Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Care Plan - Chronic Pain
Transféré par
api-246639896Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Care Plan - Chronic Pain
Transféré par
api-246639896Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
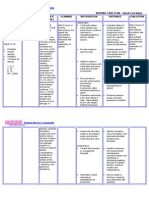
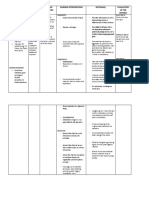
Monica Heater Nursing Diagnosis: Chronic pain r/t disease process AEB c/o pain all the time.
Long Term Goal: Patient will have adequate control of pain in one week.
Intervention 1. Monitor VS q 4 hours.
Rationale 1. Vital signs can be an indicator of pain. Mild to moderate pain will increase the heart rate, blood pressure, and respiration rate. Severe pain may decrease the heart rate, blood pressure and respirations. Vital signs are an important part of assessing pain. 2. Teach patient that 0 is no pain and 10 is the worst pain possible. Teaching patient to communicate pain using a scale can help determine what pain medication to administer if needed.
Outcome Criteria 1. Patient will have normal vital signs every shift, as her pain is well controlled.
Evaluation 1. Met. Patient verbalizes no pain on say shift.
2. Teach pain scale 0-10 upon admission.
2. Patient will using the adult pain scale when reporting pain.
2. Patient did not report pain, no need to use scale.
Intervention 3. Asses pain q 2 hours.
Rationale 3. Knowing the amount of pain is important is knowing if and what medications a patient may need. This is the first step to helping the patient achieve improved comfort. It is very important to say ahead of the pain. If the pain gets too severe, it will be more difficult to get back under control. (Nursing Diagnosis Handbook) 4. Chronic pain patients had twice the rate of suicide than the people without pain. Patients over 60 who committed suicide had physical illness especially pain, breathlessness, and disability. If depression occurs, treatment is an option. (NDH, Harwood et al 2006)
Outcome Criteria 3. Patient will report pain as soon as possible.
Evaluation 3. Patient did not report pain.
4. Monitor for signs of depression weekly.
4. Nurse and/or family will pick up on signs of depression as soon as it occurs.
4. Patient has not shown any signs of depression up to this point in her care.
Intervention 5. Assist patient OOB BID
Rationale 5. Immobility may cause the patient to experience more pain. Changing positions regularly can avoid this added pain or discomfort. Medication may be needed before transferring. 6. Tylenol is a medication that is used to treat mild to moderate pain. It works by inhibiting the synthesis of prostaglandins that may serve as mediators of pain and fever, primarily in the CNS. Has no significant antiinflammatory properties or GI toxicity, making prolonged use okay. May need to monitor liver function tests. (Daviss Drug Guide)
Outcome Criteria 5. Patient will sit in chair for 2 hours twice each day.
Evaluation 5. Met - Patient was up in chair once during our shift and tolerated it well.
6. Administer Tylenol 975mg PO daily.
6. The patients pain will be well controlled throughout the each day.
6. Met Patient reports no pain during our shift.
7. Apply Lidoderm patch daily.
7. Lidoderm is a patch that contains lidocaine which and an anesthetic used to treat pain. It produces local anesthesia by inhibiting transport of ions across neuronal membranes, thereby preventing initiation and conduction of normal nerve impulses. Health care providers will need to monitor of skin irritation caused from the patch. Sites will need to be rotated with each new patch. (Daviss Drug Guide)
7. Patient will experience well controlled pain each day.
7. Met Patient reports no pain during our shift.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Chronic Pain NandaDocument7 pagesChronic Pain NandaJude Bello-AlvearPas encore d'évaluation
- Pain Care PlanDocument18 pagesPain Care Planjordanw0613Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nusing CareplanDocument3 pagesNusing Careplanardec_143Pas encore d'évaluation
- Care Plan For Excess Fluid Volume ExampleDocument3 pagesCare Plan For Excess Fluid Volume ExampleVette Angelikka Dela CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan For AnxietyDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan For AnxietyHarinie RameshPas encore d'évaluation
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocument2 pagesImpaired Physical Mobilitygianne121391Pas encore d'évaluation
- NCP PainDocument2 pagesNCP PainApril_Ivy_Raga_3835Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan for Spinal Cord InjuryDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plan for Spinal Cord InjuryDan Leo UnicoPas encore d'évaluation
- Pain ManagementDocument2 pagesPain ManagementprokunoPas encore d'évaluation
- WHOQOL 100 InglesDocument30 pagesWHOQOL 100 Inglescristhianibo777Pas encore d'évaluation
- NCPDocument10 pagesNCPNefre Dayap DarrocaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plans For Activity IntoleranceDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plans For Activity IntolerancethebigtwirpPas encore d'évaluation
- Nurs 125 Clinical ProjectDocument20 pagesNurs 125 Clinical ProjectMelissa100% (1)
- Managing Fatigue Through Activity Pacing and RestDocument2 pagesManaging Fatigue Through Activity Pacing and ResthaniehaehaePas encore d'évaluation
- Activity Intolerance Care Plan For CFDocument8 pagesActivity Intolerance Care Plan For CFapi-314197645Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gum Bleeding Nursing CareDocument3 pagesGum Bleeding Nursing CareCrystelle MonaresPas encore d'évaluation
- CASE PRESENTATION PP - Anxiety. Tiffany GordonDocument6 pagesCASE PRESENTATION PP - Anxiety. Tiffany GordonTiffany GordonPas encore d'évaluation
- GBS Management, Medications and Nursing ConsiderationsDocument4 pagesGBS Management, Medications and Nursing Considerationssouledg3100% (1)
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationCharina AubreyPas encore d'évaluation
- Impaired Tissue Integrity - CellulitisDocument3 pagesImpaired Tissue Integrity - CellulitisKelvin Kurt B. AgwilangPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Total Hip ReplacementDocument11 pagesNCP Total Hip ReplacementDoneva Lyn MedinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocument2 pagesImpaired Physical MobilityHanya Bint PotawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care PlanDocument26 pagesNursing Care PlanDinda MaretaPas encore d'évaluation
- Careplan 5 MedsurgDocument8 pagesCareplan 5 Medsurgapi-509642710Pas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Proper CholecystectomyDocument2 pagesNCP Proper CholecystectomyGail Lian SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Urinary Tract Infection Nursing-Care-PlanDocument3 pagesUrinary Tract Infection Nursing-Care-PlanRnspeakcomPas encore d'évaluation
- Content: Outline Form Only Make A Separate Sheet For The Content. The Health Teaching Plan Should Focus On Home Care For Patients With Mood DisorderDocument4 pagesContent: Outline Form Only Make A Separate Sheet For The Content. The Health Teaching Plan Should Focus On Home Care For Patients With Mood DisorderRaffy Sebastian Seballos100% (1)
- Nursing Diagnosis: Urinary Retention: NOC Outcomes (Nursing Outcomes Classification)Document4 pagesNursing Diagnosis: Urinary Retention: NOC Outcomes (Nursing Outcomes Classification)rem_Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care Plansarah hanaPas encore d'évaluation
- 260 AssignmentDocument6 pages260 Assignmentapi-284107243Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pain AssessmentDocument15 pagesPain AssessmentAvash ZhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan for Patient with Impaired Physical MobilityDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan for Patient with Impaired Physical Mobilityssairej06100% (3)
- Psych Final ContentsDocument51 pagesPsych Final ContentsFrancis Peter Abear LahoraPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP RheumatoidDocument5 pagesNCP RheumatoidJane Elizabeth Gonzales MacahiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Post-Op Wrist Pain ManagementDocument13 pagesPost-Op Wrist Pain ManagementJay Jay JayyiPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan for Stroke PatientDocument12 pagesNursing Care Plan for Stroke PatientMj WilliamsPas encore d'évaluation
- The Ebn A. Evidence Based Nursing For Level III General QuestionDocument7 pagesThe Ebn A. Evidence Based Nursing For Level III General QuestionAvyPas encore d'évaluation
- Neurological AssessmentDocument7 pagesNeurological AssessmentErika NicaPas encore d'évaluation
- Hepatic EncephalopathyDocument16 pagesHepatic EncephalopathyChenyuZhu100% (1)
- LCPDDocument7 pagesLCPDakoismePas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan2Document3 pagesNursing Care Plan2gaeLtorvzPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP 2Document2 pagesNCP 2ampalPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan: Determine Cause of Activity - Determining The Cause of A Disease CanDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Determine Cause of Activity - Determining The Cause of A Disease Canrix07Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ranitidine, ParacetamolDocument3 pagesRanitidine, ParacetamoltaekadoPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan: Pt.'s Data Nursing Diagnosis GoalsDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Pt.'s Data Nursing Diagnosis GoalsKiran Ali100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan ForDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan ForVanessaMUellerPas encore d'évaluation
- NCPDocument6 pagesNCPNik Rose ElPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care PlanDocument10 pagesNursing Care PlanSittie Rohaina SabanPas encore d'évaluation
- Active Leg Exercises: Sitting Range of MotionDocument3 pagesActive Leg Exercises: Sitting Range of MotionfrnildegaPas encore d'évaluation
- FractureDocument1 pageFractureReechie TeasoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan For Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseDocument17 pagesNursing Care Plan For Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseLyka Joy DavilaPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Bed SoresDocument3 pagesNCP Bed SoresShe CalliPas encore d'évaluation
- Small Bowel Obstruction Concept MapDocument1 pageSmall Bowel Obstruction Concept MapTessa Claire JaranowskiPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan 2Document30 pagesNursing Care Plan 2Shayla HudsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Multiple SclerosisDocument35 pagesMultiple SclerosisJc SeguiPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP PainDocument1 pageNCP PaindwightciderPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationJhoizel VenusPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP-fluid Volume DeficitDocument4 pagesNCP-fluid Volume DeficitChrissa Mae Aranilla MayoPas encore d'évaluation
- ANXIETY RELATED TO DEATH OF CHILDDocument2 pagesANXIETY RELATED TO DEATH OF CHILDmitzi019Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pain Management GuidelinesDocument3 pagesPain Management GuidelinesMr. BamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Situation 1Document18 pagesSituation 1Maler De VeraPas encore d'évaluation
- Nurse Patient Nurse: Tugas Sir Jon. Admission Patient DialogueDocument7 pagesNurse Patient Nurse: Tugas Sir Jon. Admission Patient DialogueIndry LabungasaPas encore d'évaluation
- Modern Healthcare ArchitectureDocument15 pagesModern Healthcare ArchitectureKanak YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Clinical Data Management Ensures Trial IntegrityDocument39 pagesClinical Data Management Ensures Trial IntegrityBhavana Alapati100% (4)
- Medical Case Report, HarisDocument13 pagesMedical Case Report, HarisHarlan Putra WPas encore d'évaluation
- B. Surgical ManagementDocument20 pagesB. Surgical ManagementNickaela CalalangPas encore d'évaluation
- Health InsuranceDocument18 pagesHealth Insurancesneha sarodePas encore d'évaluation
- Theory Application PaperDocument13 pagesTheory Application Paperapi-295425485Pas encore d'évaluation
- Marfan SyndromeDocument10 pagesMarfan SyndromeHidayati IdaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assembly Bill No. 1340: Legislative Counsel's DigestDocument11 pagesAssembly Bill No. 1340: Legislative Counsel's DigestJon OrtizPas encore d'évaluation
- ###Annalsats 201409-419ocDocument9 pages###Annalsats 201409-419ocTawhid MahmudPas encore d'évaluation
- Sun PharmaceuticalsDocument8 pagesSun Pharmaceuticalspreeti_29oct100% (2)
- Resume For Marketing ManagerDocument2 pagesResume For Marketing ManagerDrPrashant KhemariyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Observational and Experimental Studies For Diabetes ResearchDocument43 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Observational and Experimental Studies For Diabetes ResearchSophia HallqvistPas encore d'évaluation
- Issues in InfromaticsDocument25 pagesIssues in InfromaticsKhemz Dalde LimPas encore d'évaluation
- Nurses Knowledge On Autism Spectrum DisordersDocument12 pagesNurses Knowledge On Autism Spectrum Disordersberrick otienoPas encore d'évaluation
- 027 Neuro PDFDocument5 pages027 Neuro PDFKarthik KoneruPas encore d'évaluation
- Addressing The Leadership Gap in HealthcareDocument21 pagesAddressing The Leadership Gap in Healthcareinfoninja0Pas encore d'évaluation
- Healthcare & Life Sciences ReviewDocument47 pagesHealthcare & Life Sciences Reviewmercadia59970% (1)
- Mapeh 10 1 Grading Examination: E. Modern NationalismDocument3 pagesMapeh 10 1 Grading Examination: E. Modern NationalismMildred Abad SarmientoPas encore d'évaluation
- Infection ControlDocument90 pagesInfection ControlferriPas encore d'évaluation
- Text of Reproductive Rights Amendment For Ballot in November 2023Document1 pageText of Reproductive Rights Amendment For Ballot in November 2023Jo InglesPas encore d'évaluation
- CareMore: Innovative Healthcare DeliveryDocument30 pagesCareMore: Innovative Healthcare DeliveryPartnership to Fight Chronic DiseasePas encore d'évaluation
- Curriculum FinalDocument202 pagesCurriculum FinalMerajuddin Ahmed100% (1)
- Medication Booklet and TicketDocument3 pagesMedication Booklet and TicketCayanne ChuaPas encore d'évaluation
- ResearchDocument11 pagesResearchAnonymous Tzn8RGBZ4Pas encore d'évaluation
- Occupational Health A. Occupational HealthDocument3 pagesOccupational Health A. Occupational HealthEry ShaffaPas encore d'évaluation
- Definition:-The Partograph Is A Simple Chart orDocument12 pagesDefinition:-The Partograph Is A Simple Chart orBharat ThapaPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Assistance in Dying Activity BookDocument30 pagesMedical Assistance in Dying Activity BookThePoliticalHatPas encore d'évaluation
- HerbalismDocument18 pagesHerbalismmiePas encore d'évaluation