Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study Case
Transféré par
Kevin Sam AguirreCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Drug Study Case
Transféré par
Kevin Sam AguirreDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
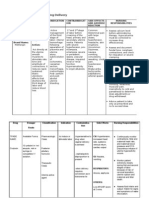
BRAND NAME
GENERIC NAME
CLASSIFICA -TION
ACTION
INDICATION
CONTRAIN DICATION
Apoferrous Ferrous sulfate Gluconate2 ; ApoFerrous Sulfate3; DexFerrum 4 ; DexIron4; Femiron1; Feosol Caplets3; Feosol Tablets3; Feostat1; Feostat Drops1; Fer-In-Sol Drops3; Fer-In-Sol Syrup3; Fer-Iron Drops3; Fer-gensol3; Feratab3
Anti anemic, Iron supplement
Elevates the serum iron concentratio n which then helps to form High or trapped in the reticuloendot helial cells for storage and eventual conversion to a usable form of iron.
Iron deficiency anemia, hemodialysisinduced (treatment) Sodium ferric gluconate complex injection and iron sucrose injection are indicated for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia in patients undergoing chronic hemodialysis who are receiving supplemental erythropoietin therapy. Iron deficiency
Hypersensiti vity Severe hypotension.
SIDE EFFECTS/ ADVERSE EFFECTS Dizziness N&V Nasal Congestion Dyspnea Hypotensio n CHF MI Muscle cramps Flushing checking with physician if black stools occur with other symptoms of internal blood loss Signs of potential side effects, especially
DOSAG E
NURSING RESPONSIBILITY
Initial: 300 to 325 mg of regularrelease ferrous sulfate orally once a day.
Advise patient to take medicine as prescribed. Caution patient to make position changes slowly to minimize orhtostatic hypotension. Instruct patient to avoid concurrent use of alcohol or OTC medicine without consulting the physician. Advise patient to consult physician if irregular heartbeat, dyspnea, swelling of hands and feet and hypotension occurs. Inform patient that angina attacks may occur 30 min.
anemia (prophylaxis and treatment) Iron supplements are indicated in the prevention and treatment of iron deficiency anemia, which may result from inadequate diet, malabsorptio n, pregnancy, rapid growth during childhood, and/or blood loss. Iron dextran and iron sorbitol are recommende d for patients in whom iron deficiency has been
abdominal or stomach pain , cramping, or soreness, allergic reaction, backache, flank, groin, or muscle pain, chills, dizziness, fever with increased sweating, headache, metallic taste, nausea or vomiting, numbness, pain, or tingling of hands or feet, chest pain, hypotensio n, fast heartbeat, flushing or redness of skin, pain
after administration due reflex tachycardia. Encourage patient to comply with additional intervention for hypertension like proper diet, regular exercise, lifestyle changes and stress management.
determined, only after the cause has been corrected, if possible, and only when oral administratio n has been found unsatisfactory or impossible.
and redness or sores at intramuscul ar injection site, redness at intravenous injection site, contact irritation in alimentary tract, diplopia, malaise, or weakness
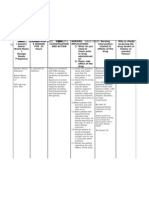
BRAND NAME
GENERIC NAME
CLASSIFICA -TION
ACTION
INDICATION
CONTRAIN DICATION Hypersensit ivity. Crosssensitivity may exist among phenothiazin
thorazine
chlorproma zine
Antipsychotic s
Block dopamine receptors in the brain; also alter dopamine
Acute and chronic psychoses, particularly when accompanied by increased
SIDE EFFECTS/ ADVERSE EFFECTS CNS: neuroleptic malignant syndrome, sedation, extrapyrami dal
DOSAG E
NURSING RESPONSIBILITY
PO 1025mg 2=4 times daily; may
Assess mental status prior to and periodically during therapy. Monitor BP and pulse prior to and frequently during
release and turnover. Prevention of seizures
psychomotor activity. Nausea and vomiting. Also used in the treatment of intractable hiccups.
es. Should not be used in narrowangle glaucoma. Should not be used in patients who have CNS depression.
reactions, tardive dyskinesia CV: hypotensio n (increased with IM, IV) EENT: blurred vision, dry eyes, lens opacities GI: constipatio n, dry mouth, anorexia, hepatitis, ileus GU: urinary retention Hematologi c: agranulocyt osis, leukopenia Skin: photosensit ivity, pigment
increase every 3-4 days (usual dose is 200ng/da y; up to 1g/day)
the period of dosage adjustment. May cause QT interval changes on ECG. Observe patient carefully when administering medication, to ensure that medication is actually taken and not hoarded. Monitor I&O ratios and daily eight. Assess patient for signs and symptoms of dehydration. Monitor for development of neuroleptic malignant syndrome (fever, respiratory distress, tachycardia, seizures, diaphoresis, hypertension or hypotension, pallor, tiredness, severe muscle
changes, rashes
stiffness, loss of bladder control. Report symptoms immediately. May also cause leukocytosis, elevated liver function tests, elevated CPK. Advise patient to take medication as directed. Take missed doses as soon as remembered, witih remaining doses evenly spaced through out the day. May require several weeks to obtain desired effects. Do not increase dose or discontinue medication without consulting health care professional. Abrupt withdrawal may cause dizziness, nausea, vomiting, GI upset, trembling, or uncontrolled
movements of mouth, tongue or jaw.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Chapter 2, Collecting Subjective DataDocument8 pagesChapter 2, Collecting Subjective DataEmvie Loyd Pagunsan-ItablePas encore d'évaluation
- Fundamental of Nursing QuizDocument15 pagesFundamental of Nursing QuizDr. Jayesh Patidar100% (1)
- Acyclovir Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComDocument3 pagesAcyclovir Drug Study WWW RNpedia ComJanaica JuanPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Classification, Action, Nursing ConsiderationsDocument14 pagesDrug Classification, Action, Nursing ConsiderationsLovely Saad TubañaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug Studyunkown userPas encore d'évaluation
- Nosocomial Infection?Document4 pagesNosocomial Infection?Sara APas encore d'évaluation
- PATHOMA Fundamentals of Pathology 2018 PDFDocument232 pagesPATHOMA Fundamentals of Pathology 2018 PDFRafael Eduardo Toro Manotas100% (2)
- Cefuroxime (Drug Study)Document2 pagesCefuroxime (Drug Study)Rosebel LaguraPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study of SleDocument7 pagesDrug Study of Slejoyrena ochondraPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Acute Pain R/T Injuring AgentsDocument4 pagesNCP Acute Pain R/T Injuring AgentsKevin Sam AguirrePas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Acute Pain R/T Injuring AgentsDocument4 pagesNCP Acute Pain R/T Injuring AgentsKevin Sam AguirrePas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Acute Pain R/T Injuring AgentsDocument4 pagesNCP Acute Pain R/T Injuring AgentsKevin Sam AguirrePas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid and Electrolyte Nursing Care Management 112Document7 pagesFluid and Electrolyte Nursing Care Management 112anne mariePas encore d'évaluation
- Oral Surgery and InfectionsDocument32 pagesOral Surgery and InfectionsTheSuperJayR100% (1)
- Drug Study CaseDocument3 pagesDrug Study CaseKatrina Ponce100% (1)
- Generic Name:: Is Used To Dissolve (Cholesterol) Gallstones and PDocument9 pagesGeneric Name:: Is Used To Dissolve (Cholesterol) Gallstones and PZAY EMPas encore d'évaluation
- How Allopurinol Works to Treat Gout and Reduce Uric AcidDocument1 pageHow Allopurinol Works to Treat Gout and Reduce Uric AcidRachel SaavedraPas encore d'évaluation
- Enteral Nutrition Administration Inconsistent With Needs (NI-2.6)Document2 pagesEnteral Nutrition Administration Inconsistent With Needs (NI-2.6)Hasna KhairunnisaGIZIPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study: Valerie V. Villanueva BN3-CDocument1 pageDrug Study: Valerie V. Villanueva BN3-CValerie VillanuevaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study - LevothyroxineDocument1 pageDrug Study - LevothyroxineCarla Tongson Maravilla100% (1)
- TerbutalineDocument1 pageTerbutalineRyan Paul BalotPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument13 pagesDrug StudyGi Ey ElPas encore d'évaluation
- Calcium Gluconate Drug SummDocument1 pageCalcium Gluconate Drug SummWarren100% (2)
- Dextrose Injection Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesDextrose Injection Nursing ResponsibilitiesSalwa ZeinPas encore d'évaluation
- OfloxacinDocument2 pagesOfloxacinCarla Arciaga100% (1)
- Drug Stidy TramadolDocument2 pagesDrug Stidy TramadolRez ApegoPas encore d'évaluation
- ONDANSETRONDocument1 pageONDANSETRONJugen Gumba Fuentes Alquizar0% (1)
- ChlorphenamineDocument1 pageChlorphenaminereinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Warfarin Dosing and Monitoring GuidelinesDocument4 pagesWarfarin Dosing and Monitoring GuidelinesbillyktoubattsPas encore d'évaluation
- DS HydralazineDocument3 pagesDS HydralazineGe LoPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study Effects and Nursing ConsiderationsDocument2 pagesDrug Study Effects and Nursing ConsiderationsCelline Isabelle ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Vit EDocument2 pagesVit EkingpinPas encore d'évaluation
- Formoterol Gonzaga.Document2 pagesFormoterol Gonzaga.Sheryl Anne GonzagaPas encore d'évaluation
- SpironolactoneDocument2 pagesSpironolactoneKatrina PoncePas encore d'évaluation
- DRUG STUDY LevetiracetamDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY LevetiracetamMaria Althea NajorraPas encore d'évaluation
- OxytocinDocument1 pageOxytocinAudrey Martin RañisesPas encore d'évaluation
- Generic Name:: Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindi-Cation Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageGeneric Name:: Drug Name Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindi-Cation Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesmaemalabonPas encore d'évaluation
- AcetazolamideDocument2 pagesAcetazolamideAlexandra Antondy0% (1)
- Beclomethasone Dipropionate (Drug Study)Document2 pagesBeclomethasone Dipropionate (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888100% (1)
- Trimethoprim Sulfamethoxazole (TMP SMZ) Co TrimoxazoleDocument1 pageTrimethoprim Sulfamethoxazole (TMP SMZ) Co TrimoxazoleRenmico Aquino0% (1)
- Drug Study: Chlorphenamine MaleateDocument1 pageDrug Study: Chlorphenamine MaleateJILLIAN MARIE BARREDO100% (1)
- Drug Study BISACODYLDocument1 pageDrug Study BISACODYLAnna Sofia ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study - Calcium GluconateDocument1 pageDrug Study - Calcium GluconatemikErlhPas encore d'évaluation
- OxytocinDocument1 pageOxytocinJoi Danielle Tabares IsturisPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study MethotrexateDocument1 pageDrug Study MethotrexatekyawPas encore d'évaluation
- Oraa, Jamie - Drug Study Surgical WardDocument1 pageOraa, Jamie - Drug Study Surgical WardJamie LeePas encore d'évaluation
- PrimidoneDocument6 pagesPrimidoneKim SunooPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluconazole drug classification, indications, side effects and nursing responsibilitiesDocument1 pageFluconazole drug classification, indications, side effects and nursing responsibilitiescen janber cabrillos0% (1)
- Ofloxacin Drug StudyDocument4 pagesOfloxacin Drug StudyMikko Anthony Pingol Alarcon100% (1)
- Chlorpheniramine Maleate: (klor-fen-AIR-uh-meen MAL-ee-ate)Document4 pagesChlorpheniramine Maleate: (klor-fen-AIR-uh-meen MAL-ee-ate)Nurginayah RusliPas encore d'évaluation
- Cyclobenzaprine Hydrochloride (Drug Study)Document1 pageCyclobenzaprine Hydrochloride (Drug Study)Franz.thenurse6888Pas encore d'évaluation
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyJan DeePas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Action Indication Side Effect Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationsDocument1 pageDrug Action Indication Side Effect Adverse Effect Nursing ConsiderationsRo-anne AkuPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study AmpicillinDocument6 pagesDrug Study AmpicillinDgjj Compuiter100% (1)
- AmilorideDocument1 pageAmilorideRox San100% (1)
- Generic Name: Brand Name:: ClassificationsDocument2 pagesGeneric Name: Brand Name:: ClassificationsbillyktoubattsPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study OxytocinDocument1 pageDrug Study OxytocinGil GanibanPas encore d'évaluation
- DRUG STUDY - FurosemideDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY - FurosemideKian HerreraPas encore d'évaluation
- GlipizideDocument3 pagesGlipizideapi-3797941100% (1)
- Drug Study (Aspirin, in Enalapril Maleate, Tramadol, AmlodipineDocument10 pagesDrug Study (Aspirin, in Enalapril Maleate, Tramadol, AmlodipineFlauros Ryu Jabien100% (1)
- Doxorubicin Dosage, Uses, Side Effects and Nursing CareDocument4 pagesDoxorubicin Dosage, Uses, Side Effects and Nursing CareMaryjoy Gabriellee De La CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study GuideDocument2 pagesDrug Study GuideAubrey SungaPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Classification Action of Drug Indication and Contraindication Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationDocument2 pagesDrug Classification Action of Drug Indication and Contraindication Side Effect Nursing ConsiderationDanica Kate GalleonPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Sudy Format MethyldopaDocument3 pagesDrug Sudy Format MethyldopaBianca Marithè RejanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Actrapid Insulin Guide - Fast-Acting Diabetes MedicationDocument2 pagesActrapid Insulin Guide - Fast-Acting Diabetes MedicationLeah Torcelino-InfantePas encore d'évaluation
- PiroxicamDocument2 pagesPiroxicamVirginia Aira Lara MarquezPas encore d'évaluation
- Metronidazole 500mg/tab 1 Tab 3xadayDocument4 pagesMetronidazole 500mg/tab 1 Tab 3xadayCrisyl LipawenPas encore d'évaluation
- Tramadol Drug StudyDocument2 pagesTramadol Drug StudyTipey Segismundo0% (1)
- Drug Study 8Document3 pagesDrug Study 8Vicky RoquePas encore d'évaluation
- Archer Review Note 5Document11 pagesArcher Review Note 5karan SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Presentation - Aurora QuezonDocument4 pagesCase Presentation - Aurora QuezonKevin Sam AguirrePas encore d'évaluation
- Curriculum Vitae. KevinDocument2 pagesCurriculum Vitae. KevinKevin Sam AguirrePas encore d'évaluation
- Paracetamol and Levofloxacin Drug StudyDocument9 pagesParacetamol and Levofloxacin Drug StudyKevin Sam AguirrePas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study QiDocument6 pagesDrug Study QiKevin Sam AguirrePas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs, Amlodipine, Cefuroxime, Drug StudyDocument8 pagesDrugs, Amlodipine, Cefuroxime, Drug StudyKevin Sam AguirrePas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Study QiDocument6 pagesDrug Study QiKevin Sam AguirrePas encore d'évaluation
- TQM - DhudaiDocument3 pagesTQM - DhudaiKevin Sam AguirrePas encore d'évaluation
- Title Page ENSP703Document3 pagesTitle Page ENSP703Kevin Sam AguirrePas encore d'évaluation
- NCM CardioDocument2 pagesNCM CardioKevin Sam AguirrePas encore d'évaluation
- Dinakaran 2017Document16 pagesDinakaran 2017Chirac OanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Indriatmi, W. 2018. Ilmu Penyakit Dan Kulit Kelamin. Edisi Ke-7. Jakarta: Badan Penerbit Fakultas Kedokteran IndonesiaDocument10 pagesIndriatmi, W. 2018. Ilmu Penyakit Dan Kulit Kelamin. Edisi Ke-7. Jakarta: Badan Penerbit Fakultas Kedokteran IndonesiaDiza Hanni PertiwiPas encore d'évaluation
- EctopicDocument4 pagesEctopicAb Staholic BoiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) Angina Pectoris: Chapter 28: Management of Patients With CVDDocument3 pagesCoronary Artery Disease (CAD) Angina Pectoris: Chapter 28: Management of Patients With CVDLizzy WayPas encore d'évaluation
- Intro V2-2Document5 pagesIntro V2-2KKKPas encore d'évaluation
- Croton TigDocument32 pagesCroton TigaedeenPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Therapy: Adesola Odunayo, DVM, MS, DACVECCDocument6 pagesFluid Therapy: Adesola Odunayo, DVM, MS, DACVECCSamantha Orozco PinedaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cancer ProjectDocument10 pagesCancer ProjectHARSH VERMA100% (1)
- Candida auris Drug-Resistant Yeast Healthcare FacilitiesDocument2 pagesCandida auris Drug-Resistant Yeast Healthcare FacilitiesPablo AvilaPas encore d'évaluation
- St. Paul University Philippines: School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences College of NursingDocument5 pagesSt. Paul University Philippines: School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciences College of NursingChristian UmosoPas encore d'évaluation
- Suxamethonium Apnoea Update 2003Document2 pagesSuxamethonium Apnoea Update 2003jira neaPas encore d'évaluation
- Reproductive Health AssignmentDocument12 pagesReproductive Health AssignmentRmanojkumar OmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Andrew Eastman Resume 3Document2 pagesAndrew Eastman Resume 3api-281509868Pas encore d'évaluation
- Personal Hygiene Habits for Better HealthDocument1 pagePersonal Hygiene Habits for Better HealthPISMP BA2100% (1)
- Schreibman - Radiology of Joint Disease - My Practical ApproachDocument16 pagesSchreibman - Radiology of Joint Disease - My Practical ApproachborstPas encore d'évaluation
- Hesi Med Surg-14Document1 pageHesi Med Surg-14GeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- ZIKA 101: CDC'S Response To ZikaDocument54 pagesZIKA 101: CDC'S Response To ZikaShirley MendezPas encore d'évaluation
- Trichuris TrichiuraDocument3 pagesTrichuris TrichiuraTwish BeraldePas encore d'évaluation
- Respiratory AcidosisDocument5 pagesRespiratory Acidosisapi-376421583% (6)
- Myofascial Pain Syndrome inDocument17 pagesMyofascial Pain Syndrome inEdogawa RakhmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Female Anatomy ExplainedDocument11 pagesFemale Anatomy ExplainedBARRIENTOS, RITCHELLE C.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Keeping Abreast of Future Need - A Report Into The Growing Demand For Breast Care NursesDocument14 pagesKeeping Abreast of Future Need - A Report Into The Growing Demand For Breast Care NursesEmmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Study On Effect of Wet Cupping (Hijama) On Blood Lipid Profile in Human at Aldyssah-Alshati, LibyaDocument4 pagesStudy On Effect of Wet Cupping (Hijama) On Blood Lipid Profile in Human at Aldyssah-Alshati, LibyaMohammed Ramzy GhifariPas encore d'évaluation