Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Notes - Chemical Reactions
Transféré par
tom65656565Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Notes - Chemical Reactions
Transféré par
tom65656565Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Name
Class
Date
Notes Chemical Reactions
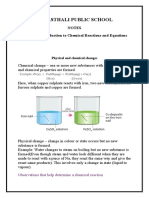
Signs of chemical reactions When a chemical reaction occurs, the reactants are used up and new substances called the products are made. These four signs generally indicate that a new substance has been formed as a result of a chemical reaction (chemical change). 1. a change of color . a change of energy (The reaction is called !endothermic" if the system absorbs energy and !exothermic" if the system releases energy.) #. a new gas is e$ol$ed (This is not %ust a physical change such as boiling or e$aporation.) &. a new solid (precipitate ) is made Chemical reactions are often classified by type. 'ne method of classification follows.
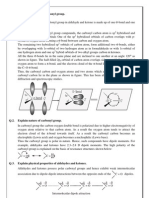
Types of chemical reactions (. )ynthesis (also called combination or composition) *. means ! +. reactants, two or more elements or C. product, one D. representati$e e-uation, * . / */ 0. e1amples 1. 2223 . 222' 2223 ' 222NaCl 222CaC'# "
. 222Na . 222Cl
#. 222Ca' . 222C' &. 2224 . 222+r 5. 2226e . 222'
222 222
((. Decomposition *. means ! +. is the C. reactant, D. products, of a synthesis reaction "
0. representati$e e-uation, */ * . / 6. e1amples 1. 2223g' 2223g . 222' . 2224Cl'# 2224Cl . 222' #. 222Ca('3) 222Ca' . 2223 '
&. 2223 )'& 2223 ' . 222)'# 5. 2223 ' 222 . 222
(Notice that each of the products in the decomposition reactions above is a neutral molecule or atom. Another type of change is called dissociation. Although its equations look similar, no new substance is produced. Dissociation is therefore a physical, not a chemical, change. Compare the following equations to decomposition equations and e plain how they are different.! a. """NaCl(s! """Na#$(aq! # """Cl%$(aq! b. """Ca(N&'!( (s! """Ca#((aq! # """N&'%$(aq!
(((. )ingle replacement (single displacement) *. one element replaces a similar element in a +. reactants, an C. products, a different and a and a new compound
D. representati$e e-uations, (* is a metal) * . +/ + . */ (7 is a nonmetal, usually a halogen) 7 . +/ / . +7 0. * metal element will try to replace the element will try to replace the on p. 9. e1amples 1. 2224 . 222NaCl 2224Cl . 222Na . 222:i . 2223 ' (or 2223'3) 222:i'3 . 2223 #. 2223g . 2223 ' N; &. 222Cl . 222Cu+r 222CuCl . 222+r of the compound8 a nonmetal of the compound. it.
6. Whether a single replacement reaction will occur can be predicted by the . *n element can replace elements
5. 222*gN'# . 222Cu 222*g . 222Cu(N'#)
<. 222(
. 222Na+r . 2223
=. 222Ca . 2223Cl 222
(>. Double replacement (double displacement) *. cations and anions in two compounds +. reactants, two compounds, usually ionic compounds in a-ueous solutions C. products, 6or these reactions to ta?e place, one of the following must be a product@ 1. a precipitate (a new compound is made that is not soluble) )olubility table on p. . water #. a gas (such as , or ) D. representati$e e-uation, */ . +7 *7 . +/ (Why wouldnAt the products *+ or /7 formB) 0. e1amples 1. 222*gN'# . 222NaCl 222*gCl . 222NaN'# . 222Cu) . 2223N'# 2223 ) . 222Cu(N'#) #. 2224'3 . 2223 )'& 2223 ' . 2224 )'& &. 222+aCl . 222:i )'&
5. 222Cg(N'#)
. 222NaCl
>. Combustion *. also called ! " to support combustion and is also produced. Combustion . C' . 3' +. reactants, a carbonDcontaining fuel and C. products, (if combustion is complete) ((f combustion is incomplete, dangerous D. Combustion reactions are
in e$eryday uses, such as car engines, fireplaces and grills, is incomplete.) 0. representati$e e-uation for complete combustion, C 13y'E . ' 6. e1amples 1. 222C3& . 222' 222C' . 2223 '
. 222C 35'3 (ethanol) . 222' #. 222C#3F (propane) . 222 ' &. 222C<31 '< (glucose) . 222 5. 222C&31G (butane) . 222
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Lab 6 Introduction - College Chemistry 1 LabsDocument8 pagesLab 6 Introduction - College Chemistry 1 LabsjuliePas encore d'évaluation
- CHEMICAL EQUATIONS Final VersionDocument33 pagesCHEMICAL EQUATIONS Final VersionFrancis Kirby BrutasPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument9 pagesChemical Reactions and EquationsRaima SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 Chemistry Notes Class 10thDocument8 pagesChapter 1 Chemistry Notes Class 10thAnshika TandonPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction to Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument6 pagesIntroduction to Chemical Reactions and EquationsayanPas encore d'évaluation
- Reaksi KimiaDocument39 pagesReaksi KimiaainulavidaPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction to Chemical ReactionsDocument54 pagesIntroduction to Chemical ReactionsGretchen Barut JavierPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument3 pagesTypes of Chemical ReactionsRuth AquinoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical FormulaDocument7 pagesChemical Formulamy3gr8kidoosPas encore d'évaluation
- CHEMICAL REACTIONS Lecture NotesDocument4 pagesCHEMICAL REACTIONS Lecture NotesHarven Lim DinerosPas encore d'évaluation
- Classification of Chemical ReactionsDocument7 pagesClassification of Chemical Reactionscalew17036Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Chemical ReactionsDocument74 pagesIntroduction To Chemical ReactionsJuan Pablo BuitragoPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Chemical Reactions NotesDocument2 pagesTypes of Chemical Reactions NotesEvaMarieEsperaPas encore d'évaluation
- India International Public School Dabra: (Portfolio Project)Document11 pagesIndia International Public School Dabra: (Portfolio Project)Varunveer DubeyPas encore d'évaluation
- Po Ram Gian Paschal - Activity 2.7 - Experiment 2 (PRE-LABORATORY)Document2 pagesPo Ram Gian Paschal - Activity 2.7 - Experiment 2 (PRE-LABORATORY)Po Ram Gian PaschalPas encore d'évaluation
- Reactions Notes IanGunchDocument8 pagesReactions Notes IanGunchZubda AttaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 11 - Chemical Reactions PDFDocument17 pagesChapter 11 - Chemical Reactions PDFapi-239855791Pas encore d'évaluation
- Recognizing Reactions and Predicting Products 116: CombinationDocument3 pagesRecognizing Reactions and Predicting Products 116: CombinationPercen7Pas encore d'évaluation
- English For ChemistsDocument27 pagesEnglish For ChemistsViet NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Notes Class 10 Chapter 1Document8 pagesChemistry Notes Class 10 Chapter 1VrindaPas encore d'évaluation
- Balancing Equations PacketDocument5 pagesBalancing Equations Packetapi-298247873Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Reactions: Intended Learning OutcomesDocument17 pagesChemical Reactions: Intended Learning OutcomesAlias SalvadorPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Reactions and Equations Notes from Vanasthali Public SchoolDocument8 pagesChemical Reactions and Equations Notes from Vanasthali Public SchoolPlatinum Gaming Warrior100% (1)
- Precipitation ReactionsDocument7 pagesPrecipitation Reactionscayla mae carlosPas encore d'évaluation
- Stoichiometry 1Document52 pagesStoichiometry 1Mero Miro100% (1)
- Chem Test 3 Study SheetDocument3 pagesChem Test 3 Study SheetDarren SischyPas encore d'évaluation
- 2q Chemical RxnsDocument3 pages2q Chemical RxnsMark Ryan RellosaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical ReactionsDocument57 pagesChemical ReactionsCassandra DadorPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Chemical Reactions and Balancing EquationsDocument11 pagesTypes of Chemical Reactions and Balancing EquationsBayot KuhPas encore d'évaluation
- "Chemical Reactions": Chemistry Experiment ReportDocument26 pages"Chemical Reactions": Chemistry Experiment ReportLivia AsriPas encore d'évaluation
- 2H + O 2H O 2hgo 2Hg + O ZN + Cuso Znso + Cu: Chemical ReactionDocument2 pages2H + O 2H O 2hgo 2Hg + O ZN + Cuso Znso + Cu: Chemical ReactionKri de AsisPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9Document17 pagesChapter 9Prajapati DahalPas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Class 10 Chemistry - Chemical Reactions and Equations ConceptsDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 10 Chemistry - Chemical Reactions and Equations ConceptsFredrick RodriguesPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Reactions and Equations: Chapter-1Document59 pagesChemical Reactions and Equations: Chapter-1Mohit ShivharePas encore d'évaluation
- Test 4 HandoutsDocument23 pagesTest 4 HandoutsAnonymous AMmNGgPPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of Chemical Reactions LECTUREDocument33 pagesTypes of Chemical Reactions LECTUREPatricia CadacioPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Reactions Equations GuideDocument21 pagesChemical Reactions Equations GuideEric ArtocilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5Document4 pagesChapter 52B VILORIA, Kristine Joyce D.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Reaction: 5. Vitamin CDocument15 pagesChemical Reaction: 5. Vitamin CAira SantosPas encore d'évaluation
- Metathesis ReactionsDocument11 pagesMetathesis Reactionsfranciscrick69Pas encore d'évaluation
- What Is Chemical Reaction and Its TypeDocument9 pagesWhat Is Chemical Reaction and Its TypekamilbismaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem 1 Week 3 Chemical Equations CompilerDocument11 pagesChem 1 Week 3 Chemical Equations CompilerMelcorr MontesclarosPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical EquationsDocument75 pagesChemical EquationsbagoljoannahPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter - 1 (S - X)Document7 pagesChapter - 1 (S - X)Víshál RánáPas encore d'évaluation
- Class 10 Chemistry Chemical ReactionsDocument12 pagesClass 10 Chemistry Chemical ReactionsSahil SwePas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry 11 Unit Test NotesDocument7 pagesChemistry 11 Unit Test NotesSyed KamranPas encore d'évaluation
- Class X Chemistry For Term IDocument74 pagesClass X Chemistry For Term Iphanikumar5100% (1)
- Chemical Reactions and Equations FinalDocument29 pagesChemical Reactions and Equations FinalRenemartin RebambaPas encore d'évaluation
- Types of EquationsDocument6 pagesTypes of EquationsmlserquiniaPas encore d'évaluation
- Precipitation Reactions: 3 (Aq) (S) (S) 3 (Aq)Document25 pagesPrecipitation Reactions: 3 (Aq) (S) (S) 3 (Aq)RonaldPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument10 pagesChapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsShabnam GolaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Reactions - SYNOPSISDocument10 pagesChemical Reactions - SYNOPSISshashwatthegamerytPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 12 Types of Chemical ReactionDocument1 pageLesson 12 Types of Chemical ReactionArman Miguel Dungao LoarPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations CBSE Notes For Class 10 Science Chemistry Download in PDFDocument9 pagesChapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations CBSE Notes For Class 10 Science Chemistry Download in PDFNaved ShaikhPas encore d'évaluation
- Expt 5 - Reactions and SolubilityDocument15 pagesExpt 5 - Reactions and SolubilitySangeeth George0% (2)
- 8 Grade Science: Adapted by T. TrimpeDocument13 pages8 Grade Science: Adapted by T. Trimpepanida SukkasemPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument6 pagesChapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equationsminimata100% (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionD'EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Organic Reaction Mechanisms 2011: An annual survey covering the literature dated January to December 2011D'EverandOrganic Reaction Mechanisms 2011: An annual survey covering the literature dated January to December 2011A. C. KnipePas encore d'évaluation
- Combining Chemicals - Fun Chemistry Book for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksD'EverandCombining Chemicals - Fun Chemistry Book for 4th Graders | Children's Chemistry BooksPas encore d'évaluation
- Notes - Chemical Reactions - TeacherDocument4 pagesNotes - Chemical Reactions - Teachertom65656565Pas encore d'évaluation
- Notes - Chemical Reactions - TeacherDocument4 pagesNotes - Chemical Reactions - Teachertom65656565Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lab - Iodine Clock - TeacherDocument3 pagesLab - Iodine Clock - Teachertom65656565Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1974 Free ResponseDocument3 pages1974 Free ResponseSimon LiangPas encore d'évaluation
- Reactions of Ions and Molecules in Aqueous SolutionsDocument71 pagesReactions of Ions and Molecules in Aqueous Solutionsmrsch 1Pas encore d'évaluation
- A2 Level Chemistry 5.3 Transition Metals Assessed Homework: Answer All Questions Max 63 MarksDocument14 pagesA2 Level Chemistry 5.3 Transition Metals Assessed Homework: Answer All Questions Max 63 Markskingman14Pas encore d'évaluation
- 525 1 Eot 3 2022Document17 pages525 1 Eot 3 2022OTTO OLIMAPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution 1176952Document4 pagesSolution 1176952arb88279Pas encore d'évaluation
- Percentage Yield & Atom Economy: Name . . FormDocument2 pagesPercentage Yield & Atom Economy: Name . . FormMeeran HassanPas encore d'évaluation
- Atomic Structure and IsotopesDocument5 pagesAtomic Structure and IsotopesRoxan Oxima ClabriaPas encore d'évaluation
- Refresh Refresh (Dynamic - Bypass - Reload) Click Here If You Are Not Automatically Redirected. For Assistance, Contact Your Network Support Team.Document9 pagesRefresh Refresh (Dynamic - Bypass - Reload) Click Here If You Are Not Automatically Redirected. For Assistance, Contact Your Network Support Team.Kelvin LimPas encore d'évaluation
- Temperature Coefficient of ResistanceDocument3 pagesTemperature Coefficient of ResistanceShailesh SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Quantitative Determination of Total Hardness of WaterDocument11 pagesQuantitative Determination of Total Hardness of WaterJoshua Oliveros50% (2)
- Experiment 2: Water of HydrationDocument10 pagesExperiment 2: Water of HydrationNur Faizatul AtiqahPas encore d'évaluation
- Astm e 467 Rev A 2006 PDFDocument10 pagesAstm e 467 Rev A 2006 PDFJORGE ARTURO TORIBIO HUERTAPas encore d'évaluation
- ShreyaDocument16 pagesShreyasunandapadvi481975Pas encore d'évaluation
- DippingDocument4 pagesDippingPolavarapu Sudheer ChowdaryPas encore d'évaluation
- Coordination CPPDocument8 pagesCoordination CPPSri KrishnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Inorganic Spectoscopy-UV-VisDocument100 pagesInorganic Spectoscopy-UV-VisUsama El-Ayaan100% (5)
- Synthesis and characterization of transition metal complexes with 4-amino-5-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-4H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thiol ligand and their antibacterial activityDocument12 pagesSynthesis and characterization of transition metal complexes with 4-amino-5-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-4H-1,2,4-triazole-3-thiol ligand and their antibacterial activityDaniela Araújo RodríguezPas encore d'évaluation
- Dwnload Full Biochemistry 4th Edition Voet Test Bank PDFDocument35 pagesDwnload Full Biochemistry 4th Edition Voet Test Bank PDFmahoutcawk.cn3ec8100% (16)
- Liebermann Nitroso Test and Ninhydrin TestDocument4 pagesLiebermann Nitroso Test and Ninhydrin Testartemis MontecastroPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbial Mining (Biomining)Document39 pagesMicrobial Mining (Biomining)Jayadev KodikalPas encore d'évaluation
- As Per Standard Tor of Organic Manufacturing Sector Issued by Moef&CcDocument69 pagesAs Per Standard Tor of Organic Manufacturing Sector Issued by Moef&CcHardikPas encore d'évaluation
- ScP019 Chemical Equations 1Document2 pagesScP019 Chemical Equations 1ORBeducationPas encore d'évaluation
- What is ChemistryDocument20 pagesWhat is ChemistryMohammad Ryyan PumbagulPas encore d'évaluation
- 93, 94Document282 pages93, 94Sulfa MubarikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Class XIDocument31 pagesChemistry Class XIPranav SaihgalPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry AlcoholsDocument44 pagesChemistry AlcoholsSayan Kumar KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 05Document31 pagesCH 05nayan159Pas encore d'évaluation
- Class 11 ChemistryDocument21 pagesClass 11 ChemistrypravinmoharilPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson Plan in Grade 9 Science: A. Routinary ActivitiesDocument7 pagesLesson Plan in Grade 9 Science: A. Routinary ActivitiesJUNELLIE TAJONERAPas encore d'évaluation
- Nitric Acid BurnsDocument4 pagesNitric Acid BurnsAFLAC ............Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pt. Tiga OmbakDocument23 pagesPt. Tiga OmbakG'mbel NingratPas encore d'évaluation