Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Decreased Cardiac Output
Transféré par
Adnan KhanTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Decreased Cardiac Output
Transféré par
Adnan KhanDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
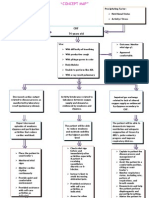
Decreased Cardiac Output The heat fails to pump enough blood to meet the metabolic needs of the body.
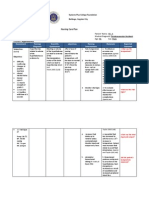
The blood flow that supplies the heart is also decreased thus decrease in cardiac output occurs, blood then is insufficient and making it difficult to circulate the blood to all parts of the body thus may cause altered heart rate and rhythm, weakness and paleness NDx: Decreased cardiac output r/t altered heart rate and rhythm AEB bradycardia Assessment Subjective: (none)Objectives: The patient manifested the following:
Planning Nursing Interventions Short Term: 1. Assess for After 3-4 abnormal hours of heart and lung nursing sounds. interventions, 2. Monitor blood the patient pressure and with pale pulse. conjunctiva, will 3. Assess mental nail beds and participate in status and buccal mucosa activities that reduce the level of irregular workload of consciousness. rhythm of the heart. 4. Assess pulse Long Term: patients skin bradycardic temperature pulse rate of 34 After 2-3 days of nursing and peripheral beats/min interventions, pulses. generalized the patient 5. Monitor weakness will be able to results of display laboratory and hemodynamic diagnostic stability. tests. 6. Monitor oxygen saturation and ABGs. 7. Give oxygen as indicated by patient symptoms, oxygen saturation and ABGs. 8. Implement strategies to treat fluid and electrolyte
Rationale Evaluation 1. Allows Short detection of Term:After left-sided nursing heart failure interventions, that may the patient occur with shall have chronic renal participated in failure activities that patients due reduce the to fluid workload of volume the excess as the heart.Long diseased Term:After 2kidneys are 3 days of unable to nursing excrete water. interventions, 2. Patients with the patient renal failure shall have are most been able to often display hypertensive, hemodynamic which is stability. attributable to excess fluid and the initiation of the renninangiotensin mechanism. 3. The accumulation of waste products in the bloodstream impairs
imbalances. 9. Administer cardiac glycoside agents, as ordered, for signs of left sided failure, and monitor for toxicity. 10. Encourage periods of rest and assist with all activities. 11. Assist the patient in assuming a high Fowlers position. 12. Teach patient the pathophysiolo gy of disease, medications 13. Reposition patient every 2 hours 14. Instruct patient to get adequate bed rest and sleep 15. Instruct the SO not to leave the client unattended
oxygen transport and intake by cerebral tissues, which may manifest itself as confusion, lethargy, and altered consciousness . 4. Decreased perfusion and oxygenation of tissues secondary to anemia and pump ineffectivenes s may lead to decreased in temperature and peripheral pulses that are diminished and difficult to palpate. 5. Results of the test provide clues to the status of the disease and response to treatments. 6. Provides information regarding the hearts ability to perfuse distal tissues with oxygenated blood
7. Makes more oxygen available for gas exchange, assisting to alleviate signs of hypoxia and subsequent activity intolerance. 8. Decreases the risk for development of cardiac output due to imbalances. 9. Digitalis has a positive isotropic effect on the myocardium that strengthens contractility, thus improving cardiac output. 10. Reduces cardiac workload and minimizes myocardial oxygen consumption. 11. Allows for better chest expansion, thereby improving pulmonary capacity. 12. Provides the patient with needed
information for management of disease and for compliance. 13. To prevent occurrence of bed sores 14. To promote relaxation to the body 15. To ensure safety and reduce risk for falls that may lead to injury
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- NCPDocument15 pagesNCPCamille PinedaPas encore d'évaluation
- Impaired Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesImpaired Tissue PerfusionLyka Mae Imbat - PacnisPas encore d'évaluation
- HypophysectomyDocument19 pagesHypophysectomyjoel david knda mj100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Risk For ConstipationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Risk For Constipationkenneth_bambaPas encore d'évaluation
- Imbalanced NutritionDocument3 pagesImbalanced NutritionIlisa ParilPas encore d'évaluation
- Case CHFDocument10 pagesCase CHFAgnes Erlita Distriani Patade50% (2)
- ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY of RabiesDocument5 pagesANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY of RabiesDavid CalaloPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity IntoleranceDocument1 pageActivity IntoleranceAndrea Francesca SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Surgical Management For Cryptorchidism With Nursing ManagementsDocument4 pagesSurgical Management For Cryptorchidism With Nursing ManagementsAprille Claire MoralesPas encore d'évaluation
- Otitis Media AcuteDocument30 pagesOtitis Media AcuteDede Gustina AyuPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Volume DeficitDocument2 pagesFluid Volume DeficitpeternohibiPas encore d'évaluation
- Concept Map - Abby !Document2 pagesConcept Map - Abby !Abegail Abaygar100% (3)
- NCP BronchopneumoniaDocument8 pagesNCP BronchopneumoniaCrisantaCasliPas encore d'évaluation
- Wk2 NCP Edited2012Document6 pagesWk2 NCP Edited2012Jessely Caling SalasPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluorosis: Fluoride Toxicity: Patient Management & MonitoringDocument24 pagesFluorosis: Fluoride Toxicity: Patient Management & MonitoringdrjriPas encore d'évaluation
- Retinopathy of PrematurityDocument15 pagesRetinopathy of Prematuritymarissa ulkhairPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP FatigueDocument2 pagesNCP FatigueKrishna Faith P. DelaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Case 2 Hydrocephalus Group 4Document27 pagesCase 2 Hydrocephalus Group 4younggirldavidPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care PlanDocument5 pagesNursing Care PlanPaola Marie VenusPas encore d'évaluation
- Ineffective Airway Clearance CareplanDocument6 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance CareplanderreshaPas encore d'évaluation
- Asthma Nanda DiagnosesDocument4 pagesAsthma Nanda DiagnosesZinya RobinsonPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP - Activity Intolerance & Excess Fluid VolumeDocument2 pagesNCP - Activity Intolerance & Excess Fluid VolumeCindy MariscotesPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Presentation HydrocephalusDocument48 pagesCase Presentation HydrocephalusSu Osman50% (2)
- NCPGDMDocument8 pagesNCPGDMChristopher LontocPas encore d'évaluation
- Scribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kDocument2 pagesScribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kKellie DPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Intervention (Epiglottitis Disease)Document2 pagesNursing Intervention (Epiglottitis Disease)Marianne Rose HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP PainDocument2 pagesNCP PainApril_Ivy_Raga_3835Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluationjennelyn losantaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Problem Explanation Goal Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument1 pageNursing Problem Explanation Goal Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveZed P. EstalillaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP BPHDocument1 pageNCP BPHyasiraPas encore d'évaluation
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPmftaganasPas encore d'évaluation
- CNN Practice QuestionsDocument5 pagesCNN Practice QuestionsUri Perez MontedeRamosPas encore d'évaluation
- Spina Bifida, Meningocele MyelomeningoceleDocument1 pageSpina Bifida, Meningocele MyelomeningocelesmilingstarsPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment For Oxy. Online BasedDocument5 pagesAssignment For Oxy. Online BasedNurhassem Nor AkangPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan HydrocephalusDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan HydrocephalusFarnii MarquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Risk For Bleeding - Cirrhosis NCPDocument2 pagesRisk For Bleeding - Cirrhosis NCPPaula AbadPas encore d'évaluation
- Student NurseDocument2 pagesStudent NurseTAYABAN, KENNETH JAKE, Q.Pas encore d'évaluation
- PeritonitisDocument6 pagesPeritonitisDiane ArgotePas encore d'évaluation
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPNaidin Catherine De Guzman-AlcalaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP FVDDocument1 pageNCP FVDsisjing88510Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan Renal FailureDocument18 pagesNursing Care Plan Renal FailureKundan KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- LRDR ProceduresDocument67 pagesLRDR ProceduresJustJ ThingsPas encore d'évaluation
- Medication ThalassemiaDocument3 pagesMedication ThalassemiaDivya ToppoPas encore d'évaluation
- Discharge Plan Post SeizureDocument2 pagesDischarge Plan Post SeizureVecky TolentinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMonica RamboyongPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan EportfolioDocument14 pagesNursing Care Plan Eportfolioapi-279212367Pas encore d'évaluation
- NCP NecDocument1 pageNCP NecandikaisnaeniPas encore d'évaluation
- Ineffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusion Related To Vasoconstriction Secondary To High Glucose Level.Document6 pagesIneffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusion Related To Vasoconstriction Secondary To High Glucose Level.SAROL, RYAN CHRISTIAN B.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument15 pagesAcute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRanusha AnushaPas encore d'évaluation
- Group B1 (Cholera)Document66 pagesGroup B1 (Cholera)Krisianne Mae Lorenzo FranciscoPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan Problem: Difficulty of BreathingDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan Problem: Difficulty of BreathingIvan Louise Fajardo ManiquizPas encore d'évaluation
- Prevention of MeaslesDocument5 pagesPrevention of MeaslesJae Yong LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Liver CirrhosisDocument3 pagesLiver CirrhosisJonica CamposPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP CvaDocument4 pagesNCP CvaMariquita BuenafePas encore d'évaluation
- NCP #2Document4 pagesNCP #2Nutz TolentinoPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Document4 pagesNCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Jessamine EnriquezPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP CHFDocument10 pagesNCP CHFMykel Jake VasquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care PlansDocument6 pagesNursing Care PlansMichelle Danica Vicente PaswickPas encore d'évaluation
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesIneffective Tissue Perfusioniammkrissa33% (3)
- Hypertension Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesHypertension Nursing Care PlanCyrus De Asis92% (13)
- Orthokeratology: Orthokeratology (Ortho-K) Is The Fitting of Specially Designed GasDocument4 pagesOrthokeratology: Orthokeratology (Ortho-K) Is The Fitting of Specially Designed GasPUSHPAK DASGUPTAPas encore d'évaluation
- Gharama Za Matibabu PKP Kituo Cha AfyaDocument14 pagesGharama Za Matibabu PKP Kituo Cha AfyashaggyzegratPas encore d'évaluation
- Single Dose VialsDocument54 pagesSingle Dose VialsKyon Asma100% (1)
- HaematologyDocument11 pagesHaematologyIkram AzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Sun002 PDFDocument8 pagesSun002 PDFmmmaw mmPas encore d'évaluation
- PediatricsDocument33 pagesPediatricsnageshwarioshPas encore d'évaluation
- 11-Iv Admixture 0Document20 pages11-Iv Admixture 0udinPas encore d'évaluation
- Histrionic Personality DisorderDocument2 pagesHistrionic Personality DisorderRodenePas encore d'évaluation
- Patient Admission Hospital Admission ChecklistDocument6 pagesPatient Admission Hospital Admission ChecklistSweetly MamukoPas encore d'évaluation
- 10a. HipoksiaDocument21 pages10a. HipoksiaputrianitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Health Certificate PDFDocument2 pagesHealth Certificate PDFPedro KunstPas encore d'évaluation
- EO094 COVIDRecommendationsDocument4 pagesEO094 COVIDRecommendationsTMJ4 News50% (2)
- PBL PrintDocument4 pagesPBL PrintShereen OngPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy Review: Blood Vessel Structure & Function: Page 1. Introduction Page 2. GoalsDocument6 pagesAnatomy Review: Blood Vessel Structure & Function: Page 1. Introduction Page 2. GoalsUta Provinsiana SukmaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Maturity Onset Diabetes of The Young: Clinical Characteristics, Diagnosis and ManagementDocument10 pagesMaturity Onset Diabetes of The Young: Clinical Characteristics, Diagnosis and ManagementatikahanifahPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Life Support (BLS) and Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support (ACLS)Document35 pagesBasic Life Support (BLS) and Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support (ACLS)rajPas encore d'évaluation
- Rcl0415i PDFDocument36 pagesRcl0415i PDFMustaphaBenselkaPas encore d'évaluation
- Adenovirus DiseasesDocument44 pagesAdenovirus Diseasestummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (1)
- Modified Finnegan ScoringDocument4 pagesModified Finnegan ScoringEdu WilliamPas encore d'évaluation
- Textbook of Clinical NeurologyDocument374 pagesTextbook of Clinical Neurologykanuparthyj100% (9)
- DownloadDocument1 pageDownloadsathish KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Allergies: A Protective Mechanism Out of ControlDocument29 pagesAllergies: A Protective Mechanism Out of Controlडा. सत्यदेव त्यागी आर्यPas encore d'évaluation
- Oral Meds ChecklistDocument2 pagesOral Meds ChecklistMonika Sarmiento100% (1)
- Placenta Previa NCP 1Document6 pagesPlacenta Previa NCP 1Nicole ArandingPas encore d'évaluation
- FCE Use ESOL 3Document2 pagesFCE Use ESOL 3Fran PasteriPas encore d'évaluation
- Teaching PlanDocument6 pagesTeaching PlanAnthony BasantaPas encore d'évaluation
- MRI Vs CT ScanDocument10 pagesMRI Vs CT ScanMunazzah IjazPas encore d'évaluation
- NP5Document19 pagesNP5Jhouleen Angelika TamPas encore d'évaluation
- Cluster 2 Gathered by MakilingDocument5 pagesCluster 2 Gathered by MakilingKeziah Kaye ManogPas encore d'évaluation
- Kode Pintar Icd 10Document48 pagesKode Pintar Icd 10Glory Stephanie Tesalonika Supit100% (2)