Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Aura One Mark Question and Answers
Transféré par
mohanmech2006886Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Aura One Mark Question and Answers
Transféré par
mohanmech2006886Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
AURA ACADEMY IIT STUDY CIRCLE - 9TH FOUNDATION PHYSICS PART B-OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTIONS CENTRE OF MASS AND
EQUILIBRIUM OF RIGID BODIES 1) A disc and a sphere of the same mass and radius are rolling. Their kinetic energies are equal. The ratio of their velocities is: (a) 10 : 7 (b) 7 : 10 (c) 2 : 5 (d) 5 : 2 2) A flywheel rotating about a fixed axis has angular speed 20 rad/s 1 and kinetic energy 360 J. The moment of inertia of the flywheel is : (a) 1.8 kg m2 (b) 2.5 kg m2 (c) 18kgm2 (d) none of these 3) If the angular momentum of a body increases by 40% its kinetic energy of rotation increases by : (a) 80% (b) 20% (c) 96% (d) none of these 4) A solid sphere of mass 2 kg rolls on a table with the linear speed 3 m/s. Its total kinetic energy is: (a) 15 J (b) 18 J (c) 12.6 J (d) 11.5 J 5) A uniform ring of mass 20 kg and radius 0.2 m is making 420/22 revolutions per minute about its geometrical axis then, the rotational kinetic energy of the ring about the axis is : (a) 22 kj (b) 1.6 J (c) 1.8 J (d) none of these 6) A disc at rest have angular velocity 30 rad/s in 6 sec, with a constant angular acceleration. The total angle turned during this interval is : (a) 216 rad (b) 144 rad (c) 108 rad (d) 90 rad 7) Two bodies A and B initially at rest, move towards each other under a mutual force of attraction. At the instant when the speed of A is v and the speed of B is 2v, the speed of the centre of mass of the system is : (a) zero (b) 3v (c) l.5v (d) v 8) If a body completes a vertical circle, then (a) total energy of body remains constant (b) angular momentum remains constant (c) angular velocity remains constant (d) none of the above 9) Moment of inertia of a copper sphere : (a) Depends upon temperature (b) Depends upon angular velocity (c) Depends upon the position of axis of rotation (d) Both (a) and (c) are correct 10) Mark correct option or options : (a) For neutral equilibrium, the potential energy is constant (b) In stable equilibrium, potential energy is minimum (c) For unstable equilibrium, potential energy is neither constant nor minimum (d) All the above
11) If a body is moving on a horizontal table with constant velocity, then equilibrium is : (a) stable (b) unstable (c) neutral (d) none of these 12) The moment of inertia of a uniform solid right circular cone of mass 10 kg, height 2 m and vertical angle 90 about a diameter of its base, is : (a) 10 kgm2 (b) 20 kgm2 (c) 30 kgm2 (d) none of these 13) Ram says, "A body may be in pure rotation in the presence of a single external force." Shyam says, "This is possible only for a non rigid body", then : (a) Ram's statement is correct (b) both statements are correct in different situations (c) both statements are wrong (d) both statements are stated by physicists 14) The formula that torque equals the rate of change of angular momentum is true in following general cases: (a) a fixed axis in inertial space (b) an axis through the centre of mass even though the object may be accelerating (c) a variable axis in inertial space (d) Both (a) and (c) are correct 15) Mark correct option or options : (a) The vector product of two polar vectors may be axial vector (b) The vector product of two polar vectors must be axial vector (c) The sense of direction of axial vector depends on the handedness of reference frame (d) Both (b) and (c) are correct 16) If a raw egg and a boiled egg are spinned on the table by applying same torque, then : (a) Boiled egg will spin faster (b) Raw egg will spin faster (c) Moment of inertia of boiled egg will be lesser than that of the raw egg (d) Both (a) and (c) are correct 17)Mark correct option or options : (a) The centre of gravity may be coincided with centre of mass (b) Due to movement of body, centre of gravity changes but centre of mass does not change (c) The centre of gravity must not be coincided with the centre of gravity (d) The centre of gravity is always above the centre of mass 18) At any instant, a rolling body may be considered to be in pure rotation about an axis through the point of contact. This axis is translating forward with speed : (a) equal to centre of mass (b) zero (c) twice of centre of mass (d) no sufficient data 19) In the case of falling, rolling and sliding from same height:
(a) the falling body reaches bottom first and rolling at last (b) the acceleration is maximum in falling and minimum in rolling (c) the velocity of sliding is greater than that of rolling (d) all the above 20) A circular disc of radius R rolls without slipping along the horizontal surface with constant velocity % We consider a point A on the surface of the disc. Then the acceleration of the point A is : (a) constant (b) constant in magnitude (c) constant in direction (d) constant in magnitude as well as direction
GRAVITATION 1) The radius of the earth shrinks by 1%. The acceleration due to gravity on the earth's surface would (mass remaining constant): (a) Increase by 2% (b) increase by 1% (c) decrease by 1% (d) decrease by 0.5% 2) If Fj is the magnitude of the force exerted on earth by moon and is the magnitude of force exerted on moon by earth then : (a) FJ>F2 (b) F1=F2 (c) Fj < F2 (d) none of these 3) The gravitational force of attraction between two spherical bodies, each of mass 100 kg, if the 1 distance between their centers is 100 m, is: (G = 6.67 x 10 Nm2 kg2) (a) 6.67 x 10 N (b) 6.67xl09N (c) 6.67 N (d) none of these 4) A particle is fired vertically upwards with a speed of v = V0.8 ve. If the radius of the earth is Re then the maximum height attained by the particle will be: (a) Re (b) 2Re n (c) 3Re (d) 4Re 5) A planet has radius and mass, both half of those of the earth, then the value of g on that planet will be : (a) 4.9 m/s2 (b) 9.8 m/s2 (c) 19.6 m/s2 (d) 13.8 m/s2 6) A body is projected vertically from the earth's surface with velocity equal to half of the escape velocity. Maximum height reached by the body is : R (a) Density of the planet (b) mass of the planet (c) radius of the planet (d) mass of the satellite 7) A body is projected with escape velocity 11.2 km/s from earth's surface. If the body is projected in a direction 30 angle to the vertical, its escape velocity in this case will be:
-1
8) A planet is moving in an elliptical orbit. If T, V, E and L are respectively the kinetic energy, potential energy, total energy and the magnitude of the angular momentum of the planet then the true statement out of the following is: (a) T is conserved (b) V is always positive (c) E is always negative (d) L is conserved but the direction continuously changes 9)The gravitational field in a E = (51 + 12 ]) N/kg then the gravitational force acting on a particle of mass 2 kg placed at the origin, will be : (a) Zero (b) 13 N (c) 26 N (d) 75 N 10) If the radius of the earth reduces by 4% density remaining the same, then the escape velocity will: (a) Increase by 4% (b) increase by 2% (c) Decrease by 4% (d) decrease by 2% 11) The time period of artificial satellite in a circular orbit of radius R is T. The radius of the orbit in which time period is 8T is: 15. (a) 2R (b) 3R (c) 4R (d) 5R 12) A satellite is orbiting very close to planet. Its time period depends only upon : (a) Density of the planet (b) mass of the planet (c) radius of the planet (d) mass of the satellite 13) The gravitational force of attraction between two spherical bodies, each of mass 1 kg placed at 10 m 1 apart (G = 6.67 x 10 1 Nm2/kg2) is: 1 -1 a) 6.67 x 10" 3 N (c) 6.67 x 10 N (b) 6.67 x 10 1 N (d) none of these 14) The gravitational potential difference between the surface of a planet and a point 20 m above it is 16 J /kg. Then the work done in moving a 2 kg mass by 8 m on a slope 60 from the horizontal, is : (a) 11.1 J (b) 5.55 J (c) 16 J 15) At the surface of a certain planet acceleration due to gravity is one-quarter of that on the earth. If a brass ball is transported to this planet, then which one of the following statements is not correct ? (a) The mass of the brass ball on this planet is quarter of its mass as measured on the earth (b) The brass ball has same mass on the other planet as on the earth (c) The brass ball has same volume on the other planet as on the earth (d) None of the above 16) If the radius of earth decreases by 10%, the mass remaining unchanged, what will happen to the acceleration due to gravity? (a) Decreases by 19% (b) Increases by 19% (c) Decreases by more than 19% (d) Increases by more than 19%
17)If earth were to rotate faster than its present speed, the weight of an object will: (a) Increase at the equator but remain unchanged at poles (b) Decrease at the equator but remain unchanged at the poles (c) Remain unchanged at the equator but decrease at the poles (d) Remain unchanged at the equator but increase at the poles 18) If the earth stops rotating about its axis, the acceleration due to gravity will remain unchanged at: (a) equator (b) latitude 45(c) latitude 60 (d) poles 19) The work done by an external agent to shift a point mass from infinity to the centre of earth is : (a) =0 (b) >0 (c) <0 (d) <0 20) A satellite S is moving in an elliptical orbit around the earth. The mass of the satellite is very small compared to the mass of the earth : (a) The acceleration of S is always directed towards the centre of the earth (b) The angular momentum of S about the centre of the earth changes in direction but its magnitude remains constant (c) The total mechanical energy of S varies periodically with time (d) The linear momentum of S remains constant in the magnitude
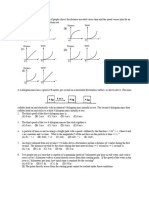
MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF SOLIDS AND LIQUIDS 1) Youngs modulus is defined for : (a) solid (b) liquid (c) gas (d) all of these 2) What will happen if a metal wire is stretched a little beyond its elastic limit (or yield point) and released ? (a) It loses its elastic property completely (b) It does not contract (c) It contracts, but its final length will be greater than its initial length (d) It contracts only up to its length at the elastic limit 1) Which of following graphs satisfies the Hooke's law under elastic limit ?
4) Elongation-load graph within elastic limit i? shown in figure of three wires A, B and C made of same material and of same length. The thickest wire is : (a) A (b) B (c) C (d) none of the above
5) Surface tension of liquid : (a) rises with rise in temperature (b) fall with rise in temperature (c) is independent of temperature (d) none of the above 6) A long rod of radius 1 cm and length 2 m which is fixed at one end is given a twist of 0.8 radian. The shear strain developed will be :
(a) 0.002 (b) 0.004 (c) 0.008 (d) 0.016 7) When a rubber cord is stretched, the change in volume with respect to change in its linear dimension is negligible, the Poisson's ratio for rubber is : (a) 1 (b) 0.25 (c) 0.5 (d)1.5 8) The Young's modulus and Bulk modulus of elastic material is 7 x 1010 Nm-2 and 11 x 1010 Nm-2 respectively then the Poisson's ratio of the material is : (a) 0.12 (b) 0.24 (c) 0.31 (d) 0.39 9) When does an elastic metal rod change its length ? (a) (b) (c) (d) If it fall vertically under its weight If it is pulled along its length by a force acting at one end If it is rotated about an axis at one end If it slides on a smooth surface
10) The dimensions of Poisson's ratio is : (a) [MLT0] (b) [M1T4] (c) [ML1T2] (d) [ML2T3] 11) A boy carries a fish in one hand and a bucket of water in the other hand; if he places the fish in the bucket, the weight now carried by him : (a) is less than before (b) is more than before (c) is the same as before (d) depends upon his speed 12) A boat full of scrap iron is floating on water in a lake. If all the iron is dropped into water the level of water will: (a) go up (b) remain the same (c) rise very high (d) go very deep 13) Which of the following is/are correct about pressure ? (a) Pressure at a point acts equally in all directions (b) Liquid at rest exerts lateral pressure which decreases with depth (c) Pressure acts normally on any area whatever orientation the area may be held (d) Both (a) and (c) are correct 14) The pressure at the bottom of a tank of liquid is not proportional to : (a) the density of the liquid
(b) the area of the liquid surface (c) the height of the liquid (d) the acceleration 15) If a liquid is subjected to a horizontal acceleration then : (a) slope of the liquid is inversely proportional to the horizontal acceleration (b) slope of the liquid is directly proportional to the horizontal acceleration (c) there is no direct relation between acceleration and inclination (d) none of above 16) A glass bulb is balanced by a brass weight in a sensitive beam balance. Now the balance is covered by a glass-jar which is then evacuated. Then : (a) the beam will remain horizontal (b) the pan containing the bulb will go down (c) the pan containing the bulb (d) none of the above 17) A block of wood floats with 1/4 of its volume under water. What is the density of the wood ? (Density of water = 1000 kg/m3) (a) 750 kg/m3 (b) 250 kg/m3 (c) 300 kg/m3 (d) 260 kg/m3 18) A boat is floating on the surface of water in a tank carrying steel balls. If the balls are thrown into the tank one by one, how will it affect the level of water ? (a) It will rise (b) It will fall (c) It will remain unchanged (d) First it will rise and then fall 19) A solid floats in a liquid in the partially submerged position : (a) the solid exerts a force equal to its weight on the liquid
(b) the liquid exerts a force of buoyancy on the solid which is equal to the weight of the solid (c) the weight of the displaced liquid equals the weight of the solid (d) all the above 20) A solid is completely immersed in a liquid. The force exerted by the liquid on the solid will: (a) increase if it pushed deeper inside the liquid (b) change if its orientation is changed (c) decrease if it is taken partially out of the liquid (d) none of the above
HEAT AND THERMODYNAMICS 1) Which of the following parameters does not characterize the thermodynamic state of matter ? (a) Volume (b) Temperature (c) Pressure (d) Work 2) Internal energy of ideal gas depends on : (a) only pressure (b) only volume (c) only temperature (d) none of these 3) In a thermodynamic system working substance is ideal gas, its internal energy is in the form of: (a) kinetic energy only (b) kinetic and potential energy (c) potential energy (d) none of the above 4) The first law of thermodynamics is essentially a statement: (a) implying that heat cannot flow from a cold body to a hot body (b) of conservation of energy (c) that gives the mechanical equivalent of heat (d) regarding isothermal process
5) If the door of a refrigerator is kept open, then which of following is true ? (a) Room is cooled (b) Room is heated (c) Room is either cooled or heated (d) Room is neither cooled nor heated 6) The process in which the heat is not transferred from one state to another, is : (a) isothermal process (b) adiabatic process (c) isobaric process (d) isochoric process 7) When the pressure of water is increased, the boiling temperature of water as compared to 100C will be: (a) lower (b) the same (c) higher (d) on the critical temperature
8) For an isolated system : (a) volume is constant (b) pressure is constant (c) temperature is constant (d) all of the above 9) The change in internal energy of perfect gas will be: (a) Cy x A0 (b) CPx AO (c) (Cp-Cy) AO (d) (Cp + Cy) A9 10) Triple point of water is : (a) 273.16 F (b) 273.16 K (c) 273.16 C (d) 273.16 R 11) A thermodynamical system is changed from state (Pi, V]) to (P2, V2) by two different processes, the quantity which will remain same will be : (a) AQ (b) AQ (c) AQ + AW (d) AQ-AW 12) Work done in converting one gram of ice at - 10C into steam at 100C is : (a) 3045 ] (b) 6056 J (c) 721 J (d) 616 J 13) An ideal gas undergoes an isothermal change in volume with pressure then : (a) PyV = constant (b) PVy = constant (c) (PV)y= constant (d) PV = constant 14) A block of mass 100 g slides on a rough horizontal surface. If the speed of the block decreases from 10 m/s to 5 m/s, the thermal energy developed in the process is : (a) 3.75 J (b) 37.5 J (c) 0.375 J (d) 0.75 J 15) If the heat of 110 J is added to a gaseous system and change in internal energy is 40 J, then the amount of external work done is : (a) 140 J (b) 70 J (c) 110 J (d) 150 J
16) When a gas is allowed to expand suddenly into a vacuum chamber, then: (a) heat supplied is zero (b) temperature remains constant (c) volume does not change (d) both (a) and (b) are correct 17) During an isothermal expansion of an ideal gas : (a) its internal energy decreases (b) its internal energy does not change (c) the work done by the gas is equal to the quantity of heat absorbed by it (d) both (b) and (c) are correct 18) If a gas is compressed adiabatically : (a) the internal energy of gas increases (b) the internal energy of gas decreases (c) the internal energy of gas does not change (d) the work done is positive 19) In a polytropic process, PV n = constant: (a) If n = 1, process is isothermal (b) If n = process is isochoric (c) If n = 0, process is isobaric (d) all the above 20) In a given process for ideal gas, dW = 0 and dH > 0. Then for the gas : (a) the volume remains constant (b) the volume will increase (c) temperature will increase (d) both (a) and (c) are correct OSCILLATIONS AND SOUND
1) Which of the following is the longitudinal wave ? (a) Sound waves (b) Waves on plucked string (c) Water waves (d) Light waves 2) Which of following can not travel through vacuum ? (a) Electromagnetic wave (b) Sound wave (c) Light wave (d) X-ray 3) A longitudinal wave consists of: (a) rarefactions and compressions (b) only compressions (c) only rarefactions (d) crest and trough 4) The velocity of sound is maximum in : (a) C02 (b) S02 (d) none of these 5) According to Laplace correction, the propagation of sound in gas takes place under : (a) isothermal condition (b) isobaric condition (c) isochoric condition (d) adiabatic condition 6) The velocity of sound in water is 1400 m/s. The density of water is 1000 kg/m . The bulk modulus of elasticity is :
(a) 5xlO11 N/m2 (b) 1.96xlO9 N/m2 (c) 4 x 109 N/m2 (d) none of these 7) The ratio of speed of ultrasonic wave and sound wave is : (a) =1 (b) >1 (c) <1 (d) >1 8) The sound of lightning flash is heard 3 second after the flash is seen. The distance of the lightning is 1020 metre. The speed of sound is : (a) 1400 m/s (b) 332 m/s (c) 340 m/s (d) none of these 9)The speed of sound in air is 340 m/s, while in water is 1445 m/s. If the wavelength of sound in water is 8.5 cm, the wavelength of sound in air is : (a) 2 cm (b) 4.5 cm (c) 5.5 cm (d) 8.5 cm 10)At which temperature, velocity of sound at 27C doubles ? (a) 54C (b) 327C (c) 927C (d) -123C 11)Calculate the speed of sound in oxygen at 0C and 1 atm. (Bulk modulus of elasticity of 02 is 1.41 x 105 Pa and density is 1.43 kg/m ) : (a) 300 m/s (b) 340 m/s (c) 314 m/s (d) none of these 11) Consider the following statements : Assertion (A): Due to variation of pressure, speed of sound does not change. Reason (R) : The variation of pressure is proportional to variation of density. (a) Both A and R are correct and R is the correct explanation of A (b) R is the wrong explanation of A (c) Both A and R are wrong (d) A is wrong but R is correct 12) An astronaut can not hear his companion's sound at the surface of moon because : (a) produced frequencies are above the audio frequency (b) sound wave does not propagate through vacuum (c) temperature is too low during night and high during day (d) none of the above 13) The speed of sound in air is 333 m/s. The fundamental frequency of the open pipe is 333 Hz. The second overtone of the open organ pipe can be produced with a pipe of length : (a) 0.5 m (b) 1 m (c) 1.5 m (d) 2 m 14) Velocity of sound waves in air is 330 m/s. For a particular sound in air, a path difference of 40 cm is equivalent to a phase difference of 1.6 n. The frequency of this wave is: (a) 165 Hz (b) 150 Hz (c) 660 Hz (d) 330 Hz 15) Which one is not produced by sound waves in air ? (a) Polarisation (b) Diffraction (c) Refraction (d) Reflection 16) the resultant amplitude due to superposition of both equations is: (a) <2 a (b) a (c) 2a (d) none of these 17) The ratio of amplitudes at distances r and 3r from a point Source is: (a) 3 : 1 (b) 3 : 2 (c) 1 : 3 (d) 2 : 3 18) The intensity for loudness 20 dB is : (a) 10watt/m2 (b) 10"10watt/m2 (c) 1010 watt/m2 (d) none of these 19) If two sources of loudness 20 dB is combined, the resultant loudness is: (a) 23 dB (b) 30 dB (c) 40 dB (d) 10 dB 20) If intensity of sound wave is increased nine times, then by what factor the pressure amplitude of the wave is increased ?
(a) 3 (b) 6 (c) 9 (d) V3
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 11.7-8, TEST - ROTATION AND GRAVITATION COMBINED MCQs 21-22Document6 pages11.7-8, TEST - ROTATION AND GRAVITATION COMBINED MCQs 21-22AJAY SINGH RAGHAVPas encore d'évaluation
- NEET: (11th) Rotational Motion: QuestionsDocument32 pagesNEET: (11th) Rotational Motion: QuestionsSuriyanarayana KPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Chapter 5Document3 pagesAssignment Chapter 5MuhammadKhalidRehanChPas encore d'évaluation
- 11c Uniform Circular Motion WsDocument7 pages11c Uniform Circular Motion WsKunal B MehtaPas encore d'évaluation
- 08 Rotation PDFDocument16 pages08 Rotation PDFAadit Kumar SahooPas encore d'évaluation
- Laws of Motion QnsDocument6 pagesLaws of Motion QnsChennaiSuperkingsPas encore d'évaluation
- Gravitation MCQ TestDocument2 pagesGravitation MCQ TestrhythmPas encore d'évaluation
- XI' Physics Examination 2022: Section A' (Multiple Choice Questions)Document4 pagesXI' Physics Examination 2022: Section A' (Multiple Choice Questions)Muneeb AlamPas encore d'évaluation
- CH-8 GravitationDocument16 pagesCH-8 Gravitationnm.ananya2008Pas encore d'évaluation
- XI Physics OriginalDocument7 pagesXI Physics OriginalRiya RPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 11-Physics - English Medium - Study Materials Download - S.ranganathanDocument32 pagesClass 11-Physics - English Medium - Study Materials Download - S.ranganathanSasi RekhaPas encore d'évaluation
- USAPhO Problems (2007-2014)Document311 pagesUSAPhO Problems (2007-2014)Science Olympiad Blog95% (19)
- Class Ix Physics GRNT TestDocument3 pagesClass Ix Physics GRNT Testkhizramubeen991Pas encore d'évaluation
- NDA Physics MCQs For PracticeDocument10 pagesNDA Physics MCQs For Practicekumar HarshPas encore d'évaluation
- (A) 2 KG, (6 M/S) IDocument10 pages(A) 2 KG, (6 M/S) Ikush jindalPas encore d'évaluation
- Paper II GeophysicsDocument24 pagesPaper II GeophysicsNavin SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Paper +1 Physics September 2022Document7 pagesSample Paper +1 Physics September 2022Sukhwinder KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Crash Chapter 4 TestDocument4 pagesCrash Chapter 4 TestKamran Ali100% (1)
- 11 GravitationDocument24 pages11 GravitationSamsul BahriPas encore d'évaluation
- Center of Mass and The Motion of A SystemDocument13 pagesCenter of Mass and The Motion of A SystemNitin SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- 11th Physics NEET 1 Mark Vol-2 EMDocument53 pages11th Physics NEET 1 Mark Vol-2 EMjohnsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Rotat PDFDocument54 pagesRotat PDFSai PragathiPas encore d'évaluation
- Phy 01Document212 pagesPhy 01Varsha Dange100% (1)
- Rotational 1Document6 pagesRotational 1Chandrakala UpretiPas encore d'évaluation
- 11th Physics PT-2Document2 pages11th Physics PT-2raghavendra jPas encore d'évaluation
- GRM M M GR M GRM M GRM: Section - A: (Physics)Document22 pagesGRM M M GR M GRM M GRM: Section - A: (Physics)pskphyPas encore d'évaluation
- P0IITU05 - Rotational Motion QnsDocument7 pagesP0IITU05 - Rotational Motion QnsxTERMINATOR007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Aims Entry Test Preparation: "Aim High"Document8 pagesAims Entry Test Preparation: "Aim High"Kinza ZafarPas encore d'évaluation
- Circular Motion - ObjectiveDocument28 pagesCircular Motion - ObjectiveUday Prakash SahuPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 6 GravitationDocument5 pagesUnit 6 GravitationSabia IdrisiPas encore d'évaluation
- 05 Circular MotionDocument8 pages05 Circular MotionVaibhav TripathiPas encore d'évaluation
- 10 Physics Laws of MotionDocument3 pages10 Physics Laws of MotionHasan shaikhPas encore d'évaluation
- AP Physics C 1988 With AnswersDocument18 pagesAP Physics C 1988 With AnswersjhbmleePas encore d'évaluation
- 1993 MC MechDocument7 pages1993 MC MechryumilovePas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanics Practice Papers 2Document13 pagesMechanics Practice Papers 2Sarvesh DubeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter Questions Uniform Circular Motion Newton S Law PF Gravitation and Rotational MotionDocument9 pagesChapter Questions Uniform Circular Motion Newton S Law PF Gravitation and Rotational MotionJunLi CaiPas encore d'évaluation
- PT 1Document8 pagesPT 1LOVELESH KHATTERPas encore d'évaluation
- Half Yearly Paper Physics Class-Xi M.Makrs-60 Questions 1 To 20 (1 Marks)Document6 pagesHalf Yearly Paper Physics Class-Xi M.Makrs-60 Questions 1 To 20 (1 Marks)Darth VaderPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit I and Unit II Multiple Choice Practice TestDocument11 pagesUnit I and Unit II Multiple Choice Practice TestChristian Firsching0% (1)
- MCQ - Rotationalfor IITDocument58 pagesMCQ - Rotationalfor IITAfifahPas encore d'évaluation
- QPDocument5 pagesQPSamuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Circular Motion (MCQ)Document17 pagesCircular Motion (MCQ)Laxman Selvam100% (5)
- Work, Energy and Power - S.R. - Part - 1Document7 pagesWork, Energy and Power - S.R. - Part - 1Abhimanyu BhasinPas encore d'évaluation
- 002 VectorsDocument9 pages002 VectorsVaibhav TripathiPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 Rot Motion MCQ PDFDocument2 pages11 Rot Motion MCQ PDFtanmayPas encore d'évaluation
- MCQ Test 9Document3 pagesMCQ Test 9Itu DeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Aipmt 2000Document49 pagesAipmt 2000pravinkhartadPas encore d'évaluation
- QUIZ-6-PCM-LOT-A, B & C CLASS XIthDocument10 pagesQUIZ-6-PCM-LOT-A, B & C CLASS XIthSubhashPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 Phy - Set B Ut-2Document4 pages11 Phy - Set B Ut-2dikshachoud44Pas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Mega Test (Part-1)Document14 pagesPhysics Mega Test (Part-1)vighneshwarvickyPas encore d'évaluation
- The Indian Community School, Kuwait: Code: M 042Document7 pagesThe Indian Community School, Kuwait: Code: M 042Lalitha GorantlaPas encore d'évaluation
- P2 PDFDocument2 pagesP2 PDFMasoom BhurgriPas encore d'évaluation
- Class Xi Physics Sample PaperDocument7 pagesClass Xi Physics Sample PaperHarekrishna DasPas encore d'évaluation
- Work and Energy WorksheetDocument24 pagesWork and Energy Worksheetcreativeinfinity18Pas encore d'évaluation
- Momentum MCQ 211Document4 pagesMomentum MCQ 211Kariem Mohamed Ragab Hamed100% (1)
- Phy102 Practise Problems For Exam2Document4 pagesPhy102 Practise Problems For Exam2Renz Dane TametaPas encore d'évaluation
- SOM Question BankDocument9 pagesSOM Question Bankmohanmech2006886Pas encore d'évaluation
- Kongu Engineering College Perundurai Erode - 638 060 (Autonomous) Academic CellDocument14 pagesKongu Engineering College Perundurai Erode - 638 060 (Autonomous) Academic Cellmohanmech2006886Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ventura 2009Document3 pagesVentura 2009mohanmech2006886Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2D TransformationDocument31 pages2D Transformationmohanmech2006886Pas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT II Need For PPC-Objectives-Functions-Information Required For PPC-ProductionDocument30 pagesUNIT II Need For PPC-Objectives-Functions-Information Required For PPC-Productionmohanmech2006886Pas encore d'évaluation
- 06 August 2021 09:13 AM: New Section 9 Page 1Document2 pages06 August 2021 09:13 AM: New Section 9 Page 1mohanmech2006886Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rapid Technologies in Integrated Product Development B. Dyba A, E. Chlebus, T. BoratyñskiDocument4 pagesRapid Technologies in Integrated Product Development B. Dyba A, E. Chlebus, T. Boratyñskimohanmech2006886Pas encore d'évaluation
- Safe Use of Metal Turning Lathes: Guidance NoteDocument8 pagesSafe Use of Metal Turning Lathes: Guidance Notemohanmech2006886Pas encore d'évaluation
- Stereo LithographyDocument21 pagesStereo Lithographymohanmech2006886Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapt13 - Kinetics of Particle - Energy and MomentumDocument88 pagesChapt13 - Kinetics of Particle - Energy and Momentummohanmech2006886Pas encore d'évaluation
- Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation F : GravityDocument16 pagesNewton's Law of Universal Gravitation F : Gravitymohanmech2006886Pas encore d'évaluation
- NITT CalendarDocument12 pagesNITT Calendarmohanmech2006886Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hy PresDocument46 pagesHy Presmohanmech2006886Pas encore d'évaluation
- CTP Teaching & Test Units 2013Document4 pagesCTP Teaching & Test Units 2013mohanmech2006886Pas encore d'évaluation
- Final ReviewDocument34 pagesFinal Reviewmohanmech2006886Pas encore d'évaluation
- Area Circle 1Document2 pagesArea Circle 1mohanmech2006886Pas encore d'évaluation
- COMSOL ApplicationLibraryManualDocument390 pagesCOMSOL ApplicationLibraryManualJessicaTorresRedondoPas encore d'évaluation
- Virtual Artificial Sensor Technique For Functional Electrical StimulationDocument11 pagesVirtual Artificial Sensor Technique For Functional Electrical StimulationCarlos Alexandre FerriPas encore d'évaluation
- Elements, Compounds, and MixturesDocument35 pagesElements, Compounds, and Mixturesapi-419037032Pas encore d'évaluation
- PVP2008-Hinnant and PaulinDocument50 pagesPVP2008-Hinnant and PaulinFeliper65Pas encore d'évaluation
- Blast Fragmentation Appraisal - Means To Improve Cost-Effectiveness in MinesDocument14 pagesBlast Fragmentation Appraisal - Means To Improve Cost-Effectiveness in Minespartha das sharma100% (1)
- 4 Bar HingeDocument9 pages4 Bar HingelalalamxPas encore d'évaluation
- Gaussian Elimination SpreadsheetDocument2 pagesGaussian Elimination Spreadsheetrodwellhead0% (1)
- De Silva Clarence W Sensors and Actuators Control Systems InstrumentationDocument346 pagesDe Silva Clarence W Sensors and Actuators Control Systems Instrumentationjhon jairoPas encore d'évaluation
- Parts Catalog (EX1200-6 LC-Type - With 1000 1100 MM Shoes) (EPM18J-OP2-1)Document40 pagesParts Catalog (EX1200-6 LC-Type - With 1000 1100 MM Shoes) (EPM18J-OP2-1)Sonta Kuguh0% (1)
- Solid-Solid Separation: Screening: LecturerDocument24 pagesSolid-Solid Separation: Screening: LecturerJane Eilyza AballaPas encore d'évaluation
- Considerations For Operating Pressure Vessels Below - 20°F PDFDocument14 pagesConsiderations For Operating Pressure Vessels Below - 20°F PDFAdnan SheikhPas encore d'évaluation
- Free Standing Tension StructuresDocument255 pagesFree Standing Tension StructuresJoaquin VieraPas encore d'évaluation
- Jack Houck - Excerpt From Energy Healing and PsychokinesisDocument12 pagesJack Houck - Excerpt From Energy Healing and PsychokinesisTuytm2Pas encore d'évaluation
- (C) Extraction of Agarwood Using Supercritical (Thailand Mahidol University)Document5 pages(C) Extraction of Agarwood Using Supercritical (Thailand Mahidol University)asiapowerdrivePas encore d'évaluation
- A Guide To HysysDocument135 pagesA Guide To HysysJack Johnson100% (1)
- Deleuze and The Genesis of Form PDFDocument6 pagesDeleuze and The Genesis of Form PDFRoman RuizPas encore d'évaluation
- Navigat X Mk1 DatasheetDocument2 pagesNavigat X Mk1 DatasheetcristianocalheirosPas encore d'évaluation
- An Essay On Condensed Matter Physics in The Twentieth CenturyDocument19 pagesAn Essay On Condensed Matter Physics in The Twentieth CenturyEmmanuel ZamoranoPas encore d'évaluation
- Water Activity and Food StabilityDocument15 pagesWater Activity and Food Stabilityanur3a31Pas encore d'évaluation
- Horowitz Singularities in String TheoryDocument46 pagesHorowitz Singularities in String TheoryEvanAdamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Kasempa Boys Boarding Secondary School Grade 10 B Chemistry Test 2 TERM: 1 YEAR: 2019 Duration: 1 Hour 20 Minutes MARKS: 51Document3 pagesKasempa Boys Boarding Secondary School Grade 10 B Chemistry Test 2 TERM: 1 YEAR: 2019 Duration: 1 Hour 20 Minutes MARKS: 51Davies MasumbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Effect of Heat Tretment On Hardness of 6082 t6 Alminium AlloyDocument5 pagesEffect of Heat Tretment On Hardness of 6082 t6 Alminium AlloyRohit SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Omnisens.comDocument3 pagesOmnisens.commedesarrolloPas encore d'évaluation
- Automatic Solar Tracker With Dust Wiper Using PID ControllerDocument6 pagesAutomatic Solar Tracker With Dust Wiper Using PID ControllerEditor IJTSRD100% (1)
- Rippability of RocksDocument4 pagesRippability of RocksAnonymous pFXVbOS9TWPas encore d'évaluation
- Physicssolutionmanuals 151015074549 Lva1 App6891Document28 pagesPhysicssolutionmanuals 151015074549 Lva1 App6891Kusumlata TomarPas encore d'évaluation
- Junior High School Department: Caldwell Adventist AcademyDocument3 pagesJunior High School Department: Caldwell Adventist Academyrosanie remotinPas encore d'évaluation
- Thesis SynopsisDocument4 pagesThesis Synopsisbhavdip_shahPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Syllabus Mapping IITJAM NET GATE BSC MSCDocument39 pagesChemistry Syllabus Mapping IITJAM NET GATE BSC MSCAshwani KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- EE364 Maxwell Simulation Assignment 1Document37 pagesEE364 Maxwell Simulation Assignment 1jalilemadiPas encore d'évaluation