Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
CCNA 3 PT 1.3.2 Reflection
Transféré par
motdflyinglowCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
CCNA 3 PT 1.3.2 Reflection
Transféré par
motdflyinglowDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
PT Activity 1.3.
2: Review of Concepts from Exploration 1 - Challenge
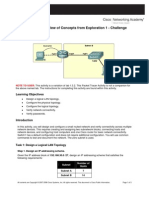
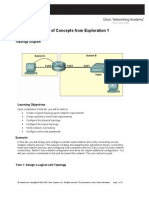
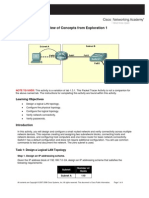
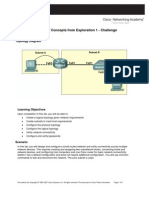
Topology Diagram
NOTE TO USER: This activity is a variation of lab 1.3.2. This Packet Tracer Activity is not a companion for the above named lab. The instructions for completing this activity are found within this activity.
Learning Objectives
Design a logical LAN topology. Configure the physical topology. Configure the logical topology. Verify network connectivity. Verify passwords.
Introduction
In this activity, you will design and configure a small routed network and verify connectivity across multiple network devices. This requires creating and assigning two subnetwork blocks, connecting hosts and network devices, and configuring host computers and one Cisco router for basic network connectivity. Switch1 has a default configuration and does not require additional configuration. You will use common commands to test and document the network. The zero subnet is used.
Task 1: Design a Logical LAN Topology
Step 1. Design an IP addressing scheme. Given the IP address block of 192.168.30.0 /27, design an IP addressing scheme that satisfies the following requirements: Subnet Subnet A Subnet B Number of Hosts 7 14
Page 1 of 3
All contents are Copyright 2007-2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
CCNA Exploration LAN Switching and Wireless: LAN Design
PT Activity 1.3.2: Review of Concepts from Exploration 1 - Challenge
Subnet zero is used. No subnet calculators may be used. Create the smallest possible subnets that satisfy the requirements for hosts. Assign the first usable subnet to Subnet A. Host computers will use the first IP address in the subnet. The network router will use the last IP address in the subnet. Step 2. Write down the IP address information for each device. Before proceeding, verify your IP addresses with the instructor.
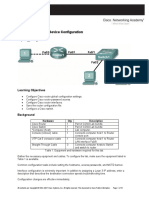
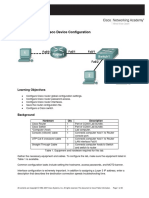
Task 2: Configure the Physical Topology
Step 1. Cable the network. Step 2. Inspect the network connections.
Task 3: Configure the Logical Topology
Step 1. Configure the host computers. Host 1: 192.168.30.1/28 DG is 192.168.30.14 Host 2: 192.168.30.17/28 DG is 192.168.30.30 Step 2. Configure Router1. Enter the following commands on the router: Router name Router1 Secret password class Set console and VTY line passwords to cisco Interface addresses Interface description ! Fa0/0 text: connection to host1 ! Fa0/1 text: connection to switch1
Task 4: Verify Network Connectivity
Step 1. Use the ping command to verify network connectivity. You can verify network connectivity using the ping command. Step 2. Check results. Your completion percentage should be 100%. If not, click Check Results to see which required components are not yet completed.
All contents are Copyright 2007-2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 2 of 3
CCNA Exploration LAN Switching and Wireless: LAN Design
PT Activity 1.3.2: Review of Concepts from Exploration 1 - Challenge
Task 5: Verify Passwords
Step 1. Telnet to the router from Host2 and verify the Telnet password. Step 2. Verify that the enable secret password has been set.
Task 6: Reflection
How are Telnet access and console access different? Console access is an out-of-band management connection requiring a direct connection to the console port of a network device. Out-of-band management connections do not require active configured network interfaces. Telnet access is an in-band management connection requiring at least one active configured network interface on the device. Telnet is useful for a remote connection to the device. When might it make sense to set different passwords on these two access ports? Using different passwords for console access versus telnet access would improve security. Why does the switch between Host2 and the router not require configuration with an IP address to forward packets? The switch is functioning at Layer 2 to provide an optimal connectivity point between hosts and the router. IP addressing is only required for remote access to a Layer 2 switch using telnet or http.
All contents are Copyright 2007-2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 3 of 3
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- ESwitching PTAct 1 3 2Document3 pagesESwitching PTAct 1 3 2Wayne E. BollmanPas encore d'évaluation
- BCS 320 Lab 1.3.1Document3 pagesBCS 320 Lab 1.3.1YeYo135Pas encore d'évaluation
- Review of Concepts Exploration 1 (Basic)Document4 pagesReview of Concepts Exploration 1 (Basic)Apriten JansutrisPas encore d'évaluation
- 03 - Review of Concepts From Exploration 1 - ChallengeDocument3 pages03 - Review of Concepts From Exploration 1 - ChallengeŽelimir Lovrenčić0% (1)
- PT Activity 1.3.1: Review of Concepts From Exploration 1: Topology DiagramDocument3 pagesPT Activity 1.3.1: Review of Concepts From Exploration 1: Topology DiagramAldo KaçorriPas encore d'évaluation
- ESwitching Lab 1 3 1Document12 pagesESwitching Lab 1 3 1Derek Ang Yew PinPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA 3 Student Lab ManualDocument192 pagesCCNA 3 Student Lab ManualNazmul HasanPas encore d'évaluation
- SW Lab1Document6 pagesSW Lab1Aiman YuuhiPas encore d'évaluation
- Packet Tracer 1.3.1Document11 pagesPacket Tracer 1.3.13qtrtymPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab - Activity CCNA Exploration 1 Chapt: 11.5.5Document12 pagesLab - Activity CCNA Exploration 1 Chapt: 11.5.5Rico Agung FirmansyahPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 1.3.1Document12 pagesLab 1.3.1Alondra CarmonaPas encore d'évaluation
- PT Activity 1.3.1: Review of Concepts From Exploration 1: Topology DiagramDocument4 pagesPT Activity 1.3.1: Review of Concepts From Exploration 1: Topology Diagrammagma871385Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1 3 2Document5 pages1 3 2Amr Mohamed RedaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab Manual For CCNA 3 Instructor VersionDocument262 pagesLab Manual For CCNA 3 Instructor VersionChiefJohnVanderpuije100% (1)
- Basic 5Document12 pagesBasic 519 04 20 Thùy LinhPas encore d'évaluation
- PT Activity 1.4.1: Packet Tracer Skills Integration ChallengeDocument3 pagesPT Activity 1.4.1: Packet Tracer Skills Integration Challengemeachamrob100% (1)
- ESwitching Lab 1 3 3Document6 pagesESwitching Lab 1 3 3Ninja NuggetPas encore d'évaluation
- Computer NetworksDocument12 pagesComputer NetworksOSCAR AHINAMPONGPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 2 HandoutDocument7 pagesLab 2 Handouthassaan tanveerPas encore d'évaluation
- CNS Lab 3Document19 pagesCNS Lab 3PRANAV POUDELPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA Exploration LAN Switching and Wireless LAN DesiginDocument5 pagesCCNA Exploration LAN Switching and Wireless LAN DesiginKIERYEPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Communication & Computer Networking-lab-ManualDocument68 pagesData Communication & Computer Networking-lab-ManualTekalign TadessePas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 1: Basic Cisco Device Configuration: Topology DiagramDocument16 pagesLab 1: Basic Cisco Device Configuration: Topology DiagramNhựt LưuPas encore d'évaluation
- PracticeDocument7 pagesPracticeLiam PattersonPas encore d'évaluation
- E1 Lab 10 6 1 SolutionDocument9 pagesE1 Lab 10 6 1 SolutionOwain RobertsPas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 11.5.4: Network Testing: Topology DiagramDocument11 pagesLab 11.5.4: Network Testing: Topology Diagramm_flagPas encore d'évaluation
- ESwitching PTAct 1 4 1Document3 pagesESwitching PTAct 1 4 1patellover770% (1)
- AIW Lab ReportDocument41 pagesAIW Lab ReportDebendra Wagle0% (1)
- CCNA Lab ManualDocument35 pagesCCNA Lab ManualMojtaba MirPas encore d'évaluation
- CcnaDocument77 pagesCcnaFadi SabbaghPas encore d'évaluation
- CSE 338-438 Lab Manual 6 (Spring 23)Document6 pagesCSE 338-438 Lab Manual 6 (Spring 23)Tanzir Bin Razzaque 1831914042Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lab 11-5-1 Basic Cisco Device ConfigurationDocument20 pagesLab 11-5-1 Basic Cisco Device ConfigurationNhật HồPas encore d'évaluation
- 7.5.2 LabDocument23 pages7.5.2 LabLHPas encore d'évaluation
- Modul 1 Subiecte Cisco CorectateDocument127 pagesModul 1 Subiecte Cisco CorectateMorar CameliaPas encore d'évaluation
- Greater Noida Institute of Technology: SESSION-2020-2021Document39 pagesGreater Noida Institute of Technology: SESSION-2020-2021Abhishek ChauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- E1 Lab 11 5 5Document19 pagesE1 Lab 11 5 5Chris LeePas encore d'évaluation
- CN FileDocument18 pagesCN FileMansiPas encore d'évaluation
- CCNA 1 v6.0 - ITN Practice Skills Assessment Packet Tracer Exam AnswersDocument1 pageCCNA 1 v6.0 - ITN Practice Skills Assessment Packet Tracer Exam AnswersMiladiPas encore d'évaluation
- Verify Connectivity and Configure IP AddressesDocument94 pagesVerify Connectivity and Configure IP AddressesvivekPas encore d'évaluation
- ESwitching Lab 7 5 2Document23 pagesESwitching Lab 7 5 2Ninja NuggetPas encore d'évaluation
- General Information: Distribution or Sharing of This Exam Content Is ProhibitedDocument23 pagesGeneral Information: Distribution or Sharing of This Exam Content Is ProhibitedDaniel BastaardooPas encore d'évaluation
- Modul 1 Subiecte Cisco (Nerezolvate)Document125 pagesModul 1 Subiecte Cisco (Nerezolvate)Morar CameliaPas encore d'évaluation
- LAB #01: Network Devices & Packet TracerDocument27 pagesLAB #01: Network Devices & Packet TracerHunter BunterPas encore d'évaluation
- CN Lab Manual VISemDocument34 pagesCN Lab Manual VISemAlwin RsPas encore d'évaluation
- Alfian Fadli P. - 16780 - Laporan SubnettingDocument35 pagesAlfian Fadli P. - 16780 - Laporan SubnettingRochmad G. SaputraPas encore d'évaluation
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationD'EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationPas encore d'évaluation
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkD'EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkPas encore d'évaluation
- Cisco Packet Tracer Implementation: Building and Configuring Networks: 1, #1D'EverandCisco Packet Tracer Implementation: Building and Configuring Networks: 1, #1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1D'EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (2)
- Exploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxD'EverandExploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1)
- First Hop Redundancy Protocol: Network Redundancy ProtocolD'EverandFirst Hop Redundancy Protocol: Network Redundancy ProtocolPas encore d'évaluation
- Network Programming in .NET: With C# and Visual Basic .NETD'EverandNetwork Programming in .NET: With C# and Visual Basic .NETÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (1)
- The Complete Guide to Getting Certified Cisco CCNA 200-301: Complete Your CCNA Exam Training and Preparation with 400 Exam Level Practice QuestionD'EverandThe Complete Guide to Getting Certified Cisco CCNA 200-301: Complete Your CCNA Exam Training and Preparation with 400 Exam Level Practice QuestionPas encore d'évaluation
- Learning OpenStack Networking (Neutron) - Second EditionD'EverandLearning OpenStack Networking (Neutron) - Second EditionPas encore d'évaluation
- Python Networking 101: Navigating essentials of networking, socket programming, AsyncIO, network testing, simulations and AnsibleD'EverandPython Networking 101: Navigating essentials of networking, socket programming, AsyncIO, network testing, simulations and AnsiblePas encore d'évaluation
- Internet Security: Cryptographic Principles, Algorithms and ProtocolsD'EverandInternet Security: Cryptographic Principles, Algorithms and ProtocolsPas encore d'évaluation
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-A: A Beginner's Guide to Next Level of NetworkingD'EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-A: A Beginner's Guide to Next Level of NetworkingPas encore d'évaluation
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksD'EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksPas encore d'évaluation
- NetSDK Programming Manual (Camera)Document93 pagesNetSDK Programming Manual (Camera)Bat-Erdene NasanbatPas encore d'évaluation
- Walkable and Bikeable Cities - PDF PENTINGDocument77 pagesWalkable and Bikeable Cities - PDF PENTINGMauliana DewiPas encore d'évaluation
- FAO - Industrial Charcoal ProductionDocument33 pagesFAO - Industrial Charcoal ProductionFabiano de Souza0% (1)
- Call Sheet: Production Title Production Group Date Producer and DirectorDocument12 pagesCall Sheet: Production Title Production Group Date Producer and Directorapi-443161282Pas encore d'évaluation
- Parent/Guardian Permission For ExcursionDocument2 pagesParent/Guardian Permission For Excursionm1i7Pas encore d'évaluation
- Certificate of Compensation Payment/Tax WithheldDocument1 pageCertificate of Compensation Payment/Tax WithheldLency FelarcaPas encore d'évaluation
- Official Secrets ActDocument3 pagesOfficial Secrets ActPrashant RohitPas encore d'évaluation
- Masonry Bridge Assessment With Archie-M: Notes For A Masonry Bridge Masterclass Bill Harvey Associates LTD March 2011Document12 pagesMasonry Bridge Assessment With Archie-M: Notes For A Masonry Bridge Masterclass Bill Harvey Associates LTD March 2011Info Aviron LavalPas encore d'évaluation
- HP MOQ Traditional BPC Mar'21 Pricelist - FTPDocument8 pagesHP MOQ Traditional BPC Mar'21 Pricelist - FTPrachamreddyrPas encore d'évaluation
- CT ES 072 RFID and GPS Combination Approach Implementation in Fisher Boat TrackingDocument2 pagesCT ES 072 RFID and GPS Combination Approach Implementation in Fisher Boat TrackingkbsmalliPas encore d'évaluation
- Verification of Hook Element in Midas GenDocument3 pagesVerification of Hook Element in Midas GenSASHIN ServiSoftPas encore d'évaluation
- 083E Relative Humidity Sensor Accurate and ReliableDocument2 pages083E Relative Humidity Sensor Accurate and Reliablehuguer1Pas encore d'évaluation
- C2022 04Document72 pagesC2022 04Leo2pbPas encore d'évaluation
- Singleton Context Nodes RevisitedDocument2 pagesSingleton Context Nodes Revisitedramakrishna_bojjaPas encore d'évaluation
- Muru Crane CV WordDocument6 pagesMuru Crane CV WordMURUGESAN PONNIAHPas encore d'évaluation
- ASTM D 5957 Flood Testing Horizontal Waterproofing InstallationsDocument5 pagesASTM D 5957 Flood Testing Horizontal Waterproofing InstallationsILSEN N. DAETPas encore d'évaluation
- VRF Plus 2011 CatalogDocument32 pagesVRF Plus 2011 CatalogJorge DovalePas encore d'évaluation
- Gear Box ReportDocument39 pagesGear Box ReportNisar HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- Manila Bay accretion disputeDocument24 pagesManila Bay accretion disputeRoman KushpatrovPas encore d'évaluation
- Consumer Preference Towards Suagr and SpiceDocument67 pagesConsumer Preference Towards Suagr and SpiceShorabh MastanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Syllabus For The 2019 Bar Examinations Labor Law and Social Legislation I. General ProvisionsDocument3 pagesSyllabus For The 2019 Bar Examinations Labor Law and Social Legislation I. General ProvisionsBret MonsantoPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To GSMDocument3 pagesIntroduction To GSMYasir LiaqatPas encore d'évaluation
- Atlassian Vladimir Yastreboff Sept21Document1 pageAtlassian Vladimir Yastreboff Sept21devk2011Pas encore d'évaluation
- AWS CWI Training Program PDFDocument22 pagesAWS CWI Training Program PDFDjamelPas encore d'évaluation
- IVMS Pharmacology Flash FactsDocument8 250 pagesIVMS Pharmacology Flash FactsMarc Imhotep Cray, M.D.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Active Directory Security Self Assessment v1.4 PDFDocument15 pagesActive Directory Security Self Assessment v1.4 PDFpaul ethikPas encore d'évaluation
- PLSQL - 5 - 6 - Brayan Ferney Perez Moreno PDFDocument5 pagesPLSQL - 5 - 6 - Brayan Ferney Perez Moreno PDFBryan PerezPas encore d'évaluation
- Dashboard - Harare PolytechnicDocument4 pagesDashboard - Harare PolytechnicTeewyz MarPas encore d'évaluation
- NL Back Pressure Valve Brochure 032613Document9 pagesNL Back Pressure Valve Brochure 032613EquilibarPas encore d'évaluation
- Tools and Techniques of Cost ReductionDocument27 pagesTools and Techniques of Cost Reductionপ্রিয়াঙ্কুর ধর100% (2)