Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Force Sbi
Transféré par
Moch. Choirul Anam,S.Si0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
295 vues2 pages__________ is the combination of all the forces acting on an object. When balanced forces act on an object, the net force is _________. ________ is a force that resists motion between two surfaces that are in contact.
Description originale:
Titre original
force sbi
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce document__________ is the combination of all the forces acting on an object. When balanced forces act on an object, the net force is _________. ________ is a force that resists motion between two surfaces that are in contact.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
295 vues2 pagesForce Sbi
Transféré par
Moch. Choirul Anam,S.Si__________ is the combination of all the forces acting on an object. When balanced forces act on an object, the net force is _________. ________ is a force that resists motion between two surfaces that are in contact.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 2
Name :
Number :
1. A (n) __________ is a push or a pull.
a. Motion c. velocity
b. Acceleration d. force
2. The __________ is the combination of all the forces acting on an object.
a. direction of motion c. force pair
b. inertia d. net force
3. Forces that cancel each other are called __________ forces.
a. Neutral c. balanced
b. Inactivated d. null
4. When balanced forces act on an object, the net force is __________.
a. Positive c. zero
b. Negative d. increased due to friction
5. When unbalanced forces act on an object, __________.
a. the object accelerates c. the net force is zero
b. the object speeds up d. friction becomes greater than the net force
6. __________ is a force that resists motion between two surfaces that are in contact.
a. Resistance c. Inertia
b. Friction d. Acceleration
7. Newton's first law of motion states that __________.
a. an object will remain at rest or keep moving with a constant velocity unless a force acts
on it
b. acceleration is calculated by dividing the force exerted on an object by the mass of the
object
c. when a force acts on an object, its acceleration is in the same direction as the force
d. when a force is applied on an object, there is an equal force applied by the object in the
opposite direction
8. __________ measures an object's tendency to resist changing its motion.
a. Gravity c. Acceleration
b. Mass d. Inertia
9. A ball is thrown straight up in the air. According to Newton's first law of motion, what is the
reason for the ball falling back to Earth?
a. A force has acted on it
b. It is accelerating in the same direction as Earth's gravitational force on it.
c. The change in the ball's acceleration is proportional to the force acting on it.
d. The ball exerts a force on the air surrounding it.
10. What causes a falling skydiver to slow down after the parachute opens?
a. air resistance c. gravity
b. inertia d. reference motion
11. Which of the following types of friction keeps an object at rest?
a. Static c. rolling
b. Sliding d. mobile
12. Newton's second law of motion states that __________.
a. an object will remain at rest or keep moving in a straight line with constant speed unless
a force acts on it
b. when a force is applied on an object, there is an equal force applied by the object in the
opposite direction
c. the force on an object can be found by dividing its mass by its acceleration
d. acceleration is calculated by dividing the force exerted on an object by the mass of the
object, and that when a force acts on an object, its acceleration is in the same direction
as the force
13. A change in motion is described by __________.
a. Inertia c. acceleration
b. net force d. speed
14. Which of the following statements is true?
a. An object does not accelerate if it turns and maintains constant speed.
b. Velocity of a moving object is the distance traveled divided by the time needed to travel
the distance.
c. When speed increases gradually, average speed and instantaneous speed are the same
d. If a moving object slows down, it is accelerating.
15. __________ is the pull that all objects exert on each other.
a. Resistance c. Friction
b. Inertia d. Gravity
16. You are moving a dresser that has a mass of 36 kg; its acceleration is 0.5 m/s2. What is the force
being applied?
a. 72 N c. 35.5 N
b. 1.8 N d. 18 N
17. The strength of the gravitational force between two objects depends on which of the following?
a. the mass of the larger object
b. the velocities of the objects
c. the mass of the objects and the distance between them
d. the orbits of the objects
18. Gravity causes all object's near Earth's surface to fall with an acceleration of __________.
a. a = F X m c. 9.8 m/s
2
b. 9.8 m/s d. 98 m2/s
19. Which of the following is not an acceleration?
a. stopping your bike at an intersection
b. slowing your bike ride so you can make it up a hill
c. riding your bike faster when you head down a hill
d. riding your bike straight down the street at a constant speed
20. In describing the acceleration given a 2-kg object by a 10-N force acting on it, which of these
units is appropriate?
a. N c. N/kg2
2
b. m/s d. kg/s2
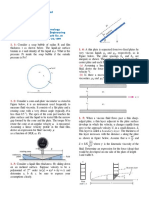
21. Look at the picture!
F1=10 N
m = 20 kg
F2 = 15 N
Calculate acceleration action in object?
22. Mention the Newton’s third law in daily life? (minimal 2)
23. Look at the picture!
Calculate net force (sum force) in action and
direction of net force?
24. When the object gives a force, what happen of object?
25. Give 2 example of application Newton’s first law in daily life?
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- BiologyDocument120 pagesBiologyMoch. Choirul Anam,S.SiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Air Powered Car ExperimentDocument9 pagesAir Powered Car ExperimentMoch. Choirul Anam,S.SiPas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Test of ElectrostaticDocument3 pagesTest of ElectrostaticMoch. Choirul Anam,S.SiPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus Science Grade 7Document12 pagesSyllabus Science Grade 7Moch. Choirul Anam,S.Si67% (6)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Lesson Plan Science Grade 7Document61 pagesLesson Plan Science Grade 7Moch. Choirul Anam,S.Si81% (27)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Soal Latihan Fisika SBIDocument4 pagesSoal Latihan Fisika SBIMoch. Choirul Anam,S.Si100% (27)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Part 3 Abut - Well Foundation DesignDocument46 pagesPart 3 Abut - Well Foundation Designshashi rajhansPas encore d'évaluation
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- SS Question 03 Book Crunch 2020Document100 pagesSS Question 03 Book Crunch 2020shashwatPas encore d'évaluation
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Finder Relays Series 56 PDFDocument6 pagesFinder Relays Series 56 PDFFrancisco Ignacio Vigorena ChavezPas encore d'évaluation
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Preview of "Chapter 15 For Credit"Document9 pagesPreview of "Chapter 15 For Credit"Dyamond SantiagoPas encore d'évaluation
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hydraulics & Fluid Mechanics 5Document16 pagesHydraulics & Fluid Mechanics 5Manaal tariqPas encore d'évaluation
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Final LP in Sci 101Document12 pagesFinal LP in Sci 101Rene Rulete MapaladPas encore d'évaluation
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Book II Class Xi - MergedDocument149 pagesBook II Class Xi - Mergedno onePas encore d'évaluation
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- DPP (54-57) 11th PQRS Physics WADocument7 pagesDPP (54-57) 11th PQRS Physics WAAyushJainPas encore d'évaluation
- HESI Math and Science Answers Exam 2023Document4 pagesHESI Math and Science Answers Exam 2023Nelson MandelaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- FluidMechanicsI HW01Document1 pageFluidMechanicsI HW01AzlPas encore d'évaluation
- (DTE) PR Sahid MuttaqinDocument5 pages(DTE) PR Sahid MuttaqinSahid MuttaqinPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan Genral Physics 2Document4 pagesLesson Plan Genral Physics 2Ron Dela RosaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Cape Physics U1 P1 2013Document11 pagesCape Physics U1 P1 2013C.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physics STPM Sem 2 DefinitionDocument2 pagesPhysics STPM Sem 2 DefinitionBen100% (4)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- EMFT Question BankDocument4 pagesEMFT Question BankSARITHAPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment 7: Work, Power and EnergyDocument8 pagesExperiment 7: Work, Power and EnergynatlasPas encore d'évaluation
- KITCHEN Roster 2018Document28 pagesKITCHEN Roster 2018Anonymous Wb2VvAC5Pas encore d'évaluation
- A-Isometer® Irdh275: Ground Fault Monitor / Ground Fault Relay For Ungrounded AC, DC, and AC/DC SystemsDocument80 pagesA-Isometer® Irdh275: Ground Fault Monitor / Ground Fault Relay For Ungrounded AC, DC, and AC/DC SystemsMauricio AguilarPas encore d'évaluation
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Certificados de Normas de InversoresDocument7 pagesCertificados de Normas de InversoresSepcaPas encore d'évaluation
- Load Flow 1 - CompleteDocument12 pagesLoad Flow 1 - CompleteKM 2 SPENTRIPas encore d'évaluation
- Transformerless Power SupplyDocument7 pagesTransformerless Power SupplyGUIDE ON BIO-MEDICAL ENGINEERING UNDERGRADUATE PROGRAM:Pas encore d'évaluation
- Volumetric Calibrations: Site MenuDocument7 pagesVolumetric Calibrations: Site MenuMlakPas encore d'évaluation
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- PHY10L - Uniform Circular MotionDocument11 pagesPHY10L - Uniform Circular Motiondenzel94Pas encore d'évaluation
- PPN j522Document16 pagesPPN j522TiowlPas encore d'évaluation
- Mebc Brave 5Document12 pagesMebc Brave 5Laxmi PrasannaPas encore d'évaluation
- English Power SupplyDocument5 pagesEnglish Power Supplyhyper officialPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronics 10 00088 v2Document17 pagesElectronics 10 00088 v2Pio_ChroniclePas encore d'évaluation
- wph12 01 Rms 20190815Document16 pageswph12 01 Rms 20190815NairitPas encore d'évaluation
- JEE Main DPYQ Full Syllabus PAPER-1Document5 pagesJEE Main DPYQ Full Syllabus PAPER-1Saravanan BPas encore d'évaluation
- P C W Davies 1978 Rep. Prog. Phys. 41 1313Document44 pagesP C W Davies 1978 Rep. Prog. Phys. 41 1313Luciano del VallePas encore d'évaluation
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)