNurshaqina SufianPas encore d'évaluation
- 04 Oxygen DemandDocument19 pages04 Oxygen DemandCharisma SubaPas encore d'évaluation
- Adsorption Review Questions and ProblemsDocument4 pagesAdsorption Review Questions and ProblemsJohn Bryan Aldovino0% (2)
- Chapter 13: Membrane Separation ProcessesDocument24 pagesChapter 13: Membrane Separation ProcessesAmit Yadav100% (2)
- Packed Bed FermentersDocument20 pagesPacked Bed FermentersGerald Owen FranzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Set 4Document3 pagesSet 4Ibtisam FarhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- 9A23401 Mass Transfer OperationsDocument8 pages9A23401 Mass Transfer OperationssivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- Mto Lab Manuals - All ExperimentsDocument121 pagesMto Lab Manuals - All ExperimentsAnmol JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Mass Transfer Part 8Document54 pagesMass Transfer Part 8SreejithPas encore d'évaluation
- Centrifugal Filtration Post-LabDocument28 pagesCentrifugal Filtration Post-LabNicole Ann PedriñaPas encore d'évaluation
- Humidification and Air Conditioning: Lecture No. 8Document6 pagesHumidification and Air Conditioning: Lecture No. 8Anonymous UFa1z9XUAPas encore d'évaluation
- Packed ColumnDocument4 pagesPacked ColumnSantosh ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- SedimentationDocument9 pagesSedimentationAutumn JohnsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Humidification and DehumidificationDocument37 pagesLecture Humidification and DehumidificationUsman Khan0% (1)
- Activity 3 - Principles of Transport PhenomenaDocument7 pagesActivity 3 - Principles of Transport PhenomenaAdelaida CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Separation Processes - I (CHE F244) Total Marks - 15 Due Date & Time: 01/07/2020, 5:00 PM AssignmentDocument4 pagesSeparation Processes - I (CHE F244) Total Marks - 15 Due Date & Time: 01/07/2020, 5:00 PM AssignmentElliot AldersonPas encore d'évaluation
- Absorption (Part 1)Document38 pagesAbsorption (Part 1)Syazwan WanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 1 Workshop HandoutDocument2 pagesChap 1 Workshop HandoutHenry RodriguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Distillation ExperimentDocument6 pagesDistillation ExperimentJureen Flores BelicarioPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Synopsis: Date of RegistrationDocument9 pagesProject Synopsis: Date of RegistrationAdeep KhahPas encore d'évaluation
- Reverse OsmosisDocument53 pagesReverse Osmosisanabloom100% (2)
- PervaporationDocument26 pagesPervaporationWasique KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- PervaporationDocument26 pagesPervaporationuddim004Pas encore d'évaluation
- PervaporationDocument18 pagesPervaporationKaustubh Dhabale50% (2)
- MicrofiltrationDocument6 pagesMicrofiltration2k17che 26Pas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment: Water Treatment by Ozonation: Objective: Equipment ProcedureDocument16 pagesExperiment: Water Treatment by Ozonation: Objective: Equipment ProcedureFurqan YousafzaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Effect UationDocument38 pagesEffect UationNithya RamPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Features of Indian and Western Political Thought - A Comparative AnalysisDocument27 pagesBasic Features of Indian and Western Political Thought - A Comparative AnalysisNithya Ram60% (5)
- Hybrid MembranesDocument1 pageHybrid MembranesNithya RamPas encore d'évaluation
- Displacement Purge AdsorptionDocument2 pagesDisplacement Purge AdsorptionNithya RamPas encore d'évaluation
- ElectrophoresisDocument2 pagesElectrophoresisNithya RamPas encore d'évaluation
- Pressure Swing AdsorptionDocument2 pagesPressure Swing AdsorptionNithya Ram0% (1)
- Unit 5 1. LyophilizationDocument2 pagesUnit 5 1. LyophilizationNithya RamPas encore d'évaluation
- Cross Flow FilterationDocument4 pagesCross Flow FilterationNithya Ram100% (1)
- Affinity ChromatographyDocument3 pagesAffinity ChromatographyNithya Ram100% (1)
- Acdc - DC Motor - Lecture Notes 5Document30 pagesAcdc - DC Motor - Lecture Notes 5Cllyan ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Development of PBAT Based Bio Filler Masterbatch: A Scientific Research Proposal OnDocument15 pagesDevelopment of PBAT Based Bio Filler Masterbatch: A Scientific Research Proposal OnManmathPas encore d'évaluation
- CNC Manuel de Maintenance 15i 150i ModelADocument526 pagesCNC Manuel de Maintenance 15i 150i ModelASebautomatismePas encore d'évaluation
- Age and Gender Detection Using Deep Learning: HYDERABAD - 501 510Document11 pagesAge and Gender Detection Using Deep Learning: HYDERABAD - 501 510ShyamkumarBannuPas encore d'évaluation
- BS en 50216-6 2002Document18 pagesBS en 50216-6 2002Jeff Anderson Collins100% (3)
- Office Administration: School-Based AssessmentDocument17 pagesOffice Administration: School-Based AssessmentFelix LawrencePas encore d'évaluation
- English 2 Q3 Week 7 DLLDocument7 pagesEnglish 2 Q3 Week 7 DLLEste R A BulaonPas encore d'évaluation
- EUCLIDDocument3 pagesEUCLIDNandini MouryaPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Logo-Faq enDocument6 pagesOrganic Logo-Faq enjcnavarro_Pas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Public RelationsDocument52 pagesWhat Is Public RelationsMarwa MoussaPas encore d'évaluation
- Application of A HAZOP Study Method To Hazard Evaluation of Chemical Unit of The Power StationDocument8 pagesApplication of A HAZOP Study Method To Hazard Evaluation of Chemical Unit of The Power Stationshinta sariPas encore d'évaluation
- EceDocument75 pagesEcevignesh16vlsiPas encore d'évaluation
- Pitch AnythingDocument8 pagesPitch AnythingDoland drumb100% (1)
- Consequences of Self-Handicapping: Effects On Coping, Academic Performance, and AdjustmentDocument11 pagesConsequences of Self-Handicapping: Effects On Coping, Academic Performance, and AdjustmentAlliah Kate SalvadorPas encore d'évaluation
- Schematic Circuits: Section C - ElectricsDocument1 pageSchematic Circuits: Section C - ElectricsIonut GrozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Eea2a - HOLIDAY HOMEWORK XIIDocument12 pagesEea2a - HOLIDAY HOMEWORK XIIDaksh YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Analog Electronics-2 PDFDocument20 pagesAnalog Electronics-2 PDFAbhinav JangraPas encore d'évaluation
- Starex Is BTSDocument24 pagesStarex Is BTSKLPas encore d'évaluation
- Ugtt April May 2019 NewDocument48 pagesUgtt April May 2019 NewSuhas SPas encore d'évaluation
- Video Course NotesDocument18 pagesVideo Course NotesSiyeon YeungPas encore d'évaluation
- SCHEMA - Amsung 214TDocument76 pagesSCHEMA - Amsung 214TmihaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Blackstone The Dash Model #1610 Owner's ManualDocument53 pagesBlackstone The Dash Model #1610 Owner's ManualSydney Adam SteelePas encore d'évaluation
- Investigation of The Microstructures, Properties, and Toughening Mechanism of Polypropylene/calcium Carbonate Toughening Masterbatch CompositesDocument16 pagesInvestigation of The Microstructures, Properties, and Toughening Mechanism of Polypropylene/calcium Carbonate Toughening Masterbatch CompositesHatchi KouPas encore d'évaluation
- 96 Dec2018 NZGeoNews PDFDocument139 pages96 Dec2018 NZGeoNews PDFAditya PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- RMC No. 122 2022 9.6.2022Document6 pagesRMC No. 122 2022 9.6.2022RUFO BULILANPas encore d'évaluation
- Ojt Evaluation Forms (Supervised Industry Training) SampleDocument5 pagesOjt Evaluation Forms (Supervised Industry Training) SampleJayJay Jimenez100% (3)
- d10 Sandra Darby FinalDocument3 pagesd10 Sandra Darby FinalFirstCitizen1773Pas encore d'évaluation
- IOM - Rampa Hidráulica - Blue GiantDocument32 pagesIOM - Rampa Hidráulica - Blue GiantPATRICIA HERNANDEZPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Concept of ProbabilityDocument12 pagesBasic Concept of Probability8wc9sncvpwPas encore d'évaluation
- File 1038732040Document70 pagesFile 1038732040Karen Joyce Costales MagtanongPas encore d'évaluation