Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Apple Company Analysis
Transféré par
dew314Description originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Apple Company Analysis
Transféré par
dew314Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Business Strategy Apple The Company is committed to bringing the best user experience to its customers through its
innovative hardware, software, peripherals, and services. The Companys business strategy leverages its ability to design and develop its own operating systems, hardware, application software, and services to provide its customers new products and solutions with superior ease-of-use, seamless integration, and innovative design. The Company believes continual investment in research and development, marketing and advertising are critical to the development and sale of innovative products and technologies. As part of its strategy the Company continues to grow its platform for the invention and delivery of third-party digital content and applications through the iTunes Store. Apples strategy also includes expanding its distribution network to effectively reach more customers and provide them with a high-quality sales and post-sales experience. Apple currently operates internationally with over 390 stores world wide, it is also considered to be the most valuable company in the world. The Company manages its business primarily on a geographic basis. Accordingly, the Company determined its reportable operating segments, which are generally based on the nature and location of its customers, to be the Americas, Europe, Japan, Asia-Pacific and Retail. The results of the Americas, Europe, Japan and Asia-Pacific segments do not include results of the Retail segment. The Americas segment includes both North and South America. The Europe segment includes European countries, as well as the Middle East and Africa. The Asia-Pacific segment includes Australia and Asian countries, other than Japan. The Retail segment operates Apple retail stores in 13 countries, including the U.S. Each operating segment provides similar hardware and software products and similar services. Net sales during 2012 increased by $48.3 billion (45%) compared to 2011. There are several factors that contributed to this increase, including the addition of a 14th week in the first quarter of 2012. All of the companys segments saw increase in sales. The Americas, which includes North and South America, saw an increase of $19.2 billion or 50% from the year before. The Europe segment, which includes European countries, Middle East and Africa and accounts for, saw an increase of 31% or $8.5 billion. The Japan segment increased $5.1 billion or 94%. Asia Pacific net sales increased by $10.7 billion or 47% and the Retail Segment increased $4.7 billion or 33% during 2012 compared to 2011. P/E Analysis In general, P/E ratios tend to be a sign of expected future growth. It is used as a measure of the value of the company taking into account the current price of the stock and projected growth of the company. Apples Price-Earnings ratio is a 12.2 compared to Microsofts 14.42. Decreases in the P/E ratio can be partially attributed to a riskier market. As risk in the market increases the required rate of return for an investment will increase and therefore the P/E ratio will drop. But what can be seen when comparing both companies is that the P/E of Apple has dropped in the past 26 weeks from 14.2 while Microsofts has increased from 10.8. Apple is currently the most valuable company in the world, with a market cap of $506.84 billion, following a 6.4% drop in the company stock on Wednesday December 5, which shed $30 billion from the companys value. This fall was attributed to a research report that said the companys share in the global tablet market was likely to slip to less than half by 2016. A
company as large as Apple can signal investors that growth could be slowing down. This projected growth decrease is a reason for a decreasing P/E ratio. But while Apple has come under fire because of supply contingencies, and increased competition, we believe this low P/E ratio to not be consistent with the financials of the company. Apple continues to show very promising expansion initiatives that could prove the current P/E ratio to be a sign of a currently undervalued company. Earnings per share have greatly increased from year to year, 82% increase from 2010 to 2011 and 59% from 2011 to 2012 while the stock price has actually decreased. The stock closed on Wednesday, December 6th at $538.79, which is considerably below its 52week high of $705.07. Apple could also be experiencing demand contractions due to its high share price. A stock split could reduce the price of each share outstanding while opening a bigger investor pool. Increased demand would drive up the price and therefore increase the P/E ratio. (Not sure if you want to include this) Microsofts increasing P/E ratio is a sign that investors see the company earnings growth to be higher than its industry. The company has a
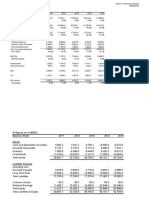
Financial Leverage Apple did not have any long-term debt during the five years ended September 29, 2012. During 2012, 2011 and 2010, the company had no debt outstanding and accordingly did not incur any related interest expense. We believe this to be a negative sign because it means the company is using its own equity to finance its operations instead of investing that money in expansion or to yield higher returns on other projects. Apple is facing increased competition and this has affected the companys finances. Gross margin has decreased in recent years and is in fact projected to continue to decrease. Given current economic times and the low interest rates that are currently in the market, we see no reason for why Apple should continue to finance its operations with its own equity. Better management of the companys capital structure could increase Apples profits by aiding continued growth and increasing competitive advantage. Apple could issue very safe debt instruments that would attract many investors. Apple would not have any trouble paying interest payments and the companys liquidity will be a great sign for investors worried about default risk. Dividend Policy & Repurchase program Apple is a very liquid company with over $10.7 billion in cash and cash equivalents and for the first time in 17 years the company chose to give out dividends to its shareholders. Apples new divided policy could prove to be very beneficial to the company and its stock price. In March 2012, the Board of Directs of the Company approved a dividend policy in which it declared planned quarterly dividends of $2.65 a share, which translates to approximately $2.5 billion each quarter in conjunction with the quarterly declared dividends. Continued dividend growth could make Apples stock a lucrative investment on dividend yield alone. As stated in the Companys 10k, the Board of Directors instituted a program to repurchase up to $10 billion of the Companys common stock beginning in 2013. The repurchase program is implemented over three years with the primary objective of neutralizing the impact of dilution from future employee equity grants and employee stock purchase programs. The Company anticipates that it will utilize approximately $45 billion of domestic cash to pay dividends, repurchase shares, and to remit withheld taxes related to net share settlement of
restricted stock units in the first three years of the dividend and stock repurchase programs. Challenges Faced Apple has many challenges to face that come along with its increased production and global involvement. Global economic conditions play an important role and could adversely affect the company. The continued debt crisis, financial market volatility, and other factors that affect consumer confidence decrease spending and demand. In addition to that the upcoming fiscal cliff and how congress decides to manage the expected increase in taxes and decrease in government spending will greatly affect the economy come the end of the year. The highly competitive market in which the company competes will continue to be a challenge. The company must continually introduce new products and services to stimulate customer demand. Part of this challenge is the importance of inventory level management. Apple has had a lot of problems this year with its suppliers in Asia. There has been problems in meeting anticipated demand which have dampened sales and have raised red flags for investors. Substantially all of the companys manufacturing is performed in whole or in part by a few outsourcing partners located primarily in Asia. The company has also outsourced much its transportation and logistics management. These arrangements help lower operating costs, but they also reduce the companys direct control over production and distribution. This makes the firm vulnerable to unexpected changes that are out of its control. I can continue to add risks (i.e intellectual property litigation) but I first want to see how you want to put all this information together. Length is becoming an issue
Profitability When we analyze each company profitability ratios it is evident that Apple is a much more profitable company than Microsoft. Profit Margin, which calculates how much of every dollar in sales the company keeps in earnings, is 26.67% for Apple and 23.03% for Microsoft. This means that for every dollar in sales Apple is profiting an extra 3.64%. Return of Assets is a measure of how efficiently the company is utilizing its assets to generate earnings. Apples ROA is 23.70% compared to Microsofts 12.90%, thats a difference of 10.8%. Apple is also out performing Microsoft when it comes to return on equity. ROE measures the amount of profit generated with the money invested by shareholders. Apples ROE is 35.30% and Microsofts is 23.80%. Effectively Apple is generating 11.5% more revenue than Microsoft from every dollar invested by shareholders.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- WestJet Airlines - Ivey Publishing - Case Study SolutionsDocument7 pagesWestJet Airlines - Ivey Publishing - Case Study SolutionsNest Imperial100% (1)
- Diagnostic Test in General MathematicsDocument4 pagesDiagnostic Test in General MathematicsDave Carlos Agustin Calixto100% (1)
- Merck Sharp and Dohme Argentina, Inc.: Written Analysis of CaseDocument4 pagesMerck Sharp and Dohme Argentina, Inc.: Written Analysis of Caseayeshaali20Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cost of Capital 2010Document105 pagesCost of Capital 2010Amit PandeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Bookbinder Case 2Document6 pagesBookbinder Case 2AbcdePas encore d'évaluation
- Mca - 204 - FM & CFDocument28 pagesMca - 204 - FM & CFjaitripathi26Pas encore d'évaluation
- Bookbinders Case StudyDocument11 pagesBookbinders Case StudyJoana ToméPas encore d'évaluation
- 07 Hewlett PackardDocument16 pages07 Hewlett Packard9874567Pas encore d'évaluation
- Debt Policy and ValueDocument7 pagesDebt Policy and ValueMuhammad Nabil EzraPas encore d'évaluation
- Running Head: Chris and Alison Weston 1Document5 pagesRunning Head: Chris and Alison Weston 1Anindya BasuPas encore d'évaluation
- Citibank CaseDocument2 pagesCitibank CaseMichi Kunugi-WangPas encore d'évaluation
- Bookbinders Case StudyDocument4 pagesBookbinders Case Studyleni thPas encore d'évaluation
- Apple Financial ReportDocument3 pagesApple Financial ReportBig ManPas encore d'évaluation
- Synthes SolDocument1 pageSynthes SolAshish KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Dell Case StudyDocument4 pagesDell Case StudyDamian Arias100% (3)
- Westjet Project - Final FinalDocument12 pagesWestjet Project - Final FinalMao KaiPas encore d'évaluation
- CIR v. CA (1999)Document2 pagesCIR v. CA (1999)kaira marie carlosPas encore d'évaluation
- FIN3CSF Case Studies in FinanceDocument5 pagesFIN3CSF Case Studies in FinanceDuy Bui100% (2)
- Primus Automation Division: Group 4Document20 pagesPrimus Automation Division: Group 4Anusha Riaz100% (1)
- Lamson Corporation, SofiDocument3 pagesLamson Corporation, SofiCarlos de la GarzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study - Walmart Update 2017Document6 pagesCase Study - Walmart Update 2017Pharmacist Affaf100% (1)
- Bookbinders Case 2Document6 pagesBookbinders Case 2KATHERINE0% (3)
- Assignment - BioPharm-Seltek Planning Document MBA Case Studies 8527018189 NareshDocument6 pagesAssignment - BioPharm-Seltek Planning Document MBA Case Studies 8527018189 NareshNaresh SehdevPas encore d'évaluation
- Kool King DivisionDocument6 pagesKool King DivisionAkhil GoyalPas encore d'évaluation
- P&G Case AnalysisDocument3 pagesP&G Case AnalysisNikhil ThaparPas encore d'évaluation
- Apple Inc. PESTLE Analysis: Apple Inc. (NASDAQ: AAPL) Is One of The World's Most Visible and Recognizable ConsumerDocument3 pagesApple Inc. PESTLE Analysis: Apple Inc. (NASDAQ: AAPL) Is One of The World's Most Visible and Recognizable ConsumerAmna KabeerPas encore d'évaluation
- Study On The Factors Affecting Investors Decision in Investing in Equity Shares in IndiaDocument104 pagesStudy On The Factors Affecting Investors Decision in Investing in Equity Shares in IndiaHridayanshu RastogiPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study 11 - The Timken Company - Market Entry Into Romania PDFDocument25 pagesCase Study 11 - The Timken Company - Market Entry Into Romania PDFCiprian Teodor Leonte100% (1)
- Emerson Electric Co.Document3 pagesEmerson Electric Co.Silver BulletPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of The Apple Business ModelDocument9 pagesAnalysis of The Apple Business ModelAndrei GiurgiuPas encore d'évaluation
- Agency Problem and The Role of Corporate GovernanceDocument19 pagesAgency Problem and The Role of Corporate GovernanceIan Try Putranto86% (22)
- Business Ethics NestleDocument20 pagesBusiness Ethics NestleAnonymous Cm1mAb100% (2)
- Michelin Fleet Solutions Swot AnalysisDocument6 pagesMichelin Fleet Solutions Swot AnalysisValentino EstebanPas encore d'évaluation
- (Group9) Cyworld Case StudyDocument8 pages(Group9) Cyworld Case StudyamiutamiPas encore d'évaluation
- KFC'Case StudyDocument8 pagesKFC'Case StudyMudit Shejwar0% (1)
- 101 Group3 Visa& Mastercard Assignment FinalDocument14 pages101 Group3 Visa& Mastercard Assignment Finalnguoilaanhsangcuadoitoi_theonePas encore d'évaluation
- Sec2 - Group4 - Hola KolaDocument2 pagesSec2 - Group4 - Hola KolaAmit BiswalPas encore d'évaluation
- BBM Group AssignmentDocument5 pagesBBM Group AssignmentKirat Chhabra100% (1)
- Kering SA: Probing The Performance Gap With LVMH: Case 2Document7 pagesKering SA: Probing The Performance Gap With LVMH: Case 2fioPas encore d'évaluation
- Warren BuffeDocument4 pagesWarren BuffeastrdppPas encore d'évaluation
- BNB Assignment QuestionsDocument2 pagesBNB Assignment QuestionsNeeraj Yadav0% (4)
- Japan's Automakers Face Endaka: Case BackgroundDocument7 pagesJapan's Automakers Face Endaka: Case BackgroundNot RealPas encore d'évaluation
- K9FuelBar Case AnalysisDocument14 pagesK9FuelBar Case AnalysisZuchrizal WinataPas encore d'évaluation
- 17020841116Document13 pages17020841116Khushboo RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Company ProfileDocument18 pagesCompany ProfileJenny GonzagaPas encore d'évaluation
- Project Quality Assurance, Human Resources & Communication Management Individual Assignment GATLA KARTHIK RAO - 110022238Document4 pagesProject Quality Assurance, Human Resources & Communication Management Individual Assignment GATLA KARTHIK RAO - 110022238Karthik RaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study K9FUELBARDocument2 pagesCase Study K9FUELBARAnonymous xH0aLu100% (1)
- Southwest Airlines - Case AnalysisDocument5 pagesSouthwest Airlines - Case AnalysisshalinpshahPas encore d'évaluation
- Netflix CaseDocument3 pagesNetflix CaseSalman EjazPas encore d'évaluation
- CadburyDocument19 pagesCadburynemchand0% (1)
- Cola WarsDocument3 pagesCola Warshithot3210Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter11 PDFDocument25 pagesChapter11 PDFBabuM ACC FIN ECOPas encore d'évaluation
- Intal BRND MGMT Q's For The CasesDocument5 pagesIntal BRND MGMT Q's For The CasesAnkaj MohindrooPas encore d'évaluation
- People Express Briefing NotesDocument6 pagesPeople Express Briefing NotesGoeedang JournalPas encore d'évaluation
- SFM Case Study CIA 3Document8 pagesSFM Case Study CIA 3Kriti ShahPas encore d'évaluation
- Strategic Management: Case AnalysisDocument28 pagesStrategic Management: Case AnalysisMohsin BashirPas encore d'évaluation
- XLS EngDocument21 pagesXLS EngRudra BarotPas encore d'évaluation
- BlackberryDocument33 pagesBlackberrybhumi_78669100% (1)
- Wyndham International HotelsDocument3 pagesWyndham International HotelsCabron InDaZonePas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Ratios-Hamna RizwanDocument5 pagesFinancial Ratios-Hamna RizwanHamna RizwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Operating in The Age of The Industrial Internet of Things (Iiot)Document12 pagesOperating in The Age of The Industrial Internet of Things (Iiot)Tareq Ziad KhalifaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Subprime Crisis ExplainedDocument9 pagesThe Subprime Crisis ExplainedMaverick TarsPas encore d'évaluation
- XEROX Study CaseDocument2 pagesXEROX Study Casemiranza100% (1)
- Hola Kola Case StudyDocument3 pagesHola Kola Case StudyRaenessa FranciscoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ratio Analysis: Liquidity RatiosDocument16 pagesRatio Analysis: Liquidity RatiosYamen SatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Banking and Allied Laws CasesDocument330 pagesBanking and Allied Laws Casesalmostthere22Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ezzell Enterprises Has The Following Capital Structure Which It ConsidersDocument2 pagesEzzell Enterprises Has The Following Capital Structure Which It ConsidersAmit PandeyPas encore d'évaluation
- 6948 26864 1 PBDocument9 pages6948 26864 1 PBmughalPas encore d'évaluation
- Particulars Yes NoDocument16 pagesParticulars Yes Nokashyappathak01Pas encore d'évaluation
- E-Fund Management SystemDocument61 pagesE-Fund Management SystemPrayag Raj GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- IFR - Asia 19.march.2022Document58 pagesIFR - Asia 19.march.2022Belu IonPas encore d'évaluation
- The Role of Managerial Finance: ProfessionalDocument39 pagesThe Role of Managerial Finance: ProfessionalYoong Xuen XuenPas encore d'évaluation
- SVFC BS Accountancy - 2nd Set Online Resources SY20-19 1st Semester PDFDocument11 pagesSVFC BS Accountancy - 2nd Set Online Resources SY20-19 1st Semester PDFLorraine TomasPas encore d'évaluation
- Swot Analysis of AssetsDocument8 pagesSwot Analysis of Assetsshinjan bhattacharyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Summer Moon Presentation December 13,2004Document25 pagesSummer Moon Presentation December 13,2004Essam Al BakryPas encore d'évaluation
- Modigliani Miller Prop 1 and 2 PDFDocument8 pagesModigliani Miller Prop 1 and 2 PDFChittisa CharoenpanichPas encore d'évaluation
- SA Case StudyDocument6 pagesSA Case StudyKanika MaheshwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Econ Chapter 7 Section 1ADocument3 pagesEcon Chapter 7 Section 1AAbi CalderalePas encore d'évaluation
- CORPORATIONS For BSBA ABMDocument15 pagesCORPORATIONS For BSBA ABMmaysel qtPas encore d'évaluation
- Circulars/Notifications: Legal UpdateDocument6 pagesCirculars/Notifications: Legal UpdateNaveen kumar MedishettyPas encore d'évaluation
- Corporate FinanceDocument66 pagesCorporate FinanceRobin SrivastavaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 NumericalsDocument10 pagesChapter 1 NumericalsPradeep GautamPas encore d'évaluation
- Faculty of Commerce & Law Department of Accounting & Auditing Bacc106: Financial Accounting 2 Assignment 1 January - June 2021 InstructionsDocument3 pagesFaculty of Commerce & Law Department of Accounting & Auditing Bacc106: Financial Accounting 2 Assignment 1 January - June 2021 Instructionsperseverance mutosvoriPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2Document73 pagesChapter 2Eyu DesPas encore d'évaluation
- Semantic MapDocument1 pageSemantic MapMarian Kaye OrlanesPas encore d'évaluation
- MBOF912D-Financial Management-Assignment-1Document15 pagesMBOF912D-Financial Management-Assignment-1Utkarsh Singh0% (1)
- A Presentation On National Stock ExchangeDocument10 pagesA Presentation On National Stock ExchangeMohit SuranaPas encore d'évaluation
- Revision Test-01 (1,2,3,14,15) SOL.Document8 pagesRevision Test-01 (1,2,3,14,15) SOL.Muhammad FaisalPas encore d'évaluation
- Duty Free International Limited (DFI)Document9 pagesDuty Free International Limited (DFI)TSEDEKEPas encore d'évaluation
- MBA711 - Chapter11 - Answers To All Homework ProblemsDocument17 pagesMBA711 - Chapter11 - Answers To All Homework ProblemsGENIUS1507Pas encore d'évaluation