Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Leprosy (Hansenosis, Hansen's Disease) - An Ancient Disease and Is
Transféré par
denodenoDescription originale:
Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Leprosy (Hansenosis, Hansen's Disease) - An Ancient Disease and Is
Transféré par
denodenoDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
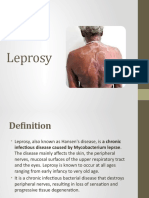
Leprosy (Hansenosis, Hansen’s disease)
- An ancient disease and is a leading cause of permanent physical disability
among the communicable diseases.
Causative Agent
Mycobacterium leprae
Modes of Transmission
Airborne-droplet, Prolonged skin-to-skin contact
Period of Communicability
5 ½ months
Clinical Manifestations
Early signs:
Change in skin color – either reddish or white
Loss of sensation on the skin lesion
Loss of sweating and hair growth
Thickened and painful nerves
Muscle weakness or paralysis or extremities
Pin and redness of the eyes
Nasal obstruction or bleeding
Ulcers that do not heal
Late Signs:
Madarosis
Loss of eyebrows
Inability to close eyelids (lagophthalmos)
Clawing of fingers and toes
Contractures
Chronic ulcers
Sinking of the nosebridge
Enlargement of the breast (gynecomastia)
Diagnostic Procedures
Slit Skin Smear - determines the presence of M. leprae; optional and done only if
clinical diagnosis is doubtful to prevent misclassification and wrong treatment
Lepromin Test – determines susceptibility to leprosy
Treatment
Ambulatory chemotherapy through use of MDT
Domiciliary treatment as embodied in RA 4073 which advocates home treatment
PAUCIBACILLARY (tuberculoid and indeterminate); noninfectious type
Duration of treatment: 6 to 9 months
Procedure:
Supervised: Rifampicin and Dapsone once a month on the health center supervised by the
rural health midwife
Self-administered: Dapsone everyday at the client’s house
MULTIBACILLARY (lepromatous and borderline); infectious type
Duration of treatment: 24-30 months
Procedure:
Supervised: Rifampicin, Dapsone, and Lamprene
Prevention
Avoid prolonged skin-to-skin contact
BCG vaccination – practical and effective preventive measure against leprosy
Good personal hygiene
Adequate nutrition
Health education
Nursing Management
Isolation and medical asepsis, psychological support
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Communicable DiseasesDocument176 pagesCommunicable DiseasesKimsha ConcepcionPas encore d'évaluation
- Leprosy NotesDocument16 pagesLeprosy NotesNicolePas encore d'évaluation
- National Leprosy Control Program For CHNDocument18 pagesNational Leprosy Control Program For CHNNaomi Cyden YapPas encore d'évaluation
- Locally Endemic Diseases ControlhandoutDocument3 pagesLocally Endemic Diseases ControlhandoutEshiebel OrganistaPas encore d'évaluation
- Leprosy Control Program: Vision: Mission: ObjectivesDocument5 pagesLeprosy Control Program: Vision: Mission: ObjectivesAngelica VillalonPas encore d'évaluation
- LeprosyDocument7 pagesLeprosytankmpPas encore d'évaluation
- Leprosy 22Document49 pagesLeprosy 22Phc ChathannoorPas encore d'évaluation
- Leprosy Ppt2Document18 pagesLeprosy Ppt2blueprincess450Pas encore d'évaluation
- LeprosyDocument51 pagesLeprosySoujanya Kundu ChoudhuryPas encore d'évaluation
- Leprosy CHNDocument14 pagesLeprosy CHNPhillip ChingPas encore d'évaluation
- Hansen's Disease GuideDocument63 pagesHansen's Disease GuideAisha MohamedPas encore d'évaluation
- LeprosyDocument16 pagesLeprosyNipul MondolPas encore d'évaluation
- HansensDocument83 pagesHansensHrishikesh NachinolkarPas encore d'évaluation
- Leprosy: Communicable Diseases FactsheetDocument2 pagesLeprosy: Communicable Diseases FactsheetelisabethPas encore d'évaluation
- Leprosy 2017Document47 pagesLeprosy 2017Mangala bote Nair PSMPas encore d'évaluation
- Leprosy ScriptDocument2 pagesLeprosy ScriptZeribinPas encore d'évaluation
- Leprae and Mycobacterium Lepromatosis. Named After Physician Gerhard Armauer HansenDocument5 pagesLeprae and Mycobacterium Lepromatosis. Named After Physician Gerhard Armauer HansenTim-Tim FerrerPas encore d'évaluation
- LeprosyDocument48 pagesLeprosyPatPas encore d'évaluation
- LeprosyDocument45 pagesLeprosyrouhanbinrashidPas encore d'évaluation
- Communicable DiseasesDocument17 pagesCommunicable DiseasesBern NerquitPas encore d'évaluation
- LeprosyDocument3 pagesLeprosyNadim DinaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Hansen's Diseases/HansenosisDocument12 pagesHansen's Diseases/HansenosisSienaPas encore d'évaluation
- Leprosy Written ReportDocument7 pagesLeprosy Written Reportnicah05Pas encore d'évaluation
- Eruptive Fever DiseaseDocument61 pagesEruptive Fever DiseasePearl DiBerardino100% (2)
- Sexually Transmitted Disease (STD)Document102 pagesSexually Transmitted Disease (STD)uhurtme100% (10)
- Treatment Scabies ControlDocument21 pagesTreatment Scabies ControlNicky SeptianaPas encore d'évaluation
- What causes leprosy and its symptomsDocument7 pagesWhat causes leprosy and its symptomsArron Buenavista AblogPas encore d'évaluation
- Hansens DiseaseDocument83 pagesHansens DiseaseSajin AlexanderPas encore d'évaluation
- Case Report on Morbus Hansen (Leprosy) in IndonesiaDocument31 pagesCase Report on Morbus Hansen (Leprosy) in Indonesiachuck55Pas encore d'évaluation
- BiodataDocument11 pagesBiodatabentubz100% (2)
- Measles virus infectionDocument3 pagesMeasles virus infectionCedric BautistaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument174 pagesSexually Transmitted DiseasesfroizkiPas encore d'évaluation
- Mycobacterium Leprae. The Disease Mainly Affects The Skin, The Peripheral NervesDocument7 pagesMycobacterium Leprae. The Disease Mainly Affects The Skin, The Peripheral NervesZulfa Zahrah HaniPas encore d'évaluation
- LeprosyDocument14 pagesLeprosyEmerald AlcalaPas encore d'évaluation
- Oral Ulceration and Vesiculobullous Diseases and 2Document107 pagesOral Ulceration and Vesiculobullous Diseases and 2JustDen09100% (1)
- NERVOUS SYSTEM Communicable Diseases LEPROSYDocument3 pagesNERVOUS SYSTEM Communicable Diseases LEPROSYFreeNursingNotesPas encore d'évaluation
- LeprosyDocument8 pagesLeprosyapi-337793184Pas encore d'évaluation
- Hansens Disease Presentation 3Document40 pagesHansens Disease Presentation 3Princewill SmithPas encore d'évaluation
- FY Leprosy PPT - RKDocument22 pagesFY Leprosy PPT - RKKaif KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Santillan LeprosyDocument22 pagesSantillan Leprosylorella_abejuelaPas encore d'évaluation
- LeprosyDocument32 pagesLeprosySiselle FajardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Leprosy FinalDocument49 pagesLeprosy FinalMeenakshi KhaprePas encore d'évaluation
- Mycobacterium Leprae (M. Leprae)Document4 pagesMycobacterium Leprae (M. Leprae)Elia JacobPas encore d'évaluation
- Leprosy - Mumal BakliwalDocument13 pagesLeprosy - Mumal BakliwalAni SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- What The Heck!Document36 pagesWhat The Heck!kami alee utoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ectoparasites and Parasites On Human'S Skin/Body Surface: Parasitology DepartmentDocument36 pagesEctoparasites and Parasites On Human'S Skin/Body Surface: Parasitology DepartmentJimmy Fran IIPas encore d'évaluation
- Ectoparasites and Parasites On Human'S Skin/Body Surface: Parasitology DepartmentDocument36 pagesEctoparasites and Parasites On Human'S Skin/Body Surface: Parasitology DepartmentmiaraissaPas encore d'évaluation
- Leprosy Research: by Sofia Truc, Beatrice Pissimbone, Cecilia Eleuteri & Daniele RimondiDocument10 pagesLeprosy Research: by Sofia Truc, Beatrice Pissimbone, Cecilia Eleuteri & Daniele RimondiDaniKebab8Pas encore d'évaluation
- Classification & Clinical Features of LeprosyDocument41 pagesClassification & Clinical Features of LeprosyteslimolakunlerajiPas encore d'évaluation
- Exanthematous Viral DiseasesDocument64 pagesExanthematous Viral DiseasesHoc Lim SeePas encore d'évaluation
- LeprosyDocument9 pagesLeprosyJohn Ribu Parampil100% (1)
- STD Guide: Syphilis Causes, Symptoms, TreatmentDocument4 pagesSTD Guide: Syphilis Causes, Symptoms, TreatmentAnna CahucomPas encore d'évaluation
- Child Care ModuleDocument6 pagesChild Care ModuleMiriam D. GutierrezPas encore d'évaluation
- CD Integu 1Document5 pagesCD Integu 1gwen manalonPas encore d'évaluation
- Pediatric Dermatology Lesions and Common Skin ConditionsDocument4 pagesPediatric Dermatology Lesions and Common Skin ConditionsRemelou Garchitorena AlfelorPas encore d'évaluation
- TP LeprosyDocument4 pagesTP LeprosyZarina RobledoPas encore d'évaluation
- Leprosy The ProjectDocument3 pagesLeprosy The ProjectshamitaguhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Skin Lichen Planus, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsD'EverandSkin Lichen Planus, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsPas encore d'évaluation
- Get Rosacea Under Control Immediately: Practical GuideD'EverandGet Rosacea Under Control Immediately: Practical GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- Rachel U. Gramonte: ObjectivesDocument2 pagesRachel U. Gramonte: ObjectivesdenodenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Dec 2010 NLE Pampanga RoomsDocument71 pagesDec 2010 NLE Pampanga RoomsCoolbuster.NetPas encore d'évaluation
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDocument593 pagesHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- Higher Algebra - Hall & KnightDocument593 pagesHigher Algebra - Hall & KnightRam Gollamudi100% (2)
- Request LetterDocument1 pageRequest LetterdenodenoPas encore d'évaluation
- SH Is To So Mi As IsDocument2 pagesSH Is To So Mi As IsdenodenoPas encore d'évaluation
- Time and Activity PlanDocument1 pageTime and Activity PlandenodenoPas encore d'évaluation