Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Cipro
Transféré par
Srkocher0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
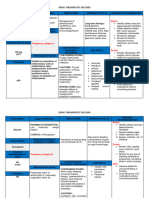
557 vues1 pageRx inhibits bacterial DNA synthesis by inhibiting DNA gyrase. Therapeutic effect: death of susceptible bacteria. May be used for intra-abdominal infections Mechanism of action and indications: (Why med ordered) Contraindications / warnings / interactions hypersensitivity. Geri: Increased risk of adverse reactions. Interactions with other patient drugs, OTC or herbal medicines (ask patient specifically)
Description originale:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentRx inhibits bacterial DNA synthesis by inhibiting DNA gyrase. Therapeutic effect: death of susceptible bacteria. May be used for intra-abdominal infections Mechanism of action and indications: (Why med ordered) Contraindications / warnings / interactions hypersensitivity. Geri: Increased risk of adverse reactions. Interactions with other patient drugs, OTC or herbal medicines (ask patient specifically)
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
557 vues1 pageDrug Cipro
Transféré par
SrkocherRx inhibits bacterial DNA synthesis by inhibiting DNA gyrase. Therapeutic effect: death of susceptible bacteria. May be used for intra-abdominal infections Mechanism of action and indications: (Why med ordered) Contraindications / warnings / interactions hypersensitivity. Geri: Increased risk of adverse reactions. Interactions with other patient drugs, OTC or herbal medicines (ask patient specifically)
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme DOC, PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
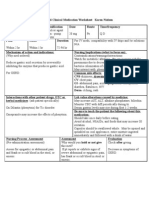
NURS 1566 Clinical Medication Worksheet
Generic Name Trade Name Classification Dose Route Time/frequency
Ciprofloxacin Cipro antibiotic
fluoroquinalone 400 mg IV Q 12 hr
Peak Onset Duration Normal Dosage Range
End of infusion Rapid 12 hr 400 mg Q 12 hr
Why is your patient getting this medication: For IV meds, compatibility with IV drips and/or solutions
May be used for intra-abdominal infections Recommended temporary suspension of other fluids when
administering Cipro.
Mechanism of action and indications: Nursing Implications (what to focus on)
(Why med ordered.) Contraindications/warnings/interactions
Hypersensitivity.
Rx inhibits bacterial DNA synthesis by inhibiting DNA gyrase. Geri: Increased risk of adverse reactions.
Therapeutic effect: death of susceptible bacteria.
Common side effects: CNS: SEIZURES, dizziness, H/A, insomnia,
acute psychosis, agitation, confusion, drowsiness.
GI: PSEUDOMEMBRANOUS COLITIS, diarrhea, N/V, abdominal
pain, increased LFTs.
Derm: photosensitivity, rash.
Endo: hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia.
MS: tendinitis, tendon rupture.
Misc: hypersensitivity reactions: ANAPHYLAXIS, STEVENS-
JOHNSON SYDROME
Interactions with other patient drugs, OTC or herbal Lab value alterations caused by medicine:
medicines (ask patient specifically): May increase serum AST, ALT, LDH, bilirubin, and alkaline
phosphatase. May increase or decrease serum glucose.
MOM may decrease the absorption of Cipro
Be sure to teach the patient the following about this medication:
May take with food to decrease GI irritation. Take 1 hour before or 2 hours
after dairy products. Encourage pt to maintain fluid intake of at least
1500- 2000 ml /day to prevent crystalluria. Report signs of superinfection;
(furry tongue, loose stools.)
Nursing Process- Assessment Assessment Evaluation
(Pre-administration assessment) Why would you hold or not give this Check after giving
med? Resolution of S/S of infection, No
Vital signs, signs of superinfection.
Observe for signs of anaphylaxis, tendon pain. Signs of tendon pain, swelling, redness.
Severe rash, pruritis.
Severe diarrhea, signs of
pseudomembranous colitis.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Antioxidant Revolution: An Idea of LongevityD'EverandThe Antioxidant Revolution: An Idea of LongevityPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology IDocument202 pagesPharmacology ISalahadinPas encore d'évaluation
- Antibiotic 2021 Online Reading TextDocument120 pagesAntibiotic 2021 Online Reading TextShailendraPas encore d'évaluation
- CiproDocument4 pagesCiproNikku SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Augmentin: Most Commonly Recommended For Bacterial Infections by GSKDocument15 pagesAugmentin: Most Commonly Recommended For Bacterial Infections by GSKsargamPas encore d'évaluation
- Thebookofgeese 130426023850 Phpapp02Document222 pagesThebookofgeese 130426023850 Phpapp02Samuel Ivan NganPas encore d'évaluation
- CTD (Form 5F) : Section Sub-Section HeadingDocument19 pagesCTD (Form 5F) : Section Sub-Section Headinganon_3034696030% (1)
- Plavix (Clopidogrel)Document1 pagePlavix (Clopidogrel)E50% (2)
- Topic: Medicial Chemistry of HormonesDocument18 pagesTopic: Medicial Chemistry of HormonesHaris AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Ethiopia National Drug FormularyDocument572 pagesEthiopia National Drug FormularyportosinPas encore d'évaluation
- Formulation of HERVEL SGC For WomenDocument2 pagesFormulation of HERVEL SGC For Womennaeem186Pas encore d'évaluation
- Film Coated Vs Sugar Coated Ibuprofen TabletDocument20 pagesFilm Coated Vs Sugar Coated Ibuprofen Tabletfad12345Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bamboo: A Structural MaterialDocument17 pagesBamboo: A Structural MaterialMunira JawadwalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Toxicology in The Drug Discovery and Development Process: UNIT 10.3Document35 pagesToxicology in The Drug Discovery and Development Process: UNIT 10.3Nilabh RanjanPas encore d'évaluation
- 07.muscle RelaxanteDocument28 pages07.muscle RelaxanteLee BoborasPas encore d'évaluation
- Flavonoids From Black Chokeberries, Aronia MelanocarpaDocument8 pagesFlavonoids From Black Chokeberries, Aronia MelanocarpaleewiuPas encore d'évaluation
- Ospe PracticalsDocument4 pagesOspe PracticalsAbid LaghariPas encore d'évaluation
- Paracetamol PDFDocument49 pagesParacetamol PDFEhb90210Pas encore d'évaluation
- TobramycinDocument3 pagesTobramycinAj MillanPas encore d'évaluation
- PDF - of - Heat Pump Water Heater PresentationDocument43 pagesPDF - of - Heat Pump Water Heater PresentationBRYMOENPas encore d'évaluation
- FDA FOIA Closed Log - January 2020 - 0Document80 pagesFDA FOIA Closed Log - January 2020 - 0Vida SanaPas encore d'évaluation
- PH Measurement Protocol For Lenwin SuspensionDocument5 pagesPH Measurement Protocol For Lenwin Suspensionnaeem186Pas encore d'évaluation
- MeningitisDocument5 pagesMeningitisliesel_12100% (1)
- Spotters GP, ANSDocument24 pagesSpotters GP, ANSjafrin22100% (1)
- N.Lakshmi Narayana: Renati Research & Training PVT LTDDocument64 pagesN.Lakshmi Narayana: Renati Research & Training PVT LTDnlakshminarayana100% (1)
- Pharmaceutical CalculationsDocument64 pagesPharmaceutical CalculationsJayrine MonteroPas encore d'évaluation
- Nattokinase Prevents ThrombosesDocument3 pagesNattokinase Prevents ThrombosesmerrickPas encore d'évaluation
- What Are IV FluidsDocument5 pagesWhat Are IV FluidsRegine Mae Encinada100% (1)
- Ciprofloxacin CiproDocument1 pageCiprofloxacin CiproKristi WrayPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs Action Indication Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Patient's TeachingDocument3 pagesDrugs Action Indication Side/Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Patient's TeachingHazel Palomares100% (1)
- CiprofloxacinDocument1 pageCiprofloxacinEPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug DilantinDocument1 pageDrug DilantinSrkocherPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study OrthoDocument12 pagesDrug Study OrthoSienaPas encore d'évaluation
- NURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications WorksheetsDocument2 pagesNURS 1566 Clinical Form 3: Clinical Medications Worksheetsm_r0se_k0hPas encore d'évaluation
- PrednisoloneDocument2 pagesPrednisoloneKatie McPeekPas encore d'évaluation
- All Small Letters For Brand Name, First Letter Is Capitalized Bold Dosage Frequency RouteDocument15 pagesAll Small Letters For Brand Name, First Letter Is Capitalized Bold Dosage Frequency RouteNiña Jean Tormis AldabaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nicu MedsDocument5 pagesNicu Medsapi-732900066Pas encore d'évaluation
- PrednisoneDocument1 pagePrednisoneCassiePas encore d'évaluation
- NLM MedicatingDocument11 pagesNLM MedicatingQuimberly ModequilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Primaxin (Imipenem - Cilistatin)Document2 pagesPrimaxin (Imipenem - Cilistatin)EPas encore d'évaluation
- Imipenem Cilastatin (Primaxin)Document1 pageImipenem Cilastatin (Primaxin)EPas encore d'évaluation
- MARCOS, ARIAN MAY S. DRUG STUDY BSN 2faDocument10 pagesMARCOS, ARIAN MAY S. DRUG STUDY BSN 2faArian May MarcosPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug MetronidazoleDocument1 pageDrug MetronidazoleSrkocherPas encore d'évaluation
- 13 Med MNGTDocument19 pages13 Med MNGTKate ChavezPas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs Study. PTB. DMDocument5 pagesDrugs Study. PTB. DMsowkiePas encore d'évaluation
- Drug NeurontinDocument1 pageDrug NeurontinSrkocher100% (2)
- B. Drug Study: Diarrhea, Ulceration, Vomiting, Abdominal CrampsDocument12 pagesB. Drug Study: Diarrhea, Ulceration, Vomiting, Abdominal CrampsSienaPas encore d'évaluation
- BenadrylDocument2 pagesBenadrylE100% (1)
- Cancer Cell-Specific AgentsDocument5 pagesCancer Cell-Specific AgentsRomwella May AlgoPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study (Hydrocortisone)Document1 pageDrug Study (Hydrocortisone)Pauline AñesPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Card MotrinDocument2 pagesDrug Card MotrinAdrianne BazoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 Drug StudyDocument9 pagesChapter 4 Drug StudyRegee Rose LacsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Therapeutic Class: Antipsychotic Pharmacologic Class: Phenothiazine Therapeutic Class: Antipsychotic Pharmacologic Class: PhenothiazineDocument10 pagesTherapeutic Class: Antipsychotic Pharmacologic Class: Phenothiazine Therapeutic Class: Antipsychotic Pharmacologic Class: PhenothiazineMiyuki Bartolaba MangondatoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmocology Drug Cards: InnovarDocument33 pagesPharmocology Drug Cards: InnovarnamitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Before: Drug Therapeutic Record Indications Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument9 pagesBefore: Drug Therapeutic Record Indications Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesIcel Jean QuimboPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study (Tapazole)Document3 pagesDrug Study (Tapazole)Izza DeloriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug 2Document4 pagesDrug 2Abie Jewel Joy RoquePas encore d'évaluation
- PiperacillinDocument3 pagesPiperacillinNicholas TaglePas encore d'évaluation
- PhenerganDocument2 pagesPhenerganKatie McPeekPas encore d'évaluation
- VancomycinDocument1 pageVancomycinE100% (2)
- Breast FeedingDocument1 pageBreast FeedingSrkocherPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathology Bipolar I DisorderDocument4 pagesPathology Bipolar I DisorderSrkocherPas encore d'évaluation
- Albuterol SulfateDocument4 pagesAlbuterol Sulfateapi-3797941Pas encore d'évaluation
- Code of Ethics Provision 4Document5 pagesCode of Ethics Provision 4SrkocherPas encore d'évaluation
- LovenoxDocument1 pageLovenoxSrkocherPas encore d'évaluation
- Neuron TinDocument1 pageNeuron TinSrkocherPas encore d'évaluation
- BactobanDocument1 pageBactobanSrkocherPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug PhenerganDocument1 pageDrug PhenerganSrkocherPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug TylenolDocument1 pageDrug TylenolSrkocherPas encore d'évaluation
- Albuterol SulfateDocument2 pagesAlbuterol SulfateSrkocherPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug ZofranDocument1 pageDrug ZofranSrkocherPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is A Team Leader in NursingDocument2 pagesWhat Is A Team Leader in NursingSrkocher100% (2)
- LovenoxDocument1 pageLovenoxSrkocherPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug PhenerganDocument1 pageDrug PhenerganSrkocherPas encore d'évaluation
- ValiumDocument1 pageValiumSrkocherPas encore d'évaluation
- Levaquin Drug CardDocument1 pageLevaquin Drug CardSheri490100% (1)
- Drug AtivanDocument1 pageDrug AtivanSrkocherPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug LopressorDocument1 pageDrug LopressorSrkocherPas encore d'évaluation
- AtivanDocument1 pageAtivanSheri490Pas encore d'évaluation
- Drug SynthroidDocument1 pageDrug SynthroidSrkocherPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug ZoloftDocument1 pageDrug ZoloftSrkocherPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Rewetting Drops, Artificial TearsDocument1 pageDrug Rewetting Drops, Artificial TearsSrkocherPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Timoptic Eye DropsDocument1 pageDrug Timoptic Eye DropsSrkocherPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug NystatinDocument1 pageDrug NystatinSrkocherPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug NorvascDocument1 pageDrug NorvascSrkocherPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug PercocetDocument1 pageDrug PercocetSrkocherPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Senna Drug CardDocument1 pageDrug Senna Drug CardSrkocher100% (2)
- Drug PepcidDocument2 pagesDrug PepcidSrkocher0% (1)
- Drug OmeprazoleDocument1 pageDrug OmeprazoleSrkocherPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug NeurontinDocument1 pageDrug NeurontinSrkocher100% (2)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plananon_984362Pas encore d'évaluation
- Screenshot 2022-10-21 at 19.56.24Document3 pagesScreenshot 2022-10-21 at 19.56.24Zafira AkramPas encore d'évaluation
- HR Policy ManualDocument34 pagesHR Policy Manualshamna AbdullaPas encore d'évaluation
- Midterms Psyc LecDocument14 pagesMidterms Psyc LecMiden AlbanoPas encore d'évaluation
- SymbicortDocument18 pagesSymbicortkaditasookdeoPas encore d'évaluation
- Checklist For RCTDocument3 pagesChecklist For RCTLeftoMlhPas encore d'évaluation
- Main Conference ProgrammeDocument7 pagesMain Conference ProgrammeFaadhilah HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- Gender M F Marital Status: Rizal Medical CenterDocument21 pagesGender M F Marital Status: Rizal Medical CentermaKitten08Pas encore d'évaluation
- Implementasi Program Antenatal Terpadu Di Puskesmas Tanjung Agung Kabupaten Ogan Komering Ulu Dengan Pendekatan Balance ScorecardDocument9 pagesImplementasi Program Antenatal Terpadu Di Puskesmas Tanjung Agung Kabupaten Ogan Komering Ulu Dengan Pendekatan Balance ScorecardRosinta Dwi OktaviaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bpac CRP Vs Esr Poem 2005 WVDocument14 pagesBpac CRP Vs Esr Poem 2005 WVTanveerPas encore d'évaluation
- Self-Care Model Application To Improve Self-Care Agency, Self-Care Activities, and Quality of Life in People With Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDocument8 pagesSelf-Care Model Application To Improve Self-Care Agency, Self-Care Activities, and Quality of Life in People With Systemic Lupus ErythematosusFerry EfendiPas encore d'évaluation
- CHN Part 2 - Vital StatisticsDocument2 pagesCHN Part 2 - Vital StatisticsMichelle Gambol100% (1)
- Mikrobiologi DiagramDocument2 pagesMikrobiologi Diagrampuguh89Pas encore d'évaluation
- DC Kit2 ObadiaDocument2 pagesDC Kit2 ObadiaErnesto KangPas encore d'évaluation
- Mean Alt Üst SD Range Mean Alt Üst SD Range Mean Alt Üst SD Mean Alt Üst SD FaktörDocument5 pagesMean Alt Üst SD Range Mean Alt Üst SD Range Mean Alt Üst SD Mean Alt Üst SD FaktörZeynep DenizPas encore d'évaluation
- Management of Chest TubeDocument22 pagesManagement of Chest TubeFatima Hafza SahiddinPas encore d'évaluation
- Best Milking Practices Checklis PDFDocument3 pagesBest Milking Practices Checklis PDFcan_orduPas encore d'évaluation
- Fauci Dossier Valentine S Day Document 2022 (1) SummaryDocument5 pagesFauci Dossier Valentine S Day Document 2022 (1) SummarySherri StreightPas encore d'évaluation
- The Clinical Significance of The Retromolar Canal and Foramen in DentistryDocument24 pagesThe Clinical Significance of The Retromolar Canal and Foramen in Dentistryمحمد عبدالرحمنPas encore d'évaluation
- Bio Investigatory ProjectDocument24 pagesBio Investigatory ProjectTIBIN DANIEL BijuPas encore d'évaluation
- By Muslimah: The Healing Powers of The Names of AllahDocument2 pagesBy Muslimah: The Healing Powers of The Names of AllahMOULIANNA8949Pas encore d'évaluation
- PrimaryCare JAWDA - Update 2022Document40 pagesPrimaryCare JAWDA - Update 2022SECRIVIPas encore d'évaluation
- Breech BabyDocument11 pagesBreech BabyscribbPas encore d'évaluation
- Community-Acquired Pneumonia CaseDocument6 pagesCommunity-Acquired Pneumonia Caseapi-648891519Pas encore d'évaluation
- Giovanni Maciocia Menorrhagia NotesDocument22 pagesGiovanni Maciocia Menorrhagia Noteshihi12100% (5)
- Evaluation of The Painful EyeDocument9 pagesEvaluation of The Painful EyeMuthia Farah AshmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ambulance App - Book An Ambulance in A ClickDocument4 pagesAmbulance App - Book An Ambulance in A ClickbloodforsurePas encore d'évaluation
- Healing Colon Liver & Pancreas Cancer - The Gerson Way - Charlotte Gerson PDFDocument18 pagesHealing Colon Liver & Pancreas Cancer - The Gerson Way - Charlotte Gerson PDFLeonardo Velez De VillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Journal of Chronic PainDocument8 pagesJournal of Chronic PainRirin TriyaniPas encore d'évaluation
- KN 4@enzl 8 Ha 4 B 6 CC 9 eDocument26 pagesKN 4@enzl 8 Ha 4 B 6 CC 9 eRamzen Raphael DomingoPas encore d'évaluation