Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
MT 02013
Transféré par
chandravinitaTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
MT 02013
Transféré par
chandravinitaDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
BANASTHALI VIDYAPITH PERIODICAL TEST II (Oct-2013) CLASS: M.TECH I SEM.
VLSI DESIGN
SUBJECT: SOLID STATE DEVICE MODELLING & SIMUALTION
NUMBER OF STUDENTS = 70
Note: attempt any 4 questions. All questions carry equal marks. Write specific answers, unnecessary long answer can deduct your marks. You19can -3 use the following parameters for silicon at 300 K: Eg=1.12 eV; Nc=2.8 X1019 cm-3; NV=1.04 X10 cm MAX. MARKS: 10 TIME: 1:30 Hrs.
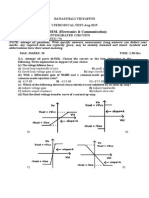
Q.1. Plot (i) Energy band diagram (ii) the charge distribution, (iii) electric-field distribution, and (iv) potential distribution of an ideal MOS diode with n-type substrate under inversion. (1+0.5+0.5+0.5) Q.2. (a) C-V curves measured for two MOS capacitors (a and b) with the same gate area are compared below.
(i) Is the semiconductor n-type or p-type? (0.25) (ii) How do the gate oxide thicknesses for the two capacitors compare? Explain. (0.50) (iii) Which capacitor has higher doping in the semiconductor? Explain. (0.75) (b) When the linear dimensions of MOSFET are scaled down by a factor of 10 based on the constant field scaling, what is the scaling factor for the corresponding power dissipation per circuit and circuit delay time? (1) 16 -3 Q.3. For an ideal Si-Si02 MOS diode with d = 10 nm, NA = 5 X 10 cm , find the maximum width of surface depletion region. Also find the applied Voltage and the electric field at the interface required to bring about strong inversion. Q.4. A Si transistor has Dp of 10 cm2/s, W of 0.5 m and common base current gain equal to 0.998. Find the cut-off frequencies of the transistor for common emitter and common base configurations. Neglect the emitter and collector delays. Q.5 A silicon p-n-p transistor has impurity concentrations of 5 x 10l8, 2 x 10l7and 1016 cm-3 in the emitter, base, and collector, respectively and the diffusion constants of minority carriers in the emitter, base, and collector are 52, 40, and 115 cm2/s, respectively; and the corresponding lifetimes are 10-8, 10-7 , 10-6 s . The base width is 1.0 m, and the device cross-sectional area is 0.2 mm2. When the emitter-base junction is forward biased to 0.5 V and the base-collector junction is reverse biased to 5 V, calculate emitter efficiency of the transistor.
P.T.O.
Q.6 (a) The power generated internally within a double-heterojunction LED is 28.4 mW at a drive current of 60 mA. Determine the peak emission wavelength from the device when the radiative and nonradioactive recombination lifetimes of the minority carriers in the active region are equal. (1.5) (b) Calculate the ratio of the stimulated emission rate to the spontaneous emission rate for an incandescent lamp operating at a temperature of 1000 K. It may be assumed that the average operating wavelength is 0.5 m. (1) Q.7 Discuss the mechanism of optical feedback to provide oscillation and hence amplification within the laser. Indicate how this provides a distinctive spectral output from the device. The longitudinal modes of a gallium arsenide injection laser emitting at a wavelength of 0.87 m are separated in frequency by 278 GHz. Determine the length of the optical cavity and the number of longitudinal modes emitted. The refractive index of gallium arsenide is 3.6. (1+1.5) *************
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Subject: Analog and Mixed Signal Ic DesignDocument2 pagesSubject: Analog and Mixed Signal Ic DesignchandravinitaPas encore d'évaluation
- AMS Design Lab ProblemsDocument2 pagesAMS Design Lab ProblemschandravinitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment BtechDocument3 pagesAssignment BtechchandravinitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment List: M.Tech. II Sem. (VLSI) Analog & Mixed Signal IC Design LabDocument1 pageExperiment List: M.Tech. II Sem. (VLSI) Analog & Mixed Signal IC Design LabchandravinitaPas encore d'évaluation
- ANALOG IC TEST PAPER FOR ELECTRONICS STUDENTSDocument3 pagesANALOG IC TEST PAPER FOR ELECTRONICS STUDENTSchandravinitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Problem 1Document2 pagesProblem 1chandravinitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Poster RapoDocument9 pagesPoster RapochandravinitaPas encore d'évaluation
- CLASS: B.TECH. VI SEM. (Electronics & Instrumentation)Document2 pagesCLASS: B.TECH. VI SEM. (Electronics & Instrumentation)chandravinitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment BtechDocument3 pagesAssignment BtechchandravinitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignmt B.tech FOLIDocument1 pageAssignmt B.tech FOLIchandravinitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Manual For Preparation of Project ReportDocument8 pagesManual For Preparation of Project ReportchandravinitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Subject: Analog and Mixed Signal Ic Design: ResistanceDocument2 pagesSubject: Analog and Mixed Signal Ic Design: ResistancechandravinitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidelines For Preparation of Project Report: (Prescribed Format and Specification) 1. GeneralDocument11 pagesGuidelines For Preparation of Project Report: (Prescribed Format and Specification) 1. GeneralchandravinitaPas encore d'évaluation
- CmnegiDocument23 pagesCmnegichandravinitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Electronics (AIM & ACT) Banasthali University Notice CompositeDocument2 pagesDepartment of Electronics (AIM & ACT) Banasthali University Notice CompositechandravinitaPas encore d'évaluation
- AMS Design Lab ProblemsDocument1 pageAMS Design Lab ProblemschandravinitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Subject: Analog and Mixed Signal Ic DesignDocument3 pagesSubject: Analog and Mixed Signal Ic DesignchandravinitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Experiment Distribution List2013Document1 pageExperiment Distribution List2013chandravinitaPas encore d'évaluation
- My WordsDocument2 pagesMy WordschandravinitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nano ElectronicsDocument1 pageNano Electronicschandravinita100% (1)
- Transistor Modeling 2003Document47 pagesTransistor Modeling 2003chandravinitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Resonant Cavity QD Photo-detector for Far-IR DetectionDocument1 pageResonant Cavity QD Photo-detector for Far-IR DetectionchandravinitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Transistor Modeling 2003Document47 pagesTransistor Modeling 2003chandravinitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus For PHDFDocument2 pagesSyllabus For PHDFchandravinitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To SPICE & Modeling of MOSDocument36 pagesIntroduction To SPICE & Modeling of MOSchandravinitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Quantum Computing 1Document6 pagesQuantum Computing 1chandravinitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Philip Larkin Is One of BritainDocument7 pagesPhilip Larkin Is One of Britainchandravinita100% (1)
- VBTS ReportDocument40 pagesVBTS ReportchandravinitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Analog PracticalDocument1 pageAnalog PracticalchandravinitaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- SamplingDocument12 pagesSamplingΔημητρηςΣαρακυρουPas encore d'évaluation
- Z 80 HelptopicsDocument5 pagesZ 80 HelptopicsEverly NPas encore d'évaluation
- PermutationDocument3 pagesPermutationKhairuddin MuhamadPas encore d'évaluation
- FINAL Painless Algebra For DavaoDocument28 pagesFINAL Painless Algebra For DavaozapleekillsPas encore d'évaluation
- Science8 Q2 Module3 (Week6)Document30 pagesScience8 Q2 Module3 (Week6)Mary Grace Lemon100% (1)
- Plasma CuttingDocument12 pagesPlasma Cuttingpavi32Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cost Estimation TechniquesDocument41 pagesCost Estimation TechniquessubashPas encore d'évaluation
- OptQuest User ManualDocument190 pagesOptQuest User ManualYamal E Askoul TPas encore d'évaluation
- QPCR Analysis DifferentlyDocument12 pagesQPCR Analysis DifferentlyIan SaundersPas encore d'évaluation
- DL-H61M-VG4: Motherboard User ManualDocument52 pagesDL-H61M-VG4: Motherboard User ManualSutripti Bardhan100% (1)
- AC Assingment 2Document3 pagesAC Assingment 2Levi Deo BatuigasPas encore d'évaluation
- Ef TechnologyDocument2 pagesEf TechnologyAdarsha SarpangalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Full Paper Template IRC 2020Document3 pagesFull Paper Template IRC 2020Mobina AbdulRaufPas encore d'évaluation
- Aeration PaperDocument11 pagesAeration PapersehonoPas encore d'évaluation
- Sensitive Albuminuria Analysis Using Dye-Binding Based Test StripsDocument24 pagesSensitive Albuminuria Analysis Using Dye-Binding Based Test StripsВалерия БедоеваPas encore d'évaluation
- JasminDocument125 pagesJasminudoraboxPas encore d'évaluation
- Booklet Momentum BWFDocument22 pagesBooklet Momentum BWFReem AshrafPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermocouple Wire Reference Guide: WWW - Omega.co - Uk +44 (0) 161 777 6611 WWW - Omega.co - Uk +44 (0) 161 777 6611Document1 pageThermocouple Wire Reference Guide: WWW - Omega.co - Uk +44 (0) 161 777 6611 WWW - Omega.co - Uk +44 (0) 161 777 6611Mohamed MaltiPas encore d'évaluation
- Arm Assembly Language ProgrammingDocument170 pagesArm Assembly Language ProgrammingAnup Kumar Yadav100% (4)
- Fix Disk & Partition ErrorsDocument2 pagesFix Disk & Partition Errorsdownload181Pas encore d'évaluation
- Forrester Roi StudyDocument30 pagesForrester Roi StudymcgettsPas encore d'évaluation
- Geotechnical Engineering Notes 333Document40 pagesGeotechnical Engineering Notes 333TinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Effect of Bond Administration On Construction Project DeliveryDocument7 pagesEffect of Bond Administration On Construction Project DeliveryOlefile Mark MolokoPas encore d'évaluation
- 124C1ADocument4 pages124C1AParthiban DevendiranPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis of Rack and Pinion Using AnsysDocument21 pagesAnalysis of Rack and Pinion Using AnsysTejas Prakash100% (1)
- CH 3Document19 pagesCH 3Abhishek GiriPas encore d'évaluation
- Math10 Week3Day4 Polynomial-EqnsDocument44 pagesMath10 Week3Day4 Polynomial-EqnsMark Cañete PunongbayanPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Computer Engineering Academic Year 2020-21 Class: SE Computer & IT Subject: 22226 PCI (Programming in C) MCQ Unit 1: Program Logic Development MCQ Question Bank With AnswersDocument8 pagesDepartment of Computer Engineering Academic Year 2020-21 Class: SE Computer & IT Subject: 22226 PCI (Programming in C) MCQ Unit 1: Program Logic Development MCQ Question Bank With AnswersVooovoPas encore d'évaluation
- TRL External CommunicationDocument3 pagesTRL External CommunicationAyushGargPas encore d'évaluation
- Presentation On Power Grid InertiaDocument47 pagesPresentation On Power Grid InertiajorjijonPas encore d'évaluation