Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
4ST Wrist Injury
Transféré par
Julius AdamsCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
4ST Wrist Injury
Transféré par
Julius AdamsDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
HAND AND WRIST INJURIES
AOSSM SPORTS TIPS
With so many bones, ligaments, tendons, and joints keeping hands and wrists working, there is ample opportunity for injury. In fact, injuries to the hand and wrists are some of the most common ailments facing athletes. If managed properly, however, most athletes can expect their injury to heal without any significant long-term disability.
WHAT SHOULD I DO IF I INJURE MY HAND OR WRIST?
Should you sustain a hand or wrist injury while participating in a game where an attending team physician is not present, seek immediate medical care if any of the following symptoms are present: Severe pain Severe swelling Numbness Coldness or grayness in the finger, hand, or wrist Abnormal twisting or bending of the finger or hand A clicking, grating, or shifting noise while moving your finger, hand, or wrist Bleeding that does not slow and persists for more than 15 minutes. Contact your physician during regular practice hours if mild wrist pain, bruising, or swelling after an injury persists and does not improve after two weeks.
one for support), splints, braces, casts, or physical therapy may be used as a treatment option. Your doctor will determine the best option, taking into consideration short and long-term damage; deformities, and stiffness.
HOW CAN I PREVENT A HAND OR WRIST INJURY?
Wearing wrist guards, gloves, and stretching are just a few ways to help prevent a traumatic hand or wrist injury. You can prevent overuse injuries by taking breaks to rest the hands or wrists, using proper posture and technique, and utilizing protective equipment. Expert Consultant Dan Matthews, MD
WHAT ARE THE MOST COMMON SPORTS-RELATED HAND AND WRIST INJURIES?
There are a number of injuries that may occur in an athletes hands or wrists. They can be classified into two main categories: traumatic (acute) and overuse (chronic). Traumatic injuries are more likely to occur in athletes who participate in sports that require higher levels of contact (i.e., football, hockey, or wrestling), whereas overuse injuries result in athletes who participate in sports that require them to overdo a particular movement (i.e., baseball, tennis, or golf). Some common traumatic injuries in athletes include joint dislocations, sprains, muscle strains, broken bones, tendon inflammation, and ligament tears. The most common fracture injury in the athletic population occurs in the fingers. Overuse injuries are stress-induced and include tendon inflammation and dislocation, nerve injury, and over use stress fractures. Long-term disability is less likely to occur from overuse injuries than from traumatic injuries. However, if left untreated, an athletes sports performance may be significantly diminished. Surgical treatment may be required if an injury persists.
ADDITIONAL RESOURCES
American Physical Therapy Association American Medical Society for Sports Medicine
For minor hand injuries, home treatment, including rest, ice, compression, and elevation to the effected limb can help relieve pain, swelling, and stiffness. An anti-inflammatory medication such as ibuprofen or naproxen may also be taken to help with the pain and inflammation.
WHAT TREATMENT OPTIONS ARE AVAILABLE FOR HAND AND WRIST INJURIES?
Treatment depends on the location, type, duration, and severity of the injury. While surgery is needed for some injuries, such as ligament tears, medication, buddy-taping (taping the injured finger to a neighboring
Sports Tips are brought to you by the American Orthopaedic Society for Sports Medicine. They provide general information only and are not a substitute for your own good judgement or consultation with a physician. To order multiple copies of this fact sheet or learn more about other orthopaedic sports medicine topics, please visit www.sportsmed.org.
Copyright 2008. American Orthopaedic Society for Sports Medicine. All rights reserved. Multiple copy reproduction prohibited.
HAND AND WRIST INJURIES
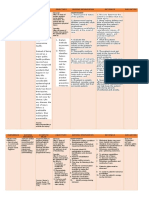
COMMON HAND AND WRIST INJURIES
INJURY
Jammed Finger
CAUSES/DESCRIPTION
Striking the end of the finger while fully extended Force of contact overwhelms strength of bone (ball, ground, helmet) Impact on tip of finger leads to rupture of tendon that holds finger tip straight Impact or crushing injury on top of nail Force on finger overwhelms ligaments and joint displaces
SYMPTOMS
Pain, swelling at the joint, difficult to bend, tenderness over the joint Pain, tenderness over the bone, deformity may be present
TREATMENT
Ice, rest, buddy tape to adjacent finger Ice, splint, doctor evaluation, X-rays
RETURN TO PLAY
As tolerated with buddy tape Only after proper evaluation, realignment from a physician, and wearing appropriate protection until healed May return as tolerated in splint which must be worn at all times for 8 weeks As tolerated
Finger Fracture
Mallet Finger
Unable to hold small joint at finger tip out straight, tender just behind nail Blood under nail, tender may represent tear in nailbed under nail Most common at middle joint of finger, with visible displacement
Doctor evaluation, splinting finger in full extension 8 weeks If blood covers >50% of nail, need doctor evaluation may need repair of nail bed Relocation of joint best performed by doctor, may require local anesthesia and X-ray evaluation. May require surgery. Needs medical evaluation within 2448 hours, requires surgery, possibly within 10 days Needs doctor evaluation may require special X-ray (CT scan). May require surgery.
Nail Bed Injury
Finger Dislocation
After proper evaluation, use buddy tape or splint as determined by physician
Tendon Tear Jersey Finger
Force of grasp with object (jersey) pulling away, ruptures tendon
Most commonly seen in ring finger, unable to flex the joint at finger tip
Only after surgical repair is fully healed. Early RTP places the athlete at risk of long-term problems with finger function and motion Not allowed until thorough evaluation by physician. If fracture present may be able to return with proper protection (cast) which is worn until healed. Not allowed until thorough evaluation by physician. Evaluation and early treatment can prevent long-term problems. May return to play in cast protection. As tolerated
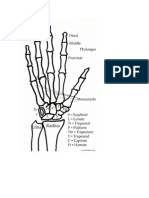
Wrist Bone Fracture Scaphoid
Fall on outstretched hand
Pain with wrist motion, tenderness in wrist at the base of thumb
Wrist Ligament Tear
Impaction or twisting injury of wrist
Pain in wrist with gripping rotation of wrist
Needs physician evaluation, X-rays, possible MRI
Ulnar Collateral Ligament Tear Skiers Thumb Tendonitis
Tear of ligament that stabilizes the thumb with grasping Repetitive activity of one specific movement Repetitive activity overcomes strength of bones and leads to small fractures Over stressing bone of still growing children, most commonly seen in gymnastics (wrist bone), baseball pitchers(shoulder, elbow)
Pain and instability of thumb with grasping objects Tenderness over the tendon may feel grading over tendon with finger or wrist motion Pain with activity, most commonly in lower extremities (running, jumping) Persistent pain, tenderness swelling over growing bone, bone pain/tenderness
Needs physician evaluation, X-rays, may need surgery or casting Rest, ice, limitation of repetitive motion, NSAIDS Physician evaluation, X-rays, bone scans, may need casting, surgery, must have rest, nutritional evaluation Physician evaluation rest, ice, must cease offending activity
Stress Fractures
Must rest and cease offending activity until fully healed. May need bone growth stimulator, casting, surgery Athlete cannot return to play until fully healed as growing problems can have long-term problems
Growth Plate Stress
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Badass EbookDocument22 pagesBadass Ebookamirkhan0278% (36)
- Jocko Willink Workout GuideDocument3 pagesJocko Willink Workout GuideJulius Adams75% (12)
- Melbourne ACL Rehabilitation Guide 2.0: A criteria driven ACL rehab protocolDocument32 pagesMelbourne ACL Rehabilitation Guide 2.0: A criteria driven ACL rehab protocolgabi balaPas encore d'évaluation
- B JJ ManifestoDocument42 pagesB JJ ManifestoJulius AdamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Brooks Kubik - Dinosaur DietDocument22 pagesBrooks Kubik - Dinosaur Dietjacksparrow291% (11)
- Animal Flow Workout (2011)Document6 pagesAnimal Flow Workout (2011)mikevlah50% (2)
- Atlas of TitanDocument380 pagesAtlas of TitanJulius Adams86% (21)
- Major Internship DTR JulyandaugustDocument1 pageMajor Internship DTR JulyandaugustGeraldineMoletaGabutin100% (1)
- Med Surg QuizDocument91 pagesMed Surg QuizCharles Gerard B. Beluan0% (1)
- Wrist PainDocument8 pagesWrist PainLev KalikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sprains and StrainsDocument15 pagesSprains and StrainsPutri ClaraPas encore d'évaluation
- SPRAINS: Overstretching or Tearing The Ligaments Results in A Sprain. Ligaments Are The Bands ofDocument7 pagesSPRAINS: Overstretching or Tearing The Ligaments Results in A Sprain. Ligaments Are The Bands ofPriyanshu KanojiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Jurnal Tennis ElbowDocument5 pagesJurnal Tennis ElbowMuhamad Fahrizal RilahiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sports Injuries in Wrist & Hand.Document72 pagesSports Injuries in Wrist & Hand.salmankhan09215Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cotul Reumatic EnglezaDocument7 pagesCotul Reumatic EnglezaElena GaneaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tendonitis Guide - Causes, Symptoms and Treatment OptionsDocument6 pagesTendonitis Guide - Causes, Symptoms and Treatment OptionsSylvia GracePas encore d'évaluation
- Patellar Tendonitis TreatmentDocument7 pagesPatellar Tendonitis TreatmentRatnaPrasadNalamPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Common Knee Injuries ExplainedDocument6 pagesTypes of Common Knee Injuries ExplainedSagarPas encore d'évaluation
- GCU Surgery Assignment on Common Knee InjuriesDocument9 pagesGCU Surgery Assignment on Common Knee InjuriesHigh TechPas encore d'évaluation
- What Is The Difference Between An Acute Injury and A Chronic Injury?Document10 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between An Acute Injury and A Chronic Injury?Tafadzwa PiyoPas encore d'évaluation
- KneeDocument3 pagesKneedoos1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Medial Epicondylitis (Golfer's Elbow) What Is Medial Epicondylitis?Document4 pagesMedial Epicondylitis (Golfer's Elbow) What Is Medial Epicondylitis?Kalamegam RamasamiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sprain: P P P PDocument4 pagesSprain: P P P PJc RocuyanPas encore d'évaluation
- PE 2 Midterm ModulesDocument20 pagesPE 2 Midterm ModulesEsra May AngadPas encore d'évaluation
- Lateral Epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow)Document8 pagesLateral Epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow)Rusu AdrianPas encore d'évaluation
- Osteoarthritis PocDocument4 pagesOsteoarthritis PocIrene Joy GomezPas encore d'évaluation
- Osteoarthritis: Applied Medicine BY: Dr. Kinza IftikharDocument16 pagesOsteoarthritis: Applied Medicine BY: Dr. Kinza IftikharsabaamjadPas encore d'évaluation
- 04 Wrist and Hand Injuries in Sport Acute Soft Tissue InjuriesDocument65 pages04 Wrist and Hand Injuries in Sport Acute Soft Tissue InjuriesKhushboo IkramPas encore d'évaluation
- PIP Joint InjuryDocument4 pagesPIP Joint InjurySAYEM AHAMMEDPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Sports Injuries Guide: Basketball, Tennis, Treatment for Ankle Sprains, Knee Issues & MoreDocument17 pagesCommon Sports Injuries Guide: Basketball, Tennis, Treatment for Ankle Sprains, Knee Issues & MoreShiela Jane Langga SanghidPas encore d'évaluation
- Osteoarthritis: T Person's of Developing Osteoarthritis. It IncludesDocument5 pagesOsteoarthritis: T Person's of Developing Osteoarthritis. It IncludesLove Shery SabrosoPas encore d'évaluation
- Knucle JointDocument2 pagesKnucle Joint12ranjPas encore d'évaluation
- Hand and Wrist InjuriesDocument25 pagesHand and Wrist InjuriesMAMA LALA100% (2)
- G11 - Pe 2 - Module 1Document7 pagesG11 - Pe 2 - Module 1John Lois VanPas encore d'évaluation
- Knee Pain: Treating Knee Pain: Preventing Knee Pain: Natural Remedies, Medical Solutions, Along With Exercises And Rehab For Knee Pain ReliefD'EverandKnee Pain: Treating Knee Pain: Preventing Knee Pain: Natural Remedies, Medical Solutions, Along With Exercises And Rehab For Knee Pain ReliefÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Stress Fracture GuideDocument11 pagesStress Fracture GuideSURWEZ'SPas encore d'évaluation
- Distal Radius Fractures (Broken Wrist) - OrthoInfo - AAOSDocument4 pagesDistal Radius Fractures (Broken Wrist) - OrthoInfo - AAOSmuhammad iqbal mahfuzhPas encore d'évaluation
- Tennis elbow treatment optionsDocument10 pagesTennis elbow treatment optionsMarliani AfriastutiPas encore d'évaluation
- Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) - OrthoInfo - AAOSDocument8 pagesTennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis) - OrthoInfo - AAOSnoony 98Pas encore d'évaluation
- Word To PDFDocument119 pagesWord To PDFshravaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Sprains, Strains and Other Soft-Tissue Injuries: CauseDocument5 pagesSprains, Strains and Other Soft-Tissue Injuries: CauseYosef OxinioPas encore d'évaluation
- Hand Injuries: by LakshmiprabhaDocument50 pagesHand Injuries: by LakshmiprabhaLakshmiprabha KalyanaramanPas encore d'évaluation
- Erbil Polytechnic University Erbil Health Technical College Physiotherapy Department Study Year 2020-2021Document13 pagesErbil Polytechnic University Erbil Health Technical College Physiotherapy Department Study Year 2020-2021Muhamad SdeqPas encore d'évaluation
- Tennis Elbow, Golfer's Elbow, Arthritis GuideDocument21 pagesTennis Elbow, Golfer's Elbow, Arthritis GuideJalil AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- Shoulder Pain and Common Shoulder ProblemsDocument14 pagesShoulder Pain and Common Shoulder ProblemsRatnaPrasadNalamPas encore d'évaluation
- Elbow Tendinopathy (Tennis and Golf Elbow)Document5 pagesElbow Tendinopathy (Tennis and Golf Elbow)Siddharth PillaiPas encore d'évaluation
- What Causes Osteoarthritis?Document9 pagesWhat Causes Osteoarthritis?jajabsPas encore d'évaluation
- Tendonitis - Harvard HealthDocument3 pagesTendonitis - Harvard Healthroadwhiz.infoPas encore d'évaluation
- Musculoskeletal TraumaDocument103 pagesMusculoskeletal TraumaJona Kristin EnclunaPas encore d'évaluation
- Arthritis Types and Treatments ExplainedDocument10 pagesArthritis Types and Treatments ExplainedMuiz SaddozaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Wrist Tendonitis - Causes, Symptoms, TreatmentsDocument1 pageWrist Tendonitis - Causes, Symptoms, TreatmentsenadPas encore d'évaluation
- Common Sports Injuries ExplainedDocument24 pagesCommon Sports Injuries ExplainedChris PatlingraoPas encore d'évaluation
- Dr. Jonaidi T, SPKFR Instalasi Rehabilitasi Medik Rsud Dr. Soedarso, PontianakDocument29 pagesDr. Jonaidi T, SPKFR Instalasi Rehabilitasi Medik Rsud Dr. Soedarso, PontianakHerlam SyahPas encore d'évaluation
- How to Treat a Sprained AnkleDocument4 pagesHow to Treat a Sprained AnkleSakthi Annamalai.cPas encore d'évaluation
- Osteoarthritis EssayDocument8 pagesOsteoarthritis EssayMeysha PPas encore d'évaluation
- Trigger Finger: AnatomyDocument4 pagesTrigger Finger: AnatomyAlfun IqbalPas encore d'évaluation
- Wrist Injury at SiteDocument10 pagesWrist Injury at SiteClark Angelo JuanPas encore d'évaluation
- Sports TreatmentDocument84 pagesSports TreatmentBASAVARAJPas encore d'évaluation
- Musculoskeletal Disorders Part 7 Sports InjuriesDocument67 pagesMusculoskeletal Disorders Part 7 Sports InjuriesCarmela Lacsa DomocmatPas encore d'évaluation
- Sprains and Strains FFDocument4 pagesSprains and Strains FFBryan De HopePas encore d'évaluation
- Common Injuries and First Aid TreatmentDocument22 pagesCommon Injuries and First Aid TreatmentebullientcynosurePas encore d'évaluation
- Different Sports InjuriesDocument11 pagesDifferent Sports InjuriesreginePas encore d'évaluation
- How To Identify and Treat Inner Knee PainDocument6 pagesHow To Identify and Treat Inner Knee PainRatnaPrasadNalamPas encore d'évaluation
- Typical Shoulder TroublesDocument7 pagesTypical Shoulder TroublesLev KalikaPas encore d'évaluation
- OsteoarthritisDocument63 pagesOsteoarthritisDuaa BalochPas encore d'évaluation
- Tennis Elbow RehabDocument8 pagesTennis Elbow RehabDarren Willis100% (2)
- What Is A Torn MeniscusDocument6 pagesWhat Is A Torn MeniscusDinesh GodhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Osteoarthritis - Surgical Therapy, Alternative Medicine and Proper ExerciseDocument5 pagesOsteoarthritis - Surgical Therapy, Alternative Medicine and Proper ExerciseElsa Novi WulansariPas encore d'évaluation
- All About Arthritis- Find Updated Causes, Symptoms, Diagnostic Tests, New Alternative Treatments, Cures and BreakthroughsD'EverandAll About Arthritis- Find Updated Causes, Symptoms, Diagnostic Tests, New Alternative Treatments, Cures and BreakthroughsPas encore d'évaluation
- Working Agile EightCCSMDocument2 pagesWorking Agile EightCCSMJulius AdamsPas encore d'évaluation
- The DeadliftDocument2 pagesThe DeadliftJulius AdamsPas encore d'évaluation
- The Nine Success Principles of Japan's Greatest Swordsman, Musashi Miyamoto PDFDocument42 pagesThe Nine Success Principles of Japan's Greatest Swordsman, Musashi Miyamoto PDFDiana RiveraPas encore d'évaluation
- Professor Atilla's Five Pound Dumb-Bell ExerciseDocument76 pagesProfessor Atilla's Five Pound Dumb-Bell ExerciseCullen O'Gorman87% (23)
- Guide To HandstandDocument23 pagesGuide To HandstandmargaritassPas encore d'évaluation
- WHM 20 Day Cold Shower Challenge2018pdf PDFDocument1 pageWHM 20 Day Cold Shower Challenge2018pdf PDFJulius AdamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Path Demanding Volume 1 PDFDocument224 pagesPath Demanding Volume 1 PDFJulius AdamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Sandwiches For MenDocument97 pagesSandwiches For MendevmohnPas encore d'évaluation
- Proteus 3Document44 pagesProteus 3Julius Adams100% (1)
- Diamond-Cut Abs, How To Engineer The Ultimate Six-PackDocument244 pagesDiamond-Cut Abs, How To Engineer The Ultimate Six-PackJulius Adams80% (5)
- Keys To Conscious ImprovementDocument10 pagesKeys To Conscious ImprovementJulius AdamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Australian Science Teachers Journal Sep 2000 46, 3 Education ModuleDocument7 pagesAustralian Science Teachers Journal Sep 2000 46, 3 Education ModuleJulius AdamsPas encore d'évaluation
- The Nine Success Principles of Japan's Greatest Swordsman, Musashi Miyamoto PDFDocument42 pagesThe Nine Success Principles of Japan's Greatest Swordsman, Musashi Miyamoto PDFDiana RiveraPas encore d'évaluation
- CostiganDocument12 pagesCostiganJulius AdamsPas encore d'évaluation
- CostiganDocument12 pagesCostiganJulius AdamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Tactical Booklet 5-5-11Document24 pagesTactical Booklet 5-5-11Raul Guerrero100% (1)
- Hand MSK ExamDocument1 pageHand MSK ExamJulius AdamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Pressure Pointer ManualDocument17 pagesPressure Pointer ManuallucymayPas encore d'évaluation
- Examination of TheElbowDocument3 pagesExamination of TheElbowJulius AdamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Examination of TheElbowDocument3 pagesExamination of TheElbowJulius AdamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Examining the Knee: A Guide to AssessmentDocument5 pagesExamining the Knee: A Guide to AssessmentJulius AdamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Performing A Regional Musculoskeletal ExaminationDocument2 pagesPerforming A Regional Musculoskeletal ExaminationJulius AdamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Excerpt From "Diabetes: A Lifetime of Being Too Sweet"Document9 pagesExcerpt From "Diabetes: A Lifetime of Being Too Sweet"waltcrockerPas encore d'évaluation
- Empagliflozin Metformin HCL: Jardiance Duo®Document2 pagesEmpagliflozin Metformin HCL: Jardiance Duo®Lord Carlo CabangalPas encore d'évaluation
- Europass Curriculum Vitae: Personal InformationDocument7 pagesEuropass Curriculum Vitae: Personal InformationAndrei TudorachePas encore d'évaluation
- Hope 11 Assessment 1 4TH QTRDocument2 pagesHope 11 Assessment 1 4TH QTRApril Rose Ferrancullo RelojPas encore d'évaluation
- CONCEPT EpidemilologyDocument13 pagesCONCEPT EpidemilologyKrishnaveni MurugeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Discharge PlanDocument4 pagesDischarge PlanPaul Loujin LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Digital Healthcare Market Research 3Document33 pagesDigital Healthcare Market Research 3Nero AngeloPas encore d'évaluation
- Medicine JC-SC WCS Summary (Neurology)Document6 pagesMedicine JC-SC WCS Summary (Neurology)Peter LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Abnormal Midwifery: by Gladys M. BSN, KRCHNDocument352 pagesAbnormal Midwifery: by Gladys M. BSN, KRCHNMercy KeruboPas encore d'évaluation
- Mis NotesDocument12 pagesMis NotesVasundharaPas encore d'évaluation
- R G C I & R C: Ajiv Andhi Ancer NstituteDocument7 pagesR G C I & R C: Ajiv Andhi Ancer NstituteShubham JainPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementatio N Rationale Evaluation Short Term: Indipendent Short TermDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Implementatio N Rationale Evaluation Short Term: Indipendent Short TermKenneth PoncialPas encore d'évaluation
- Linear Iga Dermatosis / Chronic Bullous Disease of ChildhoodDocument31 pagesLinear Iga Dermatosis / Chronic Bullous Disease of ChildhoodHoc Lim SeePas encore d'évaluation
- Olimpiada Engleza 2017 CL A 8A PDFDocument4 pagesOlimpiada Engleza 2017 CL A 8A PDFAnthony AdamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Continuum CareDocument24 pagesContinuum CareJovelyn EspanolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 Introduction FinalDocument5 pagesChapter 1 Introduction FinalDivine Grace Cabungcag0% (1)
- Nirali Final Synopsis PDFDocument31 pagesNirali Final Synopsis PDFNIRALI MISTRYPas encore d'évaluation
- PR - Teijin Pharma and SRETT Sign Exclusive Distribution Agreement For Respiratory Remote-Monitoring DeviceDocument2 pagesPR - Teijin Pharma and SRETT Sign Exclusive Distribution Agreement For Respiratory Remote-Monitoring DeviceYihui FlauxPas encore d'évaluation
- Medical Leave CertificatesDocument4 pagesMedical Leave CertificatesDhana LakshmiPas encore d'évaluation
- Mudlark CPI Medical Care Report Oct 09Document8 pagesMudlark CPI Medical Care Report Oct 09MudlarkResearchPas encore d'évaluation
- RNTCP New Guidelines 2017 Daily DosingDocument37 pagesRNTCP New Guidelines 2017 Daily DosingVidya Mohan KrithikanandPas encore d'évaluation
- Dialog Percakapan Bidan Tugas Bahs Inggris DedeDocument5 pagesDialog Percakapan Bidan Tugas Bahs Inggris DedeSardianto TurnipPas encore d'évaluation
- Bipolar 1 Disorder NCPDocument3 pagesBipolar 1 Disorder NCPJoy-Rena Sabinay OchondraPas encore d'évaluation
- Preterm Its ProblemsDocument30 pagesPreterm Its ProblemsEnlighten usPas encore d'évaluation
- Recognizing and Reporting Red Flags For The Physical Therapist Assistant 1stDocument52 pagesRecognizing and Reporting Red Flags For The Physical Therapist Assistant 1stsummer.yates611100% (38)
- PE 3 ReviewerDocument5 pagesPE 3 ReviewerZac GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- Skills Assessment Checklist: MODULE 6: Massive Hemorrhage Control in TFCDocument7 pagesSkills Assessment Checklist: MODULE 6: Massive Hemorrhage Control in TFCSae TumPas encore d'évaluation
- RICE Therapy for Common Soft Tissue InjuriesDocument2 pagesRICE Therapy for Common Soft Tissue InjuriesmoizitouPas encore d'évaluation