Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
SOLO & Bloom's Taxonomy
Transféré par
Jun YuTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
SOLO & Bloom's Taxonomy
Transféré par
Jun YuDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
24/09/2010
Introduction SOLO & Blooms Taxonomy
Different but interrelated Classify forms and levels of learning and teaching
Formulate outcomes Facilitate learning process Construct assessing tasks
24/09/2010
Copyright Donatus Justin 2010
24/09/2010
Copyright Donatus Justin 2010
Purpose
Bloom = outcomes & questions SOLO = indicate quality of learning = answer
Blooms Taxonomy
24/09/2010
Copyright Donatus Justin 2010
24/09/2010
Copyright Donatus Justin 2010
3 domains of learning (KSA)
Cognitive (Knowledge) Psychomotor (Skills) Affective (Attitudes) Intellectual skills Know that
3 domains of learning (KSA)
Three KSA Domains Most complex
Manual or physical skills Growth in feelings or emotional areas
Know how Categories/Levels Know how to express Least complex
24/09/2010
Copyright Donatus Justin 2010
24/09/2010
Copyright Donatus Justin 2010
24/09/2010
Categories in the cognitive domain
6
5 4 3 2 1
24/09/2010
Verbs associated with cognitive domain
1
2
Knowledge Thinking
List Describe Distinguish
Least complex Level
Evaluation Synthesis Analysis
Most complex
Levels
3 4 5 6
Application Comprehension
Least complex
Differentiate Devise Reflect
Copyright Donatus Justin 2010
Most Complex Level
Knowledge
Copyright Donatus Justin 2010 7 24/09/2010
Categories in the psychomotor domain
Origination Adaptation Complex response Mechanism Guided response Set Perception
24/09/2010
Verbs associated with psychomotor domain
1 2
Skills
Demonstrate Operate Install
Least complex Level
Most complex level
Creative skills Modify skill Perform automatically No assistance Needs assistance Ready to act
3 4 5
Perform Isolate Construct
Copyright Donatus Justin 2010
Most Complex Level
Least complex level
Copyright Donatus Justin 2010
Behaviour
9 24/09/2010
10
Categories in the affective domain
Internalising Organisation Valuing Responding Receiving
Least complex level Most complex level
Verbs associated with affective domain
Least complex level
Character Priorities time Value differences Active participation Willing to hear
Most complex level Receiving Listen to Perceive Be alert to Show tolerance to Responding Reflect Reply Answer Follow along Approve Obey Valuing Attain Assume Support Participate Continue Organisation Organise Select Judge Decide Identify with Characterisation Believe Practise Continue to Carry out
24/09/2010
Copyright Donatus Justin 2010
11
24/09/2010
Copyright Donatus Justin 2010
12
24/09/2010
Action words for learning outcomes
KNOWLEDGE Identify List Define Describe State Prepare Recall Express Categorize Chart Rank Distinguish Explain Outline Inform Label Specify THINKING Reflect Compare Contrast Catalogue Classify Evaluate Forecast Formulate Investigate Build Cooperate Modify Organise Research Translate Differentiate Analyse Compute Devise PSYCHOMOTOR Demonstrate Produce Assemble Install Adjust Operate Detect Arrange Isolate Conduct Check Manipulate Lay out Perform Sort Construct ATTITUDES Challenge Reflect Judge/Question Accept Adopt Advocate Accept Bargain Endorse Justify Persuade Resolve Select Express Approve
SOLO Taxonomy
24/09/2010
Copyright Donatus Justin 2010
13
24/09/2010
Copyright Donatus Justin 2010
14
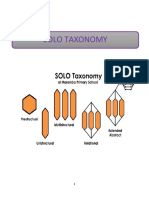
What is SOLO? Structure of Observed Learning Outcomes
Developed by Biggs and Collis (1982), and is well described in Biggs (1999).
24/09/2010 Copyright Donatus Justin 2010 15
What is SOLO?
The Structure of Observed Learning Outcome (SOLO) taxonomy is a model that describes levels of increasing complexity in student's understanding of subjects. The SOLO Taxonomy can be used to set learning objectives for where students 'should' be at particular stages of learning or, probably more appropriately, to judge or report on the learning outcomes or the levels attained.
24/09/2010 Copyright Donatus Justin 2010 16
5 typical ways to answer a question
Prestructural
SOLO Taxonomy Model
The model consists of 5 levels of understanding :
Prestructural The task is not attacked appropriately; the student hasnt really understood the point and uses too simple a way of going about it. Unistructural The student's response only focuses on one relevant aspect. Multistructural The student's response focuses on several relevant aspects but they are treated independently and additively. Assessment of this level is primarily quantitative. Relational The different aspects have become integrated into a coherent whole. This level is what is normally meant by an adequate understanding of some topic. Extended abstract The previous integrated whole may be conceptualised at a higher level of abstraction and generalised to a new topic or area.
17 24/09/2010 Copyright Donatus Justin 2010 18
Extended abstract
Unistructural
Relational
Multistructural
24/09/2010
Copyright Donatus Justin 2010
24/09/2010
SOLO Taxonomy Model
The table below summarises the model, and provides indicative verbs that you may wish to incorporate into your teaching and assessment planning. Click here.
Example
Explain why cheetahs have spots.
Example used by Killan 2004:78
24/09/2010 Copyright Donatus Justin 2010 19 24/09/2010 Copyright Donatus Justin 2010 20
1. Pre-structural
Answer I dont know. Characteristics No attempt to answer the question. So that they are different The response is irrelevant. from lions. No structure to the answer. Give no answer. Repeat what was said in class Guesses the answer: It looks right to me.
24/09/2010 Copyright Donatus Justin 2010 21
2. Uni-structural
Answer Characteristics It makes them hard to True, but with no see. explanation. Answer focuses on just one relevant fact. Gives a simple correct answer. Based on a quick decision. No explanation provided.
24/09/2010
Copyright Donatus Justin 2010
22
3. Multi-structural
Answer Characteristics The spots are formed by True, but with no melanin in the skin. The explanation. spots camouflaged them while hunting. Answer based on several relevant concrete details. Uses two or more explanation. No integration of additional knowledge.
4. Relational level
Answer Characteristics
The spots are formed by Biological explanation and melanin in the skin which is a link it to evolution chemical reaction during embryonic development. The spots evolved after mutation to camouflaged them while hunting Answer focuses on ideas that relate all the relevant details. Integrates prior knowledge. Links ideas to explain information.
23 24/09/2010 Copyright Donatus Justin 2010 24
24/09/2010
Copyright Donatus Justin 2010
24/09/2010
5. Extended abstract
Answer Characteristics
More example
Click here.
The spots are formed by melanin in the skin Extended abstract which is a chemical reaction during thought. embryotic development. The spots evolved after mutation to camouflaged them while hunting. Stripes will not be an advantage that is why the king cheetah is so rare in the wild. The spots are mathematical patterns that can be described with partial differential equations.
Answer recognises other possibilities and abstract principles. Goes beyond what has been taught. Uses logical deductions to frame the answer.
24/09/2010 Copyright Donatus Justin 2010 25 24/09/2010 Copyright Donatus Justin 2010 26
Purposes
Label achievers Framework - quality of learning Get the desired answer
List, name = uni-structural answer Describe = multi-structural answer Analyse = relational answer Predict or reflect = abstract answer
Benefits
Diagnostic tool - provides feedback Assessment tool - rubric Curriculum planning tool Describes learning outcome Setting standards Guides assessment tasks
24/09/2010
Copyright Donatus Justin 2010
27
24/09/2010
Copyright Donatus Justin 2010
28
The End
24/09/2010
Copyright Donatus Justin 2010
29
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Powerful Practices for High-Performing Special EducatorsD'EverandPowerful Practices for High-Performing Special EducatorsPas encore d'évaluation
- Bloom's & Solo TaxonomyDocument30 pagesBloom's & Solo TaxonomyNur Hidayah100% (2)
- BloomsDocument31 pagesBloomsMaira AnoshPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning and Bloom's Taxonomy Learning Goals and OutcomesDocument2 pagesLearning and Bloom's Taxonomy Learning Goals and OutcomesVera MillerPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment: Ucd Teaching and Learning/ ResourcesDocument10 pagesAssessment: Ucd Teaching and Learning/ Resourcesneha yadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Bloom's of TaxonomyDocument24 pagesBloom's of TaxonomyMelinda Cariño ChavezPas encore d'évaluation
- Training Workshop On Table Specifications PresentationDocument59 pagesTraining Workshop On Table Specifications PresentationRalph Aron100% (3)
- Implication of Bloom's Taxonomy of Learning in EducationDocument29 pagesImplication of Bloom's Taxonomy of Learning in EducationoyebanjibenedictPas encore d'évaluation
- Taxonomy of Educational ObjectivesDocument5 pagesTaxonomy of Educational Objectivesapi-3725139100% (4)
- Ivy Tech Community College: SOC 111 Introduction To SociologyDocument7 pagesIvy Tech Community College: SOC 111 Introduction To SociologyNIkolai CastilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Essay Items AssessmentDocument15 pagesEssay Items Assessmentangelica levita100% (2)
- Solo TaxonomyDocument27 pagesSolo TaxonomyFaizatun Nazirah100% (2)
- Bloom's Taxonomy Lesson Plans in The ClassroomDocument8 pagesBloom's Taxonomy Lesson Plans in The ClassroomWasakna BuhayPas encore d'évaluation
- A11 Developing Critical Thinking Skills PDFDocument33 pagesA11 Developing Critical Thinking Skills PDFRamesh Babu GarlapatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Expectations and Course Learning OutcomesDocument6 pagesExpectations and Course Learning OutcomesLisa TalPas encore d'évaluation
- Construction of Achievement Test and Its StandardizationDocument25 pagesConstruction of Achievement Test and Its StandardizationDr. Nisanth.P.MPas encore d'évaluation
- Blooms Taxonomy and Learning ThoriesDocument15 pagesBlooms Taxonomy and Learning ThoriesMuneeb AnjumPas encore d'évaluation
- Bloom's Taxonomy: HistoryDocument8 pagesBloom's Taxonomy: HistorylaseryleePas encore d'évaluation
- A11 Developing Critical Thinking SkillsDocument33 pagesA11 Developing Critical Thinking SkillsAnisa Fitri RahayuPas encore d'évaluation
- Mba 800 - Business Strategy: GRADING: AttendanceDocument11 pagesMba 800 - Business Strategy: GRADING: AttendanceShiva MogiliPas encore d'évaluation
- Case-Based Learning - Centre For Teaching and LearningDocument3 pagesCase-Based Learning - Centre For Teaching and LearningKim SolimanPas encore d'évaluation
- Rosales National High School: Mapeh DepartmentDocument59 pagesRosales National High School: Mapeh Departmentharold carbonelPas encore d'évaluation
- Differentiation - Conrad CurryDocument27 pagesDifferentiation - Conrad Currysatanizer100% (1)
- Essay TestDocument48 pagesEssay TestJosh Schultz100% (1)
- SUS101: Principles of Sustainability - SyllabusDocument6 pagesSUS101: Principles of Sustainability - SyllabusChad J. McGuirePas encore d'évaluation
- Home Site Map About Leadership Training Learning History Knowledge Performance Java Etc. News BlogDocument13 pagesHome Site Map About Leadership Training Learning History Knowledge Performance Java Etc. News BlogJoann Plaza ReforminaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bloom Taxonomy & Revised TaxonomyDocument22 pagesBloom Taxonomy & Revised TaxonomyNuyu PipahPas encore d'évaluation
- Dạng Câu Hỏi OpinionDocument16 pagesDạng Câu Hỏi Opinion7895datPas encore d'évaluation
- 7.levers - Handout.final OU T.angelo 16.sept..2016-4Document12 pages7.levers - Handout.final OU T.angelo 16.sept..2016-4Mou senPas encore d'évaluation
- Cor-Mgmt1302 - Gilbert Tan Yip WeiDocument5 pagesCor-Mgmt1302 - Gilbert Tan Yip WeiWOON YEW KIAT,XAVIERPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment: Ucd Teaching and Learning/ ResourcesDocument10 pagesAssessment: Ucd Teaching and Learning/ ResourcesAbu HudaPas encore d'évaluation
- Bloom Taxonomy of LearningDocument9 pagesBloom Taxonomy of LearningDavid BartonPas encore d'évaluation
- Table of SpecificationDocument13 pagesTable of SpecificationNeome Gaspar TadiquePas encore d'évaluation
- UT Dallas Syllabus For bps6310.mbc.07f Taught by David Deeds (dxd054000)Document14 pagesUT Dallas Syllabus For bps6310.mbc.07f Taught by David Deeds (dxd054000)UT Dallas Provost's Technology GroupPas encore d'évaluation
- MOR 465 SyllabusDocument8 pagesMOR 465 SyllabussocalsurfyPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Nursing: Week 11: Traditional Teaching StrategiesDocument28 pagesDepartment of Nursing: Week 11: Traditional Teaching StrategiesWaleed AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Facilitating Learning and Blooms Taxonomy Module 16 Carla Mae AbadDocument37 pagesFacilitating Learning and Blooms Taxonomy Module 16 Carla Mae AbadRaquel Saquing FernalenPas encore d'évaluation
- Bloom Taxonomy OutcomesDocument7 pagesBloom Taxonomy OutcomesArjay DensaPas encore d'évaluation
- HYBRID Module RW Week 4 NewDocument14 pagesHYBRID Module RW Week 4 NewDanielle CastueraPas encore d'évaluation
- Business Management 499 Strategic Management Winter Semester, 2005Document8 pagesBusiness Management 499 Strategic Management Winter Semester, 2005Ho Lam HeungPas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar On Table of Specs (TOS)Document39 pagesSeminar On Table of Specs (TOS)Paulo Israel Escobal RemulloPas encore d'évaluation
- Walsh College LCT WorkshopDocument79 pagesWalsh College LCT WorkshopTerry DoylePas encore d'évaluation
- Catherine C. Sabado Master Teacher IIDocument93 pagesCatherine C. Sabado Master Teacher IIROMAR BRAMANTE SANTOSPas encore d'évaluation
- List of VerbsDocument6 pagesList of VerbsMagali MeacaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lac On Table Specifications PresentationDocument65 pagesLac On Table Specifications PresentationMarivil De Guzman CabadduPas encore d'évaluation
- Session 1 Slides ESR2022augDocument35 pagesSession 1 Slides ESR2022augWanyue CaoPas encore d'évaluation
- 7.IEE3293 - STRATEGIC MANAGEMENTÀÌÈ ¿Í Ö ÔP2Document5 pages7.IEE3293 - STRATEGIC MANAGEMENTÀÌÈ ¿Í Ö ÔP2sephranesabajoPas encore d'évaluation
- Bloom's Taxonomy ObjectivesDocument15 pagesBloom's Taxonomy Objectivesjemil l. candilada100% (1)
- Bloom's Taxonomy - WikipediaDocument10 pagesBloom's Taxonomy - WikipediaHarshal VaidyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity 2 Education 309Document4 pagesActivity 2 Education 309Joelina March Jaspe HuangPas encore d'évaluation
- Bloom's TaxonomyDocument5 pagesBloom's TaxonomyRivanda DebiPas encore d'évaluation
- Meeting 6Document25 pagesMeeting 6Shilvia Rahmah Janati PutriPas encore d'évaluation
- Topik 2Document72 pagesTopik 2NURUL AINI100% (1)
- Theoretical and Conceptual Framework and Other Components of Chapter 1Document20 pagesTheoretical and Conceptual Framework and Other Components of Chapter 1Cyrill Mico De GuzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Bloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsDocument23 pagesBloom's Taxonomy of Learning DomainsKanwal IshaqPas encore d'évaluation
- Bloom's TaxonomyDocument9 pagesBloom's TaxonomyIsrahana Shahril100% (1)
- 2.3-Solo TaxonomyDocument9 pages2.3-Solo TaxonomyKousar YasminPas encore d'évaluation
- Integrated Course Design - L. Dee FinkDocument7 pagesIntegrated Course Design - L. Dee FinkBicente100% (2)
- Body MDocument3 pagesBody MIrisPas encore d'évaluation
- My Butterfly BookmarkDocument1 pageMy Butterfly BookmarkIrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Box e LTRDocument4 pagesBox e LTRIrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Butterfly OutlineDocument1 pageButterfly OutlineIrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Butterfly OutlineDocument1 pageButterfly OutlineIrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Five Point SnowflakeDocument1 pageFive Point SnowflakeBianca HeinzPas encore d'évaluation
- Arts and Crafts: Arrow Cut-OutsDocument1 pageArts and Crafts: Arrow Cut-OutsIrisPas encore d'évaluation
- CCTS ListDocument2 pagesCCTS ListIrisPas encore d'évaluation
- CCTS ListDocument2 pagesCCTS ListIrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Reading PAL StickersDocument2 pagesReading PAL StickersIrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Kikyo's ThemeDocument1 pageKikyo's ThemeEllie RazonPas encore d'évaluation
- Tsubasa Chronicle - You Are My LoveDocument2 pagesTsubasa Chronicle - You Are My LoveziomeklukiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sudoku For Kids: CalculationDocument1 pageSudoku For Kids: CalculationIrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Viperfish TextDocument8 pagesViperfish TextIrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Extra Notes On GinottDocument23 pagesExtra Notes On GinottIrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Holiday DestinationDocument3 pagesHoliday DestinationIrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Extra Notes On GinottDocument23 pagesExtra Notes On GinottIrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Sci Sense Bodyparts K 1Document1 pageSci Sense Bodyparts K 1IrisPas encore d'évaluation
- CCTS ListDocument2 pagesCCTS ListIrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Hanging Numbers MobileDocument2 pagesHanging Numbers MobileIrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Sci Sense Bodyparts K 1Document1 pageSci Sense Bodyparts K 1IrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Book Fair UpcomingDocument1 pageBook Fair UpcomingIrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Angel (C)Document2 pagesAngel (C)IrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 11dividerDocument1 pageWeek 11dividerIrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 10dividerDocument1 pageWeek 10dividerIrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 8dividerDocument1 pageWeek 8dividerIrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 7dividerDocument1 pageWeek 7dividerIrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 7dividerDocument1 pageWeek 7dividerIrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 16 Divider For Lecture NotesDocument1 pageWeek 16 Divider For Lecture NotesIrisPas encore d'évaluation