Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
ECE 1231 Sem 1 04/05
Transféré par
Ikram RazakCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
ECE 1231 Sem 1 04/05
Transféré par
Ikram RazakDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
INTERNATIONAL ISLAMIC UNIVERSITY MALAYSIA
END OF SEMESTER EXAMINATION SEMESTER I, 2004/2005 SESSION
KULLIYYAH OF ENGINEERING
Programme Time Duration : ENGINEERING : 3:00 pm - 06:00 pm : 3 Hrs Section(s) : 4 Level of Study Date : UG 1 : 08/10/2004
Course Code : ECE 1312 Course Title : Electronics
This Question Paper Consists of Six (6) Printed Pages (Including Cover Page) With Five (5) Questions. INSTRUCTION(S) TO CANDIDATES
DO NOT OPEN UNTIL YOU ARE ASKED TO DO SO
!" Total marks of this examination is 100. !" This examination is worth 40% of the total assessment. !" Answer all 5 (Five) questions.
Any form of cheating or attempt to cheat is a serious offence which may lead to dismissal.
Electronics
ECE 1312
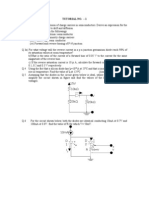
Q.1 [20 marks] (a) Sketch the output vo and determine the dc level of the output for the network shown in Fig. 1(a). Assume that vi = 100 sin(!t). (10 marks)
+ vi 2.2 k! Ideal diodes 2.2 k! 2.2 k!
+ vo
Fig. 1(a)
(b)
What are the maximum and minimum values of Vi, to operate a Zener diode of VZ (10 marks) = 20 V and IZ (max) = 60 mA. See Fig. 1(b).
220 ! + vi -
2
VZ = 20 V IZM = 60 mA 1.2 k!
+ vo -
Fig. 1(b)
Electronics
ECE 1312
Q.2 [20 marks] (a) Find the values of IBQ, ICQ, VCEQ and sketch the dc load line for the circuit shown in Fig. 2. Assume that # = 100, VBE = 0.7V and ICO has negligible effect on IC. (10 marks)
+15 V R1 C1 + vo vs vin R2 5 k! RE 1 k! C3 RL 2 k! 10 k! RC 1 k! +
RS 500 !
C2
Fig. 2 (b) Compute the voltage gain Av, input impedance Zi, current gain Ai, power gain G, and output impedance Zo for the amplifier shown in Fig. 2. (Assume, r" = 631 ! and the transistor is operating in the active region) (10 marks)
Electronics
ECE 1312
Q.3 [20 marks] (a) The MOSFET in Fig. 3 has Vto = 1 V, K = 0.25 mA/V2, # = 0. Determine the Qpoint values (VGSQ, IDQ and VDSQ) of the given circuit. (10 marks)
+20 V R1 C1 + vo vs vin R2 Fig. 3 1 M! RS 2.7 k! C3 RL 10 k! 3 M! RD 4.7 k! +
R 100 !
C2
(b)
Find the input impedance Zi, output impedance Zo and voltage gain Av for the amplifier in Fig. 3. (Assume gm = 1.77 mS and rd = $ !) (10 marks)
Electronics
ECE 1312
Q.4 [20 marks] (a) Derive an expression for feedback gain GF based on the amplifier shown in Fig. 4. (10 marks)
+ VS VF
V1
+ Vo
Fig. 4 (b) Calculate GF in each of the following cases and comment on the results. G 500 5000 10 100 1000 H 0.2 -0.01 0.08 0.01 -0.05
(10 marks)
1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Electronics
ECE 1312
Q.5 [20 marks] (a) Draw the small signal mid-frequency ac equivalent circuit for the amplifier with feedback bias shown in Fig. 5. Use Miller theorem to give the expressions for Ri (10 marks) and Ro. +VCC
C2 RS vs C1 RF + vo vin Fig. 5 (b) Write True/False (Wrong answer bears negative mark): (10 marks) -
RL
1. When the anode is more positive than the cathode of a diode, the condition is called reverse bias. 2. A semiconductor material has a negative temperature coefficient of resistance which means that as temperature increases, the resistance increases. 3. A p-type semiconductor has more valence-band holes than valence band electrons. 4. A forward bias causes a large depletion region in a p-n junction offers a large resistance and therefore only permits a small current. 5. Leakage or reverse current is the extremely small current passes through the p-n junction due to minority carriers. 6. Covalent bond is electrons shared by two neighboring atoms, which form a recombined electron-hole pair. 7. Conduction band is an energy band in which electrons can move freely within a material. 8. When an electron goes from the valence band to the conduction band, it generates an electron-hole pair. 9. In n-type semiconductor, the electrons are called minority carriers and the Fermi level lies above the middle of the band gap. 10. At a p-n junction theres an attractive force between the electrons of the n-type material and the holes of the p-type material.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Shigley's Mechanical Engineering Design 9th Edition Solutions ManualDocument6 pagesShigley's Mechanical Engineering Design 9th Edition Solutions ManualDarren Hentschel27% (26)
- Lecture 30Document59 pagesLecture 30Muhammad AdilPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Exam ECE 1312 Question Sem-1 2013-2014Document9 pagesFinal Exam ECE 1312 Question Sem-1 2013-2014Fatihah AinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Electronics Papers GATEDocument378 pagesElectronics Papers GATELav Kumar YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- EC 2012 Unsolved PDFDocument20 pagesEC 2012 Unsolved PDFShanmugarajaSubramanianPas encore d'évaluation
- IIUM Electronics ECE 1312/ECE 1231 Final Exam Sem 1 (2012 - 2013)Document8 pagesIIUM Electronics ECE 1312/ECE 1231 Final Exam Sem 1 (2012 - 2013)Ridhwan Asri100% (1)
- Final Exam ECE 1312 Question Sem-2 2013-2014Document9 pagesFinal Exam ECE 1312 Question Sem-2 2013-2014Fatihah Aina100% (1)
- Exam 2097 2005Document13 pagesExam 2097 2005Kashka IraniPas encore d'évaluation
- Ece1231 Mid Term SolnDocument10 pagesEce1231 Mid Term SolnOppa Sollehudin SapariPas encore d'évaluation
- WWW Learncbse in Electricity Chapter Wise Important Questions Class 10 ScienceDocument34 pagesWWW Learncbse in Electricity Chapter Wise Important Questions Class 10 ScienceVikas PratikPas encore d'évaluation
- Gate Ece Question PaperDocument20 pagesGate Ece Question Papers_subbulakshmiPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 EC 2151 - Electric Circuits and Electronic DevicesDocument3 pages5 EC 2151 - Electric Circuits and Electronic DevicesBIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANPas encore d'évaluation
- ECA Exams Term 1Document2 pagesECA Exams Term 1Fred RotichPas encore d'évaluation
- Mid Term Sem 1 2014 - 2015Document8 pagesMid Term Sem 1 2014 - 2015FARAZ ABDUL BASITPas encore d'évaluation
- SC Engineeri G: Bool NDocument8 pagesSC Engineeri G: Bool NRichard YangPas encore d'évaluation
- Electric Circuit and Fields QuestionsDocument38 pagesElectric Circuit and Fields Questionssamg270% (1)
- Sheet 3Document2 pagesSheet 3Nano GomeshPas encore d'évaluation
- II B. Tech I Semester, Regular Examinations, Nov - 2012 Electrical Circuit Analysis - IDocument12 pagesII B. Tech I Semester, Regular Examinations, Nov - 2012 Electrical Circuit Analysis - IViswa ChaitanyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Questions Physics 2 Lab 22-23Document17 pagesSample Questions Physics 2 Lab 22-23Tany TurkiPas encore d'évaluation
- ENEL2EEH1 - Electrical & Electronic EngineeringDocument7 pagesENEL2EEH1 - Electrical & Electronic EngineeringqanaqPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 3Document6 pagesTutorial 3SYAFIQAH ISMAILPas encore d'évaluation
- 6002x FinalReview S2012 CleanDocument80 pages6002x FinalReview S2012 CleanGemini GntPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrotechnics 1b Outcome B Test 1 Memo 2021Document7 pagesElectrotechnics 1b Outcome B Test 1 Memo 2021spm0826722Pas encore d'évaluation
- Edc 3Document10 pagesEdc 329viswa12Pas encore d'évaluation
- Elec1041y 1 2007 2 PDFDocument7 pagesElec1041y 1 2007 2 PDFchetsPas encore d'évaluation
- BE 1st Midterm Sep2009Document3 pagesBE 1st Midterm Sep2009YASHPas encore d'évaluation
- Mock Test Ee-EDocument16 pagesMock Test Ee-Esamg27Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gate Papr Set BDocument16 pagesGate Papr Set BD Avi Na ShPas encore d'évaluation
- 19 20Document3 pages19 20akshigarg0224Pas encore d'évaluation
- 3054 PDFDocument9 pages3054 PDFpadmajasivaPas encore d'évaluation
- Analogue ElectronicsDocument7 pagesAnalogue ElectronicsrizwanahbPas encore d'évaluation
- EE-D.pdf Gate 2013Document20 pagesEE-D.pdf Gate 2013Vikas SpPas encore d'évaluation
- Short Answer Questions - I (PYQ)Document31 pagesShort Answer Questions - I (PYQ)Gorima GoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Circuit END Sem) Analysis 2022Document3 pagesElectrical Circuit END Sem) Analysis 2022Udit RanaPas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Board-XII Physics - Paper - SolutionDocument15 pagesCBSE Board-XII Physics - Paper - SolutionMichelle DennisPas encore d'évaluation
- AY1920S2 EE2111A-Quiz1Document12 pagesAY1920S2 EE2111A-Quiz1ZubinJainPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Proficiency Examination: Caribbean Examinations CouncilDocument15 pagesAdvanced Proficiency Examination: Caribbean Examinations Councilpetey78Pas encore d'évaluation
- IES Conventional Electrical Engineering 2012Document28 pagesIES Conventional Electrical Engineering 2012Srujan BobbyPas encore d'évaluation
- Jee Main 2020 Sept 5 Second Shift PaperDocument38 pagesJee Main 2020 Sept 5 Second Shift Papershivam singhPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 Cse Ece It Ec2151Document2 pages2 Cse Ece It Ec2151BIBIN CHIDAMBARANATHANPas encore d'évaluation
- University of Edinburgh College of Science and Engineering School of Engineering and ElectronicsDocument15 pagesUniversity of Edinburgh College of Science and Engineering School of Engineering and ElectronicsSyed Fasih Ur RehmanPas encore d'évaluation
- r5100207 Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocument4 pagesr5100207 Electronic Devices and CircuitssivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- 2002UNIT2PAPER2Document16 pages2002UNIT2PAPER2petey78Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial Exercises 0: The Basics: E1001 Electronic Circuits Prof P BayvelDocument7 pagesTutorial Exercises 0: The Basics: E1001 Electronic Circuits Prof P BayvelraihanserajPas encore d'évaluation
- Edc 4Document10 pagesEdc 429viswa12Pas encore d'évaluation
- r059210202 Pulse and Digital CircuitsDocument11 pagesr059210202 Pulse and Digital CircuitsSrinivasa Rao GPas encore d'évaluation
- Final Question - ECE1312 - Sem1 - 14-15Document9 pagesFinal Question - ECE1312 - Sem1 - 14-15FARAZ ABDUL BASITPas encore d'évaluation
- Basics of Electrical and ElectronicsDocument11 pagesBasics of Electrical and ElectronicsannpotterPas encore d'évaluation
- Sem1 1213 SolutionDocument17 pagesSem1 1213 SolutionThinesh StPas encore d'évaluation
- 4d8f8analog 1, Tut SheetDocument19 pages4d8f8analog 1, Tut SheetmntykrPas encore d'évaluation
- EC Question PaperDocument3 pagesEC Question PaperGna Senthil KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- GATE Electrical Engineering Solved 2013 PDFDocument22 pagesGATE Electrical Engineering Solved 2013 PDFPudeti RaghusreenivasPas encore d'évaluation
- IES Conventional Electronics 2013Document32 pagesIES Conventional Electronics 2013Debi Prasad DashPas encore d'évaluation
- ECIL Electrical Question Papers With Answers 2011 PDF Model Question Papers of ECIL Electrical SolvedDocument13 pagesECIL Electrical Question Papers With Answers 2011 PDF Model Question Papers of ECIL Electrical SolvedJaniel Jawahar75% (4)
- Semester-1 - Chemistry Stream - Mid+end PaperDocument15 pagesSemester-1 - Chemistry Stream - Mid+end PaperGopiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample 1Document8 pagesSample 1nradhy2725Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ec: Electronics and Communication Engineering: Duration: Three HoursDocument14 pagesEc: Electronics and Communication Engineering: Duration: Three HourspiyalovePas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesD'EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesPas encore d'évaluation
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisD'EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Light-Emitting Transistors: Towards the Next Generation Display TechnologyD'EverandOrganic Light-Emitting Transistors: Towards the Next Generation Display TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- Vacuum Nanoelectronic Devices: Novel Electron Sources and ApplicationsD'EverandVacuum Nanoelectronic Devices: Novel Electron Sources and ApplicationsPas encore d'évaluation
- Vibrations Study MaterialDocument20 pagesVibrations Study MaterialIkram RazakPas encore d'évaluation
- ECE 1231 Sem 1 2005/2006Document3 pagesECE 1231 Sem 1 2005/2006Ikram RazakPas encore d'évaluation
- Fjaf0113 2 2011Document15 pagesFjaf0113 2 2011Ikram RazakPas encore d'évaluation
- Form 4 - Biology NotesDocument59 pagesForm 4 - Biology Notesshahmi200679% (28)
- GE FEL EW AYG Modules 1 2Document61 pagesGE FEL EW AYG Modules 1 2The UnknownPas encore d'évaluation
- Distance Protection Setting Calculator 1Document6 pagesDistance Protection Setting Calculator 1Mosa Elnaid ElnaidPas encore d'évaluation
- SIK GuideDocument80 pagesSIK GuideRadu MartinPas encore d'évaluation
- Make Your Own High Voltage ElectromagnetsDocument15 pagesMake Your Own High Voltage Electromagnetsapi-3715567100% (21)
- 22212-2019-Winter-Model-Answer-Paper (Msbte Study Resources)Document22 pages22212-2019-Winter-Model-Answer-Paper (Msbte Study Resources)pravin khadePas encore d'évaluation
- New Methodology For Design and Failure Analysis of Underground Transmission LinesDocument25 pagesNew Methodology For Design and Failure Analysis of Underground Transmission LinesUmair MansoorPas encore d'évaluation
- EC105Document23 pagesEC105api-3853441Pas encore d'évaluation
- Evaporator Temperature Sensor DiagnoseDocument2 pagesEvaporator Temperature Sensor DiagnoseJohn DarePas encore d'évaluation
- Speciality Magnetic Components: Miniature Hall Effect Current Transformer Type HTP50CPT/2KDocument2 pagesSpeciality Magnetic Components: Miniature Hall Effect Current Transformer Type HTP50CPT/2KYahya El SadanyPas encore d'évaluation
- Far LZ400895Document10 pagesFar LZ400895Soubhagya BeheraPas encore d'évaluation
- Double Gate (DG) MOSFET Using TCAD: A Lab Report OnDocument16 pagesDouble Gate (DG) MOSFET Using TCAD: A Lab Report OnmeenakshisravaniPas encore d'évaluation
- NEOM-NDS-SPC-015 - 01.00 - Neutral Earthing Resistor (NER) SpecificationDocument15 pagesNEOM-NDS-SPC-015 - 01.00 - Neutral Earthing Resistor (NER) Specificationcawoc96196Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bioinstrumentation Ii Lecture 3: Oxygen Concentrator: Hundessa Daba (MSC)Document40 pagesBioinstrumentation Ii Lecture 3: Oxygen Concentrator: Hundessa Daba (MSC)Hundessa Daba100% (1)
- Cable CalculationDocument20 pagesCable CalculationsazzadPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Project: Satya Prakash Public SchoolDocument15 pagesPhysics Project: Satya Prakash Public SchoolsanjeeviPas encore d'évaluation
- Ohm's Law - Concept Development1Document2 pagesOhm's Law - Concept Development1psychowrldPas encore d'évaluation
- Emi PPT2Document103 pagesEmi PPT2akashdeep kaurPas encore d'évaluation
- Earthing Calculation - V - 0.2Document18 pagesEarthing Calculation - V - 0.2Ravishankar.AzadPas encore d'évaluation
- Humiseal 1B31 CoatingDocument2 pagesHumiseal 1B31 CoatingHarun StyawanPas encore d'évaluation
- AAAC Stranded CondDocument13 pagesAAAC Stranded Condgvsbabu63Pas encore d'évaluation
- Fault Codes - P0627/78 Pump System Description: Click HereDocument4 pagesFault Codes - P0627/78 Pump System Description: Click HereLudwig HernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- How To Extend Yout USB Using UTPDocument8 pagesHow To Extend Yout USB Using UTPAnonymous vKD3FG6RkPas encore d'évaluation
- High VOltageDocument44 pagesHigh VOltagesam_sudanPas encore d'évaluation
- An Overview of Ac Induction Motor Testing in Accordance With BS 4999 PART 143Document12 pagesAn Overview of Ac Induction Motor Testing in Accordance With BS 4999 PART 143Gourab SahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Area 1 ProbDocument7 pagesArea 1 ProbKrisher DhayPas encore d'évaluation
- LDR Circuit Phy Class12Document29 pagesLDR Circuit Phy Class12RIYA DHAKAANPas encore d'évaluation
- Iscn-Channel Mosfet Transistor: Inchange SemiconductorDocument2 pagesIscn-Channel Mosfet Transistor: Inchange SemiconductorLEONERPas encore d'évaluation
- General Purpose Relay: Ordering InformationDocument15 pagesGeneral Purpose Relay: Ordering InformationtwinvbooksPas encore d'évaluation
- EXPT No 4 Delta-WyeDocument13 pagesEXPT No 4 Delta-Wyevillegreen9100% (2)