Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
The Digestive System
Transféré par
july3ciaCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
The Digestive System
Transféré par
july3ciaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM I. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM A. Functions 1.
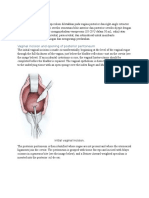
digestion process wherein food is broken down into particles small enough to pass through the cell membrane 2. absorption the transfer of food into the circulation B. Structure of wall 1. mucosa or the mucous membrane, so-called because its epithelial layer contains many mucus-secreting cells 2. submucosa the layer of connective tissue beneath the mucous membrane which contains blood vessels and some of the nerves that help regulate digestive activity 3. smooth muscle the inner layer has circular fibers and outer layer has longitudinal fibers; the alternate contractions of these muscles create the wavelike movement that propels food through the digestive tract and mixes it with digestive juices 4. serosa C. Peritoneum serous membrane that lines abdominal cavity and folds over organs 1. parietal peritoneum the portion of the peritoneum that lines the abdomen 2. visceral peritoneum covers the organ 3. mesentery a double-layered peritoneal structure shaped somewhat like a fan 4. mesocolon the section of the peritoneum that extends from the colon to the back wall 5. greater omentum a large double layer of the peritoneum containing much fat hangs like an apron over the front of the intestine; it extends from the lower border of the stomach into the pelvic part of the abdomen and then loops back up to the transverse colon 6. lesser omentum smaller membrane that extends between the stomach and the liver II. DIGESTIVE TRACT sometimes called the alimentary tract, derived from a Latin word that means food it is more commonly referred to as the gastrointestinal tract because of the major importance of the stomach and intestine in the process of digestion A. Mouth also called the oral cavity it is where a substance begins its travels through the digestive tract 1. Functions a. ingestion of food b. Mastication of foof c. Lubrication of food d. Digestion of starch with salivary amylase 2. Structures
a. Tongue a muscular organ which is used for chewing and swallowing and is one of the principal organs of speech it has in its surface a number of special organs called taste buds, by means of which taste sensations can be differentiated b. Deciduous teeth 20 (incisors, canines, molars) c. Permanent teeth 32 (incisors, canines, premolars, molars) d. salivary glands while the food is in the mouth, it is mixed with saliva, the purpose of which is to moisten the food and facilitate the processes of chewing or mastication and swallowing or deglutition saliva also helps keep the teeth and mouth clean and reduced bacterial growth it contains mucus and an enzyme called salivary amylase which begins the digestive process by converting starch to sugar. It is mainly manufactured by 3 pairs of glands that function as accessory organs 1. parotid glands, the largest of the group, are located below and in front of the ear 2. submandibular or submaxillary glands, are located near the body of the lower jaw 3. sublingual glands are under the tongue B. Pharynx (throat) moves portion of food into esophagus by reflex swallowing (deglutition) 1. soft palate tissue that forms the back of the roof of the oral cavity 2. uvula from the soft palate, it hangs a soft, fleshy, V-shaped mass bolus a small portion of chewed food mixed with saliva, is pushed into the pharynx 3. epiglottis a leaf-shaped cartilage that guards the entrance of the trachea which covers the opening of the larynx C. Esophagus long muscular tube that carries food to stomach by peristalsis esophageal hiatus a space in the diaphragm where the esophagus pass through D. Stomach is an expanded J-shaped organ in the upper left region of the abdominal cavity 1. Functions a. storage of food b. breakdown of food by churning c. liquefaction of food with hydrochloric acid to form chime d. digestion of protein with enzyme pepsin 2. Structure a. sphincter a muscular ring that permits the passage of substances in only one direction 1. lower esophageal sphincter (LES) the sphincter between the esophagus and the stomach
2. pyloric sphincter between the distal, or far, end of the stomach and the small intestine b. gastric juice substances that secreted by special cells in the lining of the stomach that mix together 1. hydrochloric acid (HCl) a strong acid that softens the connective tissue in meat and destroys foreign organisms 2. pepsin a protein-digesting enzyme. This enzyme is produced in an inactive form and is activated only when food enters the stomach and HCl is produced. chyme the semi-liquid mixture of gastric juice and food that leaves the stomach to enter the small intestine E. small Intestine the longest part of the digestive tract; 3-4 meters long and smaller in diameter 1. Functions a. digestion of food b. absorption of food through villi (small projections of intestinal lining) 2. Structures a. duodenum the first 25 cm to 27 cm of the small intestine b. jejunum forms the next two fifths of the small intestine c. ileum constitutes the remaining portion F. Large Intestine 1. Functions a. storage and elimination of waste (defecation) b. reabsorption of water 2. Structures a. cecum small pouch in the lower right region of the abdomen b. ascending extends upward along the right side of the abdomen toward the liver c. transverse large intestine then bends and extends across the abdomen d. descending it bends sharply and extends downward on the left side of the abdomen into the pelvis e. sigmoid colon the lower part of the colon bends posteriorly in an S shape and continues downward f. rectum serves as a temporary storage area for indigestible or unabsorbable food residue g. anal canal a narrow portion of the distal large intestine that leads to the outside of the body through an opening called the anus III. ACCESSORY ORGANS
A. Liver Greek word root hepat, is the largest glandular organ of the body; it is located in the upper right portion of the abdominal cavity under the dome of the diaphragm the human liver is the same reddish brown color as the animal liver it has a large right lobe and a smaller left lobe; the right lobe includes two inferior smaller lobes the liver has a double blood supply; the portal vein and the hepatic artery the two vessels deliver about 1 quarts of blood to the liver every minute 1. Functions a. storage of glucose b. formation of blood plasma proteins c. synthesis of urea d. modification of fats e. manufacture of bile f. destruction of old red blood cells
g. detoxification harmful substances h. storage of vitamins and iron B. Gallbladder a muscular sac on the inferior surface of the liver that serves as a storage pouch for bile 1. Function a. storage of bile until needed for digestion C. Pancreas long gland that extends from the duodenum to the spleen 1. Functions a. secretes powerful digestive juice b. secretes neutralizing fluid IV. PROCESS OF DIGESTION A. Products 1. simple sugars from carbohydrates 2. amino acids from proteins 3. glycerol and fatty acids from fats B. Absorption movement of digested food into circulation C. Control 1. Nervous control a. Parasympathetic system generally increases activity b. Sympathetic system generally decreases activity 2. Hormonal control a. stimulation of digestive activity b. feedback to inhibit response
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- Peritoneal LavageDocument30 pagesPeritoneal Lavageapi-3722454100% (2)
- Essential Newborn Care GuideDocument120 pagesEssential Newborn Care Guidejuly3ciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Essential Newborn Care GuideDocument120 pagesEssential Newborn Care Guidejuly3ciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Essential Newborn Care GuideDocument120 pagesEssential Newborn Care Guidejuly3ciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Vaginal HysterectomyDocument7 pagesVaginal HysterectomySleepy Winter0% (1)
- TODDLER CARE AND DEVELOPMENTDocument12 pagesTODDLER CARE AND DEVELOPMENTjuly3cia33% (3)
- Foto Polos AbdomenDocument51 pagesFoto Polos AbdomenMochamad Rizki FirmansyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Abdominal ParacentesisDocument4 pagesAbdominal ParacentesisRashmi C S100% (1)
- Health Problems Common in ToddlersDocument9 pagesHealth Problems Common in Toddlersjuly3ciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument1 pageAnatomy and Physiologyjuly3ciaPas encore d'évaluation
- GriefDocument4 pagesGriefapi-83101465Pas encore d'évaluation
- Comm HLTH NSG FinalDocument228 pagesComm HLTH NSG Finaljuly3ciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Multidimensional Social Support ScaleDocument2 pagesMultidimensional Social Support ScaleHemant KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- The Cardiovascular SystemDocument5 pagesThe Cardiovascular Systemjuly3ciaPas encore d'évaluation
- High Risk PregnancyDocument61 pagesHigh Risk Pregnancyjuly3ciaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Maternal Role Attainment TheoryDocument1 pageThe Maternal Role Attainment Theoryjuly3ciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrition During PregnancyDocument6 pagesNutrition During Pregnancyjuly3ciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nutrition During PregnancyDocument6 pagesNutrition During Pregnancyjuly3ciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Health Economics With Land Reform and TaxationDocument10 pagesHealth Economics With Land Reform and Taxationnikki81050% (4)
- GriefDocument4 pagesGriefapi-83101465Pas encore d'évaluation
- Call For Abstracts (9th NSTP Congress)Document2 pagesCall For Abstracts (9th NSTP Congress)july3ciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Choosing A Contraceptive Full VersionDocument52 pagesChoosing A Contraceptive Full Versionjuly3ciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Oral Contraceptive PillDocument21 pagesOral Contraceptive Pilljuly3ciaPas encore d'évaluation
- GriefDocument4 pagesGriefapi-83101465Pas encore d'évaluation
- SLE CaseDocument2 pagesSLE Casejuly3ciaPas encore d'évaluation
- CHAPTER 12 Abdominal PainDocument2 pagesCHAPTER 12 Abdominal PainIvanka Lizbeth PrietePas encore d'évaluation
- Renal Failure PresentationDocument110 pagesRenal Failure PresentationMusa yohana100% (1)
- Análise Temporal e Comparativa Entre Métodos de Dissecção Do Abdômen para Exposição Aorto-CavalDocument4 pagesAnálise Temporal e Comparativa Entre Métodos de Dissecção Do Abdômen para Exposição Aorto-CavalariellafisioterapeutaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kidney AnatomyDocument2 pagesKidney Anatomyameerabest100% (1)
- Body Cavities and MembranesDocument31 pagesBody Cavities and MembranesMary AkellaPas encore d'évaluation
- IM-Generalized Peritonitis Concept MapDocument21 pagesIM-Generalized Peritonitis Concept MapTrisPas encore d'évaluation
- Digestive SystemDocument7 pagesDigestive Systemmuli.michaelPas encore d'évaluation
- The Peritoneum. The Peritoneal Cavity. The Development of The Peritoneum. The Histology of Tonsils PDFDocument9 pagesThe Peritoneum. The Peritoneal Cavity. The Development of The Peritoneum. The Histology of Tonsils PDFredderdatPas encore d'évaluation
- 5801 PeritonitisDocument19 pages5801 PeritonitisIrene Sulinsia NapitupuluPas encore d'évaluation
- HemoperitoneumDocument36 pagesHemoperitoneumnovitafitri123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Burned Bodies: Post-Mortem Computed Tomography, An Essential Tool For Modern Forensic MedicineDocument13 pagesBurned Bodies: Post-Mortem Computed Tomography, An Essential Tool For Modern Forensic MedicinewendellPas encore d'évaluation
- Etiology and Diagnosis of Ascites of Undetermined Origin in A Developing Country: A Prospective StudyDocument9 pagesEtiology and Diagnosis of Ascites of Undetermined Origin in A Developing Country: A Prospective StudyIJAR JOURNALPas encore d'évaluation
- The Pathobiology of PeritonitisDocument12 pagesThe Pathobiology of PeritonitisTri PutraPas encore d'évaluation
- Guía completa sobre diálisis peritoneal: pasos, materiales, signos de alerta y másDocument3 pagesGuía completa sobre diálisis peritoneal: pasos, materiales, signos de alerta y máshanny loren0% (1)
- An Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology: Powerpoint Lecture Presentations Prepared by Jason LapresDocument67 pagesAn Introduction To Anatomy and Physiology: Powerpoint Lecture Presentations Prepared by Jason LapresLina TasamaPas encore d'évaluation
- PeritonitisDocument21 pagesPeritonitischrisyenPas encore d'évaluation
- CAz Clinic Poliserozita UMFDocument16 pagesCAz Clinic Poliserozita UMFMariaIoanaCoroiuPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 Intraabdominal Infections PDFDocument42 pagesChapter 4 Intraabdominal Infections PDFHamza BarriPas encore d'évaluation
- Acute Abdomen and PeritonitisDocument17 pagesAcute Abdomen and PeritonitisAnisaPratiwiArumningsihPas encore d'évaluation
- Collection Labelling Handling and Care of Specimen Part 2 1Document103 pagesCollection Labelling Handling and Care of Specimen Part 2 1Philip Anthony FernandezPas encore d'évaluation
- Onur Y. DaştanDocument51 pagesOnur Y. Daştanapi-26048149Pas encore d'évaluation
- In Same A A: Richmond, VrginiaDocument11 pagesIn Same A A: Richmond, VrginiaRizky AmaliahPas encore d'évaluation
- Perforated PeritonitisDocument5 pagesPerforated PeritonitisDeepak singh ratheePas encore d'évaluation
- Complications of Gynecologic SurgeryDocument80 pagesComplications of Gynecologic SurgeryJL BillsPas encore d'évaluation
- 4th Lab Bio 11 Exam ReviewDocument13 pages4th Lab Bio 11 Exam ReviewAlly YeePas encore d'évaluation
- Download Pathologic Basis Of Veterinary Disease 7Th Edition James F Zachary full chapter pdf scribdDocument67 pagesDownload Pathologic Basis Of Veterinary Disease 7Th Edition James F Zachary full chapter pdf scribdtodd.feuer645100% (3)