Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Bodies of Water
Transféré par
Fhremond ApoleCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Bodies of Water
Transféré par
Fhremond ApoleDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
A body of water or waterbody (often spelled water body) is any significant accumulation of water, usually covering the Earth
or another planet. The term body of watermost often refers to large accumulations of water, such as oceans, seas, and lakes, but it may also include smaller pools of water such as ponds, puddles or wetlands. Rivers,streams, canals, and other geographical features where water moves from one place to another are not always considered bodies of water, but there is no other term in English comprising "stationary" bodies of water as well as rivers and canals etc., and such moving bodies of water are included in this article. Some bodies of water are man-made (artificial), such as reservoirs or harbors, but most are naturally occurring geographical features. Bodies of water that are navigable are known aswaterways. Some bodies of water collect and move water, such as rivers and streams, and others primarily hold water, such as lakes and oceans. The term body of water can also refer to a reservoir of water held by a plant, technically known as a phytotelma.
Note that there are some geographical features involving water that are not bodies of water, for example waterfalls and geysers. **** A reservoir (etymology from French rservoir a "storehouse [1]) or an artificial lake is used to store water. Reservoirs may be created in river valleys by the construction of a dam or may be built by excavation in the ground or by conventional construction techniques such a brickwork or cast concrete. The term reservoir may also be used to describe underground reservoirs such as an oil or water well. **** Phytotelma (plural phytotelmata) is a term for water bodies held by plants. The water accumulated on these plants may serve as substratum for associated fauna, and often the fauna associated with phytotelmata is unique. A classification of phytotelma[1] recognizes five principal types: bromeliad tanks, pitcher plants, waterfilled tree hollows, bamboo internodes, and axil water (collected at the base of leaves, petals or bracts). **** A waterway is any navigable body of water. Waterways can include rivers, lakes, seas,oceans, and canals. In order for a waterway to be navigable, it must meet several criteria:
1. Stream - a body of water with a detectable current, confined within a bed and banks. Streams are important as conduits in the water cycle, instruments in groundwater recharge, and corridors for fish and wildlife migration. A stream may be referred to as a branch, brook, creek, or river. The smallest water channels are often called brooks but creeks are often larger than brooks but may either be permanent or intermittent. Creeks are also sometimes known as streams but the word stream is quite a generic term for any body of flowing water. Streams can be intermittent or permanent and can be on the surface of the earth, underground, or even within an ocean (such as the Gulf Stream). 2. Brooks and Creeks - a small stream. A brook is characterized by its shallowness and its bed being composed primarily of rocks. The source is a spring 3. River - a natural waterway usually formed by water derived from either precipitation or glacial meltwater, and flows from higher ground to lower ground. The river is a wide body of water that flows towards the sea. A river is a large stream that flows over land. It is often a perennial water body and usually flows in a specific channel, with a considerable volume of water. The world's shortest river, the D River, in Oregon, is only 120 feet long and connects Devil's Lake directly to the Pacific Ocean. Where is the world's shortest river located? USA. Located in Oregon, USA, the 'D' river runs between Devil's Lake and the Pacific Ocean and is only 120 feet long. What is the longest river in the world? Nile River. The Amazon is the longest river in South America, Mississippi in North America, and Yangtze in Asia. The Nile is the longest in Africa and the world. 4. Pond - a body of water smaller than a lake, especially those of man-made origin. A pond is a body of standing water, either natural or man-made, that is usually smaller than alake. A wide variety of man-made bodies of water are classified as ponds, including water gardens, water features and koi ponds; all designed for aesthetic ornamentation as landscape or architectural features, while fish ponds are designed for commercial fish breeding, and solar pondsdesigned to store thermal energy. Any lake or pond directly connected to a larger body of water can be called a lagoon and a channel explains a narrow sea between two land masses, such as the English Channel. 5. Lake - a body of water or other liquid, but usually freshwater, of considerable size contained on a body of land. A lake is a body of water surrounded by land. A very large lake that contains salt water is known as a sea (except the Sea of Galilee, which is actually a freshwater lake). A lake is a body of relatively still fresh or salt water of considerable size, localized in a basin that is
surrounded by land. Lakes are inland and not part of the ocean, and are larger and deeper than ponds.[1][2] Lakes can be contrasted with rivers orstreams, which are usually flowing. However most lakes are fed and drained by rivers and streams. What is the largest lake in the world? Caspian Sea. The Caspian sea is actually considered a lake, not a sea, despite its name. It is called a sea because the Romans called it 'mare Caspium' (or salty lake). What is the deepest lake in the world? Lake Baikal. 6. Coves - is a small type of bay or coastal inlet. They usually have narrow, restricted entrances, are often circular or oval, and are often inside a larger bay. Small, narrow, sheltered bays, inlets,creeks, or recesses in a coast are often considered coves. Colloquially, the term can be used to describe a sheltered bay. 7. Bay - an area of water bordered by land on three sides. Bays are an area of water mostly surrounded by land. Bays generally have calmer waters than the surrounding sea, due to the surrounding land blocking some waves and often reducing winds. Bays also exist as an inlet in a lake or pond. A large bay may be called a gulf, a sea, a sound, or a bight. A cove is a circular or oval coastal inlet with a narrow entrance; some coves may be referred to as bays. Bays and gulfs were significant in the history of human settlement because they can provide a safe place for fishing. Later they were important in the development of sea trade as the safe anchorage they encouraged their selection as ports. There are various ways that bays can be created. The largest bays have developed as a result ofcontinental drift. As the super-continent Gondwana broke up along curved and indented fault lines, the continents moved apart and the world's largest gulfs formed. These include the Gulf of Guinea, Persian Gulf, Gulf of Alaska, Gulf of Mexico and the Bay of Bengal which is the largest bay in the world.
8. Gulf - a part of a lake or ocean that extends so that it is surrounded by land on three sides, similar to, but larger than a bay. 9. Lagoon - a body of comparatively shallow salt or brackish water separated from the deeper sea by a shallow or exposed sandbank, coral reef, or similar feature. The enclosed body of water behind a barrier reef or barrier islands or enclosed by an atoll reef is called a lagoon.
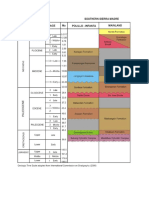
Lagoons are relatively shallow bodies of water, mostly-enclosed, with an oceanic source, separated by a low-lying swatch of land, such as a spit or barrier island. Lagoons hare protected from the waves and currents of the ocean by barrier islands, sand bars or reefs. 10. Channel - the physical confine of a river, slough or ocean strait consisting of a bed and banks. See also stream bed and strait. A channel is the physical confine of a river, slough or ocean strait consisting of a bed and banks. A channel is a wide body of water found between islands. This has to be crossed into order to move from one island to another. 11. Whirlpool - A whirlpool is a swirling body of water usually produced by ocean tides. The vast majority of whirlpools are not very powerful. More powerful ones are more properly termed maelstroms. Vortex is the proper term for any whirlpool that has a downdraft. Very small whirlpools can easily be seen when a bath or a sink is draining, but these are produced in a very different manner from those in nature. Smaller whirlpools also appear at the base of many waterfalls. In the case of powerful waterfalls, like Niagara Falls, these whirlpools can be quite strong. The most powerful whirlpools are created in narrow shallow straits with fast flowing water. 12. Rapids - a fast moving part of a river. A rapid is a section of a river where the river bed has a relatively steep gradient causing an increase in water velocity and turbulence. A rapid is a hydrological feature between a run (a smoothly flowing part of a stream) and a cascade. A rapid is characterised by the river becoming shallower and having some rocks exposed above the flow surface. As flowing water splashes over and around the rocks, air bubbles become mixed in with it and portions of the surface acquire a white colour, forming what is called "whitewater". 13. Waterfalls A waterfall is a place where flowing water rapidly drops in elevation as it flows over a steep region or a cliff. Waterfalls are most commonly formed when a river is young. What is the highest waterfall in the world? Angel falls. Located in Venezuela, and is 3,281 feet (1,000 m) tall. **Pagsanjan Falls in Laguna, Maria Christina Falls in Mindanao Laguna de Bay is one of the largest lakes in Southeast Asia and the largest and one of the most vital inland bodies of water in the Philippines. Pre-Hispanic Filipinos called the lake, Lawa ng Bai (pronounced as ba-ee), meaning Mother Lake. With Spanish colonization, the name became Laguna de Bay or Lake of Bay. The largest lake is the Laguna de Bay, which encompasses two regions: Metro Manila and Region IV with an area of 922 km
What ocean contains the deepest trench on Earth? Pacific Ocean. The Pacific Ocean's deepest point is at the Marianas trench, 36,198 feet (11,033 m).
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Geology & Earth's TreasureDocument34 pagesGeology & Earth's TreasureHelaina MarasiganPas encore d'évaluation
- Weathering Erosion and Deposition Multiple ChoiceDocument46 pagesWeathering Erosion and Deposition Multiple ChoiceMSS JPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit II Lesson 3.3 - 3.4 Mountains and Mountain BuildingDocument32 pagesUnit II Lesson 3.3 - 3.4 Mountains and Mountain BuildingTristan PereyPas encore d'évaluation
- MONETARY THEORIES EXPLAINEDDocument33 pagesMONETARY THEORIES EXPLAINEDFhremond ApolePas encore d'évaluation
- Continental Drift Theory and Plate TectonicsDocument3 pagesContinental Drift Theory and Plate TectonicsAndrea Mae CamachoPas encore d'évaluation
- Plate Tectonic TheoryDocument17 pagesPlate Tectonic TheoryNasir100% (1)
- Local Winds: Circulation (Under Primary Circulation Planetary Wind Comes I.E. Trade Winds, Westerlies andDocument7 pagesLocal Winds: Circulation (Under Primary Circulation Planetary Wind Comes I.E. Trade Winds, Westerlies andMukesh Kumar100% (1)
- Science: Quarter 4 - Module 2: Sustaining Earth's ResourcesDocument20 pagesScience: Quarter 4 - Module 2: Sustaining Earth's ResourcesMaria Conxedes GudesPas encore d'évaluation
- C1L4 - Elementary Knowledge On Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics (By MG Biscocho)Document19 pagesC1L4 - Elementary Knowledge On Continental Drift and Plate Tectonics (By MG Biscocho)Marnoel MalapitanPas encore d'évaluation
- Biome Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesBiome Lesson Planapi-252165886Pas encore d'évaluation
- Flood Mitigation PPOINTDocument36 pagesFlood Mitigation PPOINTIan Ilo BollerPas encore d'évaluation
- What is a Coral ReefDocument23 pagesWhat is a Coral Reefshreya guptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Layers of The AtmosphereDocument9 pagesLayers of The AtmosphereMysterious JollyPas encore d'évaluation
- Renewable and Non-Renewable ResourcesDocument18 pagesRenewable and Non-Renewable ResourcesPavan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Local WindsDocument28 pagesLocal WindsLouis Fetilo FabunanPas encore d'évaluation
- TheoriesDocument6 pagesTheoriesFhremond ApolePas encore d'évaluation
- Sibulan River Basin Discharge Data 1986-2010Document316 pagesSibulan River Basin Discharge Data 1986-2010Jasmine Benito100% (1)
- CE-312 Weathering ProcessesDocument35 pagesCE-312 Weathering ProcessesKhalid Khan100% (1)
- GNP and GDP Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument11 pagesGNP and GDP Multiple Choice QuestionsFhremond Apole75% (8)
- LandformsDocument13 pagesLandformssumansood19599283100% (1)
- Bodies of WaterDocument23 pagesBodies of WaterMa DaphnePas encore d'évaluation
- Lakeview Memories: Growing Up in Lakeview in The 1920s, 30s & 40sDocument14 pagesLakeview Memories: Growing Up in Lakeview in The 1920s, 30s & 40sRachel RiveraPas encore d'évaluation
- Work of Rivers, Wind AND: Sea and Their Engineering ImportanceDocument15 pagesWork of Rivers, Wind AND: Sea and Their Engineering ImportanceCrisanto EncilanPas encore d'évaluation
- SLK SCI7 Q4 W2-VersionDocument10 pagesSLK SCI7 Q4 W2-VersionJen-jen Ybanez BalderasPas encore d'évaluation
- Learn About Earth's HistoryDocument8 pagesLearn About Earth's HistoryMaorin Mari SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- How Mountains FormDocument3 pagesHow Mountains Formapi-321767399Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sedimentary RocksDocument41 pagesSedimentary RocksGelique de CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 Chapter 2 The Planet Earth The Planet Earth: © NasaDocument26 pagesChapter 2 Chapter 2 The Planet Earth The Planet Earth: © NasaGelique de CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- Geographical SettingDocument29 pagesGeographical SettingReymond CuisonPas encore d'évaluation
- WatershedDocument13 pagesWatershedRamroop SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- 27 - Prevention of Soil Erosion PDFDocument11 pages27 - Prevention of Soil Erosion PDFJen De la Cruz100% (1)
- BulacanDocument4 pagesBulacanAndrea Ü MaePas encore d'évaluation
- Cagayan de Oro: A History of ProgressDocument132 pagesCagayan de Oro: A History of ProgressMaestre Jr., EliasPas encore d'évaluation
- PPT-1 MeteorologyDocument77 pagesPPT-1 MeteorologyRatnikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Group One (General Geology)Document20 pagesGroup One (General Geology)thea4bermejoPas encore d'évaluation
- Plate Tectonic Theory States That The EarthDocument2 pagesPlate Tectonic Theory States That The EarthPRINTDESK by DanPas encore d'évaluation
- Oxygen CycleDocument4 pagesOxygen CyclePradnya GorePas encore d'évaluation
- Global WindsDocument8 pagesGlobal WindsBenjie SarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Elements of Weather and ClimateDocument13 pagesElements of Weather and ClimateAbdul Hafeez100% (1)
- Major Landforms and How They Impact Where People LiveDocument18 pagesMajor Landforms and How They Impact Where People LiveNames and QuotesPas encore d'évaluation
- Environmental LithosphereDocument44 pagesEnvironmental LithosphereRichard II RemisPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Philippine TectonicsDocument6 pagesIntroduction To Philippine TectonicsJeric OliverPas encore d'évaluation
- How volcanic eruptions and tectonic movements impact Earth's climate and surfaceDocument2 pagesHow volcanic eruptions and tectonic movements impact Earth's climate and surfaceReign Ivan C. RefuerzoPas encore d'évaluation
- Paleozoic EraDocument16 pagesPaleozoic EraJhunner BuanPas encore d'évaluation
- Who Are The Igorots?Document22 pagesWho Are The Igorots?Jessica RiparipPas encore d'évaluation
- Mangrove SwAMPSDocument26 pagesMangrove SwAMPSALmz GuiruelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Geothermal EnergyDocument7 pagesGeothermal Energyapi-291538480Pas encore d'évaluation
- Soil DegradationDocument9 pagesSoil DegradationAyesha KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Layers of The AtmosphereDocument19 pagesLayers of The AtmosphereRalph Andrew AgustinPas encore d'évaluation
- ABE 31A - Lab Exercise #1 (Agrometeorological Station Site Visit)Document7 pagesABE 31A - Lab Exercise #1 (Agrometeorological Station Site Visit)RAY MARK ABALAYANPas encore d'évaluation
- Contribution of Ancient CivilizationDocument12 pagesContribution of Ancient CivilizationIrwin FajaritoPas encore d'évaluation
- Convection CurrentsDocument9 pagesConvection Currentsjanice alquizarPas encore d'évaluation
- The Marcopper Mining DisasterDocument2 pagesThe Marcopper Mining DisasterMeiko Faye Fuentes100% (1)
- Sierra MadreDocument20 pagesSierra MadreAnonymous EpLmuDgq6CPas encore d'évaluation
- Climate Change ReviewerDocument11 pagesClimate Change ReviewerFlorie Mae ViernesPas encore d'évaluation
- Heroes of Zambales - : Source: Zambales. Ramon de Jesus. Makati City: Union Zambalena, 1989Document3 pagesHeroes of Zambales - : Source: Zambales. Ramon de Jesus. Makati City: Union Zambalena, 1989Joven Ian MarquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Groundwater Distribution-Groundwater Movement - Springs and GeyserDocument27 pagesGroundwater Distribution-Groundwater Movement - Springs and GeyserJohn Lloyd Requillo CaduyacPas encore d'évaluation
- Script : - Marine EnvironmentDocument22 pagesScript : - Marine Environmentanishc007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Earth Science Through Its Major ComponentsDocument33 pagesUnderstanding Earth Science Through Its Major ComponentsJhing Magayanes Estabillo100% (2)
- LithosphereDocument10 pagesLithosphereCandy TuftPas encore d'évaluation
- Running Water)Document8 pagesRunning Water)Kayraine Mae Edillor CaballeroPas encore d'évaluation
- Earth Systems Atmosphere Geosphere Biosphere Hydrosphere WorksheetsDocument9 pagesEarth Systems Atmosphere Geosphere Biosphere Hydrosphere Worksheetscathy mojica0% (1)
- 6 HydrosphereDocument11 pages6 HydrosphereAndrew GravesPas encore d'évaluation
- University of Caloocan City: A History of the Philippine Land and PeopleDocument23 pagesUniversity of Caloocan City: A History of the Philippine Land and PeopleDawn Illaine Reclenas100% (2)
- Mangroves Are Various Types of Trees Up To Medium Height and ShrubsDocument4 pagesMangroves Are Various Types of Trees Up To Medium Height and Shrubsdendi459Pas encore d'évaluation
- MGA ANYONG TubigDocument8 pagesMGA ANYONG TubigVal Cyril EstradaPas encore d'évaluation
- Subarans 2Document6 pagesSubarans 2Fhremond ApolePas encore d'évaluation
- Pepsi-Cola Products Philippines Inc. (Pcppi) : Fhremond C. ApoleDocument7 pagesPepsi-Cola Products Philippines Inc. (Pcppi) : Fhremond C. ApoleFhremond ApolePas encore d'évaluation
- 2009 EmployerSurveyDocument10 pages2009 EmployerSurveyFhremond ApolePas encore d'évaluation
- IntroDocument1 pageIntroFhremond ApolePas encore d'évaluation
- Areas of ConsiderationDocument1 pageAreas of ConsiderationFhremond ApolePas encore d'évaluation
- FINMANDocument30 pagesFINMANFhremond ApolePas encore d'évaluation
- VII. Marketing Strategy: A.) SegmentationDocument2 pagesVII. Marketing Strategy: A.) SegmentationFhremond ApolePas encore d'évaluation
- Big BankDocument1 pageBig BankFhremond ApolePas encore d'évaluation
- Money Andthe EconomyDocument8 pagesMoney Andthe EconomyFhremond ApolePas encore d'évaluation
- Bodies of WaterDocument4 pagesBodies of WaterFhremond ApolePas encore d'évaluation
- GR 172087Document16 pagesGR 172087Fhremond ApolePas encore d'évaluation
- The Nervous SystemDocument38 pagesThe Nervous SystemFhremond ApolePas encore d'évaluation
- AcTG TestDocument8 pagesAcTG TestFhremond ApolePas encore d'évaluation
- River ShannonDocument13 pagesRiver ShannonDavid FitzsimonsPas encore d'évaluation
- RF - Flooding Case StudyDocument9 pagesRF - Flooding Case Studyloki12354Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hydraulics of WellsDocument18 pagesHydraulics of WellsGanesh KeesaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Yellowstone River: Historic Events Timeline: Flooding, Ice Jams, Bridges, and Irrigation InfrastructureDocument58 pagesYellowstone River: Historic Events Timeline: Flooding, Ice Jams, Bridges, and Irrigation InfrastructureYellowstone River Conservation District CouncilPas encore d'évaluation
- Lahar Aand FloodDocument48 pagesLahar Aand FloodRamces SolimanPas encore d'évaluation
- Will Pacific IslandDocument16 pagesWill Pacific IslandBobby WskPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Runoff: Key Factors, Process and Cycle SummaryDocument32 pagesUnderstanding Runoff: Key Factors, Process and Cycle SummaryAafaque HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- Reg Gazetteer AlphabeticalDocument252 pagesReg Gazetteer AlphabeticalAnonymous cC2VeA9MBPas encore d'évaluation
- Estuarine EcosystemDocument22 pagesEstuarine EcosystemkontollesportsPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is A Detention PondDocument2 pagesWhat Is A Detention PondSukimin LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Optimizing Alabio Polder Irrigation for Rice ProductionDocument12 pagesOptimizing Alabio Polder Irrigation for Rice ProductionRiyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Depositional Landforms of The Lower CourseDocument4 pagesDepositional Landforms of The Lower CourseEllie WoolcottPas encore d'évaluation
- ANALYZING DRAINAGE CHANNEL DIMENSIONS TO OVERCOME FLOODING IN JALAN BAY SALIM SEKIP JAYA SUB-DISTRICT KEMUNING PALEMBANGDocument13 pagesANALYZING DRAINAGE CHANNEL DIMENSIONS TO OVERCOME FLOODING IN JALAN BAY SALIM SEKIP JAYA SUB-DISTRICT KEMUNING PALEMBANGCivil AvmPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluvial Landfrom (Final)Document29 pagesFluvial Landfrom (Final)Prakash Singh100% (1)
- U.S. Port Distances Guide: Coastal & Inland WaterwaysDocument65 pagesU.S. Port Distances Guide: Coastal & Inland WaterwaysGeani MihaiPas encore d'évaluation
- River SystemDocument22 pagesRiver SystemSophia CantonesPas encore d'évaluation
- Geo Vs HydroDocument1 pageGeo Vs HydroHumza MubarikPas encore d'évaluation
- Varaha River YieldtestreportDocument13 pagesVaraha River Yieldtestreportrama krishnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Indian River Systems and Other Geographical Facts PDFDocument38 pagesIndian River Systems and Other Geographical Facts PDFsauravrdx100Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rivers RevisionpptDocument101 pagesRivers Revisionpptb_osborne100% (1)
- Water TableDocument2 pagesWater Tablerogo2577Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physiography of Flowing Water: OutlineDocument12 pagesPhysiography of Flowing Water: OutlineHasaan WaheedPas encore d'évaluation
- Earth Science Crossword LandformsDocument1 pageEarth Science Crossword LandformsCHELCEE C. ENARIOPas encore d'évaluation
- Konvensi Hukum Laut Internasional Tahun 1982 Dan PDocument28 pagesKonvensi Hukum Laut Internasional Tahun 1982 Dan PI1C118019 LAODEARMINPas encore d'évaluation
- RPA DATA Crew 180214Document505 pagesRPA DATA Crew 180214malan12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Geo11 3 India Drainage SystemDocument11 pagesGeo11 3 India Drainage Systemsuperman_universePas encore d'évaluation
- 1 - 72 - Lecture - 6-Ground Water Surface Water InteractionDocument10 pages1 - 72 - Lecture - 6-Ground Water Surface Water Interactionhenok dersehPas encore d'évaluation