Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
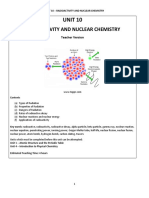
Nuclear Reactions Guide
Transféré par
Seyi Martins ObandoTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Nuclear Reactions Guide
Transféré par
Seyi Martins ObandoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
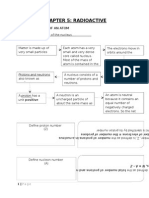
NUCLEAR REACTION Nuclear reactions change number o protons in the neutrons . Chemical .
They change the number of protons , neutrons , or both . Change the position of the pro SPONANEOUS NUCLEAR REACTION EFFECT OF RADIATION HALF LIVES Nuclear waste is hardzous because the reaction Two atoms of the sam element have different number of neutrons are reffered to as isotopes . Most elements have at least two isotopes REASONS FOR INSTABILITY There are four main reasons for nuclear instability 1. The
SPONTANEOUIS NUCLEAR EMISSION An unstable nuclide will , eventually NUCLEAR PROCSS THERE ARE 3 MAIN NUCLEAR PROCESS Alpha, Beta , Gamma ALPHA What happens to a n element when it ELEMENTS ARE NO LONGER CONSERVED . Thats the key to an alpha emission one element is changed into another called TRANSMUTATION . During an ALPHA (a) emission , nucleons are conserved . The total number of protons and neutrons in the overall reaction is conserved . SPONTANEOUS nuclear reactions (there are other kinds) are the ones called emission reactions or decay reactions Two poducts : The daughter nuclide the (Alpha, Beta, Gamma)
We need the same total on our reagent side The parent Particle = daughter
So to balance the emission reaction: 1. Write down the parent nuclide as the only reagent 2. Write the particle that is formed 3. Balanced the total mass number 4. Balance the total atomic number 5. Figure out what the daughter is based on its atomic number Weite down the parnt material POLOIUM 218 . Atomic number Po -- a Why might a nuclide undergo emission ? - Too big - Wrong ratio : n/p - Too big - Wrong place Why might a nuclide undergo alpha emission ? Alpha carries away nucleons too big means too many nucleaon . Alpha helps Any nuclide that >209 undergoes alpha emissions Removing an alpha particle does shift the neuton to proton ratio : n/p Comparing the n/p
BETA PRTICLE A very fast moving electron , emitted from the nucleus and , likely every electron , it has a mass number of 0, and a charge of -1 Mass number of 0 and Atomic number of -1.
In Beta emission , a neutron breaks apart into proton and lectron n---- P + e The electon is immediately emitted from the nucleus at very high speed . The proton stays . So neutron plitting to a proton and electron is the same as neutron splits into proton and Beta particle n-- P + B What happens to the mass number when neutron turns into one proton within the nucleus s and , the electron / eta particle has left the nucleus Mass number ? Stays the same Atomic number ? Goes up by 1 The atomic number of beta particle is a bit complicated . Neutron hass mas s of 1 and atomic number of 0. Proton has mass number of 1 and atomic number of 1 The eBeta has mass number of 0 an atomic number of -1 In a Beta process you are not convserving . You are convsering mass number and charge .
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Rdiactiove Decay ANADocument13 pagesRdiactiove Decay ANAanatoyosbenolielPas encore d'évaluation
- Nuclear Chemistry Chapter Explains Radiation TypesDocument14 pagesNuclear Chemistry Chapter Explains Radiation TypesRojim Asio DilaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Nuclear Stability and Radioactive Decay - Docx Module 09Document14 pagesNuclear Stability and Radioactive Decay - Docx Module 09Steven Christian SolisPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3. Nuclear Chemistry Part ONEDocument17 pagesChapter 3. Nuclear Chemistry Part ONEChengPas encore d'évaluation
- Nuclear ReactionsDocument18 pagesNuclear ReactionsJoanna Ruth SeproPas encore d'évaluation
- Nuclear Reactions and Origin of ElementsDocument32 pagesNuclear Reactions and Origin of Elementsmacuhajc29Pas encore d'évaluation
- Admmodule s11 12ps Iiib 12Document11 pagesAdmmodule s11 12ps Iiib 12Allan Francis FelizartePas encore d'évaluation
- Admmodule s11 12ps Iiib 12Document11 pagesAdmmodule s11 12ps Iiib 12maricar relatorPas encore d'évaluation
- Admmodule s11 12ps Iiib 12Document11 pagesAdmmodule s11 12ps Iiib 12Lebz RicaramPas encore d'évaluation
- Nuclear Decay GizmoDocument7 pagesNuclear Decay GizmoKP - 12MA 653047 Central Peel SSPas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic StructureDocument21 pagesAtomic StructureEli JnrPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 17 - Radioactivity and Half LifeDocument6 pagesLecture 17 - Radioactivity and Half LifeIbrar ahmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Nuclear Chemistry: Calculations and SimulationsDocument27 pagesNuclear Chemistry: Calculations and SimulationsCHI HIROPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Vs Nuclear ReactionsDocument47 pagesChemical Vs Nuclear Reactionsapi-236069914Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction to Nuclear ChemistryDocument47 pagesIntroduction to Nuclear ChemistryMaheshPas encore d'évaluation
- LP9 Nuclear Equations Alpha DecayDocument4 pagesLP9 Nuclear Equations Alpha DecayKeeyt KythePas encore d'évaluation
- Radiation Chemistry Notes EditedDocument15 pagesRadiation Chemistry Notes Editedkiama kariithiPas encore d'évaluation
- Radioactive Decay: BasicsDocument4 pagesRadioactive Decay: BasicssalmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 4 Nuclear TransformationDocument6 pagesLesson 4 Nuclear TransformationJoshua LimosneroPas encore d'évaluation
- Nuclear Physics - 1Document61 pagesNuclear Physics - 1Rose MusariraPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics AssignmentDocument22 pagesPhysics AssignmentanessnabelaPas encore d'évaluation
- Synthesis of New ElementsDocument45 pagesSynthesis of New ElementsJeffrey MaderaPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Science - Nuclear Reactions and Origin of ElementsDocument51 pagesPhysical Science - Nuclear Reactions and Origin of ElementsEricka ValderamaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nuclear ChemistryDocument10 pagesNuclear ChemistryMaria OzaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Nuclear Chemistry LectureDocument12 pagesNuclear Chemistry LectureAMLU Law OfficesPas encore d'évaluation
- Nuclear Chemistry and EnergyDocument14 pagesNuclear Chemistry and EnergyFrances ZeinPas encore d'évaluation
- Nuclear Chemistry: Unit 2.5Document48 pagesNuclear Chemistry: Unit 2.5Richelle CharlenePas encore d'évaluation
- Nuclear ChemistryDocument31 pagesNuclear ChemistryFatin IziantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 4-Particle PhysicsDocument11 pagesLesson 4-Particle Physicsabdulrahman alalawiPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 10 - Radioactivity and Nuclear Chemistry Teacher VersionDocument13 pagesUnit 10 - Radioactivity and Nuclear Chemistry Teacher VersionAmadu sallieuPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Report - 4!18!36652-1 - Zahid Hasan KhokaDocument9 pagesLab Report - 4!18!36652-1 - Zahid Hasan KhokaZahid Hasan KhokaPas encore d'évaluation
- 2023 AS Level CHAPTER 15 PARTICLE PHYSICSDocument38 pages2023 AS Level CHAPTER 15 PARTICLE PHYSICSRiza FirmansyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem 8Document12 pagesChem 8Ali SandsPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.1 Structure of The Atom and PTDocument4 pages3.1 Structure of The Atom and PTRoldan Delapa PachecoPas encore d'évaluation
- American GodsDocument10 pagesAmerican GodsH Patel laherPas encore d'évaluation
- Nuclear TransformationDocument16 pagesNuclear TransformationAnsel MercadejasPas encore d'évaluation
- Structure of an Atom and its Subatomic ParticlesDocument17 pagesStructure of an Atom and its Subatomic ParticlesIbaad Ur RahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Belt of Stability QuestionsDocument5 pagesBelt of Stability QuestionsJalleynegmmodePas encore d'évaluation
- College of EngineeringDocument17 pagesCollege of EngineeringClarkPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.1 The Nuclear Atom: Rutherford's ExperimentDocument8 pages2.1 The Nuclear Atom: Rutherford's ExperimentcboombeachPas encore d'évaluation
- atomic-stability-worksheet-ra4Document2 pagesatomic-stability-worksheet-ra4AdrianPas encore d'évaluation
- Theory of Radioactivity DisintegrationDocument3 pagesTheory of Radioactivity DisintegrationAthira I PPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes 12.12.2021Document5 pagesNotes 12.12.2021Shaheer UboyePas encore d'évaluation
- Radiation PhysicsDocument38 pagesRadiation PhysicsMaheshwar KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- IntronuclearchemDocument30 pagesIntronuclearchemapi-252814424Pas encore d'évaluation
- LAS 1 Nuclear Synthesis of New ElementsDocument3 pagesLAS 1 Nuclear Synthesis of New ElementsRoy OpredoPas encore d'évaluation
- atomic-stability-worksheet-teacher-key-ra4Document1 pageatomic-stability-worksheet-teacher-key-ra4AdrianPas encore d'évaluation
- Sub-Atomic Particles - Chemistry LibreTextsDocument6 pagesSub-Atomic Particles - Chemistry LibreTextsJohn ManligoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Nuclear EquationsDocument21 pagesNuclear EquationsAbigail AmorPas encore d'évaluation
- 24230-sampleDocument6 pages24230-samplekhorshid aziziPas encore d'évaluation
- Radioactive DecayDocument12 pagesRadioactive DecayAlyssaMaeCubillaPas encore d'évaluation
- RADIOACTIVITYDocument26 pagesRADIOACTIVITYHarIsh SangwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5: Radioactive: 5. 1 The Nucleus of An AtomDocument50 pagesChapter 5: Radioactive: 5. 1 The Nucleus of An AtomAdib AfhamPas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic Structure, Bohr Model and IsotopesDocument17 pagesAtomic Structure, Bohr Model and IsotopeskushanPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 2 Notes - Teacher 2Document13 pagesUnit 2 Notes - Teacher 2noPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture17 RadioactivityandHalfLifeDocument6 pagesLecture17 RadioactivityandHalfLifeIjazzzAliPas encore d'évaluation
- BCHEM 264 Lecture 10 Radioisotope TechniquesDocument16 pagesBCHEM 264 Lecture 10 Radioisotope TechniquesDuodu StevenPas encore d'évaluation
- Nuclear Stability and RadioactivityDocument35 pagesNuclear Stability and RadioactivityAmirHakimRusliPas encore d'évaluation
- Radiation: Easy As ABC in GreekDocument16 pagesRadiation: Easy As ABC in GreekvinayPas encore d'évaluation
- 6-2 Fossil Fuels Pre-Class PostDocument32 pages6-2 Fossil Fuels Pre-Class PostSeyi Martins ObandoPas encore d'évaluation
- MasteringPhysics Winter2012Document32 pagesMasteringPhysics Winter2012Seyi Martins ObandoPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam 1 Oct. 2, 2008 Chm 123 75 minutes 100 pointsDocument7 pagesExam 1 Oct. 2, 2008 Chm 123 75 minutes 100 pointsSeyi Martins ObandoPas encore d'évaluation
- Rigid BodiesDocument77 pagesRigid BodiesSeyi Martins ObandoPas encore d'évaluation
- International Material GradeDocument7 pagesInternational Material GradeDvs RameshPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Practical Test Guide For Cations and AnionsDocument2 pagesChemistry Practical Test Guide For Cations and Anionsansherina2100% (1)
- 1 H Matter & Measurement RWSDocument6 pages1 H Matter & Measurement RWSmijaggiPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm A572-50Document1 pageAstm A572-50anumnedPas encore d'évaluation
- Metals Reactivity SeriesDocument4 pagesMetals Reactivity SeriesjahangirPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment Lab ReportDocument10 pagesExperiment Lab ReportCeilo TomamakPas encore d'évaluation
- Edudigm: Chemistry For IIT-JEE & Other Entrance ExamsDocument32 pagesEdudigm: Chemistry For IIT-JEE & Other Entrance Examstapas kunduPas encore d'évaluation
- 05 - Soil StabilizationDocument23 pages05 - Soil StabilizationJonathan MamburamPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 1-Eng Materials and Iron and Steel MakingDocument44 pagesLecture 1-Eng Materials and Iron and Steel Makingم.ذكى فضل ذكى100% (1)
- Atoms and MoleculesDocument17 pagesAtoms and MoleculesJai KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Anodizado PDFDocument5 pagesAnodizado PDFValentin GuzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Rutile Oct17Document2 pagesRutile Oct17api-308735650100% (3)
- James Ruse 2013 Chemistry Trials & SolutionsDocument52 pagesJames Ruse 2013 Chemistry Trials & SolutionsYe ZhangPas encore d'évaluation
- 3M Metalworking Catalog - 61-5002-8280-3Document120 pages3M Metalworking Catalog - 61-5002-8280-3jplondonPas encore d'évaluation
- Group 17 Elements: The Halogens Family: P-Block Elements (Halogen & Noble Gases)Document20 pagesGroup 17 Elements: The Halogens Family: P-Block Elements (Halogen & Noble Gases)MoneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Modren's ABC Chemistry Part - 1 Class 11Document355 pagesModren's ABC Chemistry Part - 1 Class 11Parth Bhalaik100% (4)
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements: (I) Concentration of The Ore: Removal of UnwantedDocument17 pagesGeneral Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements: (I) Concentration of The Ore: Removal of UnwantedPriyankaPas encore d'évaluation
- Activity Quiz AssignmentDocument3 pagesActivity Quiz AssignmentAnddreah Anne PanganibanPas encore d'évaluation
- 2019-2020 Science Contest English Exam - ChemistryDocument3 pages2019-2020 Science Contest English Exam - ChemistryTheo WilsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic Structure and Amount of Substance QDocument30 pagesAtomic Structure and Amount of Substance Qlucylovesbooks6770Pas encore d'évaluation
- Steel Making IntroductionDocument17 pagesSteel Making IntroductionHari sadu100% (2)
- Method For Ultra High Purity Gold - Gold Refining ForumDocument11 pagesMethod For Ultra High Purity Gold - Gold Refining Forummladen lakicPas encore d'évaluation
- Isotopes and Atomic Mass LabDocument4 pagesIsotopes and Atomic Mass LabjustinPas encore d'évaluation
- The Present State of The Use of Waste Wood Ash As An Eco-Efficient Construction Material A ReviewDocument20 pagesThe Present State of The Use of Waste Wood Ash As An Eco-Efficient Construction Material A ReviewShaker QaidiPas encore d'évaluation
- En 573-3Document37 pagesEn 573-3Ricardo VitorianoPas encore d'évaluation
- PCA Chapter 7 - Mixing Water For ConcreteDocument29 pagesPCA Chapter 7 - Mixing Water For ConcreteMuhammad RizwanPas encore d'évaluation
- ChemchartDocument14 pagesChemchartDarshan PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- Copper Alloy Cross ReferenceDocument3 pagesCopper Alloy Cross ReferencenotZm62FPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparison SICcast Metales RaaDocument1 pageComparison SICcast Metales RaaDonald Cuadros CondoriPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Formula NotesDocument28 pagesChemical Formula NotesPrince SanjiPas encore d'évaluation