Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Preformulation Studies For Development of A Generic Capsule Formulation of Celecoxib Comparable To The Branded (Reference) Product
Transféré par
sskkaleTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Preformulation Studies For Development of A Generic Capsule Formulation of Celecoxib Comparable To The Branded (Reference) Product
Transféré par
sskkaleDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Innovations in Pharmaceuticals and Pharmacotherapy www.innpharmacotherapy.
com
eISSN: 2321323X
IPP
Original Article
Preformulation Studies for development of a generic capsule formulation of Celecoxib comparable to the branded (Reference) Product
Choubey Pravir1*, Manavalan R2, Dabre Rahul1, Jain Girish1 1. Senior vice president, Worckhardt ltd, Aurangabad, India 2. Department of Pharmaceutics, Annamalai university, Tamil Nadu, India
Abstract This study aims to provide preformulation information, which is an essential part in the development of a robust formulation for generic celecoxib capsules. Various preformulation studies were carried out including drug characterization, Reference product characterization, Drug-Excipients compatibility studies. The physical properties of the drug like Solubility profile, Bulk / tapped densities, flow properties and particle size were also studied. The Celecoxib drug was found to be having good compatibility with majority of excipients studied. The drug is found to be of fluffy nature due to low density and the drug was also observed to be having very poor flow characteristic, hence it was concluded that direct filling of powder mixture into capsules was not possible. Therefore, wet granulation method was considered for granulation in-order to improve bulk density and flow-ability of blend.
Keywords: Preformulation, Generic formulation, Drug characterization, compatibility, bulk/tapped density, flow properties, wet granulation. *Corresponding Author: Choubey Pravir, senior vice president, Worckhardt ltd, Aurangabad, India. Email address: p.choubey@hotmail.com
1. Introduction Over the past decades, pharmaceuticals have made a major contribution in improving the health status of patients. At the same time, its expenditure has increased rapidly, with spending on medicines outpacing economic growth in many countries [1]. Since generic drug products are usually marketed at
substantially lower prices than the original brand-name products and with the rising cost of healthcare; development of generics is an attractive option to healthcare providers and governments [2].. However since the regulatory expectations for approval of a generic drug product have become increasingly challenging and also to avoid setbacks at a later stages during the
Innovations in Pharmaceuticals and Pharmacotherapy, All rights reserved
Choubey Pravir et al., IPP, Vol 1 (3), 230-243, 2013
development , it is very important that sufficient efforts are made on generating the preformulation data at the initial stages during the development work for a generic formulation. A Generic drug product [3,4,5], is considered to be essentially similar or bioequivalent to an innovator (brand name) drug product. Bioequivalence implies that a generic drug product is essentially identical to the brand name drug (reference) drug product in term of active ingredient, strength, dosage form, route of administration, quality, safety, efficacy, performance characteristics and therapeutic effects. Generic drug product development may or may not use a different approach and strategy compared to that used to develop branded drug product containing a new chemical entity. This article summarizes some of the preformulation studies which have been carried out during the initial development work for a robust generic capsule formulation of Celecoxib. These preformulation studies provided a scientific understanding and a platform to develop a suitable strategy for subsequent stages of development for a generic Celecoxib Capsules which shall be stable ,comparable and bioequivalent to the US reference listed product i.e CELEBREX Capsules (of GD Searle LLC a division of Pfizer). 2. Materials and Methods: The Active ingredient was procured from Aarti Drugs India. Lactose monohydrate (Diluent) from DMV Pharm; Croscamellose Sodium (Disintegrant) from Dow Chemicals; Povidone K-30 (Binder) from ISP; Sodium Lauryl Sulphate (Wetting agent) from
Stepan; Magnesium Sterate (Lubricant) from Mallincrodt. Preformulation Studies and Results: Pre-formulation testing is designed to identify those physicochemical properties of drug substances and excipients that may influence the formulation design, method of manufacture, and pharmacokineticbiopharmaceutical properties of the resulting product. A thorough understanding of physicochemical properties may ultimately confirm that no significant barriers are present for the formulation development. The preformulation studies included characterization of the active drug substance, evaluation of the reference listed product, and compatibiliy evaluation of the active drug with various excipients [9]. Drug Characterization: Celecoxib is chemically designated as 4-[5-(4methylphenyl) -3-(trifluoromethyl)- 1Hpyrazol-1-yl] benzene sulfonamide and is a diaryl-substituted pyrazole. It is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that exhibits anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic effects. X- Ray Diffraction pattern of Celecoxib: Xray crystallography is a method of determining the arrangement of atoms within a crystal, in which a beam of X-rays strikes a crystal and diffracts into many specific directions. From the angles and intensities of these diffracted beams, a crystallographer can produce a threedimensional picture of the density of electrons within the crystal. From this electron density, the mean positions of the atoms in the crystal can be determined, as well as their chemical bonds, their disorder and various other information.
Physico-chemical characteristics of celecoxib active ingredient [06] 231
Choubey Pravir et al., IPP, Vol 1 (3), 230-243, 2013
International Non Proprietary name (INN) of drug substance: Pharmacotherapeutic Group Mol. Wt. CAS Registry Number Empirical Formula Chemical Name
Celecoxib
: : : : :
Anti-inflammatory, Analgesic 381.38 169590-42-5 C17H14F3N3O2S 4-[5-(4-Methylphenyl)-3-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrazol-1yl]benzenesulfonamide
O S H2 N N N CF 3 O
Chemical Structure
:
H 3C
Physical Description Solubility in water Solubility in other solvents such as ether, mthanol, acetone etc. Melting Point pH of solution Log P (Octanol/Water) Polymorphism PKa Assay (By HPLC) Heavy Metals Sulphated Ash
: : : : : : : : : : :
White to off white crystalline powder Very low water solubility (3.3 mg/L) Soluble in methanol 159 - 161 oC 5.2 - 6.5 3.9 Form II 11.1 98.0 102.0 % 20 ppm 0.1% 232
Choubey Pravir et al., IPP, Vol 1 (3), 230-243, 2013
Impurity Profile limits. Impurity 0.1% Impurity B: 0.1% Isomer Impurity : 0.15% Single unknown Impurity : 0.1 % Total Impurities 1.0 % Hygroscopicity UV Max : : No 250 nm
Sr no 1 2 3 4
Bulk density (g/cc) Tapped density (g/cc) Carrs index Hausner ratio Particle Size (by Malvern)
0.260 (fluffy nature) 0.431 39.68 1.66 (poor flow properties) D90 = 10.18 m
Physical properties of Celecoxib
Sr. No. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5.
Media 0.1 N Hydrochloric acid pH 4.5 Acetate Buffer pH 6.8 Phosphate Buffer pH 7.4 Phosphate Buffer pH 12 Tribasic sodium phosphate buffer
Solubility in mg/ml 0.028 0.024 0.015 0.014 0.567
Solubility in mg/250ml 7.0 6.0 3.8 3.5 141.8
233
Choubey Pravir et al., IPP, Vol 1 (3), 230-243, 2013
6.
Purified Water
0.018
4.5
Solubility profile of Celecoxib
X- Ray Diffraction pattern of Celecoxib
234
Choubey Pravir et al., IPP, Vol 1 (3), 230-243, 2013
235
Choubey Pravir et al., IPP, Vol 1 (3), 230-243, 2013
3.2 Evaluation of the reference product in USA: Celecoxib (a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent) marketed in USA under the brand name CELEBREX by G.D. Searle LLC (Division of Pfizer Inc. NY). Celebrex (Celecoxib)
Active ingredient Dosage form Strength Brand Name Average weight (mg) (RLD) Product Size of capsule Lock length (mm) (RLD) Disintegration Time (min) Celecoxib Capsule , oral
capsules are available in four strengths (50, 100, 200 and 400 mg) in different packs. The brief evaluation of Celebrex capsule 400mg (Reference Listed Product in USA) is given in the table below:
50, 100, 200 and 400 mg (RLD strength - 400mg) CELEBREX 631.6, 629.6, 625.5, 624.3 and 623.2 mg = 626.84 mg Celebrex Capsules Size of 50, 100 & 200 mg capsule = 2 Size of 400 mg capsule =0 21.61, 21.66, 21.64, 21.72 and 21.57 mm = 21.64 mm Contents: 1.15 1.5 min / Capsule Shell: 12-15 min Croscarmellose sodium, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, povidone and sodium lauryl sulfate, edible inks and gelatin. Bottles of 60s and 100s . Unit dose blister pack
Inactive ingredients
Pack
Celebrex Capsules App: USP Type II (Paddle), 50 rpm and 75 rpm for 400 mg Medium: 0.04 M Tribasic Sodium Phosphate Buffer, pH = 12 with 1% SLS; Volume: 1000 mL Celebrex Celebrex Celebrex Time (min) Celebrex 50 mg 400 mg 200 mg 100 mg
236
Choubey Pravir et al., IPP, Vol 1 (3), 230-243, 2013
B. No. 10 15 30 45 60 Similarity factor Assay (% Label Claim)
C090960 54 67 81 95 101 F2 98.2
C091104 42 64 90 91 96 56.30 98.4
C090841 73 85 87 90 91 38.50 97.8
C090160 89 92 97 96 99 34.34 97.1
Drug Release profile of reference product
Celebrex Capsules 400 mg (B. No. C090960) App: USP Type II (Paddle), 75 rpm Volume: 1000 mL Official media* pH 12 10 15 30 45 60 Similarity factor 54 67 81 95 101 F2 pH 6.8 4.5 pH Acetate 0.1 N HCl with Phosphate Buffer with 1 1 % SLS buffer with 1 % % SLS SLS 60 69 80 88 90 59.11 53 67 79 86 90 59.32 54 69 85 88 92 62.72
Time points (hrs)
Drug release profile of reference product in different medias. 237
Choubey Pravir et al., IPP, Vol 1 (3), 230-243, 2013 * 0.04 M Tribasic Sodium Phosphate Buffer, pH = 12 with 1% SLS
3.3. Sources and selection of excipients Some of the commonly used excipients which have been evaluated are tabulated below. These excipients have been chosen for the study based on the available Sr. No. 1 2 3 4 5 Ingredient Lactose monohydrate Croscarmellose sodium Povidone K30 Sodium lauryl sulfate Magnesium Stearate
information of reference product composition in package insert and the information available in patents.
Maximum Limit as per IIG (mg) 586.00 180.00 80.00 51.69 256.4
Maximum limit recommended as per USFDA inactive ingredient guidance (IIG) [8]
3.4. Drug-excipient compatibility studies Compatibility Studies of celecoxib with various excipients: In early drug development phase, excipient compatibility studies are very important as it provides a rational basis for identification of low-risk excipients with physical and chemical compatibility to the drug substance. Drug excipient compatibility studies are critical for well-formulated final dosage forms where the drug reside in contact with one or more excipients during process scale-up from clinical trials through commercial to consumer. Performing these studies at the early development stage has the potential to both accelerate drug development and minimize the risk of drug product stability failure. The study designed as follows with different ratio for drug and excipients as per their functionality. The weighed amount of API mixed well with a proposed proportion of individual excipients. Blend was filled and sealed in 5 ml glass vials. Vials were subjected to 40C 2C/75% 5% RH for 4 weeks. The control samples were stored at 2-8oC. The samples were observed for physical changes like discoloration, liquefaction and analysed for related substance by HPLC [7].
238
Choubey Pravir et al., IPP, Vol 1 (3), 230-243, 2013 Conditions 40C 75%RH Time Zero 1 week 2 weeks XY X X 4 weeks XY
Drug-Excipient time-point testing schedule. X= Visual Observation; Y= RS by HPLC
Observations Drug : Excipients RATIO Initial 40 oC/75 %RH 1W Celecoxib (CLX) CLX : Lactose monohydrate (Pharmatose 200M) CLX : Microcrystalline cellulose PH 101 CLX : Corn Starch 1:0 White to off white powder White to off white powder White to off white powder White to off white powder White to off white powder White to off white powder White to off white powder White to off white powder White to off white powder White to off white powder 2W 4W
1:1
1:1
1:1
CLX : HPC (Klucel LF)
1:0.5
CLX : Povidone (PVP K-30)
1:0.5
CLX : Crosspovidone
1:0.5
CLX : Sodium starch glycolate CLX : Croscarmellose sodium (Ac Di Sol) CLX : Sodium stearylfumerate
1:0.5
1:0.5
1:0.2
239
Choubey Pravir et al., IPP, Vol 1 (3), 230-243, 2013 White to off white powder White to off white powder White to off white powder
CLX : Magnesium Stearate CLX : Colloidal silicon dioxide (Aerosil 200) CLX : Sodium lauryl sulfate
1:0.2
1:0.2 1:0.05
Drug- excipients compatibility study for celecoxib (physical observation). = No physical change
Related Substances generated during compatibility studies: Initial and1M (4 Week) 40C/75 % RH samples were tested for change in related
substances by HPLC method. The results are tabulated below:
Drug: Excipients Celecoxib (CLX) CLX : Lactose monohydrate (Pharmatose 200M) CLX : Microcrystalline cellulose PH 101 CLX : Corn Starch CLX : HPC (Klucel LF) CLX : Povidone (PVP K-30) CLX : Crosspovidone CLX : Sodium starch glycolate CLX : Croscarmellose sodium (Ac Di Sol) CLX : Sodium stearylfumerate CLX : Magnesium Stearate
Diketone Impurity 0.000
Isomer Total unknown Total Related Impurity impurities Substance 0.081 0.000 0.081
0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000
0.039 0.041 0.040 0.051 0.056 0.052 0.048 0.056 0.070 0.074
0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000
0.039 0.041 0.040 0.051 0.056 0.052 0.048 0.056 0.070 0.074
240
Choubey Pravir et al., IPP, Vol 1 (3), 230-243, 2013 CLX : Colloidal silicon dioxide (Aerosil 200) CLX : Sodium lauryl sulfate 0.000 0.000 0.061 0.076 0.000 0.000 0.061 0.076
Drug - excipient interaction (Chemical Compatibility) for Celecoxib Initial Diketone Impurity 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 Isomer Impurity 0.077 0.041 0.044 0.042 0.053 0.054 0.054 0.055 0.054 0.068 0.067 0.078 0.077 Total unknown Total Related impurities Substance 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.000 0.077 0.041 0.044 0.042 0.053 0.054 0.054 0.055 0.054 0.068 0.067 0.078 0.077
Drug : Excipients Celecoxib (CLX) CLX : Lactose monohydrate (Pharmatose 200M) CLX : Microcrystalline cellulose PH 101 CLX : Corn Starch CLX : HPC (Klucel LF) CLX : Povidone (PVP K-30) CLX : Crosspovidone CLX : Sodium starch glycolate CLX : Croscarmellose sodium (Ac Di Sol) CLX : Sodium stearylfumerate CLX : Magnesium Stearate CLX : Colloidal silicon dioxide (Aerosil 200) CLX : Sodium lauryl sulfate
Drug- excipient interaction (Chemical Compatibility) for Celecoxib after 4 Weeks (1M) 40C/75%RH
Based on the observation of the data on compatibility studies it is observed that that celecoxib is compatible and stable with majority of excipients used. Sr. No. 1. 2. Excipients Lactose monohydrate Croscarmellose sodium Manufacturer DMV Pharm Dow 241 Specification NF NF Function Diluent Disintegrant
Choubey Pravir et al., IPP, Vol 1 (3), 230-243, 2013 3. 4. 5. 6. Povidone K30 Sodium lauryl sulfate Magnesium Stearate Purified Water ISP Stepan Mallincrodt In house NF NF NF USP Binder Wetting agent Lubricant Granulating agent
Selected raw materials for generic capsule formulation development.
Conclusion: Developing a formulation strategy based on preformulation studies: Objective of the project was to develop a stable generic product, which should be bioequivalent to the reference drug product. The drug is found to be compatible with majority of excipients .The selected
Weighing and Sifting
candidate Celecoxib is BCS class II drug and the dose required for therapeutic action is high. Hence, it was challenging to formulate a capsule dosage form to produce a bioequivalent product. Additionally, due to fluffy nature of API because of low bulk density, it was tough to select a proper method to formulate a capsule dosage form.
Dry Mixing (Rapid mixer granulator) Granulating solution Wet Granulation (Rapid mixer granulator)
Drying (Fluid bed drier) Sifting and Milling (Mechanical Sifter and Multimill)
Mixing and Lubrication (Double Cone blender) 242
Choubey Pravir et al., IPP, Vol 1 (3), 230-243, 2013
Encapsulation (Manual Filing Machine)
Fig: Flow diagram of manufacturing process adopted for Celecoxib capsules
Development of a generic product starts with the characterization of the API, evaluation of refernce product followed by compatibility studies, selection of process and equipment, formulation development experiments, optimization trials and bioequivalent studies. In order to develop bioequivalent generic formulation of selected drug candidate, initial requirement was to choose a suitable manufacturing process. As the preformulation studies indicated the fluffy nature of Celecoxib drug due to low density and also since it was observed to be having very poor flow characteristic, hence it was concluded that direct filling of powder mixture into capsules was not possible. Therefore, wet granulation method was considered for granulation in-order to improve bulk density and flow-ability of blend. References 01 Simoens, S., Coster, S.D., 2006. Sustaining Generic Medicines Markets in Europe. Research Centre for pharmaceutical care and pharmaco - economics.1-106. Available at: at:http://www.assogenerici.org/articolihom e/simoens-report_2006-04.pdf.
02 Retrieved from www.egagenerics.com/doc/ega_increasepatient-access_final.pdf. 03 Abbreviated New Drug Application updated on 20/08/2010, cited on 9/10/2010. Available from: http://www.fda.gov. 04 Retrieved from www.fda.gov/developmentApprovalprocess/ . 05 Singh, D.P., 2010. Generic drug access in global scenario. J. Pharm. Sci. and Res.2, 9098. 06. Retrieved from www.drugbank.ca/drugs/ DB00482. 07. Kadri B.V., 2009, Drug- Excipients compatibility study will find the perfect partner to your API. Available at www.pharmaquality.com /MEZ/Audience/dirmod.asp.sid). 08. www.fda.gov/drugs/ information drugs/ucm113978.htm 09. Essentials of pharmaceutical preformulation by Mark Gibson. 10. Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms (Vol-3), Herbert A Lieberman and Leon Lachman.
243
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Oral Controlled Release Formulation Design and Drug Delivery: Theory to PracticeD'EverandOral Controlled Release Formulation Design and Drug Delivery: Theory to PracticeHong WenPas encore d'évaluation
- Preformulation StudiesDocument3 pagesPreformulation StudiesKhandakar Monir100% (1)
- 1088 in Vitro & in Vivo Evaluation of Dosage Forms - USP 36 PDFDocument10 pages1088 in Vitro & in Vivo Evaluation of Dosage Forms - USP 36 PDFKarlaBadongPas encore d'évaluation
- The Blood-Brain Barrier and Drug Delivery To The CNS - Begley, Bradbury, KreuterDocument247 pagesThe Blood-Brain Barrier and Drug Delivery To The CNS - Begley, Bradbury, KreuterFilip DrzazgaPas encore d'évaluation
- Art. Enteric CoatingDocument13 pagesArt. Enteric CoatingDiana Marcela Parra BaronaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Review of On Preformulation Studies of DrugsDocument11 pagesA Review of On Preformulation Studies of DrugsPanji Wirawan0% (1)
- Bioprocessing in The Pharmaceutical Industry: (An Engineering and Technological Overview)Document39 pagesBioprocessing in The Pharmaceutical Industry: (An Engineering and Technological Overview)ManchowPas encore d'évaluation
- Topical Drug Delivery Systems: DR Khalid Sheikh Department of Pharmaceutics Room 419 EmailDocument36 pagesTopical Drug Delivery Systems: DR Khalid Sheikh Department of Pharmaceutics Room 419 Emailchegu BusinessPas encore d'évaluation
- 23160-Article Text-115680-1-10-20180130Document9 pages23160-Article Text-115680-1-10-20180130Skariah MathewsPas encore d'évaluation
- Oms 2018Document424 pagesOms 2018ROBINPas encore d'évaluation
- Development of Forced Degradation and Stability Indicating Studies of Drugs-A Review PDFDocument7 pagesDevelopment of Forced Degradation and Stability Indicating Studies of Drugs-A Review PDFtristanprPas encore d'évaluation
- Dosage Form Development and CharacterizationDocument74 pagesDosage Form Development and CharacterizationMuhd Khairul AmriPas encore d'évaluation
- USP 1086 Impurities in Drug Substances and Drug ProductsDocument3 pagesUSP 1086 Impurities in Drug Substances and Drug ProductsMuhammad JamilPas encore d'évaluation
- FDA - ICH M7 (R1) - Control of Mutagenic Impurities in Pharmaceuticals 03.2018Document131 pagesFDA - ICH M7 (R1) - Control of Mutagenic Impurities in Pharmaceuticals 03.2018Catrinescu OanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Regulatory Requirements of In Process Content UniformityDocument9 pagesRegulatory Requirements of In Process Content UniformitySiri KalyanPas encore d'évaluation
- Volume1 Eng BioavaiDocument148 pagesVolume1 Eng Bioavaihugoboss_dark100% (1)
- European Journal of Biomedical AND Pharmaceutical SciencesDocument14 pagesEuropean Journal of Biomedical AND Pharmaceutical SciencesSACHIN BHASKAR NARKHEDEPas encore d'évaluation
- DEC Study in Formulation DevelopmentDocument9 pagesDEC Study in Formulation Developmentfad12345Pas encore d'évaluation
- Quality by Design Approaches For Topical Dermatological Dosage FormsDocument19 pagesQuality by Design Approaches For Topical Dermatological Dosage FormsDoinița UrsuPas encore d'évaluation
- Formulation and DevelopmentDocument38 pagesFormulation and Developmentapi-3810976100% (2)
- Semisolid Dosage Forms: Industrial ProcessingDocument35 pagesSemisolid Dosage Forms: Industrial ProcessingSharon Fredric SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Development ProcessDocument14 pagesDrug Development Processsnaren76100% (1)
- Occupational Health Hazards for Women in the Pharmaceutical IndustryDocument61 pagesOccupational Health Hazards for Women in the Pharmaceutical IndustryCostas JacovidesPas encore d'évaluation
- 1992-1997 and 2004 Questions and AnswersDocument56 pages1992-1997 and 2004 Questions and AnswersEmad MerganPas encore d'évaluation
- Blood Brain BarrierDocument25 pagesBlood Brain BarrierAdlai PappyPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmaceutical excipients where do we beginDocument5 pagesPharmaceutical excipients where do we beginmads56091Pas encore d'évaluation
- Preventing of Cross ContaminationDocument27 pagesPreventing of Cross ContaminationOmar FaruqPas encore d'évaluation
- Preformulation NotesDocument19 pagesPreformulation NotesAnkit Arora67% (3)
- SUPPOSITORIESDocument38 pagesSUPPOSITORIESRahul LakhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Scale Up and Postapproval Changes (Supac) Guidance For Industry: A Regulatory NoteDocument9 pagesScale Up and Postapproval Changes (Supac) Guidance For Industry: A Regulatory NoteAKKAD PHARMAPas encore d'évaluation
- Biopharmaceutics Drug Classification and International Drug Regulation 1Document187 pagesBiopharmaceutics Drug Classification and International Drug Regulation 1Kamilo ÁlvarezPas encore d'évaluation
- Guidance Manual: Quality Control Testing of Human AlbuminDocument35 pagesGuidance Manual: Quality Control Testing of Human AlbuminNataraja Sekhar Reddy VaddamaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Risk Assessment in The Pharmaceutical Industry ToxicologyDocument41 pagesRisk Assessment in The Pharmaceutical Industry ToxicologyJasonPas encore d'évaluation
- An Overview On Tablet CoatingDocument4 pagesAn Overview On Tablet Coatingronahaniifah11Pas encore d'évaluation
- ANDA Impurities GuidanceDocument11 pagesANDA Impurities GuidanceFDA Lawyers BlogPas encore d'évaluation
- Use and Limitations of in Vitro Dissolution Testing: Topic Introduction and OverviewDocument114 pagesUse and Limitations of in Vitro Dissolution Testing: Topic Introduction and OverviewMuthu Venkatesh100% (1)
- B 03 110921e Solubility Enhance CompendiumDocument130 pagesB 03 110921e Solubility Enhance CompendiumMostofa RubalPas encore d'évaluation
- PreviewpdfDocument63 pagesPreviewpdfFardina SafitriPas encore d'évaluation
- Industrial Training PRESENTATION (Benazir)Document6 pagesIndustrial Training PRESENTATION (Benazir)Benazir ShuguftaPas encore d'évaluation
- A John Blacker - Mike T Williams - Pharmaceutical Process Development - Current Chemical and Engineering Challenges-Royal Society of Chemistry (2011)Document375 pagesA John Blacker - Mike T Williams - Pharmaceutical Process Development - Current Chemical and Engineering Challenges-Royal Society of Chemistry (2011)Nguyen Dang Binh ThanhPas encore d'évaluation
- CTD CMC-Information-Human-Gene-Therapy-IND-Applications - Jan - 2020Document56 pagesCTD CMC-Information-Human-Gene-Therapy-IND-Applications - Jan - 2020Shiraz KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Usp Review AlbuterolDocument82 pagesUsp Review Albuterolsrayu2603Pas encore d'évaluation
- FDS StudyDocument8 pagesFDS StudyAnnisaIndahPPas encore d'évaluation
- Quality by Design in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: A Systematic Review of Current Status, Challenges and Future PerspectivesDocument19 pagesQuality by Design in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing: A Systematic Review of Current Status, Challenges and Future PerspectivesArturo T. Sánchez-MoraPas encore d'évaluation
- Wurstertechnology ProcessvariablesinvolvedandScaleupscienceDocument11 pagesWurstertechnology ProcessvariablesinvolvedandScaleupsciencemadhuPas encore d'évaluation
- List of cytotoxic chemotherapy drugs and trade namesDocument1 pageList of cytotoxic chemotherapy drugs and trade namesempr404100% (1)
- FDA Guidance For Industry S7a Safety Pharmacology Studies For Human Pharmaceuticals PDFDocument14 pagesFDA Guidance For Industry S7a Safety Pharmacology Studies For Human Pharmaceuticals PDFbmartindoyle6396Pas encore d'évaluation
- 1st BWC Abstract BookDocument199 pages1st BWC Abstract BookMeri Sunder100% (1)
- Drug DPMTDocument27 pagesDrug DPMTapi-3842711100% (1)
- Nonclinical Safety Assessment: A Guide to International Pharmaceutical RegulationsD'EverandNonclinical Safety Assessment: A Guide to International Pharmaceutical RegulationsWilliam J. BrockPas encore d'évaluation
- Basic Concept of Process Validation in Solid Dosage Form (Tablet)Document9 pagesBasic Concept of Process Validation in Solid Dosage Form (Tablet)edgar palominoPas encore d'évaluation
- Analytical Methods Transfer ConsiderationsDocument26 pagesAnalytical Methods Transfer ConsiderationsamolPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Drug Polymorphism and Dosage Form Design A Practical PerspectiveDocument13 pages1 Drug Polymorphism and Dosage Form Design A Practical Perspectivejulieth vPas encore d'évaluation
- PLASMA and PLASMA PROTEINSDocument24 pagesPLASMA and PLASMA PROTEINSJude ChinecheremPas encore d'évaluation
- Supac GuidelineDocument30 pagesSupac GuidelineSalman ShaikhPas encore d'évaluation
- Risk Assessment Single-Use White Paper en MRK March 2017 LowDocument4 pagesRisk Assessment Single-Use White Paper en MRK March 2017 LowRui PiresPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmaceutical DevelopmentDocument18 pagesPharmaceutical DevelopmentmekaielPas encore d'évaluation
- ICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation GuideD'EverandICH Quality Guidelines: An Implementation GuideAndrew TeasdalePas encore d'évaluation
- Trndes in Prid DevelompmetnDocument3 pagesTrndes in Prid DevelompmetnsskkalePas encore d'évaluation
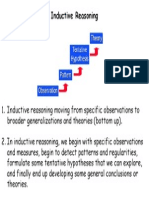
- Inductive Reasoning: From Specific to GeneralDocument1 pageInductive Reasoning: From Specific to GeneralsskkalePas encore d'évaluation
- Serpbrp Asfdgp RTRTPRTDocument2 pagesSerpbrp Asfdgp RTRTPRTsskkalePas encore d'évaluation
- Product Development GuideDocument8 pagesProduct Development GuidesskkalePas encore d'évaluation
- Asking QuestionsDocument2 pagesAsking QuestionssskkalePas encore d'évaluation
- Drug Release Kinetics ModelsDocument7 pagesDrug Release Kinetics ModelsSajid Khan SadozaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacognosy Lab Manual for Pharmacy StudentsDocument53 pagesPharmacognosy Lab Manual for Pharmacy StudentsKrunal Chorey71% (7)
- A Classification of Prescription ErrorsDocument3 pagesA Classification of Prescription ErrorssskkalePas encore d'évaluation
- Patel 123Document18 pagesPatel 123sskkalePas encore d'évaluation
- AskingDocument1 pageAskingsskkalePas encore d'évaluation
- Cold Cream FormDocument2 pagesCold Cream FormsskkalePas encore d'évaluation
- Research Proposal ElementsDocument1 pageResearch Proposal ElementssskkalePas encore d'évaluation
- About KvpyDocument5 pagesAbout KvpysskkalePas encore d'évaluation
- Semester Syllabus For V Sem. To Viii SemDocument41 pagesSemester Syllabus For V Sem. To Viii SemAmit KhairnarPas encore d'évaluation
- Semester Syllabus For V Sem. To Viii SemDocument41 pagesSemester Syllabus For V Sem. To Viii SemAmit KhairnarPas encore d'évaluation
- Latent HeatDocument12 pagesLatent HeatsskkalePas encore d'évaluation
- 2006-07 B. Pharm. Sem VII & VIII (09-10)Document34 pages2006-07 B. Pharm. Sem VII & VIII (09-10)sskkalePas encore d'évaluation
- M.pharm. SyllabiDocument43 pagesM.pharm. SyllabivijaykparmarPas encore d'évaluation
- 2006-07 B. Pharm. Sem VII & VIII (09-10)Document34 pages2006-07 B. Pharm. Sem VII & VIII (09-10)sskkalePas encore d'évaluation
- Team Quastars ReportDocument25 pagesTeam Quastars ReportMedhansh GargPas encore d'évaluation
- PT Chapter 1Document13 pagesPT Chapter 1shubhamPas encore d'évaluation
- ESAS Objectives 1Document15 pagesESAS Objectives 1Jayven VillamaterPas encore d'évaluation
- Enzyme Controlled Reaction LabDocument2 pagesEnzyme Controlled Reaction Labapi-291218692Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanics of motion and forces solved problemsDocument5 pagesMechanics of motion and forces solved problemsWilliamPas encore d'évaluation
- Spectrophotometric Analysis of A Commercial Aspirin TabletDocument5 pagesSpectrophotometric Analysis of A Commercial Aspirin TabletHasan RajabPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 6 (Materials & Hardware) SubModule 6.4 (Corrosion)Document26 pagesModule 6 (Materials & Hardware) SubModule 6.4 (Corrosion)daniaPas encore d'évaluation
- Toc VWDocument16 pagesToc VWanilkumar995472Pas encore d'évaluation
- Instrumental ChemistryDocument3 pagesInstrumental ChemistrypepePas encore d'évaluation
- AWWA Standard for Filtering MaterialDocument21 pagesAWWA Standard for Filtering Materialmaldush100% (2)
- Snay Soler Part3Document3 pagesSnay Soler Part3jajcePas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Second QuantizationDocument34 pagesIntroduction To Second QuantizationPABLO ISMAEL LUJAN PRADOPas encore d'évaluation
- 2.water Hardness - Ion Exchange MethodDocument5 pages2.water Hardness - Ion Exchange MethodElden GonsalvesPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 24 Molecular Absorption Spectrometry Molecular Spectrometry Uv / Vis / Ir Widely Used Identification Inorganic Organic Biochemical SpeciesDocument42 pagesChapter 24 Molecular Absorption Spectrometry Molecular Spectrometry Uv / Vis / Ir Widely Used Identification Inorganic Organic Biochemical Species陳奕廷go.thuPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemguard 3% x 6% AR-AFFF for hydrocarbon and polar solvent fuelsDocument2 pagesChemguard 3% x 6% AR-AFFF for hydrocarbon and polar solvent fuelsTri Cahyono YuniantoPas encore d'évaluation
- 11 Physics Practice PaperDocument10 pages11 Physics Practice PaperIshan AhujaPas encore d'évaluation
- Gravity and AntigravityDocument3 pagesGravity and AntigravityAnon BoletusPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculation of Corrosion RateDocument2 pagesCalculation of Corrosion RateVũ Phi YếnPas encore d'évaluation
- An Initial Investigation of The Electrochemical Dissolution of Fragments of Nickel-Titanium Endodontic FilesDocument5 pagesAn Initial Investigation of The Electrochemical Dissolution of Fragments of Nickel-Titanium Endodontic FilesAlyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Vernier Calipers (Procedure) - Class 11 - Physics - Amrita Online LabDocument3 pagesVernier Calipers (Procedure) - Class 11 - Physics - Amrita Online Labgetashishvaid100% (1)
- Natural Gas Energy Measurement PDFDocument354 pagesNatural Gas Energy Measurement PDFHenry Maeda100% (3)
- Shinkolite™ L NF30Document2 pagesShinkolite™ L NF30Jayant Kumar JhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Archimedes Number ExplainedDocument86 pagesArchimedes Number ExplainedRicardo Zevallos CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- Selecting Systems: Membrane FiltrationDocument4 pagesSelecting Systems: Membrane FiltrationRaul TejedaPas encore d'évaluation
- Tanol Speed: Developing Times ChartDocument1 pageTanol Speed: Developing Times ChartArkady YakhnisPas encore d'évaluation
- Geog 213Document365 pagesGeog 213Fatima TwumasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Sediment Transport Rates ReviewedDocument29 pagesSediment Transport Rates ReviewedJorge Sandoval UlloaPas encore d'évaluation
- 결정학개론 6 (1)Document15 pages결정학개론 6 (1)pmn07050Pas encore d'évaluation
- Anton FilikovDocument7 pagesAnton FilikovKatrina ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- Ceramic Tiles and Vitrified TilesDocument15 pagesCeramic Tiles and Vitrified TilesSamyukthaPas encore d'évaluation