Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
RPH m3 f3
Transféré par
Lynne JbDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
RPH m3 f3
Transféré par
Lynne JbDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Zeckfetty's Weblog
Just another WordPress.com weblog
Navigation Skip to content
Home About DOKUMEN STANDARD PRESTASI MATEMATIK TINGKATAN 2 MATHEMATICS SYLLABUS FOR SECONDARY SCHOOL PEMETAAN DSP MATEMATIK TINGKATAN 2 RANCANGAN TAHUNAN MATEMATIK TINGKATAN 2- 2013 RANCANGAN TAHUNAN MATEMATIK TINGKATAN 3- 2013 RPH MINGGU 1 3 (02.01.13 18.01.13) RPH MINGGU 10 12 (04.03.13 22.03.13) RPH MINGGU 14 15 (01.04.13 12.04.13) RPH MINGGU 16 17 (15.04.13 26.04.13) RPH MINGGU 18 19 (29.04.13 03.04.13) RPH MINGGU 20 21 (13.05.13 24.05.13) RPH MINGGU 24 25 (10.06.13 21.06.13) RPH MINGGU 26 27 (24.06.13 05.07.13) RPH MINGGU 28 29 (08.07.13 19.07.13) RPH MINGGU 30 31 (22.07.13 02.08.13) RPH MINGGU 32 34 (08.08.13 23.08.13) RPH MINGGU 35 36 (26.08.13 06.09.13) RPH MINGGU 37 38 (09.09.13 20.09.13) RPH MINGGU 39 40 (23.09.13 04.10.13) RPH MINGGU 4 6 (21.01.13 07.02.13) RPH MINGGU 41 42 (07.10.13 18.10.13) RPH MINGGU 43 44 (21.10.13 01.11.13) RPH MINGGU 45 46 (04.11.13 15.11.13) RPH MINGGU 7 9 (11.02.13 02.03.13) SURAT AKU JANJI
RANCANGAN TAHUNAN MATEMATIK TINGKATAN 3- 2013
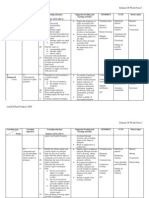
Week/Date 1 4 5 Jan Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes Remarks Introduction to Mathematics Form 3 1 LINES AND Students will be able to:i. Identify: ANGLES IIStudents will be 1. transversals taught to:1.1 Understand and use 2. corresponding angles properties of angles 3. alternate angles
12 6 15 Jan
associated with transversal and parallel lines.
4.
interior angles
ii. Determine that for parallel lines: a) b) c) corresponding angles are equal alternate angles are equal sum of interior angles is 1800
iii. Find the values of: a) b) c) corresponding angles alternate angles interior angles
associated with parallel lines. iv. Determine if two given lines are parallel based on the properties of angles associated with transversals. v. Solve problems involving properties of angles associated with transversals.
Students will be able to:i. Determine if a given polygon is a regular polygon. ii. Find: (a) (b) the axes if symmetry the number of axis of a symmetry
of a polygon. iii. Sketch regular polygons iv. Draw regular polygons by dividing equally the angle at the centre.
2 POLYGONS II Students will be v. Construct equilateral triangles, squares taught to: and regular hexagons. 2.1 Understand the concept of regular i. Identify the interior angles and exterior angles of a polygon. polygon. 2.2 Understand and ii. Find the size of an exterior angle when use the knowledge the interior angle of a polygon is given and 3 vice versa. of exterior and interior angles of 16 22 Jan polygons. iii. Determine the sum of the interior angles of polygons.
iv. Determine the sum of the exterior angles of polygons. v. Find: a. the size of an interior angle of a regular polygon given the number of sides. b. the size of an exterior angle of a regular polygon given the number of sides. c. the number of sides of a regular polygon given the size of the interior or exterior angle. vi. Solve problems involving angles and sides of polygons.
4 23 29 Jan Chinese New Year i. Identify a diameter of a circle as an axis of symmetryii. Determine that: a) a radius that is perpendicular to a chord divides the chord into two equal parts and vice versa. b) Perpendicular bisectors of two chord intersect at the centre. c) Two chords that are equal in length are equidistant from the centre and vice versa. d) Chords of the same length cut arcs of the same length iii. Solve problems involving symmetry, chords and arcs of circles. 3 CIRCLES II 3.1 Understand i. Identify angles subtended by an arc at the and use properties centre and at the circumference of a circle. of circles involving, symmetry, chords ii. Determine that the angles subtended at the and arcs circumference by the same arc are equal. 3.2 Understand and iii. Determine that the angles subtended: use properties of angles in circles. a. at the circumference 56 30 Jan 11 Feb 3.3 Understand and use the concept of b. cyclic quadrilaterals c. at the centre by arcs of the same length are equal.
Cuti peristiwa1Cuti ganti 1Cuti ganti 2
6 Feb- Cuti Maulid11 FebSabtu Ganti 1
iv. Determine the relationship between the angles at the centre and the angle at the circumference subtended by an arc. v. Determine the size of an angle subtended at the circumference in a semicircle. vi. Solve problems involving angles subtended at the centre and angles at the circumference of circles. i. Identify cyclic quadrilaterals. ii. Identify the interior opposite angles of cyclic quadrilaterals. iii. Determine the relationship between interior opposite angles of cyclic quadrilaterals. iv. Identify exterior angles and the corresponding interior opposite angles of cyclic quadrilaterals v. Determine the relationship between exterior angles and the corresponding interior opposite angle of cyclic quadrilaterals. vi. Solve problems involving angles of cyclic quadrilaterals vii. Solve problems involving circles.
i. Obtain and interpret information from pie charts.ii. Construct pie charts to represent data. iii. Solve problems involving pie charts.
iv. Determine suitable representation of data. i. Determine the mode of:
78 13 26 Feb
4 STATISTICS a. sets of data II4.1 Represent and interpret data in pie b. data given in frequency tables charts to solve problems.4.2 Understand and use ii.Determine the mode and the respective frequency from pictographs, bar charts, line the concept of mode, median and graphs and pie charts. mean to solve iii. Determine the median for sets of data. problems. iv. Determine the median of data in
frequency tables. v. a. b. Calculate the mean of : sets of data data in frequency tables.
vi. Solve problems involving mode, median and mean. i. Express repeated multiplication as an and vice versa.ii. Find the value of an. iii. i. 5 INDICES5.1 Understand the concept of indices.5.2 Perform computations involving multiplications of numbers in Index notation. ii. Express numbers in index notation. Verify Simplify multiplication of:
a) numbers. b) algebraic terms expressed in Index notation with he same base.
iii. Simplify multiplication of: 5.3. Perform computation involving a) numbers division of numbers in index notation. b) algebraic terms 5.4. Perform expressed in Index notation with different computations bases. involving raising numbers and 1. Verify algebraic terms in index notation to a ii. Simplify division of: power. a) numbers 5.5. Perform computations involving negative b) algebraic terms indices. 5.6. Perform computations involving fractional indices. 5.7. Perform computation involving laws of indices. expressed in index notation with the same base. i. ii. Derive Simplify:
a) numbers b) algebraic terms expressed in index notation raised to a 3 Mac Sabtu Ganti 2
9 10 27 Feb 11 Mac
power. iii. of: Simplify multiplication and division
a) numbers b) algebraic terms expressed in index notation with different bases raised to a power. iv. Perform combined operations involving multiplication, division, and raised to a power on: a) numbers b) algebraic terms. i. Verify ii. State and vice versa. iii. Perform combined operations of multiplication, division and raising to a power involving negative indices on: a) numbers b) algebraic terms. i. ii. iii. iv. a) b) v. Perform combined operations of multiplications, divisions and raising to a power involving fractional indices on : a) numbers b) algebraic terms vi. Find the value of . Verify State and vice versa. Find the value of State as:
i. Perform multiplication, division, raised to a power or combination of these operations on several numbers expressed in
index notation. ii. Perform combined operations of multiplication, division and raised to a power involving positive, negative and fractional indices. 10 5 11 Mac Ujian Bulanan 1
Week 11 Mid Semester 1 Holiday
Week/Date Learning Objectives
(12 18 Mac 2012)
Learning Outcomes i. Expand single brackets.ii. Expand two brackets. i. State factors of an algebraic term. Remarks
ii. State common factors and the HCF for several algebraic terms. iii. Factorise algebraic expressions:
a) using common factor b) the difference of two squares. iv. Factorise and simplify algebraic fractions. i. Add or subtract two algebraic fractions with the same denominator. ii. Add or subtract two algebraic fractions with one denominator as a multiple of the other denominator. iii. Add or subtract two algebraic 6 ALGEBRAIC fractions with denominators: EXPRESSIONS III6.1. Understand and a) without any common factor use the concept of expanding brackets.6.2 Understand and use the b) with a common factor. concept of factorization of algebraic expressions i. Multiply to algebraic fractions to solve problems. involving denominator with: 6.3. Perform addition a) one term and subtraction on algebraic fractions. b) two terms 6.4. Perform multiplication and division on algebraic fractions. ii. Divide two algebraic fractions involving denominator with: a) one term 19Mac 1 Apr
12 13
b) two terms iii. Perform multiplication and division of two algebraic fractions using factorization involving common factors and the difference of two squares. i. Determine if a quantity in a given situation is a variable or a constant.ii. Determine the variable in a given situation and represent it with a letter symbol iii.Determine the possible valuesof a variable in a given situation i. a. b. Write a formula based on a given: Statement Situation
ii. Identify the subject of a given formula iii. Express a specified variable as the subject of a formula involving: a) b) one of the basic operation: +,-,x ,/ powers or root
c) combination of the basic operations and powers or roots 7 ALGEBRAIC iv. Find the value of a variable when it FORMULA7.1 is: Understand the concept of variables and constant7.2 Understand a) the subject of the formula the concept of formulae b) not the subject of the formula to solve problems. v. Solve problems involving formulae. 8 SOLID GEOMETRY III8.1 i. Derive the formula for volume Prisms Understand and use the of:a) concept of volume of right prisms and b) Cylinders circular cylinders to solve problems.8.2 ii. Calculate the volume of right prism Understand and use the in cubic units given the height and: concept of volume of right pyramids and right the area of the base circular cones to solve a) problems. b) dimensions of the base 8.3 Understand and use the concept of volume iii. Calculate the height of a prism of sphere to solve given the volume and the area of the 6 Apr Good Friday9 Apr Cuti peristiwa 214 AprSabtu Ganti 3
14 -15 2 15 Apr
16 17 16 29Apr
6 Apr Good Friday9 Apr Cuti peristiwa 214 AprSabtu Ganti 3
problems.
base
8.4 Apply the concept iv. Calculate the area of the base of a prism given the volume and the height of volume to solve problems involving composite solids. v. Calculate the volume of a cylinder in cubic units given: a. b. area of the base and the height radius of the base and the height
of the cylinders vi. Calculate the height of a cylinder given the volume and the radius of the base vii. Calculate the radius of the base of a cylinder given the volume and the height viii. Convert volume in one metric unit to another a. b. mm,cm and m cm, ml and l
ix. Calculate volume of liquid in a container. x. Solve problems involving volume of prisms and cylinder i. Derive the formula for the volume of: a) b) pyramids cones
ii. Calculate the volume of pyramids in mm, cm and m, given the height and: a) b) area of the base dimensions of base
iii. Calculate the height of a pyramids given the volume and the dimension of the base iv. Calculate the area of the base of a pyramid given the volume and the height. v. Calculate the volume of a cone in
mm, cm, and m, given the height and radius of the base. vi. Calculate the height of a cone, given the volume and radius of the base. vii. Calculate the radius of the base of a cone given the volume and the height. viii. Solve problems involving volume of pyramids and cones. i. Calculate the volume of a sphere given the radius of the sphere. ii. Calculate the radius of a sphere given the volume of the sphere iii. Solve problems involving volume of sphere. i. Calculate the volume composite solids. ii. Solve problems involving volumes of composite solids. i. Sketch shapes:(a) of the same size as the object (b) smaller than the object (c) larger than the object using grid paper ii. Draw geometric shapes according to scale 1 : n, where n = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5,, 1/10 iii. Draw composite shapes according to given scale using: (a) grid paper (b) blank paper Hari iv. Redraw shapes on grids of different Buruh(1/5)Wesak sizes. 9 SCALE 18 (5/5) DRAWINGS9.1 Understand the concept v. Solve problems involving scale 30Apr 6 May of scale drawing. drawing 10 19 20 TRANFORMATIONS i. Identify if given shapes are II10.1 Understand similar.ii. Calculate the lengths of 7 -20 May and use the concept of unknown sides of two similar shapes.
similarity10.2 Understand and use the i. Identify an enlargement. concept of enlargement ii. Find the scale factor, given the object and its image of an enlargement when: a) b) scale factor > 0 scale factor < 0
iii. Determine the centre of enlargement, given the object and its image. iv. Determine the image of an object given the centre of enlargement and the scale factor. v. Determine the properties of enlargement. vi. Calculate: a) b) c) d) the scale factor lengths of the side of the image length of the side of the object an enlargement
vii. Determine the relationship between the area of the image and its object. viii. Calculate the: a) b) c) area of image area of object scale factor
of an enlargement. ix. Solve problems involving enlargement. 212127 May 1st semester Examination
Week 22 23 = Mid Year Holidays
Week/Date 24 Learning Objectives 11 LINEAR EQUATIONS II11.1
( 28 May 10 June 2011 )
Learning Outcomes i. Determine if an equation is a linear equation in two variables.ii. Write Remarks
11 -17Jun
Understand and use the linear equations in two variables from concept of linear equations given information. in two variables11.2 Understand and use the iii. Determine the value of a variable concept of two simultaneous given the other variables. linear equations in two variables to solve problems iv. Determine the possible solutions for a linear equation in two variables. i. Determine if two given equations are simultaneous linear equations. ii. Solve two simultaneous linear equations in two variables by a) b) substitution elimination
iii. Solve problems involving two simultaneous linear equations in two variables. i. Identify the relationship:a) greater than b) less than
based on given situations. ii. Write the relationship between two given numbers using the symbol >or <. 12 LINEAR iii. Identify the relationship: INEQUALITIES12.1 Understand and use the a) greater than or equal to concept of inequalities12.2 b) less than or equal to Understand and use the concept of linear inequalities in one unknown based on given situations. 12.3 Perform i. Determine if a given relationship is a computations involving linear inequality. addition, subtraction, multiplication and division ii. Determine the possible solutions for on inequalities a given linear inequality in one unknown: 12.4 Perform computations to solve a) x > h; inequalities in one variable 12.5 Understand the concept of simultaneous linear inequalities in one variable b) c) d) 18 Jun 1 Jul x < h; x h; x h.
25 26
iii. Represent a linear inequality: a) b) c) d) x > h; x < h; x h; x h.
on a number line and vice versa. iv. Construct linear inequalities using symbols: a) b) > or < or
from given information. i. State a new inequality for a given inequality when a number is: a) b) added to subtracted from
both sides of the inequalities. ii. State a new inequality for a given inequality when both sides of the inequalities are: a) b) multiplied by a number divided by a number.
iii. Construct inequalities a) b) c) d) from given information. i. Solve a linear inequality by a) b) adding a number subtracting a number x+k>m+k xk>mk kx > km
on both sides of the inequality. ii. Solve a linear inequality by a) b) multiplying a number dividing a number
on both sides of the inequality. iii. Solve linear inequalities in one variable using a combination of operations. i. Represent the common values of two simultaneous linear inequalities on a number line. ii. Determine the equivalent inequalities for two given linear inequalities. iii. Solve two simultaneous linear inequalities. 27 2 -8 Jul 6 Jul Cuti Minggu Pertandingan Olahraga Peristiwa 3 1. State the relationship between two variables based on the given information 2. Identify the dependent and independent variables in a given relationship involving two variables. Calculate the value of the dependent variable given the value of the independent variable. Construct tables of values for given functions. Draw graphs of functions using given scale. Determine from graph the value of y, given value of x and vice versa. Solve problems involving graphs of functions.
3.
1.
2. 13 GRAPHS OF FUNTIONS 13.1 Understand and use the concept of function 13.2 Draw and use graph of functions.
3.
28 9 22 Jul 29 16 22 Jul
4.
14 RATIOS, RATES AND PROPORTIONS II14.1 Understand the concept of rate and perform
1.
Determine the rates involved in given situations and identify the two quantities
computations involving rates.14.2 Understand and use the concept of speed. 14.3 Understand and use the concept of average speed. 14.4 Understand and use the concept of acceleration
involved. 2. Calculate the rate given two different quantities. Calculate a certain quantity given the rate and the other quantity. Convert rates from one unit of measurement to another. Solve problems involving rates. Identify the two quantities involved in speed. Calculate and interpret speed. Calculate:
3.
4.
5.
1.
2. 3.
a). the distance, given the speed and the time. b). the time, given the speed and the distance. 4. Convert speed from one unit of measurement to another. Differentiate between uniform speed and non-uniform speed. Calculate the average speed in various situations. Calculate the distance given the average speed and the time. the time, given the average speed and the distance. Solve problems involving speed and average speed
5.
1.
2. 1. 2.
3.
i. Identify the two quantities involved in acceleration. ii. Calculate and interpret acceleration. 15 TRIGONOMETRY15.1 Understand and use tangent an acute angle in a rightangled triangle.15.2 30 Understand and use sine of an acute angle in a right23 29 Jul angled triangle. i. Identify the:a. Hypotenuse
b. The opposite side and the adjacent side with respect to one of the acute angles. ii. Determine the tangent of an
angle. 15.3 Understand and use cosine of an acute angle in a iii. Calculate the tangent of an angle right-angled triangle. given the lengths of sides of the triangle. 15.4 Use the values of tangent, sine and cosine to iv. Calculate the lengths of sides of a solve problems. triangle given the value of tangent and the length of another side. i. Determine the sine of an angle.
ii. Calculate the sine of an angle given the lengths of sides of the triangle. iii. Calculate the lengths of sides of a triangle given the value of sine and length of another side. i. angle. Determine the cosine of an
ii. Calculate the cosine of an angle given the lengths of sides of the triangle iii. Calculate the lengths of sides of a triangle given the value of cosine and the length of another side.. i. Calculate the value of other trigonometric ratios given the value of a trigonometric ratio. ii. Convert the measurement of angles from a. b. degrees to degrees and minutes. degrees and minutes to degrees.
iii. Find the value of : a. b. c. tangent sine cosine
of 30o, 45o and 60o without using scientific calculator. iv. Find the value of: a. Tangent
b. c.
Sine cosine
using scientific calculator. v. Find the angles given the values of: a) b) c) tangent sine cosine
using scientific calculators. vi. Solve problems involving trigonometric ratios. *Percubaan PMR (13 17 Ogos) *Revision (27 Ogos 30 Sept)Hari Raya Aidilfitri / Cuti pertengahan penggal 2 (18 -26 Ogos) Hari Kebangsaan (31 Ogos) 33 39 40 Hari Malaysia (17 Sept)
31 32
Okt Nov
PMR Program pasca PMR
Share this:
Like this:
Leave a comment
Leave a Reply
CATEGORIES A links Uncategorized PAGES About
DOKUMEN STANDARD PRESTASI MATEMATIK TINGKATAN 2 MATHEMATICS SYLLABUS FOR SECONDARY SCHOOL PEMETAAN DSP MATEMATIK TINGKATAN 2 RANCANGAN TAHUNAN MATEMATIK TINGKATAN 2- 2013 RANCANGAN TAHUNAN MATEMATIK TINGKATAN 3- 2013 RPH MINGGU 1 3 (02.01.13 18.01.13) RPH MINGGU 10 12 (04.03.13 22.03.13) RPH MINGGU 14 15 (01.04.13 12.04.13) RPH MINGGU 16 17 (15.04.13 26.04.13) RPH MINGGU 18 19 (29.04.13 03.04.13) RPH MINGGU 20 21 (13.05.13 24.05.13) RPH MINGGU 24 25 (10.06.13 21.06.13) RPH MINGGU 26 27 (24.06.13 05.07.13) RPH MINGGU 28 29 (08.07.13 19.07.13) RPH MINGGU 30 31 (22.07.13 02.08.13) RPH MINGGU 32 34 (08.08.13 23.08.13) RPH MINGGU 35 36 (26.08.13 06.09.13) RPH MINGGU 37 38 (09.09.13 20.09.13) RPH MINGGU 39 40 (23.09.13 04.10.13) RPH MINGGU 4 6 (21.01.13 07.02.13) RPH MINGGU 41 42 (07.10.13 18.10.13) RPH MINGGU 43 44 (21.10.13 01.11.13) RPH MINGGU 45 46 (04.11.13 15.11.13) RPH MINGGU 7 9 (11.02.13 02.03.13) SURAT AKU JANJI
Blog at WordPress.com. | The Confit Theme. Follow
Follow Zeckfetty's Weblog
Get every new post delivered to your Inbox.
Sign me up
Powered by WordPress.com
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Explorations and Discoveries in Mathematics, Volume 1, Using The Geometer's Sketchpad Version 4D'EverandExplorations and Discoveries in Mathematics, Volume 1, Using The Geometer's Sketchpad Version 4Pas encore d'évaluation
- RPT Math Form 2Document16 pagesRPT Math Form 2Hartini KosnanPas encore d'évaluation
- First Semester: Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form Three - 2008Document23 pagesFirst Semester: Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form Three - 2008dirza82Pas encore d'évaluation
- RPT: Mathematic Form 3Document15 pagesRPT: Mathematic Form 3zulmajdiPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly MM F3Document20 pagesYearly MM F3Yusraay SuePas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Plan 2012 Mathematics Form 2Document14 pagesYearly Plan 2012 Mathematics Form 2FikriSalimPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Lesson Plan f5 2007Document10 pagesYearly Lesson Plan f5 2007hazwani_sPas encore d'évaluation
- RPT Maths f4 2013Document16 pagesRPT Maths f4 2013Kang CkPas encore d'évaluation
- Rancangan Tahunan P&P Mathematics Form 4Document25 pagesRancangan Tahunan P&P Mathematics Form 4Mohd Sani Abd HamidPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Teaching PlanDocument7 pagesYearly Teaching PlanSean GomezPas encore d'évaluation
- F4 Maths YPDocument10 pagesF4 Maths YPKelvinYongPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Plan Math f3Document33 pagesYearly Plan Math f3Faziyana Busu NollahPas encore d'évaluation
- Standard Akademik Sekolah-Sekolah Negeri Kelantan: Catatan: Masukkan Tarikh Seperti Di Dalam Takwim SekolahDocument14 pagesStandard Akademik Sekolah-Sekolah Negeri Kelantan: Catatan: Masukkan Tarikh Seperti Di Dalam Takwim SekolahFarid YusofPas encore d'évaluation
- YLP Form 5 MathematicsDocument18 pagesYLP Form 5 MathematicsRisma RobinPas encore d'évaluation
- Math F4 (2013)Document49 pagesMath F4 (2013)Mohd Azizi Mohd NoorPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Lesson Plan2011Document18 pagesYearly Lesson Plan2011Che'ras IbrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form2 2013Document11 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form2 2013Norliza SapatanohPas encore d'évaluation
- Maths Cs Form 5Document6 pagesMaths Cs Form 5juriah binti ibrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics Form 2Document18 pagesMathematics Form 2Hilmi Abd GhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Scheme of Work Mathematics Form 2Document16 pagesScheme of Work Mathematics Form 2Stephanie Kimi100% (2)
- Yearly Lesson Addmathsf413Document10 pagesYearly Lesson Addmathsf413SasiKalaRamayahPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Lesson Plan Math Form 4Document10 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Math Form 4hazwani_sPas encore d'évaluation
- Scheme of Work Mathematics Form 2 2013Document31 pagesScheme of Work Mathematics Form 2 2013Puteri NorhanaPas encore d'évaluation
- School: SM Agama Kota Tinggi Subject: Mathematics Form: 2Document7 pagesSchool: SM Agama Kota Tinggi Subject: Mathematics Form: 2adawiyah_04Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tingkatan 2 Week Learning Area Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes Remark 1. Directed NumbersDocument8 pagesTingkatan 2 Week Learning Area Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes Remark 1. Directed NumbersMuhammad ElhamPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Plan Maths Form 4Document24 pagesYearly Plan Maths Form 4JiaJia LauPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Lesson Plan - Form2Document16 pagesYearly Lesson Plan - Form2petersiewPas encore d'évaluation
- SMKK Imtiaz Kuala Terengganu Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form Two 2012Document12 pagesSMKK Imtiaz Kuala Terengganu Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form Two 2012norhasmizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Date Learning Objectives Learning Outcome Remark 1. Directed Numbers. Students Will Be Able To:i. MultiplyDocument20 pagesDate Learning Objectives Learning Outcome Remark 1. Directed Numbers. Students Will Be Able To:i. MultiplyHe Si RuPas encore d'évaluation
- RPT Math Form2Document7 pagesRPT Math Form2Teobeng LimauPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics: Form 4 / 2013 Week Topics/Learning Area Learning Outcomes Points To NoteDocument29 pagesMathematics: Form 4 / 2013 Week Topics/Learning Area Learning Outcomes Points To NoteAmri AwalludinPas encore d'évaluation
- Sekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Bidor: Shceme of Work Mathematics Form 2 2012Document9 pagesSekolah Menengah Kebangsaan Bidor: Shceme of Work Mathematics Form 2 2012Zarina JusohPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Lesson Plan (2012) Mathematics Form 5Document19 pagesYearly Lesson Plan (2012) Mathematics Form 5Nie Anthon100% (1)
- Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form2 2009-AdleenDocument11 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form2 2009-AdleenFadhlina FadilPas encore d'évaluation
- RPT Add Math Form 4Document9 pagesRPT Add Math Form 4Norhapidah Mohd SaadPas encore d'évaluation
- Le Math Q3 W3Document10 pagesLe Math Q3 W3julianne cartenaPas encore d'évaluation
- SMK Tanjung Adang, Gelang Patah, Johor Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form Two 2009Document12 pagesSMK Tanjung Adang, Gelang Patah, Johor Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form Two 2009Adibah AliasPas encore d'évaluation
- First Semester: Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form Two - 2008Document27 pagesFirst Semester: Yearly Lesson Plan Mathematics Form Two - 2008dirza82Pas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of MathematicDocument19 pagesAnalysis of MathematicadleenshazPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics Form 2 CSDocument17 pagesMathematics Form 2 CSAnita MuhdPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Lesson Plan Math F2Document13 pagesYearly Lesson Plan Math F2Yd MnPas encore d'évaluation
- Matematik Form 3Document2 pagesMatematik Form 3b385319Pas encore d'évaluation
- School: SMK Dato' Sri Amar Diraja, Muar Subject: Mathematics Form: 2Document8 pagesSchool: SMK Dato' Sri Amar Diraja, Muar Subject: Mathematics Form: 2zarina binti jusohPas encore d'évaluation
- Sheme of Work Mat F5Document17 pagesSheme of Work Mat F5mpuziahPas encore d'évaluation
- RPT Math F4 2013Document34 pagesRPT Math F4 2013ummuinsyirahPas encore d'évaluation
- Form 5Document21 pagesForm 5dirza82Pas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Teaching Plan For Mathematics Form 2 2012 Date Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes Point To Note Vocabulary Directed NumberDocument8 pagesYearly Teaching Plan For Mathematics Form 2 2012 Date Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes Point To Note Vocabulary Directed NumberMohd Nazmi RahimiPas encore d'évaluation
- Form 4 Modern Mathematics SyllabusDocument9 pagesForm 4 Modern Mathematics Syllabusjuriah binti ibrahim100% (2)
- 2014 Annual Scheme of Work: SMK Penangah Telupid Form 5 Additional MathematicsDocument9 pages2014 Annual Scheme of Work: SMK Penangah Telupid Form 5 Additional Mathematicsjosnih bin murniPas encore d'évaluation
- f5 Add Maths Annual Scheme (2008)Document6 pagesf5 Add Maths Annual Scheme (2008)Abdul ManafPas encore d'évaluation
- Yearly Plan Maths F 5 2011Document20 pagesYearly Plan Maths F 5 2011ysheng98Pas encore d'évaluation
- Math Yearly Plan f4 2012Document14 pagesMath Yearly Plan f4 2012Soh Tyan JiinPas encore d'évaluation
- 6th Grade Math - Covering and Surrounding Unit PlanDocument7 pages6th Grade Math - Covering and Surrounding Unit PlanBecky JohnsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Area: 1) Number Bases Mathematics: Form 5 Week/Date Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes Generics Ccts Moral Value NotesDocument17 pagesLearning Area: 1) Number Bases Mathematics: Form 5 Week/Date Learning Objectives Learning Outcomes Generics Ccts Moral Value NotesNur BainiPas encore d'évaluation
- Matematik Tingkatan 3. Sukatan PelajaranDocument19 pagesMatematik Tingkatan 3. Sukatan Pelajaranb385319Pas encore d'évaluation
- Add Maths Form 4Document10 pagesAdd Maths Form 4Azrul AkmarPas encore d'évaluation
- MathsDocument11 pagesMathsscorpionketanPas encore d'évaluation
- RPT Mathematics Form5 - 2011Document14 pagesRPT Mathematics Form5 - 2011Madiah JaafarPas encore d'évaluation
- Es Table Grade 6 Pba Mya For Parcc FinalDocument8 pagesEs Table Grade 6 Pba Mya For Parcc Finalapi-115680157Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fizik: Peperiksaan Percubaan SPM TAHUN 2018 Majlis Pengetua Sekolah Malaysia (Kedah)Document9 pagesFizik: Peperiksaan Percubaan SPM TAHUN 2018 Majlis Pengetua Sekolah Malaysia (Kedah)Lynne JbPas encore d'évaluation
- Student ManualDocument2 pagesStudent ManualLynne JbPas encore d'évaluation
- Latihan 2Document3 pagesLatihan 2Lynne JbPas encore d'évaluation
- 2005 Physics P2 PDFDocument63 pages2005 Physics P2 PDFLynne JbPas encore d'évaluation
- 80 Leburaya 90 KM/J 40 Passengers Only: UNDERSTANDING (Section B) / Paper 2Document4 pages80 Leburaya 90 KM/J 40 Passengers Only: UNDERSTANDING (Section B) / Paper 2Lynne JbPas encore d'évaluation
- Piawai Akademik Fizik t4 2011Document2 pagesPiawai Akademik Fizik t4 2011Lynne JbPas encore d'évaluation
- Solar CarDocument1 pageSolar CarLynne JbPas encore d'évaluation
- Soalan WaveDocument8 pagesSoalan WaveLynne JbPas encore d'évaluation
- 01 Parking LotDocument1 page01 Parking LotLynne JbPas encore d'évaluation
- WaveDocument16 pagesWaveLynne JbPas encore d'évaluation
- RPH m3 f3Document19 pagesRPH m3 f3Lynne JbPas encore d'évaluation
- WaveDocument16 pagesWaveLynne JbPas encore d'évaluation
- Red Bin Analysis PDF Notes - 10020477 - 2023 - 10 - 13 - 09 - 28Document7 pagesRed Bin Analysis PDF Notes - 10020477 - 2023 - 10 - 13 - 09 - 28Sameer SutarPas encore d'évaluation
- Isentropic ExponentDocument2 pagesIsentropic ExponentAlf OtherspacePas encore d'évaluation
- Kluang (A) S2 STPM 2019Document9 pagesKluang (A) S2 STPM 2019Rex KalPas encore d'évaluation
- Cj2m-Cpu, - md21 Cpu Units, Pulse I o Modules Datasheet en PDFDocument29 pagesCj2m-Cpu, - md21 Cpu Units, Pulse I o Modules Datasheet en PDFKhairy YaakobPas encore d'évaluation
- Competition Systems IGN1A Inductive Smart Coil - IGN1ADocument2 pagesCompetition Systems IGN1A Inductive Smart Coil - IGN1AJoão Lucas ZaionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter26to29-Bolt Tightening TorqueDocument36 pagesChapter26to29-Bolt Tightening TorqueEnam SembilanPas encore d'évaluation
- S/Mime (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions)Document15 pagesS/Mime (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions)Vishnupriya100% (1)
- Notebook PC Service Manual System Disassembly Model: - AMILO D 1845 (257SA0)Document16 pagesNotebook PC Service Manual System Disassembly Model: - AMILO D 1845 (257SA0)Robert DumitrescuPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidelines For Utility Impact Assessment For Local Roads in Developed Areas MME 2012 Cross-SectionDocument81 pagesGuidelines For Utility Impact Assessment For Local Roads in Developed Areas MME 2012 Cross-Sectionirfan mohammedPas encore d'évaluation
- 07a80809 OperationsresearchDocument11 pages07a80809 OperationsresearchSharanya ThirichinapalliPas encore d'évaluation
- TUC5+ Modbus ID Details PDFDocument10 pagesTUC5+ Modbus ID Details PDFvijikeshPas encore d'évaluation
- SM 89Document36 pagesSM 89Camilo RamosPas encore d'évaluation
- OS Prelude-1Document16 pagesOS Prelude-1YayatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Rodriguez-Castro Et Al 2022 Human Highly Modified Landscapes Restrict Gene FlowDocument20 pagesRodriguez-Castro Et Al 2022 Human Highly Modified Landscapes Restrict Gene FlowShara MotaPas encore d'évaluation
- From Navier Stokes To Black Scholes - Numerical Methods in Computational FinanceDocument13 pagesFrom Navier Stokes To Black Scholes - Numerical Methods in Computational FinanceTrader CatPas encore d'évaluation
- Anomaly Detection Principles and Algorithms: Mehrotra, K.G., Mohan, C.K., Huang, HDocument1 pageAnomaly Detection Principles and Algorithms: Mehrotra, K.G., Mohan, C.K., Huang, HIndi Wei-Huan HuPas encore d'évaluation
- JVR Fingerprint Attendance User ManualDocument30 pagesJVR Fingerprint Attendance User ManualDomingo MonteroPas encore d'évaluation
- Decision Analysis: Learning ObjectivesDocument30 pagesDecision Analysis: Learning ObjectivesMorgan AfrizalPas encore d'évaluation
- OSHA Module 3Document17 pagesOSHA Module 3Varsha GPas encore d'évaluation
- SIF Corporate-Presentatie 2017Document35 pagesSIF Corporate-Presentatie 201766apenlullenPas encore d'évaluation
- Science July Assignment Grade 8Document3 pagesScience July Assignment Grade 8G PPas encore d'évaluation
- User Manual of Egov 11.0 Implementation of It Solution For RVNL D3799 Document Version / DetailsDocument64 pagesUser Manual of Egov 11.0 Implementation of It Solution For RVNL D3799 Document Version / DetailsRVNLPKG6B VBL-GTLMPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics in The Modern World: Course No. Course Title Dean's InformationDocument5 pagesMathematics in The Modern World: Course No. Course Title Dean's InformationJayson SantelicesPas encore d'évaluation
- KDW1.1 100 300 W1 220 Mainspindle Drive Indramat ManualDocument146 pagesKDW1.1 100 300 W1 220 Mainspindle Drive Indramat ManualSven TackPas encore d'évaluation
- Pert PPT PresentationDocument13 pagesPert PPT PresentationDhanjay Das100% (2)
- Harnack and Mean Value Inequalities On Graphs: 1 Introduction and Main ResultsDocument8 pagesHarnack and Mean Value Inequalities On Graphs: 1 Introduction and Main ResultsNo FacePas encore d'évaluation
- TMS Advanced TreeViewDocument64 pagesTMS Advanced TreeViewDanilo CristianoPas encore d'évaluation
- Atma Ram Sanatan Dharma College: PresentationDocument6 pagesAtma Ram Sanatan Dharma College: PresentationRishikeshav RaviPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Science Admissions Test: Avengers CollegeDocument4 pagesComputer Science Admissions Test: Avengers CollegeSaad Bin AzimPas encore d'évaluation
- Andrew KC Chan (2003) - Observations From Excavations - A ReflectionDocument19 pagesAndrew KC Chan (2003) - Observations From Excavations - A ReflectionMan Ho LamPas encore d'évaluation