Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Soalan-Soalan JSU
Transféré par
Masyitah Ahmad MaulanaDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Soalan-Soalan JSU
Transféré par
Masyitah Ahmad MaulanaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Appendix 13
Physics Form 4 1 hours 2010
MONTHLY TEST
PHYSICS FORM FOUR FORCE AND MOTION Apr/Mei 1 Hours One hour thirty minutes ____________________________________________________________________________ DO NOT OPEN THE QUESTION PAPER UNTIL INSTRUCTED (JANGAN BUKA KERTAS SOALAN INI SEHINGGA DIBERITAHU)
NAME : .. NO.IC : ........... FORM : ......
Appendix 13
INFORMATION FOR CANDIDATES
1. This question paper consists of two section : Section A and Section B 2. Answer all questions in Section A. Write your answer for Section A in this question paper. 3. Answer all questions in Section B. Write your answer for Section B in the space provided in this question paper. 4. Show your working. It may help you to get marks. 5. The diagrams in the question are not drawn to scale unless stated. 6. If you wish to change your answer, cross out the answer that you have done. Then wrote down the new answer. 7. You may use a non-programmable scientific calculator. 8. You are advised to spend 45 minutes to answer questions in Section A and 45 minutes for Section B.
Appendix 13
The following information may be useful. The symbols have their usual meaning. vu t v2 = u2 + 2 as
1.
a=
2.
3.
s = ut
1 at2 2
4.
Momentum = mv
5.
F = ma = 1 mv2 2 = mgh
6.
Kinetic energy (Tenaga kinetik ) Potential energy
7.
8.
g = 10 ms-2
Appendix 13
SECTION A [ 15 marks] Answer all questions in this section.
1.
A student carried out an experiment using a ticker timer and a trolley. She obtained a chart from the ticker tape by cutting it into five dot lengths as shown in the figure.
Which statement describes the motion of the trolley?
A B C
the trolley is coming to a stop with constant deceleration the trolley moves from rest with uniform acceleration the trolley moves from rest with increasing velocity
2.
This graph contains information about the motion of a bicycle. At which of the following times is the bicycles acceleration zero?
Appendix 13
A B C D
1s 2s 4s 8s
3.
A student rides her bicycle from her home to the library. She stays there for a while and then goes to a friends house. Which graph best matches this situation?
Appendix 13
4.
Which object has the greatest inertia?
5.
Diagram 4 shows two trolleys, P and Q, on a frictionless plane. Trolley P moves and collides with the stationary trolley, Q.
Appendix 13 Which of the following statements is true?
A The collision is an elastic collision B Both trolleys do not undergo changes in momentum C The total momentum before and after the collision is the same D The total kinetic energy before and after the collision is conserved
6.
The diagram shows an athlete performing the high jump.
Mattress
What is the function of the mattress?
A To reduce the collision time between the athlete and the mattress B To reduce the change of momentum of the athlete when he hits the mattress C To reduce the impulsive force acting on the athlete when he hits the mattress
7.
This test paper is sitting at rest on your desk. Which of the following statements best describes this situation?
A B C D
There are no forces acting on your paper. Your paper is at rest in any coordinate system. Your paper exerts no force on the desk. There are several forces acting on your paper, but they balance each other.
Appendix 13
8.
An object of mass 1 kg is moving with a velocity of 5 ms-1. The object then hits a wall and stops in 0.2 s. The impulsive force exerted on the object during collision is 25 N. What is the velocity of the object before hitting the wall?
A 0.2 ms-1 B 1 ms-1 C 5 ms-1 D 25 ms-1
9.
Diagram 1 shows a coconut falling from a tree.
What is the physical quantity of the coconut is constant?
A B C D
Potential energy Kinetic energy Acceleration Velocity
Appendix 13
10. The figure shows the forces acting on a moving airplane
F1
F4
F2
F3
What is the upward force, F1?
A Lift B Drag C Thrust D Weight
11. Diagram 3 shows a car is moving at zero acceleration.
Diagram 3
Appendix 13
Which relationship of the forces is correct? A B F >Fg F=Fg C F<Fg D W>R
12. The figure shows the energy conversion involved in three energy converters, P, Q and R.
Energy converter P Q R
Energy conversion Chemical energy Mechanical energy Electrical energy kinetic energy electrical energy kinetic energy
Which energy converter does not involve kinetic energy?
A P B Q C R
13. Diagram 1 shows a weightlifter successfully lifting a load of 60 kg.
Calculate the work done in lifting the load
Appendix 13
A 30 J B 120 J C 600 J D 1200 J
14. Choose the terminology that best describes the situation shown in the figure.
Spring without load
Spring after the load is removed
A Inertia B Elasticity C Kinetic energy D Impulsive force
15. A spring of length 15.0 cm stretches to 17.0 cm when a mass of 3.0 kg is hung on it. What is the mass of the load hung on the spring?
A 2.0 cm B 3.0 kg C 15.0 cm D 17.0 cm
Appendix 13
SECTION B [16 marks] Answer all questions in this section.
1. Ahmad cycles to school every day. The graph below shows a typical velocity-time graph of Ahmad's journey to school.
B C D
(a)
During which part of the journey is Ahmad : (i) (ii) Accelerating :. Decelerating : [2 marks]
(b)
For how long is Ahmad cycling with constant velocity?
[1 marks] (c) How far is Ahmad's school from his house?
[2marks]
Appendix 13
2. The figure below shows the arrangement of the apparatus to study the effect of the extension of a spring produced by a load hung at the end of the spring.
The result of the experiment is represented by the graph below.
(a) Name the law involved in the relation above.
[1mark]
(b) Mark 'X' on the graph above to show the upper limit to which the law mentioned in (a) is valid. [1 mark]
(c) What physical quantity is represented by the gradient of the graph?
[1 mark]
(d) If the elastic potential energy stored in the spring is represented by the area under the graph, how much energy is stored when the spring is acted upon by a load of weight 0.5 N? [2 marks]
Appendix 13
3. Diagram 3.1 and Diagram 3.2 show two methods of transferring a heavy load of 50 kg from the ground to the lorry. The forces needed to transfer the heavy load are not the same. However, the work done for both methods of transfering are the same.
Diagram 3.1
Diagram 3.2
i) What is meant by work?
[1 mark]
ii) Using diagram 3.1 and 3.2, compare the forces needed to transfer the load, the distance travelled by the load and the potential energy gained by the load. Relate the forces needed to transfer the load and the distance travelled by the load with the work done. State the relationship between the potential energy gained by the load and the work done on transferring the load. [5 marks]
Appendix 13
ANSWERS
Section A 1. C 2. C 3. A 4. D 5. C 6. C 7. D 8. C 9. C 10. A 11. B 12. B 13. D 14. B 15. B
Appendix 13
Section B
1.
a) i: From point A to B ii: From point B to C & D to E
b) ( )
c) 4875 m
a) Hookes Law b)
c) kg s-2 d) 0.03 J
3. i) Work = force x displacement ii) - Force in diagram 3.1 > force in Diagram 3.2 - Distance travelled in 3.1 < Distance in Diagram 3.2 - The Potential energy is the same - When Force is higher the distance traveled is shorter - Potential energy = Work done
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Mindray Wato EX-65 Anaesthesia Machine - Service Manual-6Document50 pagesMindray Wato EX-65 Anaesthesia Machine - Service Manual-6Rene GonzalesPas encore d'évaluation
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Inch and Metric Linear Ball Bushings and 60 HRC ShaftingDocument66 pagesInch and Metric Linear Ball Bushings and 60 HRC Shaftingphilip conniePas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Turbines and ExpandersDocument8 pagesTurbines and ExpandersMusa KaleemPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Data LovejoyDocument4 pagesTechnical Data LovejoyAmandeep SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- JR - Fluid Controls Brochure - SPM0838-FOR-WEBDocument16 pagesJR - Fluid Controls Brochure - SPM0838-FOR-WEBMai Tuan AnhPas encore d'évaluation
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- 2006-01-3380 - The Effect of Ethanol Fuel On A Spark Ignition Engine - Nakata - Toyota PDFDocument9 pages2006-01-3380 - The Effect of Ethanol Fuel On A Spark Ignition Engine - Nakata - Toyota PDFFabio GuedesPas encore d'évaluation
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- U 25Document90 pagesU 25baracuss323iPas encore d'évaluation
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
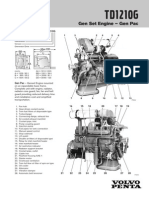
- Td1210g Volvo PentaDocument2 pagesTd1210g Volvo PentaMaría Rosa Tomapasca0% (1)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Air Chain Hoist MLK SerieDocument20 pagesAir Chain Hoist MLK SerieSergei KurpishPas encore d'évaluation
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Soppec Power Cleaner SDSDocument2 pagesSoppec Power Cleaner SDSSteffen Grønli KaroliussenPas encore d'évaluation
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Damper BernardDocument16 pagesDamper BernardSarah ThanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- X Braced Frame Analysis Using Finite Element Method: Input Data & SummaryDocument259 pagesX Braced Frame Analysis Using Finite Element Method: Input Data & SummaryFranklyn GenovePas encore d'évaluation
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- Internal FlowDocument7 pagesInternal FlowLester Lim0% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- STM WDocument18 pagesSTM WEdgardo GambandePas encore d'évaluation
- Boiler Tube Steam Generating CapacityDocument2 pagesBoiler Tube Steam Generating CapacityAA GGPas encore d'évaluation
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- A Comprehensive Review On Process and Engineering Aspects of Pharmaceutical Wet GranulationDocument31 pagesA Comprehensive Review On Process and Engineering Aspects of Pharmaceutical Wet GranulationManuel AlemanPas encore d'évaluation
- Neyveli Uttar Pradesh Power Limited (Nuppl) Desein Private LimitedDocument23 pagesNeyveli Uttar Pradesh Power Limited (Nuppl) Desein Private LimitedSimran singhPas encore d'évaluation
- Aqua SilencerDocument24 pagesAqua SilencerShon JoyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Merc Service Manual 30Document355 pagesMerc Service Manual 30Hayduke them100% (6)
- 2123imguf ESE 2023 Mains Offline-Test SeriesDocument9 pages2123imguf ESE 2023 Mains Offline-Test SeriesDgate IrmsPas encore d'évaluation
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- SGP SyllabusDocument2 pagesSGP SyllabusPrathap VuyyuruPas encore d'évaluation
- 440 Skid Steer CatalogDocument1 226 pages440 Skid Steer CatalogCHRISPas encore d'évaluation
- IRC 22 2015 Road Bridges Composite - Limit StateDocument91 pagesIRC 22 2015 Road Bridges Composite - Limit StateAnil Suryawanshi0% (1)
- Executive SummaryDocument11 pagesExecutive SummaryNitish Kumar SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- RooftankDocument1 pageRooftankwennycantikPas encore d'évaluation
- 2/2-Way Globe Control Valve With Stainless Steel Design For Media Up To +185ºC, DN 10-100Document15 pages2/2-Way Globe Control Valve With Stainless Steel Design For Media Up To +185ºC, DN 10-100ademilsoncaetanooPas encore d'évaluation
- 4018 DSK Multi Skid Operation Maintenance Manual Issue 5Document55 pages4018 DSK Multi Skid Operation Maintenance Manual Issue 5Mostafa ElhamadyPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 19 PDFDocument3 pagesLecture 19 PDFMd SohailPas encore d'évaluation
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Kayaba B0240-18027 - 2Document4 pagesKayaba B0240-18027 - 2TSPSRL Import ExportPas encore d'évaluation
- Brake SystemDocument200 pagesBrake SystemLacatusu MirceaPas encore d'évaluation
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)