Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
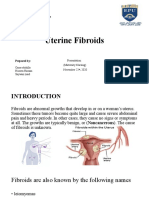
Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive System
Transféré par
Syed IsamilCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive System
Transféré par
Syed IsamilDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
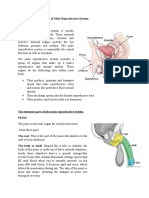
Anatomy and physiology of female reproductive system The female reproductive system consists of the external genitalia and
internal reproductive organs: the vagina,the uterus,two uterine tubes,and two ovaries.internal reproductive organs are situated within a true pelvis. VULVA
The vulva includes the mons pubis,labia majora,labia minora,clitoris and the perineum.The mons pubis is a pad of fat lying over the symphysis pubis.It covered with pubic hair from the time of puberty. The labia majora are two fold of fat and areolar tissue covered with skin and pubis hair on the outer surface. The labia minora are two thin folds of skin lying between the labia majora.Anteriorly devide to enclose the clitoris,the frenum is formed by the two medial parts,posteriorly they fuse ,forming the fourchette. The clitoris is small rudimentary sexual organ corresponding to the male penis.The prepuce a retractable piece of the skin surrounds and protect the clitoris. The vestibule is the area enclosed by the labia minora in which the opening of the urethra and the vagina situated. The urethra orifice lies 2.5cm posterior to the clitoris and infront of the vagina orifice.On either side lie the openings of the Skenes ducts,two small blind ended tubules 0.5cm long running within the urethral wall.
The vagina orifice occupies the posterior two-thirds of the vestibule.The remaining tags of hymen are known as the carunculae myrtiformes because they are though to resemble myrtle berries. Bartholin glands are two small glands that open on either side of the vaginal orifice and lie in the posterior part of the labia majora BLOOD SUPPLY From the external pudendal arteries.The blood drains through corresponding veins. NERVE SUPPLY Derived from branches of the pudendal nerve.The vaginal nerves supply the erectile tissue of the vestibular bulbs and clitoris and their parasympathetic fibres have a vasodilator effect.
VAGINA
The vagina is a hollow distensible fibromuscular tube that extends from the vaginal orifice in the vestibule to the cervix.It is approximately 10 cm length and 2.5cm diameter.When women gives birth and during sexual intercourse the vagina temporarily widens and lengthen.when the women stands upright,the vaginal canal points in an upward backward direction and forms an angel of slightly more thn 45degree with the uterus.
FUNCTION It allows the escape of the menstrual fluids,received the penis and ejected sperm during sexual intercourse and exit for the fetus during birth. RELATION The relations of the vagina to other pelvic organs is essential for the accurate examination of the pregnant women and safe birth of the baby. Anterior to the vagina lie the bladder and the erethra,closely connected to the anterior vaginal wall Posterior-lie the pouch of douglas Laterally-on the upper two-third are the pelvic fascia and the ureter,pass beside the cervix Superior-lie the uterus Inferior-lie the external genitalia
STRUCTURE Posterior wall of vagina is 10cm long and the anterior wall is 7.5cm.the upper ends of the vagina is known as the voult.The posterior fornix is the largest of these because the vagina is attached to the uterus at a higher level behind then in front.The vaginal wall are pink appearance and thrown into small folds called rugue. LAYER It composed by 3 layer mucosa,muscle and fascia. Mucosa- most superficial layer and consist of squamous epithelium Muscle devided into a weak inner coat of circular fibre and stronger outer coat of longitudinal fibres Fascia-sorrounds the vagina and adjacent pelvic organs and allow the independent expansion and contraction
BLOOD SUPPLY Blood supply comes from the branches of the internal iliac artery,vaginal artery and descending branch of the uterine cavity.the blood drains through corresponding veins LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE Is from the inguinal,the internal iliac and the sacral glands
NERVE SUPPLY Derived from pelvic plexus.The vaginal nerves follow the vaginal arteries to supply the vaginal wall and the erectile tissue of the vulva.
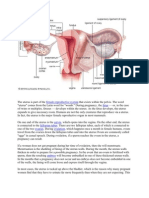
UTERUS
The uterus is hollow pear shaped mascular organ.located in true pelvis between the bladder and rectum.The position is anterversion and anteflexion.When standinguterus is in horizontal position with the fundus resting on the bladder. Anterversion-The uterus leans forward Anteflexion- it bends forward upon itself
FUNCTION The main function of uterus is to nourish the developing fetus prior birth.It preparesfor pregnancy each month and following pregnancy expels the product of conception. RELATIONS Relations of the uterus to other pelvic organ is desirable particularlywhen giving women advice about bladder and bowel care during pregnancy and child birth. Anterior-uterus lie to the uterovesical pouch and the bladder Posterior-the uterus are the recto uterine pouch of dauglas and the rectum Lateral-the uterus are the broad ligaments,the uterines tubes and the ovaries Superior-the uterus lie the intestines Inferior-the uterus is the vagina
SUPPORTS The uterus is supported by the pelvic floor and maintained in position by several ligaments. The transverse cervical ligaments/cardinal ligaments/Mackenrodts ligaments fan out from the sides of the cervix to the side wall of pelvis. The uterosacral ligaments pass backwards from the cervix to the sacrum. The pubocervical ligamentpass forwards from the cervix under the bladder to the pubic bone, The round ligament have little value as a support but tend to maintain the anteverted position of the uterus. The ovarian ligament begin at the cornua of the uterus but behind the uterine tube.
STRUCTURE The uterus for non pregnant is 7.5cm long,5cm wide and 2.5cm depth.each wall 1.25cm thick.the cervix forms the lower third of the uterus and measures 2.5cm in each. LAYERS Uterus has three layer Endometrium-lining of ciliated epithelium on a base of connective tissue or stroma. Myometrium-thick in upper part of the uterus and spaser in the isthmus and cervix.The outer layer formed of longitudinal fibres. Perimetrium-double serous membrane,an extension of the peritoneum,draped over the fundus and the anterior surface of the uterus to the level of the internal os. The cornua-upper outer angles of the uterus where the uterine tubes joins The fundus-domed upper wall between the insertion of the uterine tubes . The body or corpus-makes up the upper two thirds of the uterus and is the greater part. The isthmus-narrow area between the cavity and the cervix which is 7mm long The cervix-upper half above the vagina. Internal os-the narrow opening between the isthmus and cervix External os-small round openibg at the lower end of the cervix Cervical canal-is a continuation of the uterine cavity.
BLOOD SUPPLY The ovarian artery is a branch of the abdominal aorta leaving near the renal artery
NERVE SUPPLY Mainly from the autonomic nerves system,sympathetic and parasympathetic
THE UTERINE TUBES/ FALLOPIAN TUBES
Two fined tubes leading from the ovaries into the uterus FUNCTION Propel s the ovum toward the uterus and received the spermatozoa travel upwards and provides a site for fertilization.
POSITION The uterine tubes extends laterally from the cornua of the uterus toward the side wall of the pelvis.arch over the ovaries,the fringed ends hovering near the ovaries to recived ovum.
RELATIONS Anterior ,posterior and superior to the uterine tubes are the peritoneal cavity and the intestine Lateral-the uterine tubes are the side walls of the pelvis Inferior-the uterine tubes lie the broad ligament and ovaries Medial-the two uterine tubes lies the uterus
SUPPORTS By broad ligaments and extending at the sides to form the infundibulopelvic ligament. STRUCTURE Each tubes is 10cm long.it has four portion LAYERS Lining with mucous membranes of coliated cubical epithelium.Benaeth the lining is a layer of vascular connective tissue BLOOD SUPPLY From the uterine and ovarian arteries,returning by corresponding veins. LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE Lymph is drained to the lumbar gland NERVE SUPPLY It from the ovarian plexus Intestinal portion-1.25cm long and lies within the wall of the uterus.lumen is 1mm wide Isthmus-annother narrow part that extends for 2.5cm from the uterus Ampulla-the wider portion fertilization occurs.It is 5cm long Infundibulum-it funnel shapefringed or called fimbria.
OVARIES
The ovaries are component of the female reproductive system and endocrine system FUNCTION The ovaries produce oocytes and the hormons oestrogen and progesterone POSITION The ovaries are attached to the back of the broad ligament within the peritoneal cavity RELATION Anterior to the ovaries are the broad ligament Posterior to the ovariesare the intestines Lateral to the ovaries are the infundibulopelvic ligaments and the side walls of the pelvis Superior to the ovaries lie the uterine tubes Medial to the ovaries lie the ovarian ligaments and the uterus
SUPPORTS The ovaries is attached to the broad ligament.It support from above by the ovarian ligament medially and the infundibulopelviv ligament laterally.
STRUCTURE The ovary is composed of a medulla and cortex,covered with germinal epithelium. Medulla-Is the supporting framework.made of fibrous tissue Cortex-Functioning part of the ovary.Contains of ovarian follicles in different stages of development and surrounded by stroma
BlOOD SUPPLY From the ovarian arteries and drains via the ovarian veins..The right ovarian vein joins the inferior vena cava and the left returns blood to left renal vein. LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE Lymphatic drainage is to the lumbar gland NERVE SUPPLY Is from the ovarian plexus
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Anatomy Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDocument96 pagesAnatomy Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemRabin BasnetPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Physiology of the Reproductive SystemDocument93 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of the Reproductive SystemMelizza Fajardo BañanoPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Retained PlacentaDocument7 pagesWhat Is Retained PlacentaA Xiao Yhing TrancoPas encore d'évaluation
- Female Reproductive System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesFemale Reproductive System Anatomy and PhysiologyIkea Balhon100% (3)
- CP Ovarian Cyst Chap5Document11 pagesCP Ovarian Cyst Chap5Katherine 'Chingboo' Leonico LaudPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Physiology of The BreastDocument42 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The BreastNicole SooPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive Systemannyeong_123Pas encore d'évaluation
- PartographDocument33 pagesPartographKathrynne Mendoza100% (1)
- Foetal Membrane and Amniotic Fluid FunctionsDocument10 pagesFoetal Membrane and Amniotic Fluid FunctionsN. SivaPas encore d'évaluation
- Uterine Fibroids: By: DR Dolapo AduDocument35 pagesUterine Fibroids: By: DR Dolapo AduAdu DolapoPas encore d'évaluation
- Female PelvisDocument7 pagesFemale PelvissubashikPas encore d'évaluation
- Premature Cervical DilationDocument22 pagesPremature Cervical DilationJanelle Lois EscolanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Molar Pregnancy: November 2018 Jis Dungca, Delos Santos, CrisostomoDocument99 pagesMolar Pregnancy: November 2018 Jis Dungca, Delos Santos, CrisostomoDarnell DelgadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Female Pelvis: Anatomy, Types and FunctionsDocument217 pagesFemale Pelvis: Anatomy, Types and Functionsaiswarya ppPas encore d'évaluation
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument4 pagesEctopic PregnancyJovie Anne BorjaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gross Anatomy of Uterus: D R. Vibhash Kumar Vaidya Department of AnatomyDocument25 pagesGross Anatomy of Uterus: D R. Vibhash Kumar Vaidya Department of AnatomyAhsan TariqPas encore d'évaluation
- High Risk Pregnancy 1Document205 pagesHigh Risk Pregnancy 1Vanessa Angel Bugarin100% (3)
- Cervical Cancer Stage III Case StudyDocument32 pagesCervical Cancer Stage III Case StudyEvangel Padua100% (2)
- Ovarian Cyst FinalDocument26 pagesOvarian Cyst FinalReicy Aquino SacularPas encore d'évaluation
- 35 - Retained PlacentaDocument11 pages35 - Retained Placentadr_asalehPas encore d'évaluation
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum PresentationDocument22 pagesHyperemesis Gravidarum PresentationMaricar Sanson FelicianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDocument6 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemFarlyn Real MoralesPas encore d'évaluation
- Diagnosis of PregnancyDocument26 pagesDiagnosis of PregnancyMounikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Newborn Physical Exam GuideDocument47 pagesNewborn Physical Exam GuideJuliane100% (1)
- CPD and Contracted PelvisDocument55 pagesCPD and Contracted PelvisShaells JoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- AbortionDocument22 pagesAbortionwindows3123100% (2)
- Uterine Fibroids Nursing PresentationDocument27 pagesUterine Fibroids Nursing PresentationCapitan SaywanPas encore d'évaluation
- OB-Gyn Case Presentation - BicornuateDocument53 pagesOB-Gyn Case Presentation - BicornuateZari Novela100% (1)
- Gavino and Aguilera (Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive Organ)Document4 pagesGavino and Aguilera (Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive Organ)Allyne GavinoPas encore d'évaluation
- 40 1/7 Weeks Pregnancy Delivered by C-SectionDocument78 pages40 1/7 Weeks Pregnancy Delivered by C-SectionEira Rajkumar50% (2)
- BUBBLEHEBDocument13 pagesBUBBLEHEBJeffrey Viernes100% (1)
- Case Study About Cervical CancerDocument11 pagesCase Study About Cervical CancerJisel-Apple Bulan100% (1)
- Ectopic Pregnancy: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment Options Under 40 CharactersDocument45 pagesEctopic Pregnancy: Causes, Symptoms and Treatment Options Under 40 CharactersHoney May Rollan VicentePas encore d'évaluation
- Diagnosis of Pregnancy - Signs, Differential DiagnosisDocument39 pagesDiagnosis of Pregnancy - Signs, Differential DiagnosisKripa SusanPas encore d'évaluation
- Abnormal Labor. BBBB WWPPTXDocument53 pagesAbnormal Labor. BBBB WWPPTXHamss Ahmed100% (2)
- Uterine RuptureDocument19 pagesUterine RuptureAna Denise Quinajon0% (1)
- Female PelvisDocument18 pagesFemale PelvisNeelofur Ibran Ali100% (1)
- Management of PPHDocument24 pagesManagement of PPHMutabazi SharifPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive SystemNicole Anne TungolPas encore d'évaluation
- Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseDocument43 pagesPelvic Inflammatory DiseaseFauzia Jamiri - Abdurasid100% (2)
- Abruptio Placenta: Prepared By: Claire Alvarez Ongchua, RNDocument42 pagesAbruptio Placenta: Prepared By: Claire Alvarez Ongchua, RNclaireaongchua1275100% (2)
- Incomplete Abortion MINI CASE STUDY Group 3Document23 pagesIncomplete Abortion MINI CASE STUDY Group 3Katrina TinapianPas encore d'évaluation
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVEDocument6 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVEJazmin Venice LasalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Evolution of Nursing ResearchDocument10 pagesEvolution of Nursing ResearchStar AlvarezPas encore d'évaluation
- Partograph Monitoring Labor ProgressDocument65 pagesPartograph Monitoring Labor ProgressAmyAgustinPas encore d'évaluation
- Stages of LaborDocument51 pagesStages of LaborZeen_Zeen_Fern_3128100% (4)
- Table Presumptive Probable and Positive Signs of PregnancyDocument2 pagesTable Presumptive Probable and Positive Signs of Pregnancykylah gonzaga100% (1)
- MenstruationDocument33 pagesMenstruationmskot100% (3)
- Family PlanningDocument36 pagesFamily PlanningSofia Monique50% (2)
- Incompetent Cervix As One of The Antenatal ComplicationsDocument14 pagesIncompetent Cervix As One of The Antenatal ComplicationsKenje Kate Agripo100% (2)
- HemorrhoidsDocument26 pagesHemorrhoidsDini Norviatin0% (1)
- Uterine Fibroid - Viva VoceDocument77 pagesUterine Fibroid - Viva VoceK Haynes Raja100% (1)
- Antenatal Examination According To WHODocument6 pagesAntenatal Examination According To WHOManisha ThakurPas encore d'évaluation
- Postpartum Hemorrhage FinalDocument6 pagesPostpartum Hemorrhage FinalIanne Merh50% (2)
- Postpartum HemorrhageDocument50 pagesPostpartum HemorrhageSamuel SutantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Presentation Endometriosis 1Document15 pagesCase Presentation Endometriosis 1Muhammad Ahmad Syammakh0% (1)
- Per Vaginal ExaminationDocument25 pagesPer Vaginal Examinationazulqaidah95Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3rd Stage of LaborDocument40 pages3rd Stage of Laborjeny patel100% (1)
- Female reproductive anatomyDocument22 pagesFemale reproductive anatomyIGA ABRAHAMPas encore d'évaluation
- The Female Reproductive SystemDocument25 pagesThe Female Reproductive Systemavin xsroPas encore d'évaluation
- List of Regular VerbsDocument5 pagesList of Regular Verbssasauball100% (1)
- Bacaan Pra SekolahDocument2 pagesBacaan Pra SekolahSyed IsamilPas encore d'évaluation
- Tenancy Agreement Rental PropertyDocument3 pagesTenancy Agreement Rental PropertySyed Isamil75% (8)
- Slide Purperal Sepsis 5Document16 pagesSlide Purperal Sepsis 5Syed IsamilPas encore d'évaluation
- Subject and PredicateDocument1 pageSubject and PredicateSyed IsamilPas encore d'évaluation
- Intro Journak CriticDocument2 pagesIntro Journak CriticSyed IsamilPas encore d'évaluation
- Subject and PredicateDocument1 pageSubject and PredicateSyed IsamilPas encore d'évaluation
- Scope of Mid Practice (Legal Ethic)Document2 pagesScope of Mid Practice (Legal Ethic)Syed IsamilPas encore d'évaluation
- Physiological Changes in The Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesPhysiological Changes in The Reproductive SystemSyed IsamilPas encore d'évaluation
- Trial PMR Bi Kelantan 2012Document19 pagesTrial PMR Bi Kelantan 2012Sal LiePas encore d'évaluation
- Journal Pueperal Sepsis 4Document3 pagesJournal Pueperal Sepsis 4Syed IsamilPas encore d'évaluation
- ImuoneDocument4 pagesImuoneSyed IsamilPas encore d'évaluation
- Journal Pueperal Sepsis 3Document18 pagesJournal Pueperal Sepsis 3Syed IsamilPas encore d'évaluation
- Journal Pueperal Sepsis 2Document5 pagesJournal Pueperal Sepsis 2Syed IsamilPas encore d'évaluation
- Physiological Changes in The Reproductive SystemDocument4 pagesPhysiological Changes in The Reproductive SystemSyed IsamilPas encore d'évaluation
- Journal Pueperal Sepsis 1Document5 pagesJournal Pueperal Sepsis 1Syed IsamilPas encore d'évaluation
- Soalan Matematik (Math) Paper 2 Tahun 1Document5 pagesSoalan Matematik (Math) Paper 2 Tahun 1sasauball100% (5)
- Anatomy LE5 Samplex 2017BDocument6 pagesAnatomy LE5 Samplex 2017BHanako Sasaki AranillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ectopic Pregnancy Nursing CareDocument27 pagesEctopic Pregnancy Nursing CareEduard GarchitorenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Formative Test Science 5Document55 pagesFormative Test Science 5elizaldePas encore d'évaluation
- Block 4 Quiz+ Lab Exam ReviewDocument47 pagesBlock 4 Quiz+ Lab Exam ReviewMira ThakkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Analaysis On infertility-BALLON-Karlo CDocument4 pagesCase Analaysis On infertility-BALLON-Karlo CMelinda Cariño BallonPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiologychinchin ramosPas encore d'évaluation
- Ass Ectopic PregnancyDocument10 pagesAss Ectopic PregnancyPriyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pretes OBGYNEDocument4 pagesPretes OBGYNEAltheaPas encore d'évaluation
- Accepted Manuscript: Carica PapayaDocument26 pagesAccepted Manuscript: Carica PapayaAl Bukhari SubulussalamPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 13 Medical TerminologyDocument30 pagesChapter 13 Medical TerminologycharliePas encore d'évaluation
- Uterus AnatomyDocument7 pagesUterus AnatomyJoseph RadislaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care of Mother and ChildDocument15 pagesNursing Care of Mother and ChildRichard SonsingPas encore d'évaluation
- Evolution of Urogenital Ducts Part-2 27.03.2020Document10 pagesEvolution of Urogenital Ducts Part-2 27.03.2020Sonali SahooPas encore d'évaluation
- @medicalbook - Store 2020reDocument203 pages@medicalbook - Store 2020reAhmad FitriawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute AbdomenDocument45 pagesAcute AbdomenVeronikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Science10 Q3 SLM4Document15 pagesScience10 Q3 SLM4Jomelyn Arzaga100% (2)
- Reproductive System ReviewerDocument4 pagesReproductive System ReviewerJewel Arcega PartoPas encore d'évaluation
- RRB Staff Nurse 21 July 2019 Shift 1 (English)Document30 pagesRRB Staff Nurse 21 July 2019 Shift 1 (English)karmakarsomnath84Pas encore d'évaluation
- Wa0002.Document21 pagesWa0002.Deepak E deepakPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 - OB 1 (Maternal Anatomy)Document13 pages1 - OB 1 (Maternal Anatomy)Gen XPas encore d'évaluation
- AnatomyDocument86 pagesAnatomysushruta0% (1)
- Genbio2 q2 Mod1.1 Reproduction-And-DevelopmentDocument9 pagesGenbio2 q2 Mod1.1 Reproduction-And-DevelopmentHazel AbitriaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2nd Quarter TestDocument7 pages2nd Quarter TestMelanie ParazoPas encore d'évaluation
- AP2 Lab13 Reproductive System Anatomy Lab SP21finalDocument14 pagesAP2 Lab13 Reproductive System Anatomy Lab SP21finalBella DonnaAriesta LumbanGaolPas encore d'évaluation
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument10 pagesEctopic PregnancyRegine AldamarPas encore d'évaluation
- Postpartum home visit scheduling and constipation preventionDocument96 pagesPostpartum home visit scheduling and constipation preventionJapheth CanalesPas encore d'évaluation
- 40 TS1M1 Sex and Sexuality-Vol. 2 (Praeger 2006)Document289 pages40 TS1M1 Sex and Sexuality-Vol. 2 (Praeger 2006)bfdscaPas encore d'évaluation
- 24 Lecture PPT - Reproductive SystemDocument47 pages24 Lecture PPT - Reproductive Systemjohnjay3110100% (2)
- (BIO) Chapter 16 - Reproduction in HumansDocument17 pages(BIO) Chapter 16 - Reproduction in HumansMahi NoorPas encore d'évaluation
- Sexual Reproduction in Humans Notes (CAPE)Document29 pagesSexual Reproduction in Humans Notes (CAPE)Desmond JonesPas encore d'évaluation