Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Image Size
Transféré par
Vibhav SinghDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Image Size
Transféré par
Vibhav SinghDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
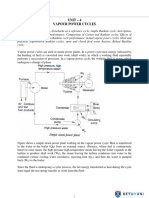
Abstract A setup consisting of a long filament lamp, screen, and convex lens was used to determine the height
of the image formed. The distance of the image from the lenses was measured and then compared to the expected distance predicted by the thin lens equation in order to verify the equation. A graph of the magnification vs object distance divided by image distance was constructed to measure the relationship between these two quantities.
Introduction The purpose of the experiment was to test whether our results matched what the thin lens equation predicts what our image distance should be as well as to analyze the relationship between magnification (M) vs object distance divided by image distance (s/s). The setup is shown in Figure 2. Prediction
The image distance should always be so that the 1/s + 1/s = 1/f where f is the focal length. In other words, the image distance should satisfy the thin lens equation. The relationship between m and s/s should be inverse because the magnification equation is, m = hi/ho = -s/s where hi and ho are image and object height respectively. Due to the minus sign, the graph should look similar to the graph of the equation y= -1/x shown below.
Procedure
Figure 2: Experimental setup that was used. This report uses S and S for the object and image distance but the figure shows O and i respectively simply because the figure was obtained from an outside source1. The focal length is shown as f.
The object was placed at varying distances from the convex lens but always outside the focal length so a real image would form on the screen. The object distance and image distances were measured as well as the heights. The focal length was varied by using a different convex lens.
Results
Trial 1 2 3 4 5 6 Focal length S (cm) (cm) 20 20 10 10 10 20 65 27 14 40 19 42 S (cm) 27 67 30 13 19 36 H0 (cm) 10.9 10.9 10.9 10.9 10.9 10.9 Hi (cm) 3.3 18.5 17 2.8 8.1 6.2 M -0.42 -2.48 -2.14 -0.33 -1.0 -0.86
Table 1: Summary of parameters of trials.
Figure 3: Plot of M vs S/S. The plot shows the relationship between magnification and S/S.
Analysis As predicted the relationship between the magnification and the object distance divided by image distance was an inverse one because as seen in Figure 3 when the magnitude of the
magnification increases, S/S decreases. The negative on the magnification means that the image was inverted. The measured values for the image distance, S, matched closely with what the thin lens equation predicted. A sample calculation of trial 1 can verify this. 1/f = 1/s + 1/s (1/20) (1/65) = 1/s s= 28.9 Comparing this value to our measured value of 27, it can be seen that our results do indeed verify the thin lens equation within error.
Conclusion
It was found that the magnification and s/s are inversely related and that the thin lens equation can indeed be used to find the image distance accurately given the focal length and object distance.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 2016 Dec From Conflict To Illicit Mapping The Diamond Trade From Central African Republic To CameroonDocument36 pages2016 Dec From Conflict To Illicit Mapping The Diamond Trade From Central African Republic To CameroonVibhav Singh100% (1)
- Bnym Sanctions SummaryDocument2 pagesBnym Sanctions SummaryVibhav SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- FisheriesAct Cap378 1991 Revised 2012Document176 pagesFisheriesAct Cap378 1991 Revised 2012Vibhav SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Debating Dos and DontsDocument23 pagesDebating Dos and DontsMahassen MgadmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Upayas (Diplomacy)Document1 pageUpayas (Diplomacy)Vibhav SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Jordan B. Peterson - Template For Writing EssaysDocument24 pagesJordan B. Peterson - Template For Writing EssaysvojarufosiPas encore d'évaluation
- Visual Impact - Special Report 5Document21 pagesVisual Impact - Special Report 5raamsid100% (1)
- OSC NorthKorea ForeignJointVenturesDocument23 pagesOSC NorthKorea ForeignJointVenturesVibhav SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Dawson JAHDocument29 pagesDawson JAHVibhav SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- The Korean Wave (Hallyu) in East Asia A Comparison of Chinese, Japanese, and Taiwanese Audiences Who Watch Korean TV Dramas ) JONGHOE YANGDocument46 pagesThe Korean Wave (Hallyu) in East Asia A Comparison of Chinese, Japanese, and Taiwanese Audiences Who Watch Korean TV Dramas ) JONGHOE YANGVibhav SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Artha ShastraDocument17 pagesArtha ShastraVibhav SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning Micro-Management Skills in RTS Games by Imitating ExpertsDocument7 pagesLearning Micro-Management Skills in RTS Games by Imitating ExpertsVibhav SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- North Korea Ups Pace of Ballistic Missile Launches EditDocument7 pagesNorth Korea Ups Pace of Ballistic Missile Launches EditVibhav SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- The bacteriophage φ29 portal motor can package DNA against a large internal forceDocument5 pagesThe bacteriophage φ29 portal motor can package DNA against a large internal forceapi-3745879Pas encore d'évaluation
- Wild Fisheries Reform Web PageDocument1 pageWild Fisheries Reform Web PageVibhav SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Study: Vietnamese Frozen Pangasius and Shrimp Exports: Rejections of Vietnamese Agri-Food Exports at Major MarketsDocument22 pagesCase Study: Vietnamese Frozen Pangasius and Shrimp Exports: Rejections of Vietnamese Agri-Food Exports at Major MarketsVibhav SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Laundering Fish in The Global Undercurrents - Illegal UnreportedDocument60 pagesLaundering Fish in The Global Undercurrents - Illegal UnreportedVibhav SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- The Role of Export Taxes in The Field of Primary CommoditiesDocument28 pagesThe Role of Export Taxes in The Field of Primary CommoditiesManisha BhanushaliPas encore d'évaluation
- EtiquetteDocument4 pagesEtiquetteasnarPas encore d'évaluation
- Japan-North Korea Relations.: Bad and Not Getting BetterDocument7 pagesJapan-North Korea Relations.: Bad and Not Getting BetterVibhav SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- North Korea Famine PDFDocument47 pagesNorth Korea Famine PDFVibhav SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Opposition Research - "I Dabbled in Witchcraft" or How To Conduct Opposition ResearchDocument11 pagesOpposition Research - "I Dabbled in Witchcraft" or How To Conduct Opposition ResearchBenPas encore d'évaluation
- C 4.1.7 Course Study StrategiesDocument2 pagesC 4.1.7 Course Study StrategiesVibhav SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- NMDMP Report April 2008Document74 pagesNMDMP Report April 2008Vibhav SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- CF137 Chap10Document14 pagesCF137 Chap10Vibhav SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- South Sudan LHZ Report - FinalDocument49 pagesSouth Sudan LHZ Report - FinalVibhav SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Seksse HemDocument9 pagesSeksse HemEdyWibowoPas encore d'évaluation
- Website Opposition ResearchDocument24 pagesWebsite Opposition ResearchVibhav SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- C 4.1.1 Instant Study SkillsDocument6 pagesC 4.1.1 Instant Study SkillsVibhav SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- InternationalDocument5 pagesInternationalVibhav SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (344)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (587)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (265)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Copper Electrowinning From Cyanide Solutions by Lu Jianming PDFDocument306 pagesCopper Electrowinning From Cyanide Solutions by Lu Jianming PDFFerudun AkyolPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanical Properties of MaterialsDocument45 pagesMechanical Properties of MaterialsRonan SeePas encore d'évaluation
- Application of Epoxy Resins in Electrical ApparatusDocument8 pagesApplication of Epoxy Resins in Electrical ApparatusDulon22Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mn-Cu Alloying Improves Mechanical Properties of Ductile IronDocument7 pagesMn-Cu Alloying Improves Mechanical Properties of Ductile IronabhiPas encore d'évaluation
- Model Exam - 1Document6 pagesModel Exam - 1Bipul Poudel100% (2)
- Integriwise Assessment Report: Project InformationDocument3 pagesIntegriwise Assessment Report: Project Informationsanu patilPas encore d'évaluation
- Tensar Structural Geogrid Product SpecificationsDocument7 pagesTensar Structural Geogrid Product SpecificationsVereș RăzvanPas encore d'évaluation
- Distillation Column DesignDocument66 pagesDistillation Column Designsalmanmuddsar83% (6)
- Titanium Alloys in Total Joint Replacement - A Materials Science PerspectiveDocument9 pagesTitanium Alloys in Total Joint Replacement - A Materials Science PerspectiveSatria Adi NugrohoPas encore d'évaluation
- Natural Ventilation Explained in MinesDocument16 pagesNatural Ventilation Explained in Minesalwcastillo100% (2)
- Applsci 12 11268Document19 pagesApplsci 12 11268Yuvaraj muthukrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Traversable Wormholes: Some Simple Examples: Matt VisserDocument7 pagesTraversable Wormholes: Some Simple Examples: Matt VisserllapeyrePas encore d'évaluation
- Catalog 2023 FinalDocument55 pagesCatalog 2023 FinalHana VũPas encore d'évaluation
- Rankine and Carnot NumericalsDocument59 pagesRankine and Carnot NumericalsBhargav PrajwalPas encore d'évaluation
- Tablas SI - Moran & Shapiro - Fundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics 5th Edition (Con R12)Document53 pagesTablas SI - Moran & Shapiro - Fundamentals of Engineering Thermodynamics 5th Edition (Con R12)Yasir MumtazPas encore d'évaluation
- UNIT 4 Raman Spectroscopy 12309Document24 pagesUNIT 4 Raman Spectroscopy 12309NathanianPas encore d'évaluation
- The NDT TechnicianDocument12 pagesThe NDT TechnicianAnca ElenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Walking Column Detailed DesignDocument1 pageWalking Column Detailed DesignTommaso Pascon100% (1)
- 12 Chemistry Important Questions Solid State 01Document7 pages12 Chemistry Important Questions Solid State 01Shahariya ShejeerPas encore d'évaluation
- Fresh Water GeneratorDocument22 pagesFresh Water GeneratorCungkringPas encore d'évaluation
- RBDPSDocument1 pageRBDPSSriyonoPas encore d'évaluation
- Group Delay and Mode Delay Factor: Fiber MaterialsDocument49 pagesGroup Delay and Mode Delay Factor: Fiber MaterialsPavani MandapatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Nptel: Computational Fluid Dynamics For Turbomachinery - Web CourseDocument3 pagesNptel: Computational Fluid Dynamics For Turbomachinery - Web CourseAissa AMOURPas encore d'évaluation
- Group member list and safety procedures for engine ground power and control system toolsDocument9 pagesGroup member list and safety procedures for engine ground power and control system toolsAQALILY SOFIENAPas encore d'évaluation
- Single Counterbalance, Relief Compensated: A-VBSO-SE-CC-30-PL 08.45.17 - X - Y - ZDocument2 pagesSingle Counterbalance, Relief Compensated: A-VBSO-SE-CC-30-PL 08.45.17 - X - Y - Znemi90Pas encore d'évaluation
- Equilibrium WorksheetDocument7 pagesEquilibrium WorksheetCJ RhodesPas encore d'évaluation
- A As Suction Accumulators (PA 00307)Document2 pagesA As Suction Accumulators (PA 00307)scualoboy2006Pas encore d'évaluation
- MomentumDocument7 pagesMomentumSaberPas encore d'évaluation
- Duaso Test YourselfDocument42 pagesDuaso Test YourselfSharmaine Cruzat Austria100% (1)
- Measurement of Condensation Heat Transfer Coefficient Inside A Vertical Tube in The Presence of Noncondensable Gas PDFDocument11 pagesMeasurement of Condensation Heat Transfer Coefficient Inside A Vertical Tube in The Presence of Noncondensable Gas PDFmintuPas encore d'évaluation