Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
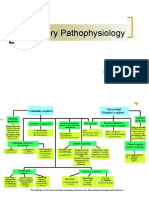
Contributing factors and risk of developing bacterial pneumonia
Transféré par
billiam123Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Contributing factors and risk of developing bacterial pneumonia
Transféré par
billiam123Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
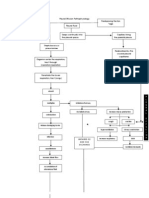
Contributing Factor bacteria
Risk Factors -Tobacco or alcohol use -Exposure to viral or influenza infections -Inhalation of toxic gases, chemicals, smoke
Staph lococcus pneumoniae
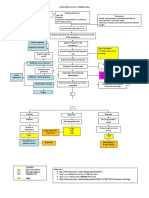
!rganisms enter the respirator tract through inspiration"aspiration
#ctivation of $efense mechanism
%ose effectiveness of $efense mechanism &enetrate the sterile lo'er respirator tract (lungs)
alveoli
multiplies Colonization
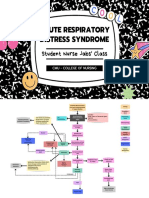
Irritation of air'a Increase goblet cell
Release $amaging toxins !cclu$e$ the air'a Increase mucus pro$uction cracklessss cough Continuous coughing Inflammation #cute &ain r"t $isease process h perventilation Increase bloo$ flo' &lasma an$ C+!, rich flui$ leakage #ccumulation of e$ematous flui$ Increase$ respirator -iagnostic Test -Chest 0-Ra revealing &neumonia -S&!. 12-134
Infection
Exu$ates come from bacteriaero$e the lung
Ineffective air'a clearance r"t retaine$ secretions in the tracheobronchial
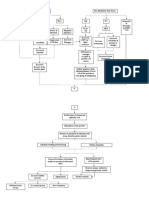
*asoli$ation -ea$ space happene$
#ir'a Constriction
-ifficult of breathing
Inflamme$ an$ flui$ fille$ alveolar sacs -ecrease C!.
Impaire$ !. an$ C!. exchange
*entilator $eman$s Impaire$ /as exchange r"t $ecrease$ lung expansion Ineffective breathing pattern r"t $ecrease$ lung expansion
%ung consoli$ation
h poxia
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Community Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandCommunity Acquired Pneumonia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory Pathophysiology: B. Pimentel, M.D. University of Makati College of NursingDocument12 pagesRespiratory Pathophysiology: B. Pimentel, M.D. University of Makati College of NursingDoc JacquePas encore d'évaluation
- Oxygen Deficiency Body EffectsDocument3 pagesOxygen Deficiency Body EffectsKevin T. KatadaPas encore d'évaluation
- Copd PathoDocument2 pagesCopd PathoAlvin RamirezPas encore d'évaluation
- Patho PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPatho Pneumoniaailyne_galicia100% (2)
- Modifiable and Non-Modifiable Risk Factors for Tuberculosis and the Pathophysiology of Pneumonia and Respiratory FailureDocument2 pagesModifiable and Non-Modifiable Risk Factors for Tuberculosis and the Pathophysiology of Pneumonia and Respiratory FailurehannahleatanosornPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology SARSDocument4 pagesPathophysiology SARSStephanie Joy Escala71% (7)
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaAzria John DemetriPas encore d'évaluation
- Patho Pleural EffusionDocument2 pagesPatho Pleural EffusionJess Prodigo50% (2)
- Pneumonia PresentationDocument20 pagesPneumonia PresentationsetanpikulanPas encore d'évaluation
- (Patho) PTB COPDDocument1 page(Patho) PTB COPDKyle HannahPas encore d'évaluation
- Concept Map WK 10 LesterDocument1 pageConcept Map WK 10 Lesterapi-277683144Pas encore d'évaluation
- PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesPathophysiologyKarla Karina Dela CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- PneumoniaDocument1 pagePneumoniaAyen FornollesPas encore d'évaluation
- TOF Pathophysiology and TreatmentDocument4 pagesTOF Pathophysiology and TreatmentDoreen Claire M. WallangPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Airway Blockage Causes and SymptomsDocument2 pagesAcute Airway Blockage Causes and SymptomsBudy CaecarianPas encore d'évaluation
- Asthma: Prepared by Fatima Hirzallah RN, MSN, CNS, PHDDocument21 pagesAsthma: Prepared by Fatima Hirzallah RN, MSN, CNS, PHDناصر دويكاتPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology Copd-ChfDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Copd-ChfZaira Batalo100% (2)
- Influenza PATHOPHYSIOLOGYDocument3 pagesInfluenza PATHOPHYSIOLOGYElle RosalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Pulmonary EmbolismDocument8 pagesPulmonary EmbolismspoilttbrattPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Assessment, Planning, Implementation and EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Assessment, Planning, Implementation and EvaluationDiana MuañaPas encore d'évaluation
- Ards Cmap FinalDocument4 pagesArds Cmap FinalPam Araune67% (3)
- TracheostomyDocument17 pagesTracheostomyCalimlim KimPas encore d'évaluation
- COPD PathoDocument1 pageCOPD PathoLeah May AnchetaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaMaria Cristina100% (1)
- Patho COPDDocument2 pagesPatho COPDrsdrPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of Shock Sepsis and Organ Failure PDFDocument1 179 pagesPathophysiology of Shock Sepsis and Organ Failure PDFNotInterested100% (1)
- Age - Weather: Aspiration of Secretions Containing MicrobesDocument4 pagesAge - Weather: Aspiration of Secretions Containing Microbeslouie john abilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Respiratory Failure: R. Bhakialakshmi M.Sc. Nursing 2 Year PSG College of NursingDocument31 pagesAcute Respiratory Failure: R. Bhakialakshmi M.Sc. Nursing 2 Year PSG College of NursingassumptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pneumonia Teaching PlanDocument5 pagesPneumonia Teaching PlanRaghav RoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology Schistosomiasis: Table in New WindowDocument7 pagesPathophysiology Schistosomiasis: Table in New WindowKaren Leigh MagsinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaJunePas encore d'évaluation
- Bronchiectasis PathophysiologyDocument1 pageBronchiectasis PathophysiologyRayne Dunstan Pascual VergaraPas encore d'évaluation
- Pa Tho Physiology of URTIDocument3 pagesPa Tho Physiology of URTIJericho Moris U. LagmayPas encore d'évaluation
- Pneumonia PathophysiologyDocument1 pagePneumonia PathophysiologyDee Sarajan100% (3)
- Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Etiology, Types, Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument6 pagesMycobacterium Tuberculosis Etiology, Types, Diagnosis and TreatmentChloé Jane HilarioPas encore d'évaluation
- The Patient and His Illness A. Pathophysiology (Book Based)Document5 pagesThe Patient and His Illness A. Pathophysiology (Book Based)Edmar Francis SabilePas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology: Non-Hodgkin's LymphomaDocument1 pagePathophysiology: Non-Hodgkin's LymphomaExernest Joever ZausaPas encore d'évaluation
- Scribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kDocument2 pagesScribd 020922 Case Study-Oncology A&kKellie DPas encore d'évaluation
- Causes and Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure (CHFDocument1 pageCauses and Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure (CHFLance MarquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Revised NCP (Baiae)Document9 pagesRevised NCP (Baiae)Jennifer BactatPas encore d'évaluation
- ARDS Concept Map - BunayogDocument2 pagesARDS Concept Map - BunayogJacela Annsyle BunayogPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology Community Aquired Pneumonia and AnemiaDocument3 pagesPathophysiology Community Aquired Pneumonia and Anemiapa3kmedina100% (2)
- BPH Pathophysio 4CDocument2 pagesBPH Pathophysio 4CPatricia Camille Ponce JonghunPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of AtherosclerosisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of AtherosclerosisAzrul Hakim100% (2)
- Case AnalysisDocument12 pagesCase AnalysisFroilan TaracatacPas encore d'évaluation
- Diarrhea TBLDocument9 pagesDiarrhea TBLB-BallerPas encore d'évaluation
- COPD Case PresentationDocument50 pagesCOPD Case PresentationSarah Ann Jamilla FaciolanPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute TonsillopharyngitisDocument17 pagesAcute TonsillopharyngitisRachel Haide NaravalPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of HyperthyroidismDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of HyperthyroidismKitty YuffiePas encore d'évaluation
- College of Nursing Case Study on COPD ManagementDocument23 pagesCollege of Nursing Case Study on COPD ManagementFritzie NagacPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 5ADocument7 pagesUnit 1 5AArvin O-CaféPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 NCP AsthmaDocument6 pages3 NCP AsthmajaninenicolePas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaGeevine Cansino91% (11)
- Pathophysiology of Pneumonia Risk Factors and TransmissionDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Pneumonia Risk Factors and TransmissionAnn Wincel Nobleza82% (17)
- Case Study of PNEUMONIADocument12 pagesCase Study of PNEUMONIAAriaPas encore d'évaluation
- IX: Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factor Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesIX: Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factor Precipitating FactorsCandace AlcarazPas encore d'évaluation
- Approach To A Child With Cough and Difficulty in BreathingDocument23 pagesApproach To A Child With Cough and Difficulty in BreathingKashif Burki100% (2)
- Cap PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesCap PathophysiologyNoriel Henricks Acuna100% (3)
- Patho EcomodelDocument2 pagesPatho EcomodelAnna BeatricePas encore d'évaluation
- Development and GrowthDocument7 pagesDevelopment and Growthbilliam123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Status Epilepticus Signs and SymptomsDocument4 pagesStatus Epilepticus Signs and Symptomsbilliam123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Slip Ring Motor Speed ControlDocument1 pageSlip Ring Motor Speed Controlbilliam123Pas encore d'évaluation
- ESP OperationDocument22 pagesESP OperationVishnu Vardhan . C100% (1)
- Verification of Feeding Tube PlacementDocument4 pagesVerification of Feeding Tube Placementbilliam123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study NursingDocument27 pagesDrug Study Nursingbilliam123Pas encore d'évaluation
- ESP OperationDocument22 pagesESP OperationVishnu Vardhan . C100% (1)
- Hypertension and StrokeDocument8 pagesHypertension and Strokebilliam123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Journals AbstractsDocument11 pagesNursing Journals Abstractsbilliam123Pas encore d'évaluation
- RSL in X Classic GRGDocument62 pagesRSL in X Classic GRGbilliam123Pas encore d'évaluation
- SR-Bridge@59-8,62-10 14.12.12Document6 pagesSR-Bridge@59-8,62-10 14.12.12Rayar ArvindPas encore d'évaluation
- j104 YamashitaDocument4 pagesj104 Yamashitabilliam123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mechatronics For The Evil GeniusDocument225 pagesMechatronics For The Evil Geniusbilliam123Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Reactive Power Compensation PDFDocument97 pages1 Reactive Power Compensation PDFSorin ChirilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and Physiology of Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Respiratory Systembilliam123Pas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Cva Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument1 pageNCP Cva Ineffective Tissue Perfusionexcel21121Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gouty Arthritissss PathophyDocument2 pagesGouty Arthritissss Pathophybilliam123Pas encore d'évaluation
- j104 YamashitaDocument4 pagesj104 Yamashitabilliam123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ais Romney 2006 Slides 06 Control and Ais Part 1 091101082444 Phpapp01Document73 pagesAis Romney 2006 Slides 06 Control and Ais Part 1 091101082444 Phpapp01billiam123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tomorrow WorldDocument1 pageTomorrow Worldbilliam123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hello WorldDocument1 pageHello Worldbilliam123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hello Pokemon WorldDocument1 pageHello Pokemon Worldbilliam123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ais Romney 2006 Slides 06 Control and Ais Part 1 091101082444 Phpapp01Document73 pagesAis Romney 2006 Slides 06 Control and Ais Part 1 091101082444 Phpapp01billiam123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Activity Intolerance NCPDocument2 pagesActivity Intolerance NCPrhieyan82% (11)
- Hello UniverseDocument1 pageHello Universebilliam123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Geography Lessons for Classes IX & XIDocument51 pagesGeography Lessons for Classes IX & XInatthha100% (1)
- Aircraft Power PlantDocument20 pagesAircraft Power PlantAizzat CarerraPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample MBA Admissions EssaysDocument4 pagesSample MBA Admissions EssayshelvadjianPas encore d'évaluation
- Hello WorldDocument1 pageHello Worldbilliam123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Beginner's Guide To Procreate: Characters: How to create characters on an iPad ®D'EverandBeginner's Guide To Procreate: Characters: How to create characters on an iPad ®3dtotal PublishingÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Creative Abstract Watercolor: The beginner's guide to expressive and imaginative paintingD'EverandCreative Abstract Watercolor: The beginner's guide to expressive and imaginative paintingPas encore d'évaluation
- The Botanical Hand Lettering Workbook: Draw Whimsical & Decorative Styles & ScriptsD'EverandThe Botanical Hand Lettering Workbook: Draw Whimsical & Decorative Styles & ScriptsÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- The Art of Tinkering: Meet 150+ Makers Working at the Intersection of Art, Science & TechnologyD'EverandThe Art of Tinkering: Meet 150+ Makers Working at the Intersection of Art, Science & TechnologyÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (11)
- Acrylic Painting: Learn How to Paint Easy Techniques with Acrylic Paint (with photos)D'EverandAcrylic Painting: Learn How to Paint Easy Techniques with Acrylic Paint (with photos)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (4)
- Art Models AnaRebecca002: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceD'EverandArt Models AnaRebecca002: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceÉvaluation : 1 sur 5 étoiles1/5 (1)
- Painting Perspective, Depth & Distance in WatercolourD'EverandPainting Perspective, Depth & Distance in WatercolourÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- Coloring Book for Adults & Grown Ups : An Easy & Quick Guide to Mastering Coloring for Stress Relieving Relaxation & Health Today!: The Stress Relieving Adult Coloring PagesD'EverandColoring Book for Adults & Grown Ups : An Easy & Quick Guide to Mastering Coloring for Stress Relieving Relaxation & Health Today!: The Stress Relieving Adult Coloring PagesÉvaluation : 2 sur 5 étoiles2/5 (12)
- Art Models KatarinaK034: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceD'EverandArt Models KatarinaK034: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (2)
- Art Models Adrina032: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceD'EverandArt Models Adrina032: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Discovering Watercolor: An Inspirational Guide with Techniques and 32 Skill-Building Projects and ExercisesD'EverandDiscovering Watercolor: An Inspirational Guide with Techniques and 32 Skill-Building Projects and ExercisesÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Secrets of the Millionaire Mind: Mastering the Inner Game of WealthD'EverandSecrets of the Millionaire Mind: Mastering the Inner Game of WealthÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (197)
- Painting Successful Watercolours from PhotographsD'EverandPainting Successful Watercolours from PhotographsÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (3)
- Art Models SarahAnn031: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceD'EverandArt Models SarahAnn031: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (4)
- Stunning Watercolor Seascapes: Master the Art of Painting Oceans, Rivers, Lakes and MoreD'EverandStunning Watercolor Seascapes: Master the Art of Painting Oceans, Rivers, Lakes and MorePas encore d'évaluation
- The Fundamentals of Watercolour Landscapes: Paintings for all seasonsD'EverandThe Fundamentals of Watercolour Landscapes: Paintings for all seasonsÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- Beginner's Guide to Drawing the Future: Learn how to draw amazing sci-fi characters and conceptsD'EverandBeginner's Guide to Drawing the Future: Learn how to draw amazing sci-fi characters and concepts3dtotal PublishingÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Journal with Purpose: Over 1000 motifs, alphabets and icons to personalize your bullet or dot journalD'EverandJournal with Purpose: Over 1000 motifs, alphabets and icons to personalize your bullet or dot journalÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (39)
- Art Models AnaIv309: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceD'EverandArt Models AnaIv309: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (2)
- Art Models 7: Dynamic Figures for the Visual ArtsD'EverandArt Models 7: Dynamic Figures for the Visual ArtsÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (7)
- Zentangle 2, Expanded Workbook EditionD'EverandZentangle 2, Expanded Workbook EditionÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (3)
- Draw Every Little Thing: Learn to Draw More Than 100 Everyday Items, From Food to FashionD'EverandDraw Every Little Thing: Learn to Draw More Than 100 Everyday Items, From Food to FashionÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (4)
- Art Models Saju027: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceD'EverandArt Models Saju027: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (6)
- Art Models Ginger040: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceD'EverandArt Models Ginger040: Figure Drawing Pose ReferenceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5)
- Watercolor For The Soul: Simple painting projects for beginners, to calm, soothe and inspireD'EverandWatercolor For The Soul: Simple painting projects for beginners, to calm, soothe and inspireÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (6)
- Gelli Arts® Printing Guide: Printing Without a Press on Paper and Fabric Using the Gelli Arts® PlateD'EverandGelli Arts® Printing Guide: Printing Without a Press on Paper and Fabric Using the Gelli Arts® PlatePas encore d'évaluation
- One Zentangle a Day: A 6-Week Course in Creative Drawing for Relaxation, Inspiration, and FunD'EverandOne Zentangle a Day: A 6-Week Course in Creative Drawing for Relaxation, Inspiration, and FunÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (25)