Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Distribution Systems
Transféré par
vagoliyoDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Distribution Systems
Transféré par
vagoliyoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
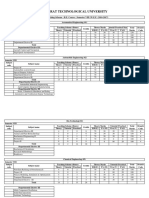
ELECTRICAL POWER (140902) QUESTIONS AND EXAMPLES FROM GTU QUESTIONS PAPER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM
Sr. No.
QUESTIONS AND EXAMPLES Compare (i) radial distribution system (ii) ring or loop distribution system (iii) network or grid distribution system. Also state applications. Explain string efficiency and methods to improve this for insulators. How are these tested to determine flashover voltage? Name the place with reasons where the following conductors are used. (i) All aluminum conductor (ii) ACSR conductor (ii) Stay (Guy wire) (iv) GI wire. Why are stranded conductors used? Classify the underground cables according to insulation used, voltage rating and number of cores .Sketch a typical 3 core cable and label the important parts With the help of neat diagrams explain the relative advantages and disadvantages of Radial, Ring Main and rconnected Grid systems of distribution. What is string efficiency? Explain the methods of improving string efficiency. In the following figs., which represent equivalent capacitor arrangements for strings of suspension insulators, C = 0.125C and the maximum voltage across any unit is not to exceed 13.2 kV. Find the maximum voltage that each arrangement can withstand.
MARKS
EXAM
1 2 3 4 5 6
4 3 7 7 6 6
S'10 S'10 S'10 W'10 W'10 W'10
W'10
8 9 10 11 12 13 14
Write a short note on Pressure cables. Explain different types of distribution system with diagram. Discuss the various conductor materials used for overhead lines. What are their relative advantages and disadvantages. Give reason for unequal potential distribution over string of suspension insulators. Define string efficiency. Can its value be equal to 100%? Explain various types of insulators used for overhead lines. Each line of a 3 phase system is suspended by a string of 3 similar insulators .If the voltage across the line unit is 17.5 kV ,calculate the string efficiency .Assume that the shunt capacitance between each insulator and earth is 1/8th of the capacitance of the insulator itself. Explain the different types of distribution system with diagram.
6 7
W'10 S'11 S'11
7 7 7 7
S'11 W'11 W'11 W'11
15
16 17
18
19 20 21 22 23 24 25 Compare overhead transmission system with underground transmission system. 26 Explain with diagram (i) Pin type and (ii) Suspension type of insulators. In 33KV, overhead lines there are three units in the string of insulators. If the capacitance between each insulator pin and earth is 11 % of self capacitance of 27 each insulator, find (i) The distribution of voltage over three insulators and (ii) String efficiency. Each line of a 3-phase system is suspended by a string of 3 similar insulators. If the voltage across the line unit is 175 kV, calculate the line to neutral voltage. 28 Assume that the shunt capacitance between each insulator and earth is 1/8th of the capacitance of the insulator itself. Also find the string efficiency. A 2-wire d.c. distributor AB is fed from both ends. At feeding point A, the voltage is maintained as at 230 V and at B 235 V. The total length of the distributor is 200 metres and loads are tapped off as under :25 A at 50 metres 29 from A ; 50 A at 75 metres from A30 A at 100 metres from A ; 40 A at 150 metres from A ,the resistance per kilometre of one conductor is 03. Calculate (i) currents in various sections of the distributor (ii) minimum voltage and the point at which it occurs Draw and explain the construction of pin type insulator. Also Explain How does 30 skin effect vary with conductor material ? A single phase a.c. distributor AB 300 metres long is fed from end A and is loaded as under : (i) 100 A at 0707 p.f. lagging 200 m from point A (ii) 200 A 31 at 08 p.f. lagging 300 m from point A The load resistance and reactance of the distributor is 02 and 01 per kilometre. Calculate the total voltage drop in the istributor. The load power factors refer to the voltage at the far end. Draw and explain the general construction of an underground cable. Also only 32 draw key diagram of 66Kv/ 11Kv substation
Distinguish between a feeder, distributor and service main in distribution scheme show that the x-section of a feeder and distributor would be reduced to 1/k and 1/k2 of their respect value with an increase in working voltage by k times. Compare over head line with underground cable as medium of power transmission, Also discuss the special features of alternators used in hydro plants. Explain the methods used for improving the voltage distribution along the string of insulators in over head lines (deduce the relation) Write a short note in different types of insulator used for over head lines and their application. Show with the help of a neat-sketch, the electrostatic field of a pin insulator and explain how far the shape of modern insulator confirm to these requirements Draw and explain generalized cable construction and explain them detail. Compare overhead transmission line v/s underground transmission line. Enlist types of insulator and explain any two with neat sketch Discuss types of distributors in dc distribution. What is string efficiency? Explain various methods of improving string efficiency. Explain general construction of cable with neat diagram.
S'12
7 7
S'12 S'12
7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7 7
S'12 W'12 W'12 W'12 W'12 S'13 S'13 S'13 S'13 S'13
W'13
W'13
W'13
W'13
W'13
Derive the expression for power loss in the distributor which is uniformly loaded with: 33 a) fed at one end b) feed at both ends with equal voltage
W'13
ELECTRICAL POWER (140902)
QUESTIONS AND EXAMPLES FROM GTU QUESTIONS PAPER
DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM
Sr. No.
QUESTIONS AND EXAMPLES Compare over head line with underground cable as medium of power transmission, Also discuss the special features of alternators used in hydro plants.
MARKS EXAM
TOPIC
S'12
Compare overhead transmission line v/s underground transmission line.
W'12
Compare overhead transmission system with underground transmission system. Compare (i) radial distribution system (ii) ring or loop distribution system (iii) network or grid distribution system. Also state applications. With the help of neat diagrams explain the relative advantages and disadvantages of Radial, Ring Main and rconnected Grid systems of Explain different types of distribution system with diagram. Explain the different types of distribution system with diagram. Distinguish between a feeder, distributor and service main in distribution scheme show that the x-section of a feeder and distributor would be reduced to 1/k and 1/k2 of their respect value with an increase in working voltage by k times. Discuss types of distributors in dc distribution.
S'13
4 5 6 7 8 9
4 6 7 7 7 7
S'10 W'10 S'11 W'11 S'12 W'12
Overhead & underground transmission of power Overhead & underground transmission of power Overhead & underground transmission of power Distribution system Distribution system Distribution system Distribution system Distribution system Distribution system
A 2-wire d.c. distributor AB is fed from both ends. At feeding point A, the voltage is maintained as at 230 V and at B 235 V. The total length of the distributor is 200 metres and loads are tapped off as under :25 A at 50 metres 10 from A ; 50 A at 75 metres from A30 A at 100 metres from A ; 40 A at 150 metres from A ,the resistance per kilometre of one conductor is 03. Calculate (i) currents in various sections of the distributor (ii) minimum voltage and the point at which it occurs A single phase a.c. distributor AB 300 metres long is fed from end A and is loaded as under : (i) 100 A at 0707 p.f. lagging 200 m from point A (ii) 200 A at 08 p.f. lagging 300 m from point A The load resistance and reactance of the distributor is 02 and 01 per kilometre. Calculate the total voltage drop in the istributor. The load power factors refer to the voltage at the far end. Derive the expression for power loss in the distributor which is uniformly loaded with: a) fed at one end b) feed at both ends with equal voltage Classify the underground cables according to insulation used, voltage rating and number of cores .Sketch a typical 3 core cable and label the important parts Write a short note on Pressure cables. Draw and explain generalized cable construction and explain them detail.
W'13
Distribution system
11
W'13
Distribution system
12
W'13
Distribution system Cables Cables Cables
13 14 15
7 6 7
W'10 W'10 W'12
16 Explain general construction of cable with neat diagram.
S'13
Cables
17 18 19 20 21
Draw and explain the general construction of an underground cable. Also only draw key diagram of 66Kv/ 11Kv substation Name the place with reasons where the following conductors are used. (i) All aluminum conductor (ii) ACSR conductor (ii) Stay (Guy wire) (iv) GI wire. Why are stranded conductors used? Discuss the various conductor materials used for overhead lines. What are their relative advantages and disadvantages. Explain various types of insulators used for overhead lines. Write a short note in different types of insulator used for over head lines and their application. Show with the help of a neat-sketch, the electrostatic field of a pin insulator and explain how far the shape of modern insulator confirm to these requirements
7 7
W'13 S'10 S'11
Cables Conductors Conductors Insulator Insulator Types of insulator Types of insulator Types of indulator String efficiency String efficiency
7 7
W'11 S'12
22 Enlist types of insulator and explain any two with neat sketch 23 Explain with diagram (i) Pin type and (ii) Suspension type of insulators. Draw and explain the construction of pin type insulator. Also Explain How does skin effect vary with conductor material ? Explain string efficiency and methods to improve this for insulators. How are 25 these tested to determine flashover voltage? 24 26 What is string efficiency? Explain the methods of improving string efficiency. In the following figs., which represent equivalent capacitor arrangements for strings of suspension insulators, C = 0.125C and the maximum voltage across any unit is not to exceed 13.2 kV. Find the maximum voltage that each arrangement can withstand.
7 7 7 3 6
W'12 S'13 W'13 S'10 W'10
27
W'10
String efficiency
28
29
30 31 32
33
Give reason for unequal potential distribution over string of suspension insulators. Define string efficiency. Can its value be equal to 100%? Each line of a 3 phase system is suspended by a string of 3 similar insulators .If the voltage across the line unit is 17.5 kV ,calculate the string efficiency .Assume that the shunt capacitance between each insulator and earth is 1/8th of the capacitance of the insulator itself. Explain the methods used for improving the voltage distribution along the string of insulators in over head lines (deduce the relation) What is string efficiency? Explain various methods of improving string efficiency. In 33KV, overhead lines there are three units in the string of insulators. If the capacitance between each insulator pin and earth is 11 % of self capacitance of each insulator, find (i) The distribution of voltage over three insulators and (ii) String efficiency. Each line of a 3-phase system is suspended by a string of 3 similar insulators. If the voltage across the line unit is 175 kV, calculate the line to neutral voltage. Assume that the shunt capacitance between each insulator and earth is 1/8th of the capacitance of the insulator itself. Also find the string efficiency.
S'11
String efficiency String efficiency String efficiency String efficiency String efficiency
W'11
7 7 7
S'12 S'13 S'13
W'13
String efficiency
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Electrical PowerDocument2 pagesElectrical PowerKeyur PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- T&DDocument5 pagesT&DMATHANKUMAR.SPas encore d'évaluation
- Transmission Line Design FactorsDocument5 pagesTransmission Line Design FactorspPas encore d'évaluation
- 9A02502 Transmission of Electric PowerDocument6 pages9A02502 Transmission of Electric PowersivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- BDocument7 pagesBrajbir kaurPas encore d'évaluation
- Distribution of Electric PowerDocument4 pagesDistribution of Electric Powersreenivasroyal8Pas encore d'évaluation
- PS PaperDocument8 pagesPS PaperBhavani Chandra UniquePas encore d'évaluation
- PS1 Assignment-1Document2 pagesPS1 Assignment-1Edu RightPas encore d'évaluation
- Power Transmission and DistributionDocument16 pagesPower Transmission and DistributionLinh Cao100% (1)
- Question Bank T&DDocument9 pagesQuestion Bank T&DcoolkannaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityHemang S. PandyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Pse Supple 2021Document2 pagesPse Supple 2021Aditya JhaPas encore d'évaluation
- R5310203 Power Systems - IIDocument2 pagesR5310203 Power Systems - IIsivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- EE2303 TD PART B With KeysDocument54 pagesEE2303 TD PART B With KeysMohammed OvaizPas encore d'évaluation
- Transmission and Distribution QBDocument5 pagesTransmission and Distribution QBkrishnandrkPas encore d'évaluation
- EE301 POWER GENERATION TRANSMISSION AND PROTECTION QUESTION BANKDocument6 pagesEE301 POWER GENERATION TRANSMISSION AND PROTECTION QUESTION BANKMohammed NadheerPas encore d'évaluation
- PsDocument8 pagesPsAlluri Appa RaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ee335-Transmission and Distribut PDFDocument2 pagesEe335-Transmission and Distribut PDFPradeep AmmasaikuttiPas encore d'évaluation
- Expressions for inductance and capacitance of transmission linesDocument7 pagesExpressions for inductance and capacitance of transmission linesvenki249Pas encore d'évaluation
- 9A02502 Transmission of Electric PowerDocument6 pages9A02502 Transmission of Electric PowersivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- SVC College EE8402 Transmission and Distribution Model ExamDocument2 pagesSVC College EE8402 Transmission and Distribution Model ExamkrishnandrkPas encore d'évaluation
- Nov 2008Document8 pagesNov 2008Viswa ChaitanyaPas encore d'évaluation
- 601Document5 pages601Parupally Bharath ChowdaryPas encore d'évaluation
- T&D Question Bank Aug 2019Document15 pagesT&D Question Bank Aug 2019thenithyanagrajPas encore d'évaluation
- BE Semester - (ELECTRICAL) Question Bank 4 Sem (E-403) (Electrical Power System-1) All Questions Carry Equal Marks (10 Marks)Document2 pagesBE Semester - (ELECTRICAL) Question Bank 4 Sem (E-403) (Electrical Power System-1) All Questions Carry Equal Marks (10 Marks)NADZIRUL NAIM HAYADINPas encore d'évaluation
- Question Bank On T & DDocument4 pagesQuestion Bank On T & DArpita BanikPas encore d'évaluation
- Transmission Distribution EE 2303 Exam Question PaperDocument2 pagesTransmission Distribution EE 2303 Exam Question PaperMohammed OvaizPas encore d'évaluation
- R7310203 Power Systems - IIDocument1 pageR7310203 Power Systems - IIsivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- bt3114 Part2 14 11 09rahulDocument38 pagesbt3114 Part2 14 11 09rahulSwathi ChinnuPas encore d'évaluation
- BE 3rd SEMESTER QUESTION BANK BASIC ELECTRICAL MACHINE UNIT-1Document32 pagesBE 3rd SEMESTER QUESTION BANK BASIC ELECTRICAL MACHINE UNIT-1RajkumarJhapte0% (1)
- PTEE7304 April-2014Document2 pagesPTEE7304 April-2014imman46920Pas encore d'évaluation
- EE8402-Transmission and Distribution - Model - QPDocument2 pagesEE8402-Transmission and Distribution - Model - QPkrishnandrkPas encore d'évaluation
- Power System - IDocument8 pagesPower System - Isatya_vanapalli3422Pas encore d'évaluation
- PsiiDocument8 pagesPsiiAlluri Appa RaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Poewr System 2Document4 pagesPoewr System 2కెవి సాయిPas encore d'évaluation
- Modeling Power System ComponentsDocument30 pagesModeling Power System ComponentsEngr Imtiaz Hussain GilaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Cap 6Document67 pagesCap 6ccprado1100% (1)
- rr310203 Power Systems IIDocument8 pagesrr310203 Power Systems IISRINIVASA RAO GANTAPas encore d'évaluation
- Transmission Line Parameters ExplainedDocument76 pagesTransmission Line Parameters Explaineddesalegn gebriePas encore d'évaluation
- Ch1 Current Volt Relationship Trasmission LineDocument84 pagesCh1 Current Volt Relationship Trasmission Linerathorsumit2006Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction to Electric Power TRANSMISSION & DISTRIBUTIONDocument100 pagesIntroduction to Electric Power TRANSMISSION & DISTRIBUTIONUmair BeygPas encore d'évaluation
- 9A02304 Basic Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDocument8 pages9A02304 Basic Electrical & Electronics EngineeringsivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- SVS COLLEGE EEE QUESTION BANK UNIT I TRANSMISSION LINE PARAMETERSDocument20 pagesSVS COLLEGE EEE QUESTION BANK UNIT I TRANSMISSION LINE PARAMETERSFurqan WarisPas encore d'évaluation
- 9 TransformerDocument7 pages9 TransformerMThana BalanPas encore d'évaluation
- 3453Document7 pages3453Bnr GoudPas encore d'évaluation
- Power System Analysis and Simulation Question PaperDocument2 pagesPower System Analysis and Simulation Question PaperKeyur PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- EE2303 - T&D Line Parameters, Transposition & EffectsDocument34 pagesEE2303 - T&D Line Parameters, Transposition & EffectsSaran Arun100% (1)
- Eee NoteDocument4 pagesEee NoteNusaeb Ahmed FarhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Probable Questions - EptdDocument3 pagesProbable Questions - EptdManas ChakrabortyPas encore d'évaluation
- Question BankDocument9 pagesQuestion Bankanuavi93Pas encore d'évaluation
- Ehvac Previous QuestionsDocument4 pagesEhvac Previous QuestionsVenkatPas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment BEE CompleteDocument5 pagesAssignment BEE CompleteHarshit YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Comparison of Transformerless Converter Topologies For Photovoltaic Application Concerning Efficiency and Mechanical VolumeDocument6 pagesComparison of Transformerless Converter Topologies For Photovoltaic Application Concerning Efficiency and Mechanical VolumeKarim EfthuPas encore d'évaluation
- Question Bank - 14ELE15Document6 pagesQuestion Bank - 14ELE15Rakesh ThapliyalPas encore d'évaluation
- Over Head LinesDocument8 pagesOver Head LinesDdumbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution Manual for 100 Genesys Design Examples: Second EditionD'EverandSolution Manual for 100 Genesys Design Examples: Second EditionPas encore d'évaluation
- It Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingD'EverandIt Is Quite Another Electricity: Transmitting by One Wire and Without GroundingPas encore d'évaluation
- Electricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and PracticeD'EverandElectricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and PracticePas encore d'évaluation
- DibangarayDocument1 pageDibangarayvagoliyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Murd HaniDocument1 pageMurd HanivagoliyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Namh ShivDocument1 pageNamh ShivvagoliyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Bhram Ni LimpDocument1 pageBhram Ni LimpvagoliyoPas encore d'évaluation
- NirjariDocument1 pageNirjarivagoliyoPas encore d'évaluation
- TrilochanayDocument1 pageTrilochanayvagoliyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Tano TunahDocument1 pageTano TunahvagoliyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Krupa KaroDocument1 pageKrupa KarovagoliyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Vidhyavan Guni AtiDocument1 pageVidhyavan Guni AtivagoliyoPas encore d'évaluation
- As Bar Din Janki MataDocument1 pageAs Bar Din Janki MatavagoliyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chakar Chand TandavamDocument1 pageChakar Chand TandavamvagoliyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Meli Mukha MahiDocument1 pageMeli Mukha MahivagoliyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Man Kram Bachan Dhyan Jo LaaveDocument1 pageMan Kram Bachan Dhyan Jo LaavevagoliyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Hanumat Se Hi Sarv Sukh KarahiDocument1 pageHanumat Se Hi Sarv Sukh KarahivagoliyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Tum Upkar Sugrivahi KinhaDocument1 pageTum Upkar Sugrivahi KinhavagoliyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Shree RamDocument1 pageShree RamvagoliyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Tumharo Mantra BibhishanDocument1 pageTumharo Mantra BibhishanvagoliyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Jay Jay GujaratDocument1 pageJay Jay GujaratvagoliyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Electrical Power SystemDocument3 pagesElectrical Power SystemPatel Keyur NPas encore d'évaluation
- Jay Saraswati MataDocument1 pageJay Saraswati MatavagoliyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Jay MatajiDocument1 pageJay MatajivagoliyoPas encore d'évaluation
- GTU Semester IV SubjectsDocument16 pagesGTU Semester IV Subjectskapiljoshi007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Life Without Limits 2Document31 pagesLife Without Limits 2Kalpesh PrajapatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Jai HanumanDocument1 pageJai HanumanvagoliyoPas encore d'évaluation
- 01082016Document20 pages01082016vagoliyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Mid - Int Circlar For Sem-12 Winter 2016Document1 pageMid - Int Circlar For Sem-12 Winter 2016vagoliyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ramanjuam Magic Square PDFDocument15 pagesRamanjuam Magic Square PDFvagoliyoPas encore d'évaluation
- BE6Document17 pagesBE6vagoliyoPas encore d'évaluation
- 2140909Document3 pages2140909vagoliyoPas encore d'évaluation
- Gujarat Technological University: Draft Teaching Scheme: B.E. Course: Semester VIII (W.E.F.: 2016-2017)Document15 pagesGujarat Technological University: Draft Teaching Scheme: B.E. Course: Semester VIII (W.E.F.: 2016-2017)DeveshPrajapatiPas encore d'évaluation
- Airman Power Generators Enu PDFDocument6 pagesAirman Power Generators Enu PDFderenokPas encore d'évaluation
- Panasonic TX-14b4tp B Tc-14b4rp B CH z185Document17 pagesPanasonic TX-14b4tp B Tc-14b4rp B CH z185Marius IonescuPas encore d'évaluation
- Datasheet 1n4733Document4 pagesDatasheet 1n4733PabloEzequielRamosPas encore d'évaluation
- ISO9001 Certified Solar Pump CatalogDocument56 pagesISO9001 Certified Solar Pump CatalogRyan TrươngPas encore d'évaluation
- 70sco00184 5Document43 pages70sco00184 5watkinskarlPas encore d'évaluation
- Welding Equipment Guide and SpecificationsDocument97 pagesWelding Equipment Guide and SpecificationsfraemddPas encore d'évaluation
- Diversified Accumulation Conveyor ManualDocument32 pagesDiversified Accumulation Conveyor ManualProyectos Trans roll, C.A. OficinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Preview ANSI+NETA+ATS-2017Document22 pagesPreview ANSI+NETA+ATS-2017hendro suprianto nugroho0% (1)
- Forum On New Colour Code-17 Dec 2009Document14 pagesForum On New Colour Code-17 Dec 2009Bob JohnsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Build a Better Future with Reliable MCCBsDocument16 pagesBuild a Better Future with Reliable MCCBsluxofPas encore d'évaluation
- ECE330 HW6 SolutionDocument4 pagesECE330 HW6 SolutionHuynh BachPas encore d'évaluation
- Nexans - N2XSY 8 7 15 KV DNC ET 031b 2Document1 pageNexans - N2XSY 8 7 15 KV DNC ET 031b 2Joel Carhuancho NanaPas encore d'évaluation
- 33-50-14 (Epu301)Document30 pages33-50-14 (Epu301)BehroozPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of GeneratorsDocument13 pagesPrinciples of GeneratorsRica JosephinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Derive The Expressions For The Average DC Current, DC Load Voltage, Rectifier Efficiency, Ripple Factor, Piv Rating For The Bridge Rectifier CircuitDocument9 pagesDerive The Expressions For The Average DC Current, DC Load Voltage, Rectifier Efficiency, Ripple Factor, Piv Rating For The Bridge Rectifier CircuitS DispiserPas encore d'évaluation
- Cable Size Calculation For LT & HT MotorsDocument14 pagesCable Size Calculation For LT & HT MotorssupermannonPas encore d'évaluation
- ARL-300 Error Codes - enDocument4 pagesARL-300 Error Codes - enDaceDrop79% (29)
- LED RUNNER Surface 1125: Specification Sheet Exenia Pendant - Ceiling LampsDocument1 pageLED RUNNER Surface 1125: Specification Sheet Exenia Pendant - Ceiling LampsCafeeFunny bunnyPas encore d'évaluation
- Nexans Türkiye Instrumentation Cable SpecDocument2 pagesNexans Türkiye Instrumentation Cable SpecRijo RajanPas encore d'évaluation
- SVT CableDocument1 pageSVT Cabletwo travellerPas encore d'évaluation
- Iec SimbolosDocument31 pagesIec SimbolosAlberto Rodriguez100% (1)
- Standard Frequency Radiographic Generator: Spectra 325eDocument2 pagesStandard Frequency Radiographic Generator: Spectra 325eJairo Manzaneda67% (3)
- Trouble Shooting Guide For Loco Pilots On Microprocessor MEP-660 (Ver-2.0) WDM3A & WDG3A Locomotives (English)Document58 pagesTrouble Shooting Guide For Loco Pilots On Microprocessor MEP-660 (Ver-2.0) WDM3A & WDG3A Locomotives (English)Khajahussain Syed89% (19)
- A Comparative Analysis Bi-Directional DC-DC Converters: of Non-IsolatedDocument6 pagesA Comparative Analysis Bi-Directional DC-DC Converters: of Non-IsolatedTeam RaagPas encore d'évaluation
- Three Mile Island ClosesDocument2 pagesThree Mile Island ClosesPennLivePas encore d'évaluation
- ATLAS 530 550W 144M (M10) MONO 10BB English - 221222 - 110237Document3 pagesATLAS 530 550W 144M (M10) MONO 10BB English - 221222 - 110237MajstorskiFilipPas encore d'évaluation
- Inventux VoordelenDocument2 pagesInventux VoordelenJohan BeijertPas encore d'évaluation
- Ans B4Document4 pagesAns B4StudentPas encore d'évaluation
- PCS-902 X Instruction Manual en Customized ECKF100721 R1.00 (En XLBH5102.0063.1101)Document251 pagesPCS-902 X Instruction Manual en Customized ECKF100721 R1.00 (En XLBH5102.0063.1101)TheaBinPas encore d'évaluation