Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Me3 Tom1 May 2007
Transféré par
draculagurdeep0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
17 vues1 pageThis document provides information about an exam for a Theory of Machines course, including 10 short questions in Section A and 3 longer question options in Sections B and C. Section A covers topics like types of joints, degrees of freedom, steering mechanisms, belt and chain drives, cam profiles, types of governors, balancing rotating masses, and lubrication. The questions in Sections B and C involve more in-depth explanations and calculations related to mechanisms like pantographs, rope drives, belt drives, balancing rotating masses, cam profiles, governors, and vehicle braking dynamics.
Description originale:
papers
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentThis document provides information about an exam for a Theory of Machines course, including 10 short questions in Section A and 3 longer question options in Sections B and C. Section A covers topics like types of joints, degrees of freedom, steering mechanisms, belt and chain drives, cam profiles, types of governors, balancing rotating masses, and lubrication. The questions in Sections B and C involve more in-depth explanations and calculations related to mechanisms like pantographs, rope drives, belt drives, balancing rotating masses, cam profiles, governors, and vehicle braking dynamics.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
0 évaluation0% ont trouvé ce document utile (0 vote)
17 vues1 pageMe3 Tom1 May 2007
Transféré par
draculagurdeepThis document provides information about an exam for a Theory of Machines course, including 10 short questions in Section A and 3 longer question options in Sections B and C. Section A covers topics like types of joints, degrees of freedom, steering mechanisms, belt and chain drives, cam profiles, types of governors, balancing rotating masses, and lubrication. The questions in Sections B and C involve more in-depth explanations and calculations related to mechanisms like pantographs, rope drives, belt drives, balancing rotating masses, cam profiles, governors, and vehicle braking dynamics.
Droits d'auteur :
© All Rights Reserved
Formats disponibles
Téléchargez comme PDF, TXT ou lisez en ligne sur Scribd
Vous êtes sur la page 1sur 1
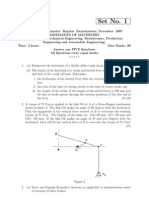
Theory of Machines
(ME-203, May 2007)
Time: 3 Hrs Max Marks: 60
Note: Section A is compulsory. Attempt any four questions from Section B and any two questions from Section C.
Section-A
1. (a) Define and explain the terms: binary joints, quaternary joints.
(b) What do you understand by degrees of freedom?
(c) What is the principal of steering gear mechanism?
(d) What are relative advantages and disadvantages of chain and belt drives?
(e) What is the condition for the maximum power transmitted by a belt from one pulley to another?
(f) Define and explain the terms: base circle and pitch curve in a Cam.
(g) What is the difference between porter governor and proell governor?
(h) Differentiate between theory of uniform pressure and theory of uniform wear.
(i) Define and explain the term Balancing of rotating masses.
(j) What are thick and thin film lubrications?
Section-B
2. What do you mean by a pantograph and what are its uses? Describe with a neat sketch the principal and working of the
pantograph.
3. Derive an expression for the ratio of the driving tensions in a rope drive assuming the angle of the groove of the pulley to be as
2.
4. A shaft rotating at 200 rpm drives another shaft at 300 rpm and transmits 6 KW through a belt. The belt is 100 mm wide and 10
mm thick. The distance between the shafts is 4m. The smaller pulley is 0.5m in diameter. Calculate the stress in the belt, if it is an
open belt drive. Take = 0.3.
5. Four masses A, B, C and D are attached to a rotating shaft with radii 50mm, 62.5mm, 100mm and 75mm respectively. The
distances between planes A and B; between planes B and C and between planes C and D are 600mm each. The masses B, C
and D are 20 kg, 10kg and 8kg respectively. If the shaft is in complete balance, then find:
(a) Magnitude of mass A, and
(b) Angular positions of the four masses.
6. For a uniform acceleration and retardation of the follower, derive expressions for the maximum velocity and acceleration during
the return stroke and outstroke.
Section-C
7. A cam rotating clockwise with a uniform speed is to give the roller follower of 20mm diameter the following motion:
(i) Follower to move outwards through a distance of 30mm during 120of cam rotation.
(ii) Follower to dwell for 60of cam rotation.
(iii) Follower to return to its original position during 90of cam rotation.
(iv) Follower to dwell for the remaining 90of cam rotation.
The minimum radius of the cam is 45mm and the line of stroke of the follower is off-set 15mm from the axis of the cam and the
displacement of the follower is to take place with simple harmonic motion on both the outward and return strokes. Draw the cam
profile.
8. (a) Calculate the minimum speed, maximum speed and range of the speed of a Porter governor, which has equal arms each
200mm long and pivoted an the axis of rotation. The mass of each ball is 4kg and the central mass on the sleeve is 20kg. The
radius of rotation of the ball is 100mm when the governor begins to lift and 130mm when the governor is at maximum speed.
(b) What is meant by term stability of a governor? Derive the necessary condition of stability for a centrifugal governor.
9. (a) A vehicle moving on a rough plane inclined at 10 with the horizontal at a speed of 36km/hr has a wheel base 1.8m. The center of
gravity of the vehicle is 0.8m from the rear wheel and 0.9m above the inclined plane. Find the distance traveled by the vehicle
before coming to rest and the time taken to do so when the vehicle moves up the plane. The brakes are applied to all the four
wheels and the coefficient of friction is 0.5.
(b) Differentiate between
(i) Brakes and dynamometer
(ii) Absorption dynamometer and transmission dynamometer.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3D'EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Évaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (1)
- Balancing ChapterDocument15 pagesBalancing ChapterJolani Allie50% (2)
- Welding PositionsDocument116 pagesWelding PositionsASAPASAPASAPPas encore d'évaluation
- High Speed Off-Road Vehicles: Suspensions, Tracks, Wheels and DynamicsD'EverandHigh Speed Off-Road Vehicles: Suspensions, Tracks, Wheels and DynamicsPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanics by Basudeb BhattaacharysaDocument167 pagesMechanics by Basudeb BhattaacharysaAwesome GameplayPas encore d'évaluation
- Hydrodynamics Horace LambDocument632 pagesHydrodynamics Horace LambRoberto Cañas100% (3)
- A Guide to Making a Leather Belt - A Collection of Historical Articles on Designs and Methods for Making BeltsD'EverandA Guide to Making a Leather Belt - A Collection of Historical Articles on Designs and Methods for Making BeltsÉvaluation : 3 sur 5 étoiles3/5 (1)
- Mechanics of Machines II ExamsDocument2 pagesMechanics of Machines II ExamsCharles OndiekiPas encore d'évaluation
- John Wilson - Lost Solar System of The Ancient (Vol 1)Document506 pagesJohn Wilson - Lost Solar System of The Ancient (Vol 1)Rajat K Bose100% (2)
- Civil Engineering R AGOR Objective TypeDocument831 pagesCivil Engineering R AGOR Objective TypeJohn Carlo SabadoPas encore d'évaluation
- PBR Visvodaya Institute of Technology and Science: Kavali: Mechanical EngineeringDocument7 pagesPBR Visvodaya Institute of Technology and Science: Kavali: Mechanical Engineeringhod mechPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanics of Machines II ExamsDocument2 pagesMechanics of Machines II ExamsCharles Ondieki100% (2)
- Dynamics of MachineryDocument8 pagesDynamics of Machineryrajamutyala4uPas encore d'évaluation
- WWW - Manaresults.co - In: (Mechanical Engineering)Document3 pagesWWW - Manaresults.co - In: (Mechanical Engineering)rajuPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamics of MachineryDocument8 pagesDynamics of MachineryNORIMAR24Pas encore d'évaluation
- 2mid Imp Questions ModelsDocument4 pages2mid Imp Questions ModelsSrimanthula SrikanthPas encore d'évaluation
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.joe_134Pas encore d'évaluation
- Upto 2010 KomDocument36 pagesUpto 2010 KompsnasabariPas encore d'évaluation
- Upto 2010 KomDocument36 pagesUpto 2010 KomRajueswarPas encore d'évaluation
- DOM QuestionsDocument14 pagesDOM QuestionsManda Ramesh BabuPas encore d'évaluation
- Part B & Part C Questions - Unit WiseDocument3 pagesPart B & Part C Questions - Unit WiseShobiPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamics of Machinery QuestionsDocument11 pagesDynamics of Machinery Questionslogeshboy0070% (1)
- TM II TutorialDocument3 pagesTM II TutorialkrishnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamics of Machinery-QbDocument11 pagesDynamics of Machinery-QbkarthisanPas encore d'évaluation
- QB For Mid-IiDocument3 pagesQB For Mid-Iihod mechPas encore d'évaluation
- Theory of Machine - IIDocument4 pagesTheory of Machine - IIKetan V. JoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Time: 3 Hours Total Marks: 70: Printed Pages: Sub Code: Paper Id: Roll NoDocument3 pagesTime: 3 Hours Total Marks: 70: Printed Pages: Sub Code: Paper Id: Roll NoAwanish SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Analysis OF Mechanisms GTU IMPDocument5 pagesAnalysis OF Mechanisms GTU IMPSwastik PanchalPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamics of MachineDocument3 pagesDynamics of MachinegokulavaannanPas encore d'évaluation
- Term End Examination - November 2014 Course: MEE354 - Kinematics and Dynamics of Machinery Slot: B1+TB1 Class NBR: 4443 Time: Three Hours Max - Marks:100Document3 pagesTerm End Examination - November 2014 Course: MEE354 - Kinematics and Dynamics of Machinery Slot: B1+TB1 Class NBR: 4443 Time: Three Hours Max - Marks:100Akash SoniPas encore d'évaluation
- Sample Question Paper Kinematics of MachinesDocument3 pagesSample Question Paper Kinematics of MachinesAnonymous utfuIcnPas encore d'évaluation
- MET301 Dec 2021Document3 pagesMET301 Dec 2021Sudeesh SudevanPas encore d'évaluation
- Kinematics of MachineryDocument9 pagesKinematics of MachineryChinmay SahooPas encore d'évaluation
- Jntu Question PaperDocument3 pagesJntu Question Paperrohitchanakya76Pas encore d'évaluation
- ME1301Document8 pagesME1301kannanviknesh086319Pas encore d'évaluation
- Assignment Unit - 1: 2) .A Pair of Involute Gears Is in Mesh. The Application Restricts The Space To Accommodate TheseDocument4 pagesAssignment Unit - 1: 2) .A Pair of Involute Gears Is in Mesh. The Application Restricts The Space To Accommodate TheserahulPas encore d'évaluation
- Me3 Tom1 Dec 2006Document1 pageMe3 Tom1 Dec 2006Irfan AhmadPas encore d'évaluation
- DOM QP ScribdDocument5 pagesDOM QP ScribdvsanthanamPas encore d'évaluation
- 9A14402 Theory of MachinesDocument8 pages9A14402 Theory of MachinessivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- 9A21506 Mechanisms & Mechanical DesignDocument8 pages9A21506 Mechanisms & Mechanical DesignsivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- 1424R05310304 Kinematics of MacDocument10 pages1424R05310304 Kinematics of Macأحمد جمالPas encore d'évaluation
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document3 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.Tejaswi PilakaPas encore d'évaluation
- Our Official Android App - REJINPAUL NETWORK FromDocument3 pagesOur Official Android App - REJINPAUL NETWORK FromAjay KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: III B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, May - 2017 Dynamics of MachineryDocument2 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: III B. Tech I Semester Supplementary Examinations, May - 2017 Dynamics of MachineryMusalam prabhu tejaPas encore d'évaluation
- Kinematics of Machinery Question BankDocument5 pagesKinematics of Machinery Question BankSree MurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- R7220302 Kinematics of MachineryDocument2 pagesR7220302 Kinematics of MachinerysivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- University QuestionsDocument4 pagesUniversity QuestionsMartin De Boras PragashPas encore d'évaluation
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument3 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityKRISHI JANIPas encore d'évaluation
- DOM2Document7 pagesDOM2ds_shivaPas encore d'évaluation
- 081 - ME8594, ME6505 Dynamics of Machines - Question BankDocument11 pages081 - ME8594, ME6505 Dynamics of Machines - Question Banksara vanaPas encore d'évaluation
- Me6401 Kinematics of Machinery UNIT-I (Basics of Mechanism)Document8 pagesMe6401 Kinematics of Machinery UNIT-I (Basics of Mechanism)Ãraviñdhañ RändýPas encore d'évaluation
- Me201 2017 06-1 PDFDocument5 pagesMe201 2017 06-1 PDFPromise GwaindepiPas encore d'évaluation
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To Ame, MSNT, Me, MCT)Document3 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To Ame, MSNT, Me, MCT)Sameer MDPas encore d'évaluation
- NR-310304 - Dynamics of MachineryDocument8 pagesNR-310304 - Dynamics of MachinerySrinivasa Rao GPas encore d'évaluation
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: II B. Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations, Nov/Dec-2016 Theory of MachinesDocument2 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: II B. Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations, Nov/Dec-2016 Theory of Machineskotika_somarajuPas encore d'évaluation
- 07a60304 - Dynamics of MachineryDocument8 pages07a60304 - Dynamics of MachineryRajaganapathy GanaPas encore d'évaluation
- r05310304 Kinematics of MachineryDocument10 pagesr05310304 Kinematics of MachinerySRINIVASA RAO GANTAPas encore d'évaluation
- (W-19) Dynamics of MachinesDocument4 pages(W-19) Dynamics of MachinesNabeel KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- MTM CYCLE Test 1 Question BankDocument3 pagesMTM CYCLE Test 1 Question BankRanilprabhu MPas encore d'évaluation
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: II B. Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations, November - 2018 Kinematics of MachinaryDocument2 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: II B. Tech II Semester Supplementary Examinations, November - 2018 Kinematics of MachinaryPavaniPas encore d'évaluation
- 9A03401 Kinematics of MachineryDocument8 pages9A03401 Kinematics of MachinerysivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamics of Machinery R2009 20-11-2014Document2 pagesDynamics of Machinery R2009 20-11-2014manoj gokikarPas encore d'évaluation
- 16ME5DCDOMDocument3 pages16ME5DCDOMyyy 4uPas encore d'évaluation
- Dynamics of Machines (Mech 3105)Document6 pagesDynamics of Machines (Mech 3105)132 Arindam DattaPas encore d'évaluation
- School of Mechanical and Building Sciences Mee 301 Dynamics of MachineryDocument4 pagesSchool of Mechanical and Building Sciences Mee 301 Dynamics of MachineryNirman ParasharPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Tut 101Document53 pagesPhysics Tut 101Kyle Moolman50% (2)
- ECE 6401: MEMS Design & Micromachining: Engineering Mechanics For Microsystem DesignDocument18 pagesECE 6401: MEMS Design & Micromachining: Engineering Mechanics For Microsystem DesignAbcPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Lec 24 MoreStaticsDocument11 pagesPhysics Lec 24 MoreStaticsAnthony Wijaya, S.Pd., M.Si.Pas encore d'évaluation
- Question BankDocument7 pagesQuestion BankmunirajPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 Machinery Fault Diagnosis Using Vibration AnalysisDocument45 pages5 Machinery Fault Diagnosis Using Vibration AnalysisjudarangocaPas encore d'évaluation
- Analiza MersuluiDocument31 pagesAnaliza MersuluiBeatrice AncaPas encore d'évaluation
- Geislinger SAE-couplings - enDocument50 pagesGeislinger SAE-couplings - entommy lanyonPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics NumericalDocument10 pagesPhysics NumericalmuzammalsafdarPas encore d'évaluation
- Name:-Manvi Gour Branch: - AIDS CODE: - #IncludeDocument6 pagesName:-Manvi Gour Branch: - AIDS CODE: - #IncludeManvi GourPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 - Introduction To Machinery PrinciplesDocument51 pagesChapter 1 - Introduction To Machinery PrinciplesGopinath SubramaniPas encore d'évaluation
- 07 - System of Particles and Rotational MotionDocument20 pages07 - System of Particles and Rotational Motionᴍᴏᴊᴏ JOJOPas encore d'évaluation
- Moments of ForcesDocument24 pagesMoments of ForcesChristine Torrepenida RasimoPas encore d'évaluation
- Turbo Machinery (ME 5001) - Unit 1 - WWW - Rgpvnotes.in PDFDocument11 pagesTurbo Machinery (ME 5001) - Unit 1 - WWW - Rgpvnotes.in PDFMohammed AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Screw ConveyorDocument7 pagesScrew Conveyorjdsheth2004100% (1)
- Rotation WorkbookDocument57 pagesRotation Workbookanimemania251Pas encore d'évaluation
- Helical Hydraulic Rotary Actuators: Series L and TDocument20 pagesHelical Hydraulic Rotary Actuators: Series L and TDesign IPGEPas encore d'évaluation
- En Cat RV PDFDocument122 pagesEn Cat RV PDFCosmina Anna MPas encore d'évaluation
- Flexible RotorDocument22 pagesFlexible RotormghgolPas encore d'évaluation
- Mulitilayer Winindg - Grooves - KOMAGDocument14 pagesMulitilayer Winindg - Grooves - KOMAGkazdanoPas encore d'évaluation
- Demolition by Controlled BlastingDocument7 pagesDemolition by Controlled BlastingEr Manak Chand SainiPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5 Airplanes Stability and ControlDocument40 pagesChapter 5 Airplanes Stability and ControlIshaq AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- GRFP01 Gr11 Ch01toCh06Document126 pagesGRFP01 Gr11 Ch01toCh06AidanPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 5Document8 pagesModule 5Benson MataPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics Rev 1Document6 pagesPhysics Rev 1Calvin LabialPas encore d'évaluation