Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Complete Mix Activated Sludge
Transféré par
Ahmed Salem AmrDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Complete Mix Activated Sludge
Transféré par
Ahmed Salem AmrDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
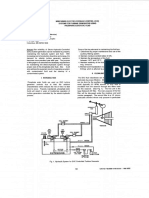
Complete Mix Activated Sludge (CMAS) system
The Complete Mix Activated Sludge (CMAS) system removes soluble, suspended solids and ammonia by exposing the waste to organisms that will feed on it. Air is blown into the tank to keep the waste mixed with the organisms and to add oxygen to the water. The CMAS system consists of four aeration basins, five centrifugal blowers and 200 coarse bubble diffusers per basin.
Aeration Basins The basins are 105 feet by 105 feet with 15-foot side water depth. The volume of one aeration basin is 1.23 million gallons. The plant design is to have one blower for each basin in service plus one backup. Each basin is capable of independent operation for seasonal flexibility.
Multi-stage Centrifugal Blowers The blowers are multi-stage centrifugal blowers rated at 300 Hp with an output of 4700 scfm each. Each blower has a throttling valve before the blower to adjust the actual scfm output. Through trial and error, it has been determined that the process can run with half of the design aeration, which saves on maintenance and electric usage. The plant was designed to have two basins on line during the summer and three basins during the winter. With a lower Return Activated Sludge (RAS) rate the plant is still able to handle the treatment of the flow and lower the electricity usage. The design for the Sludge Retention Time (SRT) is 4.8 days in the summer and 9.2 days in the winter. To be at the design SRT the MLSS in the summer would be 700 mg/L and 1200 mg/L in the winter. The plant has been running at an average of 1300 mg/L MLSS with all four basins in service in the summer and an average of 1770 mg/L MLSS in the winter. The Complete-Mix Activated Sludge process handles slug loads better then the typical activated sludge system. This is achieved by having the identical concentration of activated sludge throughout the tank. A disadvantage is that a C-MAS system is prone to filamentous bulking and hydraulic short-circuiting. This plant has never had a problem with either of the two. The effluent from the trickling filters is mixed with Return Activated Sludge and then sent to the CMAS system. Each of the CMAS basins has its own influent line feeding into the bottom on the side away from the basins effluent. Air is added to the system to keep the D.O. above 1 mg/L. The biological floc consists of bacteria, protozoa, rotifers, and nematodes. The floc is used to reduce the carbonaceous BOD and oxidize ammonia content of the sewage. Bacteria make up about 95% of the activated sludge biomass. These organisms grow in the wastewater by consuming bio-
degradable materials such as proteins, carbohydrates, fats and many other compounds. A sign of a healthy floc is the present of higher forms of animal life like Protozoa & Rotifers.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- MBBR OM Manual-250Document42 pagesMBBR OM Manual-250senthil2002100% (3)
- Emulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingD'EverandEmulsions and Oil Treating Equipment: Selection, Sizing and TroubleshootingÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (3)
- Waterproof coating MSDSDocument5 pagesWaterproof coating MSDSErwin75% (4)
- 19 Aerobic Treatment ProcessDocument26 pages19 Aerobic Treatment ProcessOladunni Afolabi100% (1)
- 09-Ash Handling PlantDocument26 pages09-Ash Handling PlantKumar Ganesh100% (2)
- Erma First Ballast Water Treatment SystemDocument5 pagesErma First Ballast Water Treatment Systemvangeliskyriakos8998Pas encore d'évaluation
- Extended Aeration Wastewater Treatment SystemDocument12 pagesExtended Aeration Wastewater Treatment Systemashe zinab100% (2)
- How Industrial Businesses Can Reduce Production Costs With Reverse Osmosis: Industrial Reverse OsmosisD'EverandHow Industrial Businesses Can Reduce Production Costs With Reverse Osmosis: Industrial Reverse OsmosisÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Treatment PlantDocument19 pagesTreatment PlantShreyans Dodia100% (6)
- LOT-5 Akaki I WWTP BOQ FinalDocument95 pagesLOT-5 Akaki I WWTP BOQ FinalMesfin100% (1)
- 19 Aerobic Treatment ProcessDocument26 pages19 Aerobic Treatment ProcessOladunni Afolabi100% (1)
- Aerated Lagoons - EPA Fact SheetDocument5 pagesAerated Lagoons - EPA Fact SheetlazopaPas encore d'évaluation
- Activated Sludge ProcessDocument5 pagesActivated Sludge ProcessshambhavipathakPas encore d'évaluation
- Tubular Sidestream (Cross Flow) MBR Applications For Industrial EffluentsDocument6 pagesTubular Sidestream (Cross Flow) MBR Applications For Industrial EffluentsDileep C DileepPas encore d'évaluation
- Attach 4Document6 pagesAttach 4akbarmulangathPas encore d'évaluation
- General Arrangement of Ash Handling EquipmentDocument24 pagesGeneral Arrangement of Ash Handling EquipmentPrakashPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 8 - Activated Sludge PDFDocument12 pagesChapter 8 - Activated Sludge PDFRieskaYuniarPas encore d'évaluation
- Solução Solar para Purificação de ÁguaDocument14 pagesSolução Solar para Purificação de ÁguaEnric ToledoPas encore d'évaluation
- A Partial-Reuse System For Coldwater AquacultureDocument25 pagesA Partial-Reuse System For Coldwater AquacultureAdeyinka OluwoPas encore d'évaluation
- Complexity of EA - 1Document7 pagesComplexity of EA - 1Don BakerPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Aspects of Desalination PlantDocument12 pagesTechnical Aspects of Desalination PlantMonica UrbietaPas encore d'évaluation
- With Membrane Technolgy For Oil Sands and Power Generation ApplicationsDocument8 pagesWith Membrane Technolgy For Oil Sands and Power Generation ApplicationsMarcelo Varejão CasarinPas encore d'évaluation
- Aerated Lagoons Leaflet EnglishDocument10 pagesAerated Lagoons Leaflet EnglishMian Ghulam HussainPas encore d'évaluation
- Filtration and water reuse in fish farmingDocument39 pagesFiltration and water reuse in fish farmingJosé Antonio Retamal TosoPas encore d'évaluation
- WWTP Synopsis1Document14 pagesWWTP Synopsis1malgendy0Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gas Turbine Air Filter System OptimizationDocument10 pagesGas Turbine Air Filter System Optimizationsevero97Pas encore d'évaluation
- Report OF Sewage Treatment PlantDocument17 pagesReport OF Sewage Treatment PlantSanand Karwa100% (3)
- Desalination Design Fundamentals in OmanDocument16 pagesDesalination Design Fundamentals in OmanJayfeson Gotuanco100% (2)
- Waste Water Recycling System Effluent Treatment OverviewDocument15 pagesWaste Water Recycling System Effluent Treatment OverviewVishal NakraniPas encore d'évaluation
- Ash HandlingDocument30 pagesAsh Handlingrmm99rmm99100% (2)
- Palm Oil Mill EffluentDocument3 pagesPalm Oil Mill EffluentAmir AimanPas encore d'évaluation
- A. Short Description I-A. The SystemDocument3 pagesA. Short Description I-A. The SystemmbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Operation & Maintenance Manual for Sewage Treatment PlantDocument39 pagesOperation & Maintenance Manual for Sewage Treatment PlantAjith KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding Ammonia SystemsDocument8 pagesUnderstanding Ammonia Systemshatassa100% (1)
- Chapter-14 Final Aerobic-DigestionDocument18 pagesChapter-14 Final Aerobic-DigestionIrvin josePas encore d'évaluation
- Performance Evaluation of The Belt FilterDocument52 pagesPerformance Evaluation of The Belt FilterHAMZA ZAKIPas encore d'évaluation
- Maintaining Electrohydrauliccontrol Ehc Systems For Turbine GeneDocument3 pagesMaintaining Electrohydrauliccontrol Ehc Systems For Turbine GeneveronikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Doc-20240327-Wa0029 240329 163445Document14 pagesDoc-20240327-Wa0029 240329 163445rakshithnayak678Pas encore d'évaluation
- Overview of Activated Sludge ProcessDocument32 pagesOverview of Activated Sludge ProcesssoorajTVMPas encore d'évaluation
- Aquaculture Aeration ModulesDocument7 pagesAquaculture Aeration ModulesecosafePas encore d'évaluation
- Recirculating Aquaculture Tank Production SystemsDocument12 pagesRecirculating Aquaculture Tank Production Systemsharshubhoskar3500Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reverse Osmosis: IntroductionDocument6 pagesReverse Osmosis: IntroductionMjb OhiekuPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydra Laminar Tube Flow Aerator SystemsDocument4 pagesHydra Laminar Tube Flow Aerator Systems21smithPas encore d'évaluation
- Reverse Osmosis User's Manual: ModelDocument28 pagesReverse Osmosis User's Manual: ModelHamid SuliamanPas encore d'évaluation
- Reverse Osmosis Plant Report 2019 (RODocument5 pagesReverse Osmosis Plant Report 2019 (ROAli Hassan RazaPas encore d'évaluation
- Recirculating Aquaculture Tank Production Systems An Overview of Critical ConsiderationsDocument38 pagesRecirculating Aquaculture Tank Production Systems An Overview of Critical ConsiderationsSteveTillPas encore d'évaluation
- Recirculating Aquaculture Tank Production Systems: An Overview of Critical ConsiderationsDocument6 pagesRecirculating Aquaculture Tank Production Systems: An Overview of Critical Considerationsseabear77Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pervaporation 2Document2 pagesPervaporation 2sean1491Pas encore d'évaluation
- Amine Gas Sweetening PlantDocument13 pagesAmine Gas Sweetening Plantmuki10Pas encore d'évaluation
- WE Credit 3Document2 pagesWE Credit 3Paramdeep SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Bioreactor DesignDocument18 pagesBioreactor DesignAmrie IamPas encore d'évaluation
- Wehrle MBR Treats Distillery WastewaterDocument4 pagesWehrle MBR Treats Distillery WastewaterPaula MertensPas encore d'évaluation
- Operating Philosophy and Control Description For Saudi Aramco Bulk Plants Y00002 and Y00003Document25 pagesOperating Philosophy and Control Description For Saudi Aramco Bulk Plants Y00002 and Y00003Nawaf ALaskariPas encore d'évaluation
- RO System Quotation 20m3/h 73% RecoveryDocument6 pagesRO System Quotation 20m3/h 73% Recoverytata_77Pas encore d'évaluation
- Solvent extraction process for copper recoveryDocument5 pagesSolvent extraction process for copper recoveryRamoutar (Ken) Seecharran100% (5)
- Sistemas Respiratorios AnestesiaDocument5 pagesSistemas Respiratorios AnestesiaAiled CastroPas encore d'évaluation
- Desalination in Oman and The Fundamentals of Reverse Osmosis DesignDocument14 pagesDesalination in Oman and The Fundamentals of Reverse Osmosis DesignNguyen Van DzungPas encore d'évaluation
- Design Criteria SBRDocument8 pagesDesign Criteria SBRranbeer41100% (1)
- Potential Water and Energy Savings in Textile Bleaching: by Bruce A. EvansDocument3 pagesPotential Water and Energy Savings in Textile Bleaching: by Bruce A. EvansSonet SahaPas encore d'évaluation
- Eco Pools: Figure 1-Ecopool With Beach Entry Figure 2 - Ecopool With Step EntryDocument9 pagesEco Pools: Figure 1-Ecopool With Beach Entry Figure 2 - Ecopool With Step EntryAviram DhyanPas encore d'évaluation
- IrrigationD'EverandIrrigationPas encore d'évaluation
- How Reverse Osmosis Works: A Look at Industrial ROD'EverandHow Reverse Osmosis Works: A Look at Industrial ROÉvaluation : 2.5 sur 5 étoiles2.5/5 (2)
- Aquaponics system, fish. Volume 1: Sistemas de acuaponíaD'EverandAquaponics system, fish. Volume 1: Sistemas de acuaponíaPas encore d'évaluation
- AED Grease Trap Design RequirementsDocument5 pagesAED Grease Trap Design RequirementsbmacavanzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Aerated Anoxic PrinciplesDocument45 pagesAerated Anoxic PrinciplesAhmed Salem AmrPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 9 - Attached Growth ProcessDocument30 pagesCH 9 - Attached Growth Processxuantra92100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Grit Removal and Grit System Evaluation - Part 2 - Color Very GoodDocument62 pagesFundamentals of Grit Removal and Grit System Evaluation - Part 2 - Color Very GoodAhmed Salem Amr100% (1)
- 01-Introduction To Air Pollution ControlDocument32 pages01-Introduction To Air Pollution ControlAhmed Salem AmrPas encore d'évaluation
- Methods For Comparing Wastewater Treatment OptionsDocument206 pagesMethods For Comparing Wastewater Treatment OptionsAhmed Salem AmrPas encore d'évaluation
- Process Performance Evaluation of The Contact Stabilization SystemDocument7 pagesProcess Performance Evaluation of The Contact Stabilization SystemAhmed Salem AmrPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Sanitary Wastewater Treatment OverviewDocument180 pagesBasic Sanitary Wastewater Treatment OverviewAhmed Salem Amr100% (2)
- Guidelines For Design Constr Oper WssDocument525 pagesGuidelines For Design Constr Oper WssNurali MamenPas encore d'évaluation
- A1 PDFDocument2 pagesA1 PDFAhmed Salem AmrPas encore d'évaluation
- Introcfd PDFDocument7 pagesIntrocfd PDFAhmed Salem AmrPas encore d'évaluation
- 3257, Case Study Mars NL 1Document1 page3257, Case Study Mars NL 1Ryan PasupathyPas encore d'évaluation
- SAIC-S-4002 Rev 7Document6 pagesSAIC-S-4002 Rev 7Muhammad TariqPas encore d'évaluation
- Optimize Crude Oil Desalting with Membrane FiltrationDocument14 pagesOptimize Crude Oil Desalting with Membrane FiltrationDucViking100% (1)
- An Waste DR HammadDocument19 pagesAn Waste DR Hammadmsph2009Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment of Groundwater Quality in The Gaza Strip, Palestine Using GIS MappingDocument12 pagesAssessment of Groundwater Quality in The Gaza Strip, Palestine Using GIS MappingabuhazemPas encore d'évaluation
- MBR Package Plant For Sewage TreatmentDocument4 pagesMBR Package Plant For Sewage TreatmentVeera-2008Pas encore d'évaluation
- Water Technology Lecture 11 Sludge TreatmentDocument46 pagesWater Technology Lecture 11 Sludge TreatmentDeep SinojiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Zero Emissions Eco-Town in Kawasaki CityDocument21 pagesZero Emissions Eco-Town in Kawasaki CityAlwi AmarPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 Basic Design ConsiderationDocument38 pagesChapter 1 Basic Design ConsiderationAce ThunderPas encore d'évaluation
- XII Study Material English 2022-23Document156 pagesXII Study Material English 2022-23jegapriyan0Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cover With SynopsisDocument4 pagesCover With Synopsisnandan vPas encore d'évaluation
- Design Criteria SBRDocument8 pagesDesign Criteria SBRmah61Pas encore d'évaluation
- What Is MBBR, and How Does It WorkDocument8 pagesWhat Is MBBR, and How Does It WorkManuel AlejandroPas encore d'évaluation
- DAO 2014-02 (Revised Guidelines For PCO Accreditation) - EdDocument48 pagesDAO 2014-02 (Revised Guidelines For PCO Accreditation) - EdJayvee ArimbuyutanPas encore d'évaluation
- Metro PWO Seminar May 23, 2012 Ammonia Based Aeration Control Case Study 2Document44 pagesMetro PWO Seminar May 23, 2012 Ammonia Based Aeration Control Case Study 2Eko Setyo BudiPas encore d'évaluation
- ANDRITZ Separation - Your Separation SpecialistDocument24 pagesANDRITZ Separation - Your Separation SpecialistMostafaPas encore d'évaluation
- Alexandra v. LLDA - CaseDocument5 pagesAlexandra v. LLDA - CaseRobeh AtudPas encore d'évaluation
- Activated Sludge Calculations Excel CourseDocument22 pagesActivated Sludge Calculations Excel CoursesahatPas encore d'évaluation
- Environmental Chemistry: Ninth Edition Stanley E. ManahanDocument17 pagesEnvironmental Chemistry: Ninth Edition Stanley E. ManahanMarcPas encore d'évaluation
- Biosolids Management Feasibility StudyDocument42 pagesBiosolids Management Feasibility StudyAdrian FrantescuPas encore d'évaluation
- Bacteria in Daily Life by Mrs. Percy FranklandDocument90 pagesBacteria in Daily Life by Mrs. Percy Franklandalexa alexa100% (1)
- STP Final Boq-Etp+stpDocument9 pagesSTP Final Boq-Etp+stpT M Murshed MukulPas encore d'évaluation
- Waterchar IwasteDocument8 pagesWaterchar IwasteCharisma CabanogPas encore d'évaluation
- Technical Description For New Habour Village WWTP Editedjun 30 PDFDocument139 pagesTechnical Description For New Habour Village WWTP Editedjun 30 PDFKhang TrầnPas encore d'évaluation
- Gopu Venugopala Reddy Team Labs and Consultants India PDFDocument22 pagesGopu Venugopala Reddy Team Labs and Consultants India PDFHardik VavdiyaPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 s2.0 S2590123023001469 MainDocument22 pages1 s2.0 S2590123023001469 MainElmehdi BenbouazzaPas encore d'évaluation