Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Central Dogma Tutorial
Transféré par
Mohd Hasrul RamleeCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Central Dogma Tutorial
Transféré par
Mohd Hasrul RamleeDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
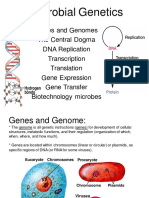
Genes structure
Chromosomes become visible during ___________ and meiosis. Chromosomes come in pairs (_______________); one from ______________ and one from __________ Chromosomes contain genes; each gene is made of two _______________.
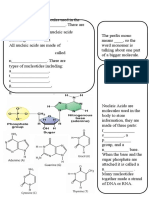
Structure of nucleic acids Two types: 1. !" # ______________________ $. %!" # ______________________ !ucleotide is the monomer& polynucleotide is the polymer. 'ach monomer consists of : 1. ____________________________ $. ____________________________ (. ____________________________ 1. )hosphate group *ive negative charge to !". )hosphates carry negative charges at cellular p+ and give the nucleotides their acidic character. $. )entose sugar unit , C sugar %!" is ribose !" is deo-yribose (. atom at C$ is removed)
(. !itrogenous base $ types: 1. )urine ("&*) $ rings $. )yrimidine (/& T& C) 1 ring
%ibose %ibose
Base adenine guanine cytosine thymine uracil
Nucleoside adenosine guanosine cytidine tymidine uridine
Nucleotide adenylic acid guanylic acid cytidylic acid thymidylic acid uridylic acid
Abbreviation in RNA / DNA "0) 1 d"0) *0) 1 d*0) C0) 1 dC0) 222222 1 dT0) /0) 1 222222
"denosine (nucleoside) RNA and DNA
"denylic acid (nucleotide)
ifferences between %!" and !"
DNA replication
!" twist into double heli- (4atson and Cric5 model& 16,() The polynucleotides are anti2parallel to each other. Complementary base pairing ouble heli-. 7emiconservative replication The Meselson-Stahl experiment was an e-periment by 0atthew 0eselson and 8ran5lin 7tahl to prove that !" replication was semiconservative. 7emiconservative replication means that when the double stranded !" heli- was replicated& each of the two double stranded !" helices consisted of one strand coming from the original heli- and one newly synthesi9ed.
%eplication of !" is semiconservative: each daughter heli- contains one strand of the parental heli-. (Conservative replication would be where the entire parental double heli- was used as a template for the formation of an entirely new daughter double heli-). 7emi2conservative replication: )arental _____________________ separate 'ach ________________________ acts as a template "fter replication& each new !" double heli- has one ________ !" strand and one _________ !" strand.
Gene expression / protein synthesis The central dogma of biology 1. Transcription $. translation (. *ene e-pression 1. $. (. Transcription: messenger %!" (m%!") is made on a ________ template in the _______________. Translation: m%!" moves into the ____________________& m%!" combines with ribosomes to direct protein synthesis. *ene e-pression: the information in a cistron (genes on !") is used to ma5e a functional polypeptide chain by transcription and translation.
he !enetic code - /sing triplet codon on m%!". - Three2base (triplet) code on the m%!" codes for ____________________ of polypeptides. - 1 amino acid is coded by ( bases& e.g. /// for phenylalanine.
)ossible combinations: __________ combinations& more than enough for $; amino acids re<uired by a cell.
2 egenerate code: one amino acid coded by more than one codon& e.g. alanine coded by *C"& *CC& *C*& *C/. - 7tart code& "/* code for methionine ; stop code: /""& /"* and /*". - /niversal for all organisms; chloroplast and mitochondrial !" slight modification. Ma"in! RNA 1. $. (. 1.Transcription - Transfer of information from !" to %!" - +elicase brea5s hydrogen bonds of !" where gene is located (not the whole !") - 7tart at "/* (______________) - %!" polymerase adds nucleotides (/ to __& C to ___& etc) starts from the promoter site - %!" polymerase moves along cistron in ,= to (= direction - .ne !" strand is sense strand (cistron is located). The complementary !" strand is the antisense strand (other genes not re<uired at this time).
7o& the m%!" se<uence is ________________________________ Transcription is terminated at stop codon (___________________________) !" is 9ipped& %!" is released to nucleoplasm.
>
$. )rocessing - )rocessed to ribosomal %!" (r%!") ?;@& m%!" ,@& and transfer %!" (t%!") 1,@. m%!" - 8or eu5aryotic m%!"& it consists of __________ and e-ons. - Antrons will be removed and ____________ are spliced together. - 8inal m%!" - The #$ cap is a specially altered nucleotide end to the ,B end of precursor messenger %!" as found in eu5aryotes. The process of ,B capping is vital to creating mature messenger %!" which is then able to undergo translation. Capping ensures the messenger %!"Bs stability while it undergoes translation in the process of protein synthesis& and is a highly regulated process which occurs in the nucleus. %olyadenylation is the covalent lin5age of a poly(") tail to a messenger %!" (m%!") molecule. At is part of the route to producing mature messenger %!" for translation& in the larger process of protein synthesis to produce proteins. An eu5aryotic organisms& most messenger %!" molecules end with a poly2" stretch at their (B ends. The polyadenosine (poly2") tail protects the m%!" molecule from e-onucleases and is important for transcription termination& for e-port of the m%!" from the nucleus& and for translation.
t%!" - t%!" and r%!" are transcript by special genes (cistrons on !") - "mino acids are carried by t%!" (anticodon) using information in m%!" (codon) - $; types of t%!"& e.g. t%!"cys & t%!"his & t%!"ala & etc. - 7ingle strand& folded& clover leaf arrangement - .ne end attached to amino acid - "nticodon complementary to codon on m%!"
r%!"
r%!" maCor component of ribosomes most abundent ?;@ synthesised in nucleolus: nucleolar organiser. '-ported to cytoplasm Coin with proteins to form ribosomes
(. Transport r%!"& m%!" and t%!" are transported through __________________ pore to the cytoplasm. %rotein synthesis 1. 1. $. (.
t%!" activation "n en9yme _________________________ ma5es sure t%!" is carrying the correct amino acid by its anticodon before it moves to a ribosome. Dinding in ,= to (= direction "T) is re<uired
$. Translation - 7mall subunit of ribosome (r%!"E protein) searches for "/* (_____________) codon on m%!" - Dig subunit of ribosome clamps to them. - Creates two sites: _____________(peptidyl) and ______________(aminoacyl) - %ibosome moves so that "/* is at the "2site - t%!" with ______________ ("/*) attached enters "2site and binds its anticodon /"C to codon "/* on m%!". %ibosome moves one triplet codon in ,= to (= direction - met2r%!" now enters )2site leaving "2site empty - 7econd t%!" with proline enters "2site and binds its anticodon ( ) to codon ( ) on m%!".
1;
"n en9yme peptidyl transferase forms a peptide bond between methionine and the second a.a. proline. The t%!" that was holding methionine is now released from the ribosome& and is free to carry another methionine molecule. %ibosome moves one more triplet codon in ,= to (= direction 7econd a.a proline occupies )2site and the third t%!" ( ) is entering the "2site The process continues until ribosome reaches a Fstop= codon: /""& /*" or /"*. The m%!"& ribosome& and t%!" molecules separate& and the polypeptide chain is released. Complementary base pairing between anticodons and codons ensure correct se<uence of a.a.
A8 # initiation factor
11
1$
1(
%8 # release factor (. )rocessing - "ccording to the final destination - Ancludes folding& and adding chains. - )rotein in cell& e.g. haemoglobin& directly from ribosome to cytoplasm. - 'n9ymes& are made on %'%& transported to *olgi apparatus& modified and pac5aged. Transported by *olgi vesicles and secreted by e-ocytosis. - 0embranes proteins are made on %'% and remain1fused in the membrane.
13
8(h) )olysomes: speeding up translation - 7ingle ribosome: a single polypeptide chain 1, amino acids per second - "ccelerated by polysomes - , to ,; ribosomes on the same m%!" - "t end of m%!"& ribosomes detached and returns to the beginning on the same m%!" - Garge number of the same polypeptide chains produced The figure below shows an electron micrograph and its interpretation. DNA and strings of individual ribosomes attached to a single mRNA (polyribosome) are visible. The mRNA and RNAPol molecules are barely visible& and the protein polypeptides are too small to be seen.
7elf test: 1. Dased on figure below& name the process "________________________ D________________________ C________________________
1,
7tructure ____________________ ' ____________________ 0olecule 8 _____________________
$. Dased on the figure below& a. (i) !ame the amino acid ) (ii) 7tate the base se<uence at 7 (iii) 7tate the name given to the triplet base se<uences on m%!" (iv) escribe the change that would occur to the protein if the base se<uence at % was /// instead of "//. b. escribe what happens to the en9yme molecule after it has left the ribosome until it leaves the cell.
1:
(. 3. ,. :. >. ?. 6.
istinguish between a nucleoside and a nucleotide. Dy what type of chemical reaction does a phosphodiester bond formH Af one strand of !" has the three base se<uence ""TCC*& what will be the corresponding base se<uence of its complementary strandH 4hat is a nucleosomeH Centromeres contain no genes. 4hat is their main functionH 4hy have telomeres been compared with the tips of shoelacesH 4hat are the functions of : (i) helicases (ii) !" binding proteins (iii) !" polymerase (iv) !" ligaseH
1;. 4hat is the name given to the result of adding one or two nucleotide bases to a !" se<uenceH 11. /se the genetic table to wor5 out which amino acid has the codon C"/. 1$. istinguish between transcription and translation. 1(. " transcribing !" strand contains the base se<uence C**""TC*T. 4hat will be the base se<uence in the m%!" transcribed from itH 13. 4hat is the role of t%!". 1,. 4hat type of bond attaches a new amino acid to a polypeptide chainH 1:. Dy what process does a t%!" molecule attach onto m%!" during translationH 1>. 4hat is a polysome or polyribosomeH
1>
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- Mitochondria in Health and DiseasesDocument436 pagesMitochondria in Health and DiseasesRoberta MorganaPas encore d'évaluation
- (PDF) Mcqs in Microbiology - Mohammed Bilal - Academia - Edu PDFDocument1 page(PDF) Mcqs in Microbiology - Mohammed Bilal - Academia - Edu PDFM AdnanPas encore d'évaluation
- GSC SelfPrint TicketDocument2 pagesGSC SelfPrint TicketMohd Hasrul RamleePas encore d'évaluation
- 2210 Tut04Document1 page2210 Tut04Mohd Hasrul RamleePas encore d'évaluation
- 2013 14 Sem2 ISM Lecture Timetable Draf 3Document1 page2013 14 Sem2 ISM Lecture Timetable Draf 3Mohd Hasrul RamleePas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 10Document3 pagesTutorial 10Mohd Hasrul RamleePas encore d'évaluation
- NEET Biology MCQDocument6 pagesNEET Biology MCQIsh MalikPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetic DisordersDocument7 pagesGenetic DisordersDesirie Rose LopenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Study Material - MIB11044 - Unit-2 - 2Document9 pagesStudy Material - MIB11044 - Unit-2 - 2Nani Gopal SahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Animal Cell PDFDocument5 pagesAnimal Cell PDFPerry Sin67% (3)
- Asymmetrical Cell: Submitted byDocument5 pagesAsymmetrical Cell: Submitted byJeffrey VictoryPas encore d'évaluation
- Midterm Reviewer BiochemDocument26 pagesMidterm Reviewer BiochemTiffany Shane VallentePas encore d'évaluation
- Transcription Practice WorksheetDocument3 pagesTranscription Practice Worksheetbrimej4513Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Organelles Worksheet-PrintDocument2 pagesCell Organelles Worksheet-PrintmuraliMu0% (1)
- BIF401 MID Term Exam 2022 Preparation by BADSHA ALIDocument6 pagesBIF401 MID Term Exam 2022 Preparation by BADSHA ALIGum Naam SingerPas encore d'évaluation
- Genetik MikrobDocument33 pagesGenetik MikrobekasukmawatyPas encore d'évaluation
- Week 1 Intro of BiotechnologyDocument31 pagesWeek 1 Intro of BiotechnologyMauiPas encore d'évaluation
- DNA and Proteins Doodle Notes 2Document10 pagesDNA and Proteins Doodle Notes 2Leila BeyyoudhPas encore d'évaluation
- Affinity ChromatographyDocument21 pagesAffinity ChromatographyAttaullah Khan100% (1)
- Genetic Engineering and CloningDocument22 pagesGenetic Engineering and CloningAndrei OrdoñaPas encore d'évaluation
- R. R. Dhutmal, Et AlDocument10 pagesR. R. Dhutmal, Et AlFernando Castro EchavezPas encore d'évaluation
- Day 29 - Daily MCQ Workout - 40 Revision MCQsDocument5 pagesDay 29 - Daily MCQ Workout - 40 Revision MCQsnorah araujoPas encore d'évaluation
- Impacts of Gmo'S On Genetically Modified Organisms Produced by Philippine ResearchersDocument3 pagesImpacts of Gmo'S On Genetically Modified Organisms Produced by Philippine ResearchersIrish Cheska EspinosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Flashcards - Topic 4.2 Cell Transport Mechanisms - Edexcel (B) Biology A-Level PDFDocument27 pagesFlashcards - Topic 4.2 Cell Transport Mechanisms - Edexcel (B) Biology A-Level PDFPrasanthanPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Biology and Genetics Notes On All Lectures PDFDocument62 pagesCell Biology and Genetics Notes On All Lectures PDFMR ManalangPas encore d'évaluation
- Thermo Scientific Revertaid Reverse Transcriptase: Lot: - Expiry DateDocument4 pagesThermo Scientific Revertaid Reverse Transcriptase: Lot: - Expiry Dateinvestbiz optionstarPas encore d'évaluation
- Test Review Cell Processes PDFDocument4 pagesTest Review Cell Processes PDFJeyser T. GamutiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Practical 20epidemiology 20 20for 20students 20and 20residentsDocument143 pagesPractical 20epidemiology 20 20for 20students 20and 20residentsIonutStanciuPas encore d'évaluation
- Coenzyme ListDocument1 pageCoenzyme ListhvgtachPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Theory - CSIR NET LS (Post Transcription Modification) (UNIT-3)Document26 pagesSample Theory - CSIR NET LS (Post Transcription Modification) (UNIT-3)Er Purushottam PalPas encore d'évaluation
- Worksheet Biological MoleculesDocument5 pagesWorksheet Biological MoleculesЕгор БиндерPas encore d'évaluation
- Kendriya Vidyalaya Nad, Sunabeda: Genetically Modified OrganismsDocument17 pagesKendriya Vidyalaya Nad, Sunabeda: Genetically Modified OrganismsDillip kumar ParidaPas encore d'évaluation
- An in Vitro Study On Antiproliferative and Antiestrogenic Effects ofDocument5 pagesAn in Vitro Study On Antiproliferative and Antiestrogenic Effects ofJose Alberto PbPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Molecular Introduction To Molecular Biology BiologyDocument18 pagesIntroduction To Molecular Introduction To Molecular Biology BiologyNur AdilahPas encore d'évaluation