Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Adult Combined Schedule BW
Transféré par
lcmurillo0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
57 vues5 pagesThe 2014 ACIP Adult Immunization Schedule was approved by the center for Disease Control and Prevention's Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) all clinically significant postvaccination reactions should be reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) Reporting forms and instructions on filing a VAERS report are available at www.vaers.hhs.gov or by telephone, 800-822-7967.
Description originale:
Titre original
Adult Combined Schedule Bw
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThe 2014 ACIP Adult Immunization Schedule was approved by the center for Disease Control and Prevention's Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) all clinically significant postvaccination reactions should be reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) Reporting forms and instructions on filing a VAERS report are available at www.vaers.hhs.gov or by telephone, 800-822-7967.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
57 vues5 pagesAdult Combined Schedule BW
Transféré par
lcmurilloThe 2014 ACIP Adult Immunization Schedule was approved by the center for Disease Control and Prevention's Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) all clinically significant postvaccination reactions should be reported to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS) Reporting forms and instructions on filing a VAERS report are available at www.vaers.hhs.gov or by telephone, 800-822-7967.
Droits d'auteur :
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 5
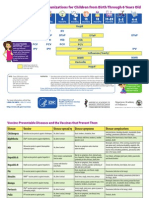
Recommended Adult Immunization Schedule
United States - 2014
The 2014 ACIP Adult Immunization Schedule was approved by the Centers for
Disease Control and Preventions (CDC) Advisory Committee on Immunization
Practices (ACIP), American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP), the American
College of Physicians (ACP), the American College of Obstetricians and
Gynecologists (ACOG), and the American College of Nurse-Midwives (ACNM). On
February 3, 2014, the adult immunization schedule and a summary of changes
from 2013 were published in Annals of Internal Medicine, and a summary of
changes was published in the MMWR on February 7, 2014.
All clinically significant postvaccination reactions should be reported to
the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS). Reporting forms and
instructions on filing a VAERS report are available at www.vaers.hhs.gov or by
telephone, 800-822-7967.
Additional details regarding ACIP recommendations for each of the vaccines listed in
the schedule can be found at: http://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/acip-recs/index.html
American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP)
http://www.aafp.org/home.html
American College of Physicians (ACP)
http://www.acponline.org/
American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG)
http://www.acog.org/
American College of Nurse-Midwives (ACNM)
http://www.midwife.org/
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
VACCINE AGE GROUP 19-21 years 22-26 years 27-49 years 50-59 years 60-64 years 65 years
Infuenza
2,*
Tetanus, diphtheria, pertussis (Td/Tdap)
3,*
Varicella
4,*
Human papillomavirus (HPV) Female
5,*
Human papillomavirus (HPV) Male
5,*
Zoster
6
Measles, mumps, rubella (MMR)
7,*
Pneumococcal 13-valent conjugate (PCV13)
8,*
Pneumococcal polysaccharide (PPSV23)
9,10
Meningococcal
11,*
Hepatitis A
12,*
Hepatitis B
13,*
Haemophilus infuenzae type b (Hib)
14,*
*Covered by the Vaccine Injury Compensation Program
3 doses
1 or 3 doses
2 doses
1 or more doses
1 dose
1 dose 1 or 2 doses
1 or 2 doses
1 dose
3 doses
2 doses
Substitute 1-time dose of Tdap for Td booster; then boost with Td every 10 yrs
1 dose annually
For all persons in this category who
meet the age requirements and who
lack documentation of vaccination or
have no evidence of previous infection;
zoster vaccine recommended regardless
of prior episode of zoster
Recommended if some other risk
factor is present (e.g., on the basis of
medical, occupational, lifestyle, or other
indication)
No recommendation
Recommended Adult Immunization ScheduleUnited States - 2014
Note: These recommendations must be read with the footnotes that follow
containing number of doses, intervals between doses, and other important information.
Figure 1. Recommended adult immunization schedule, by vaccine and age group
1
Report all clinically signifcant postvaccination reactions to the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS). Reporting forms and instructions on fling
a VAERS report are available at www.vaers.hhs.gov or by telephone, 800-822-7967.
nformation on how to fle a Vaccine njury Compensation Program claim is available at www.hrsa.gov/vaccinecompensation or by telephone, 800-338-2382.
To fle a claim for vaccine injury, contact the U.S. Court of Federal Claims, 717 Madison Place, N.W., Washington, D.C. 20005; telephone, 202-357-6400.
Additional information about the vaccines in this schedule, extent of available data, and contraindications for vaccination is also available at
www.cdc.gov/vaccines or from the CDC-NFO Contact Center at 800-CDC-NFO (800-232-4636) in English and Spanish, 8:00 a.m. - 8:00 p.m. Eastern
Time, Monday - Friday, excluding holidays.
Use of trade names and commercial sources is for identifcation only and does not imply endorsement by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
The recommendations in this schedule were approved by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention's (CDC) Advisory Committee on mmunization
Practices (ACP), the American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP), the American College of Physicians (ACP), American College of Obstetricians and
Gynecologists (ACOG) and American College of Nurse-Midwives (ACNM).
VACCINE INDICATION Pregnancy
Immuno-
compromising
conditions
(excluding human
immunodefciency
virus [HIV])
4,6,7,8,15
HIV infection
CD4+ T lymphocyte
count
4,6,7,8,15
Men who
have sex
with men
(MSM)
Kidney failure,
end-stage renal
disease, receipt
of hemodialysis
Heart
disease,
chronic
lung disease,
chronic
alcoholism
Asplenia (including
elective splenectomy
and persistent
complement
component
defciencies)
8,14
Chronic
liver
disease Diabetes
Healthcare
personnel
< 200
cells/L
200
cells/L
Infuenza
2,*
Tetanus, diphtheria, pertussis (Td/Tdap)
3,*
Varicella
4,*
Human papillomavirus (HPV) Female
5,*
Human papillomavirus (HPV) Male
5,*
Zoster
6
Measles, mumps, rubella (MMR)
7,*
Pneumococcal 13-valent conjugate (PCV13)
8,*
Pneumococcal polysaccharide (PPSV23)
9,10
Meningococcal
11,*
Hepatitis A
12,*
Hepatitis B
13,*
Haemophilus infuenzae type b (Hib)
14,*
These schedules indicate the recommended age groups and medical indications for which administration of currently licensed vaccines is commonly
indicated for adults ages 19 years and older, as of February 1, 2014. For all vaccines being recommended on the Adult mmunization Schedule:
a vaccine series does not need to be restarted, regardless of the time that has elapsed between doses. Licensed combination vaccines may be
used whenever any components of the combination are indicated and when the vaccine's other components are not contraindicated. For detailed
recommendations on all vaccines, including those used primarily for travelers or that are issued during the year, consult the manufacturers' package
inserts and the complete statements from the Advisory Committee on mmunization Practices (www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/acip-recs/index.html). Use of
trade names and commercial sources is for identifcation only and does not imply endorsement by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
3 doses
1 or 3 doses
2 doses
1 or more doses
1 dose
1 or 2 doses
1 or 2 doses Contraindicated
1 dose Contraindicated
3 doses through age 21 yrs 3 doses through age 26 yrs
3 doses through age 26 yrs 3 doses through age 26 yrs
2 doses Contraindicated
Substitute 1-time dose of Tdap for Td booster; then boost with Td every 10 yrs
1 dose IIV or LAIV
annually
1 dose IIV annually
1 dose IIV or
LAIV annually
1 dose Tdap each
pregnancy
1 dose IIV annually
Figure 2. Vaccines that might be indicated for adults based on medical and other indications
1
post-HSCT recipients only
For all persons in this category who meet the age requirements and who
lack documentation of vaccination or have no evidence of previous infection;
zoster vaccine recommended regardless of prior episode of zoster
Recommended if some other risk factor
is present (e.g., on the basis of medical,
occupational, lifestyle, or other indications)
No recommendation
*Covered by the Vaccine
Injury Compensation Program
3 doses
1. Additional information
- Addltlonal guldance for the use of the vacclnes descrlbed ln thls supplement
is available at www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/acip-recs/index.html.
- |nformatlon on vacclnatlon recommendatlons when vacclnatlon status ls
unknown and other general immunization information can be found in
the General Recommendations on Immunization at
www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/rr6002a1.htm.
- |nformatlon on travel vacclne requlrements and recommendatlons (e.g.,
for hepatitis A and B, meningococcal, and other vaccines) is available at
http://wwwnc.cdc.gov/travel/destinations/list.
- Addltlonal lnformatlon and resources regardlng vacclnatlon of pregnant women
can be found at http://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/adults/rec-vac/pregnant.html.
2. Infuenza vaccination
- Annual vacclnatlon agalnst lnnuenza ls recommended for all persons
aged 6 months or older.
- Persons aged 6 months or older, lncludlng pregnant women and persons
wlth hlves-only allergy to eggs, can recelve the lnactlvated lnnuenza
vaccine (IIV). An age-appropriate IIV formulation should be used.
- Adults aged l8 to 49 years can recelve the recomblnant lnnuenza vacclne
(RIV) (FluBlok). RIV does not contain any egg protein.
- Healthy, nonpregnant persons aged 2 to 49 years wlthout hlgh-rlsk medlcal
conditions can receive either intranasally administered live, attenuated
lnnuenza vacclne (LA|v) (PluMlst), or ||v. Health care personnel who care
for severely lmmunocompromlsed persons (l.e., those who requlre care ln
a protected envlronment) should recelve ||v or P|v rather than LA|v.
- The lntramuscularly or lntradermally admlnlstered ||v are optlons for
adults aged 18 to 64 years.
- Adults aged 65 years or older can recelve the standard-dose ||v or the
high-dose IIV (Fluzone High-Dose).
3. Tetanus, diphtheria, and acellular pertussis (Td/Tdap) vaccination
- Admlnlster l dose of Tdap vacclne to pregnant women durlng each
pregnancy (preferred during 27 to 36 weeks gestation) regardless of
interval since prior Td or Tdap vaccination.
- Persons aged ll years or older who have not recelved Tdap vacclne
or for whom vaccine status is unknown should receive a dose of Tdap
followed by tetanus and diphtheria toxoids (Td) booster doses every 10
years thereafter. Tdap can be administered regardless of interval since
the most recent tetanus or diphtheria-toxoid containing vaccine.
- Adults wlth an unknown or lncomplete hlstory of completlng a 3-dose
primary vaccination series with Td-containing vaccines should begin or
complete a primary vaccination series including a Tdap dose.
- Por unvacclnated adults, admlnlster the rst 2 doses at least 4 weeks apart
and the third dose 6 to 12 months after the second.
- Por lncompletely vacclnated (l.e., less than 3 doses) adults, admlnlster
remaining doses.
- Pefer to the AC|P statement for recommendatlons for admlnlsterlng Td/
Tdap as prophylaxis in wound management (see footnote 1).
4. Varicella vaccination
- All adults wlthout evldence of lmmunlty to varlcella (as dened below)
should receive 2 doses of single-antigen varicella vaccine or a second
dose if they have received only 1 dose.
- vacclnatlon should be emphaslzed for those who have close contact
with persons at high risk for severe disease (e.g., health care personnel
and family contacts of persons with immunocompromising conditions)
or are at high risk for exposure or transmission (e.g., teachers; child
care employees; residents and staf members of institutional settings,
including correctional institutions; college students; military personnel;
adolescents and adults living in households with children; nonpregnant
women of childbearing age; and international travelers).
- Pregnant women should be assessed for evldence of varlcella lmmunlty.
women who do not have evldence of lmmunlty should recelve the rst
dose of varicella vaccine upon completion or termination of pregnancy
and before discharge from the health care facility. The second dose should
be admlnlstered 4 to 8 weeks after the rst dose.
- Lvldence of lmmunlty to varlcella ln adults lncludes any of the followlng:
documentation of 2 doses of varicella vaccine at least 4 weeks apart;
U.S.-born before 1980, except health care personnel and pregnant women;
hlstory of varlcella based on dlagnosls or verlcatlon of varlcella dlsease
by a health care provider;
hlstory of herpes zoster based on dlagnosls or verlcatlon of herpes
zoster disease by a health care provider; or
laboratory evldence of lmmunlty or laboratory conrmatlon of dlsease.
5. Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination
- Two vacclnes are llcensed for use ln females, blvalent HPv vacclne (HPv2)
and quadrlvalent HPv vacclne (HPv4), and one HPv vacclne for use ln
males (HPV4).
- Por females, elther HPv4 or HPv2 ls recommended ln a 3-dose serles for
routine vaccination at age 11 or 12 years and for those aged 13 through
26 years, if not previously vaccinated.
- Por males, HPv4 ls recommended ln a 3-dose serles for routlne vacclnatlon
at age 11 or 12 years and for those aged 13 through 21 years, if not
previously vaccinated. Males aged 22 through 26 years may be vaccinated.
5. Human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination (contd)
- HPv4 ls recommended for men who have sex wlth men through age 26
years for those who did not get any or all doses when they were younger.
- vacclnatlon ls recommended for lmmunocompromlsed persons
(including those with HIV infection) through age 26 years for those who
did not get any or all doses when they were younger.
- A complete serles for elther HPv4 or HPv2 conslsts of 3 doses. The second
dose should be administered 4 to 8 weeks (minimum interval of 4 weeks)
after the rst dose, the thlrd dose should be admlnlstered 24 weeks after
the rst dose and l6 weeks after the second dose (mlnlmum lnterval of
at least 12 weeks).
- HPv vacclnes are not recommended for use ln pregnant women. However,
pregnancy testing is not needed before vaccination. If a woman is found
to be pregnant after initiating the vaccination series, no intervention
is needed; the remainder of the 3-dose series should be delayed until
completion of pregnancy.
6. Zoster vaccination
- A slngle dose of zoster vacclne ls recommended for adults aged 60 years
or older regardless of whether they report a prior episode of herpes zoster.
Although the vaccine is licensed by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration
for use among and can be admlnlstered to persons aged 50 years or older,
ACIP recommends that vaccination begin at age 60 years.
- Persons aged 60 years or older wlth chronlc medlcal condltlons may be
vaccinated unless their condition constitutes a contraindication, such as
pregnancy or severe lmmunodeclency.
7. Measles, mumps, rubella (MMR) vaccination
- Adults born before l957 are generally consldered lmmune to measles and
mumps. All adults born ln l957 or later should have documentatlon of l or
more doses of MMR vaccine unless they have a medical contraindication
to the vaccine or laboratory evidence of immunity to each of the three
diseases. Documentation of provider-diagnosed disease is not considered
acceptable evidence of immunity for measles, mumps, or rubella.
Measles component:
- A routlne second dose of MMP vacclne, admlnlstered a mlnlmum of 28
days after the rst dose, ls recommended for adults who:
are students in postsecondary educational institutions;
work in a health care facility; or
plan to travel internationally.
- Persons who recelved lnactlvated (kllled) measles vacclne or measles
vaccine of unknown type during 19631967 should be revaccinated with
2 doses of MMR vaccine.
Mumps component:
- A routlne second dose of MMP vacclne, admlnlstered a mlnlmum of 28
days after the rst dose, ls recommended for adults who:
are students in a postsecondary educational institution;
work in a health care facility; or
plan to travel internationally.
- Persons vacclnated before l979 wlth elther kllled mumps vacclne
or mumps vaccine of unknown type who are at high risk for mumps
infection (e.g., persons who are working in a health care facility) should
be considered for revaccination with 2 doses of MMR vaccine.
Rubella component:
- Por women of chlldbearlng age, regardless of blrth year, rubella lmmunlty
should be determined. If there is no evidence of immunity, women who
are not pregnant should be vaccinated. Pregnant women who do not have
evidence of immunity should receive MMR vaccine upon completion or
termination of pregnancy and before discharge from the health care facility.
Health care personnel born before 1957:
- Por unvacclnated health care personnel born before l957 who lack
laboratory evldence of measles, mumps, and/or rubella lmmunlty or
laboratory conrmatlon of dlsease, health care facllltles should conslder
vaccinating personnel with 2 doses of MMR vaccine at the appropriate
interval for measles and mumps or 1 dose of MMR vaccine for rubella.
8. Pneumococcal conjugate (PCV13) vaccination
- Adults aged l9 years or older wlth lmmunocompromlslng condltlons
(including chronic renal failure and nephrotic syndrome), functional or
anatomlc asplenla, cerebrosplnal nuld leaks, or cochlear lmplants who
have not previously received PCV13 or PPSV23 should receive a single
dose of PCV13 followed by a dose of PPSV23 at least 8 weeks later.
- Adults aged l9 years or older wlth the aforementloned condltlons who
have previously received 1 or more doses of PPSV23 should receive a dose
of PCV13 one or more years after the last PPSV23 dose was received. For
adults who requlre addltlonal doses of PPSv23, the rst such dose should
be glven no sooner than 8 weeks after PCvl3 and at least 5 years after
the most recent dose of PPSV23.
- when lndlcated, PCvl3 should be admlnlstered to patlents who are
uncertain of their vaccination status history and have no record of previ-
ous vaccination.
- Although PCvl3 ls llcensed by the U.S. Pood and Drug Admlnlstratlon
for use among and can be admlnlstered to persons aged 50 years or
older, ACIP recommends PCV13 for adults aged 19 years or older with
the speclc medlcal condltlons noted above.
Footnotes
Recommended Immunization Schedule for Adults Aged 19 Years or Older: United States, 2014
9. Pneumococcal polysaccharide (PPSV23) vaccination
- when PCvl3 ls also lndlcated, PCvl3 should be glven rst (see footnote 8).
- vacclnate all persons wlth the followlng lndlcatlons:
all adults aged 65 years or older,
adults younger than 65 years wlth chronlc lung dlsease (lncludlng
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, emphysema, and asthma),
chronic cardiovascular diseases, diabetes mellitus, chronic renal fail-
ure, nephrotic syndrome, chronic liver disease (including cirrhosis),
alcohollsm, cochlear lmplants, cerebrosplnal nuld leaks, lmmunocom-
promising conditions, and functional or anatomic asplenia (e.g., sickle
cell dlsease and other hemogloblnopathles, congenltal or acqulred
asplenia, splenic dysfunction, or splenectomy [if elective splenectomy
is planned, vaccinate at least 2 weeks before surgery]);
residents of nursing homes or long-term care facilities; and
adults who smoke cigarettes.
- Persons wlth lmmunocompromlslng condltlons and other selected
conditions are recommended to receive PCV13 and PPSV23 vaccines. See
footnote 8 for information on timing of PCV13 and PPSV23 vaccinations.
- Persons wlth asymptomatlc or symptomatlc H|v lnfectlon should be
vaccinated as soon as possible after their diagnosis.
- when cancer chemotherapy or other lmmunosuppresslve therapy ls
being considered, the interval between vaccination and initiation of
immunosuppressive therapy should be at least 2 weeks. Vaccination
during chemotherapy or radiation therapy should be avoided.
- Poutlne use of PPSv23 vacclne ls not recommended for Amerlcan |ndlans/
Alaska Natlves or other persons younger than 65 years unless they have
underlying medical conditions that are PPSV23 indications. However, pub-
lic health authorities may consider recommending PPSV23 for American
|ndlans/Alaska Natlves who are llvlng ln areas where the rlsk for lnvaslve
pneumococcal disease is increased.
- when lndlcated, PPSv23 vacclne should be admlnlstered to patlents who
are uncertain of their vaccination status and have no record of vaccination.
10. Revaccination with PPSV23
- One-tlme revacclnatlon 5 years after the rst dose of PPSv23 ls recom-
mended for persons aged 19 through 64 years with chronic renal failure
or nephrotic syndrome, functional or anatomic asplenia (e.g., sickle cell
disease or splenectomy), or immunocompromising conditions.
- Persons who recelved l or 2 doses of PPSv23 before age 65 years for any
lndlcatlon should recelve another dose of the vacclne at age 65 years or
later lf at least 5 years have passed slnce thelr prevlous dose.
- No further doses of PPSv23 are needed for persons vacclnated wlth
PPSv23 at or after age 65 years.
11. Meningococcal vaccination
- Admlnlster 2 doses of quadrlvalent menlngococcal con[ugate vacclne
(MenACWY-D [Menactra]) at least 2 months apart to adults of all
ages with functional asplenia or persistent complement component
declencles. H|v lnfectlon ls not an lndlcatlon for routlne vacclnatlon
with MenACWY-D. If an HIV-infected person of any age is vaccinated, 2
doses of MenACWY-D should be administered at least 2 months apart.
- Admlnlster a slngle dose of menlngococcal vacclne to mlcroblologlsts
routinely exposed to isolates of Neisseria meningitidis, military recruits,
persons at risk during an outbreak attributable to a vaccine serogroup,
and persons who travel to or live in countries in which meningococcal
disease is hyperendemic or epidemic.
- Plrst-year college students up through age 2l years who are llvlng ln
residence halls should be vaccinated if they have not received a dose on
or after their 16th birthday.
- MenACw-D ls preferred for adults wlth any of the precedlng lndlcatlons
who are aged 55 years or younger as well as for adults aged 56 years
or older who a) were vaccinated previously with MenACWY-D and are
recommended for revaccination, or b) for whom multiple doses are
anticipated. Meningococcal polysaccharide vaccine (MenACWY-CRM
|Menveo|) ls preferred for adults aged 56 years or older who have not
recelved MenACw-D prevlously and who requlre a slngle dose only (e.g.,
travelers).
- Pevacclnatlon wlth MenACw-D every 5 years ls recommended for
adults previously vaccinated with MenACWY-D or MenACWY-CRM
who remain at increased risk for infection (e.g., adults with anatomic or
functlonal asplenla, perslstent complement component declencles, or
microbiologists).
12. Hepatitis A vaccination
- vacclnate any person seeklng protectlon from hepatltls A vlrus (HAv)
infection and persons with any of the following indications:
men who have sex wlth men and persons who use ln[ectlon or non-
ln[ectlon llllclt drugs,
persons working with HAV-infected primates or with HAV in a research
laboratory setting;
persons with chronic liver disease and persons who receive clotting
factor concentrates;
persons traveling to or working in countries that have high or inter-
mediate endemicity of hepatitis A; and
12. Hepatitis A vaccination (contd)
unvaccinated persons who anticipate close personal contact (e.g.,
household or regular babysitting) with an international adoptee
durlng the rst 60 days after arrlval ln the Unlted States from a coun-
try with high or intermediate endemicity. (See footnote 1 for more
lnformatlon on travel recommendatlons.) The rst dose of the 2-dose
hepatitis A vaccine series should be administered as soon as adoption
is planned, ideally 2 or more weeks before the arrival of the adoptee.
- Slngle-antlgen vacclne formulatlons should be admlnlstered ln a 2-dose
schedule at either 0 and 6 to 12 months (Havrix), or 0 and 6 to 18 months
(vaqta). |f the comblned hepatltls A and hepatltls 8 vacclne (Twlnrlx) ls
used, administer 3 doses at 0, 1, and 6 months; alternatively, a 4-dose
schedule may be used, administered on days 0, 7, and 21 to 30 followed
by a booster dose at month 12.
13. Hepatitis B vaccination
- vacclnate persons wlth any of the followlng lndlcatlons and any person
seeking protection from hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection:
sexually active persons who are not in a long-term, mutually monoga-
mous relationship (e.g., persons with more than 1 sex partner during
the previous 6 months); persons seeking evaluation or treatment for
a sexually transmltted dlsease (STD), current or recent ln[ectlon drug
users; and men who have sex with men;
health care personnel and public safety workers who are potentially
exposed to blood or other lnfectlous body nulds,
persons with diabetes who are younger than age 60 years as soon as
feasible after diagnosis; persons with diabetes who are age 60 years or
older at the discretion of the treating clinician based on the likelihood
of acqulrlng H8v lnfectlon, lncludlng the rlsk posed by an lncreased
need for assisted blood glucose monitoring in long-term care facili-
tles, the llkellhood of experlenclng chronlc sequelae lf lnfected wlth
HBV, and the likelihood of immune response to vaccination;
persons with end-stage renal disease, including patients receiving
hemodialysis, persons with HIV infection, and persons with chronic
liver disease;
household contacts and sex partners of hepatitis B surface anti-
genpositive persons, clients and staf members of institutions for
persons with developmental disabilities, and international travelers
to countries with high or intermediate prevalence of chronic HBV
infection; and
all adults in the following settings: STD treatment facilities, HIV test-
ing and treatment facilities, facilities providing drug abuse treatment
and prevention services, health care settings targeting services to
ln[ectlon drug users or men who have sex wlth men, correctlonal
facilities, end-stage renal disease programs and facilities for chronic
hemodialysis patients, and institutions and nonresidential day care
facilities for persons with developmental disabilities.
- Admlnlster mlsslng doses to complete a 3-dose serles of hepatltls 8
vaccine to those persons not vaccinated or not completely vaccinated.
The second dose should be admlnlstered l month after the rst dose, the
third dose should be given at least 2 months after the second dose (and
at least 4 months after the rst dose). |f the comblned hepatltls A and
hepatitis B vaccine (Twinrix) is used, give 3 doses at 0, 1, and 6 months;
alternatively, a 4-dose Twinrix schedule, administered on days 0, 7, and
21 to 30 followed by a booster dose at month 12 may be used.
- Adult patlents recelvlng hemodlalysls or wlth other lmmunocompromlslng
condltlons should recelve l dose of 40 mcg/mL (Pecomblvax H8)
administered on a 3-dose schedule at 0, 1, and 6 months or 2 doses of 20
mcg/mL (Lngerlx-8) admlnlstered slmultaneously on a 4-dose schedule
at 0, 1, 2, and 6 months.
14. Haemophilus infuenzae type b (Hib) vaccination
- One dose of Hlb vacclne should be admlnlstered to persons who have
functional or anatomic asplenia or sickle cell disease or are undergoing
elective splenectomy if they have not previously received Hib vaccine.
Hib vaccination 14 or more days before splenectomy is suggested.
- Peclplents of a hematopoletlc stem cell transplant should be vacclnated
with a 3-dose regimen 6 to 12 months after a successful transplant,
regardless of vaccination history; at least 4 weeks should separate doses.
- Hlb vacclne ls not recommended for adults wlth H|v lnfectlon slnce thelr
risk for Hib infection is low.
15. Immunocompromising conditions
- |nactlvated vacclnes generally are acceptable (e.g., pneumococcal,
menlngococcal, and lnactlvated lnnuenza vacclne) and llve vacclnes
generally are avoided in persons with immune deficiencies or
lmmunocompromlslng condltlons. |nformatlon on speclc condltlons
is available at http://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/acip-recs/index.html.
TABLE. Contraindications and precautions to commonly used vaccines in adults: United States, 2014
1*|
Vaccine Contraindications Precautions
nfuenza, inactivated vaccine
(V)
2
Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after previous dose of any
V or LAV or to a vaccine component, including egg protein.
Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever.
History of Guillain-Barr Syndrome within 6 weeks of previous infuenza
vaccination.
Persons who experience only hives with exposure to eggs may receive RIV
(if age 18-49 years) or, with additional safety precautions, V.
2
nfuenza, recombinant (RV) Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after previous dose of RV
or to a vaccine component. RIV does not contain any egg protein.
2
Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever.
History of Guillain-Barr Syndrome within 6 weeks of previous infuenza
vaccination.
nfuenza, live attenuated
(LAV)
2,3
Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after previous dose of any
V or LAV or to a vaccine component, including egg protein.
Conditions for which the Advisory Committee on mmunization
Practices (ACP) recommends against use, but which are not
contraindications in vaccine package insert: immune suppression,
certain chronic medical conditions (such as asthma, diabetes, heart or
kidney disease). and pregnancy.
2,3
Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever.
History of Guillain-Barr Syndrome within 6 weeks of previous infuenza
vaccination.
Receipt of specifc antivirals (i.e., amantadine, rimantadine, zanamivir, or
oseltamivir) within 48 hours before vaccination. Avoid use of these antiviral
drugs for 14 days after vaccination.
Tetanus, diphtheria, pertussis
(Tdap);
tetanus, diphtheria (Td)
Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose or to
a vaccine component.
For pertussis-containing vaccines: encephalopathy (e.g., coma,
decreased level of consciousness, or prolonged seizures)
not attributable to another identifable cause within 7 days of
administration of a previous dose of Tdap or diphtheria and tetanus
toxoids and pertussis (DTP) or diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and
acellular pertussis (DTaP) vaccine.
Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever.
Guillain-Barr Syndrome within 6 weeks after a previous dose of tetanus toxoid
containing vaccine.
History of Arthus-type hypersensitivity reactions after a previous dose of tetanus
or diphtheria toxoidcontaining vaccine; defer vaccination until at least 10 years
have elapsed since the last tetanus toxoid-containing vaccine.
For pertussis-containing vaccines: progressive or unstable neurologic disorder,
uncontrolled seizures, or progressive encephalopathy until a treatment regimen
has been established and the condition has stabilized.
Varicella
3
Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose or to
a vaccine component.
Known severe immunodefciency (e.g., from hematologic and solid
tumors, receipt of chemotherapy, congenital immunodefciency,
or long-term immunosuppressive therapy
4
or patients with
human immunodefciency virus (HV) infection who are severely
immunocompromised).
Pregnancy.
Recent (within 11 months) receipt of antibody-containing blood product
(specifc interval depends on product).
5
Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever.
Receipt of specifc antivirals (i.e., acyclovir, famciclovir, or valacyclovir) 24
hours before vaccination; avoid use of these antiviral drugs for 14 days after
vaccination.
Human papillomavirus (HPV) Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose or to
a vaccine component.
Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever.
Pregnancy.
Zoster
3
Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) to a vaccine component.
Known severe immunodefciency (e.g., from hematologic and solid
tumors, receipt of chemotherapy, or long-term immunosuppressive
therapy
4
or patients with HV infection who are severely
immunocompromised).
Pregnancy.
Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever.
Receipt of specifc antivirals (i.e., acyclovir, famciclovir, or valacyclovir) 24
hours before vaccination; avoid use of these antiviral drugs for 14 days after
vaccination.
Measles, mumps, rubella
(MMR)
3
Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose or to
a vaccine component.
Known severe immunodefciency (e.g., from hematologic and solid
tumors, receipt of chemotherapy, congenital immunodefciency, or
long-term immunosuppressive therapy
4
or patients with HV infection
who are severely immunocompromised).
Pregnancy.
Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever.
Recent (within 11 months) receipt of antibody-containing blood product
(specifc interval depends on product).
5
History of thrombocytopenia or thrombocytopenic purpura.
Need for tuberculin skin testing.
6
Pneumococcal conjugate
(PCV13)
Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose or to
a vaccine component, including to any vaccine containing diphtheria
toxoid.
Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever.
Pneumococcal polysaccharide
(PPSV23)
Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose or to
a vaccine component.
Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever.
Meningococcal,
conjugate, (MenACYW-D);
meningococcal, polysaccharide
(MenACWY-CRM)
Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose or to
a vaccine component.
Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever.
Hepatitis A (HepA) Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose or to
a vaccine component.
Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever.
Hepatitis B (HepB) Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose or to
a vaccine component.
Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever.
Haemophilus infuenzae Type
b (Hib)
Severe allergic reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis) after a previous dose or to
a vaccine component.
Moderate or severe acute illness with or without fever.
1. Vaccine package inserts and the full ACP recommendations for these vaccines should be consulted for additional information on vaccine-related contraindications and precautions and for more
information on vaccine excipients. Events or conditions listed as precautions should be reviewed carefully. Benefts of and risks for administering a specifc vaccine to a person under these
circumstances should be considered. f the risk from the vaccine is believed to outweigh the beneft, the vaccine should not be administered. f the beneft of vaccination is believed to outweigh the
risk, the vaccine should be administered. A contraindication is a condition in a recipient that increases the chance of a serious adverse reaction. Therefore, a vaccine should not be administered
when a contraindication is present.
2. For more information on use of infuenza vaccines among persons with egg allergies and a complete list of conditions that CDC considers to be reasons to avoid receiving LAV, see CDC. Prevention
and control of seasonal infuenza with vaccines: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on mmunization Practices (ACP) United States, 201314. MMWR 2013;62(RR07):1-43. Available at
http://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/rr6207a1.htm.
3. LAV, MMR, varicella, or zoster vaccines can be administered on the same day. f not administered on the same day, live vaccines should be separated by at least 28 days.
4. Immunosuppressive steroid dose is considered to be >2 weeks of daily receipt of 20 mg of prednisone or the equivalent. Vaccination should be deferred for at least 1 month after discontinuation of
such therapy. Providers should consult ACP recommendations for complete information on the use of specifc live vaccines among persons on immune-suppressing medications or with immune
suppression because of other reasons.
5. Vaccine should be deferred for the appropriate interval if replacement immune globulin products are being administered. See CDC. General recommendations on immunization: recommendations
of the Advisory Committee on mmunization Practices (ACP). MMWR 2011;60(No. RR-2). Available at www.cdc.gov/vaccines/hcp/acip-recs/index.html.
6. Measles vaccination might suppress tuberculin reactivity temporarily. Measles-containing vaccine may be administered on the same day as tuberculin skin testing. f testing cannot be performed
until after the day of MMR vaccination, the test should be postponed for at least 4 weeks after the vaccination. f an urgent need exists to skin test, do so with the understanding that reactivity
might be reduced by the vaccine.
* Adapted from CDC. Table 6. Contraindications and precautions to commonly used vaccines. General recommendations on immunization: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on
mmunization Practices. MMWR 2011;60(No. RR-2):4041 and from Atkinson W, Wolfe S, Hamborsky J, eds. Appendix A. Epidemiology and prevention of vaccine preventable diseases. 12th ed.
Washington, DC: Public Health Foundation, 2011. Available at www.cdc.gov/vaccines/pubs/pinkbook/index.html.
| Regarding latex allergy, consult the package insert for any vaccine administered.
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services
Centers for Disease and Prevention
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- 04 Immunizations and Developmental Milestones For Your Child From Birth Through 6 Years OldDocument2 pages04 Immunizations and Developmental Milestones For Your Child From Birth Through 6 Years Oldapi-309082881Pas encore d'évaluation
- Generic Price List (Aug'21)Document24 pagesGeneric Price List (Aug'21)kiba elgibraPas encore d'évaluation
- Insulin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesInsulin Drug StudyRai Hanah92% (13)
- Qualicaps - Technical Brochure - Quali-VDocument4 pagesQualicaps - Technical Brochure - Quali-VrattychattyPas encore d'évaluation
- Obgm Feb2018 Vol.30 No.2 PDFDocument55 pagesObgm Feb2018 Vol.30 No.2 PDFlcmurilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Pregnancy Following Miscarriage What Is The Optimum Interpregnancy IntervalDocument3 pagesPregnancy Following Miscarriage What Is The Optimum Interpregnancy IntervallcmurilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Patient-Centered Risk Assessment For Ovarian CancerDocument13 pagesPatient-Centered Risk Assessment For Ovarian CancerlcmurilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Alteration of The Hormone-Free IntervalDocument2 pagesAlteration of The Hormone-Free IntervalAnonymous d4X4wZLDPas encore d'évaluation
- Obgm Mar2018 Vol.30 No.3Document57 pagesObgm Mar2018 Vol.30 No.3lcmurilloPas encore d'évaluation
- ACOG Practice Advisory On Annual Pelvic Examination RecommendationsDocument1 pageACOG Practice Advisory On Annual Pelvic Examination RecommendationslcmurilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Tamizaje CancerDocument1 pageTamizaje CancerlcmurilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Obgm Modern Day Laboring FinalDocument8 pagesObgm Modern Day Laboring FinallcmurilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Obgm Mar2018 Vol.30 No.3Document57 pagesObgm Mar2018 Vol.30 No.3lcmurilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Caffeine Intake - Even Dad's - Linked To Miscarriage, Study Says - MedlinePlusDocument3 pagesCaffeine Intake - Even Dad's - Linked To Miscarriage, Study Says - MedlinePluslcmurilloPas encore d'évaluation
- A Randomized Trial Comparing SkinDocument9 pagesA Randomized Trial Comparing SkinlcmurilloPas encore d'évaluation
- P 4065Document2 pagesP 4065lcmurilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Everyday Contraception ConsiderationsDocument15 pagesEveryday Contraception ConsiderationslcmurilloPas encore d'évaluation
- 11complications of Unsafe Abortion in Sub-SaharanDocument15 pages11complications of Unsafe Abortion in Sub-SaharanlcmurilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Pelvic Examination 3Document1 pagePelvic Examination 3lcmurilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Pelvic ExaminationDocument14 pagesPelvic ExaminationlcmurilloPas encore d'évaluation
- HBV Screening 4Document1 pageHBV Screening 4lcmurilloPas encore d'évaluation
- HBV Screening 5Document3 pagesHBV Screening 5lcmurilloPas encore d'évaluation
- HBV ScreeningDocument24 pagesHBV ScreeninglcmurilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Pi Is 074937970300120 XDocument7 pagesPi Is 074937970300120 XlcmurilloPas encore d'évaluation
- 2013 Recommended Adolescent ImmunizationDocument2 pages2013 Recommended Adolescent ImmunizationArvi MandawePas encore d'évaluation
- Parent Ver SCH 0 6yrsDocument2 pagesParent Ver SCH 0 6yrslcmurilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Pelvic Examination 2Document7 pagesPelvic Examination 2lcmurilloPas encore d'évaluation
- HBV Screening 2Document10 pagesHBV Screening 2lcmurilloPas encore d'évaluation
- P 4036Document3 pagesP 4036lcmurilloPas encore d'évaluation
- P 4060Document2 pagesP 4060lcmurilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Catchup ScheduleDocument4 pagesCatchup ScheduleAisha SyedPas encore d'évaluation
- Summary of Recommendations For Adult Immunization: (Age 19 Years & Older)Document4 pagesSummary of Recommendations For Adult Immunization: (Age 19 Years & Older)gyna_2002Pas encore d'évaluation
- Common Drugs Used inDocument44 pagesCommon Drugs Used inrajkumar871992100% (1)
- IOM Pharmacology IDocument93 pagesIOM Pharmacology ISahara MahatPas encore d'évaluation
- Efficacy and Safety of Biologics in Psoriatic Arthritis - A Systematic Literature Review and Network Meta-Analysis 2020Document12 pagesEfficacy and Safety of Biologics in Psoriatic Arthritis - A Systematic Literature Review and Network Meta-Analysis 2020Diana GCPas encore d'évaluation
- CALABANGA MONITORING - OdsDocument10 pagesCALABANGA MONITORING - Odsglecy malatePas encore d'évaluation
- Pricelist Pharmasolindo 2018Document11 pagesPricelist Pharmasolindo 2018Niken Claudya Ecfrencylie0% (1)
- CPCS Antidote ChartDocument1 pageCPCS Antidote ChartWesam Al-TawilPas encore d'évaluation
- Foundations of Pharmacology NotesDocument5 pagesFoundations of Pharmacology NotesSheril MarekPas encore d'évaluation
- Anne DocsDocument3 pagesAnne DocsRobi SuaresPas encore d'évaluation
- One Compartment Oral Admin - Solved ProblemsDocument10 pagesOne Compartment Oral Admin - Solved ProblemsLeader Leyva Hernandez100% (2)
- Inlay Tablets A Novel Approach PDFDocument10 pagesInlay Tablets A Novel Approach PDFTakeshi MondaPas encore d'évaluation
- 508-Prowell-Final Slides5Document25 pages508-Prowell-Final Slides5dfsdjgflksjgnawPas encore d'évaluation
- Surat Pesanan Obat Apotek Ym 123Document4 pagesSurat Pesanan Obat Apotek Ym 123ymPas encore d'évaluation
- Injection Product List HDocument11 pagesInjection Product List Halnikki25kPas encore d'évaluation
- Part Two ResourcesDocument4 pagesPart Two Resourcesapi-158169273Pas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study 2Document1 pageDrug Study 2Cris Anne AlvarezPas encore d'évaluation
- Vasotec EnalaprilDocument1 pageVasotec EnalaprilCassie100% (1)
- Introduction To DrugsDocument4 pagesIntroduction To DrugsTaufik Abdul HadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Template Dan Panduan Data ObatDocument10 pagesTemplate Dan Panduan Data ObatAini SavitriPas encore d'évaluation
- Formulation and Evaluation of Zolpidem Tartrate Extended Release Matrix TabletsDocument8 pagesFormulation and Evaluation of Zolpidem Tartrate Extended Release Matrix Tabletserminb1525Pas encore d'évaluation
- Master Papakrivos JDocument76 pagesMaster Papakrivos JRaghavendra NaveenPas encore d'évaluation
- Bimbingan UKMPPD - IPDDocument50 pagesBimbingan UKMPPD - IPDlinggarPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study DiazepamDocument1 pageDrug Study DiazepamAnjae GariandoPas encore d'évaluation
- 21 CFR Part 111, Dietary Supplement CGMP - Background, Development, Content, Comparison To Drug CGMP, and The FutureDocument9 pages21 CFR Part 111, Dietary Supplement CGMP - Background, Development, Content, Comparison To Drug CGMP, and The Futuremelimaulani-1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pharm Quiz 1Document59 pagesPharm Quiz 1Anonymous vXOM1Wxt100% (1)
- Obat High Alert Dan T. EmergencyDocument2 pagesObat High Alert Dan T. EmergencyMaria CerlitaPas encore d'évaluation
- CIOMS Guideline Preparing Clinical and Safety InformationDocument4 pagesCIOMS Guideline Preparing Clinical and Safety InformationNataliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Card Tricyclic DepressantsDocument2 pagesDrug Card Tricyclic DepressantsAaLona RobinsonPas encore d'évaluation