Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
M408L Exam 1
Transféré par
Nathan ThaiCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
M408L Exam 1
Transféré par
Nathan ThaiDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Version 047 L EXAM 1 guntel (55200) 1
This print-out should have 17 questions.
Multiple-choice questions may continue on
the next column or page nd all choices
before answering.
001 10.0 points
A function h has graph
-2
-1
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
2 4 2
2
4
on (3, 4). If
f(x) =
_
x
2
h(t) dt, (x 2),
which of the following is the graph of f on
(3, 4)?
1.
-4
-3
-2
-1
0
1
2
3
4
2 4 2
2
2
2.
-4
-3
-2
-1
0
1
2
3
2 4 2
2
2
3.
-4
-3
-2
-1
0
1
2
3
4
2 4 2
2
2
4.
-4
-3
-2
-1
0
1
2
3
4
2 4 2
2
2
5.
-4
-3
-2
-1
0
1
2
3
4
2 4 2
2
2
correct
6.
-4
-3
-2
-1
0
1
2
3
2 4 2
2
2
Explanation:
Since f(x) is dened only for x 2, there
will be no graph of f on the interval (3, 2).
Version 047 L EXAM 1 guntel (55200) 2
This already eliminates two of the possible
graphs. On the other hand,
f(2) =
_
2
2
h(x) dx = 0 ,
eliminating two more graphs. Finally, by the
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus, f
(x) =
h(x) on (2, 4), so f(x) will be increasing on
any interval on which h > 0, and decreasing
on any interval on which h < 0. To determine
which of the remaining two possible graphs is
the graph of f we thus have to look at the sign
of h on an interval and the slope of a possible
graph of f on that interval. Consequently, the
only possible graph of f is
-4
-3
-2
-1
0
1
2
3
2 4 2
2
2
002 10.0 points
Determine g
(x) when
g(x) =
_
4
x
3t
2
sec t dt .
1. g
(x) = 6x sec x tanx
2. g
(x) = 6x sec
2
x
3. g
(x) = 3x
2
tan x
4. g
(x) = 6x sec x tanx
5. g
(x) = 6x sec
2
x
6. g
(x) = 3x
2
sec x correct
7. g
(x) = 3x
2
sec x
8. g
(x) = 3x
2
tanx
Explanation:
By Properties of integrals and the Funda-
mental Theorem of Calculus,
d
dx
_
_
a
x
f(t) dt
_
=
d
dx
_
_
x
a
f(t) dt
_
= f(x) .
When
g(x) =
_
4
x
f(t) dt , f(t) = 3t
2
sec t ,
therefore,
g
(x) = 3x
2
sec x .
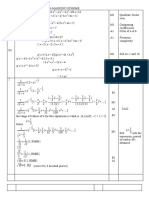
003 10.0 points
Evaluate the integral
I =
_
4
3
8
x
2
6x + 10
dx .
1. I = 2 correct
2. I = 2
3. I =
4. I = 1
5. I = 4
6. I = 4
Explanation:
By completing the square we see that
x
2
6x + 10 = (x
2
6x + 9) + 10 9
= (x 3)
2
+ 1 .
In this case
I =
_
4
3
8
(x 3)
2
+ 1
.
Version 047 L EXAM 1 guntel (55200) 3
Now set x 3 = u. For then dx = du, while
x = 3 = u = 0,
x = 4 = u = 1 ,
and so
I = 8
_
1
0
1
1 +u
2
du = 8
_
tan
1
u
_
1
0
.
Consequently,
I = 2 .
004 10.0 points
Evaluate the integral
I =
_
1
0
_
4x x
1/3
_
dx .
1. I =
3
4
2. I = 1
3. I =
5
4
correct
4. I =
1
3
5. I =
2
3
6. I =
2
3
Explanation:
By the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus,
I =
_
F(x)
_
1
0
= F(1) F(0)
for any anti-derivative F of
f(x) = 4x x
1/3
.
Taking
F(x) = 2x
2
3
4
x
4/3
,
we thus see that
I = 2
3
4
.
Consequently,
I =
5
4
.
005 10.0 points
Evaluate the denite integral
I =
_
e
1
3x
2
ln x dx.
1. I =
1
3
(2e
3
1)
2. I = (2e
3
1)
3. I =
2
3
e
3
4. I =
1
3
(2e
3
+ 1) correct
5. I = (2e
3
+ 1)
Explanation:
After integration by parts,
I =
_
x
3
lnx
_
e
1
_
e
1
x
2
dx
= e
3
_
e
1
x
2
dx ,
since ln e = 1 and ln1 = 0. But
_
e
1
x
2
dx =
1
3
(e
3
1).
Consequently,
I = e
3
1
3
(e
3
1) =
1
3
(2e
3
+ 1) .
006 10.0 points
Version 047 L EXAM 1 guntel (55200) 4
Evaluate the integral
I =
_
/2
0
3 sin
2
x cos
3
x dx .
1. I =
8
5
2. I =
1
5
3. I =
6
5
4. I =
2
5
correct
5. I =
4
5
Explanation:
Since
sin
2
x cos
3
x = (sin
2
x cos
2
x) cos x
= sin
2
x(1 sin
2
x)cos x
= (sin
2
x sin
4
x)cos x ,
the integrand is of the form cos xf(sinx), sug-
gesting use of the substitution u = sin x. For
then
du = cos x dx ,
while
x = 0 = u = 0
x =
2
= u = 1 .
In this case
I =
_
1
0
3(u
2
u
4
) du.
Consequently,
I =
_
u
3
3
5
u
5
_
1
0
=
2
5
.
keywords: Stewart5e, indenite integral,
powers of sin, powers of cos, trig substitu-
tion,
007 10.0 points
Determine the integral
I =
_
x
3
x
2
+ 13
dx .
1. I = x
2
+x ln(x
2
+ 13) +C
2. I =
1
2
x
2
13
2
ln(x
2
+13) +C correct
3. I = x
2
x ln(x
2
+ 13) +C
4. I =
1
3
x
3
13 ln(x
2
+ 13) +C
5. I =
1
2
x
2
+
13
2
ln(x
2
+ 13) +C
6. I =
1
3
x
3
+ 13 ln(x
2
+ 13) +C
Explanation:
After long division on the integrand,
x
3
x
2
+ 13
= x
13x
x
2
+ 13
.
Thus
I =
_
x dx
_
13x
x
2
+ 13
dx .
To evaluate the last integral we use the sub-
stitution u = x
2
+ 13. For then du = 2x dx,
so
I =
1
2
x
2
13
2
_
1
u
du.
Consequently,
I =
1
2
x
2
13
2
ln(x
2
+ 13) +C .
008 10.0 points
Determine the integral
I =
_
1
1/2
2
2 x
dx . .
Version 047 L EXAM 1 guntel (55200) 5
1. I =
1
6
2. I =
2
3
3. I =
2
3
4. I =
1
3
correct
5. I =
1
6
6. I =
1
3
Explanation:
Set u
2
= x. Then 2udu = dx, while
x =
1
2
= u =
1
2
x = 1 = u = 1 .
In this case,
I = 4
_
1
1/
2
1
2 u
2
du
= 4
_
sin
1
u
2
_
1
1/
2
.
Consequently,
I = 4
_
4
6
_
=
1
3
.
keywords:
009 10.0 points
Evaluate the integral
I =
_
0
e
x
sin x dx .
1. I = e
1
2. I = e
+ 1
3. I =
1
2
(e
+ 1)
4. I =
1
2
(e
+ 1) correct
5. I =
1
2
(e
+ 1)
6. I = 1 e
7. I =
1
2
(1 e
)
8. I = e
+ 1
Explanation:
After integration by parts,
I =
_
e
x
sin x
_
_
0
e
x
cos x dx
= 0
_
0
e
x
cos x dx .
To evaluate this last integral we integrate by
parts once again. For then
_
0
e
x
cos x dx
=
_
e
x
cos x
_
0
+
_
0
e
x
sin x dx
= e
1 +I ,
in which case
I = e
+ 1 I .
Consequently,
I =
1
2
(e
+ 1) .
010 10.0 points
Evaluate the integral
I =
_
1
0
2
(x
2
+ 3)
3/2
dx .
Version 047 L EXAM 1 guntel (55200) 6
1. I =
2
3
2. I = 2
3. I = 1
4. I =
1
2
5. I =
1
3
correct
Explanation:
Set x =
3 tan u. Then
dx =
3 sec
2
udu,
while
x = 0 = u = 0 ,
x = 1 = u =
6
.
On the other hand,
(x
2
+ 3)
3/2
=
_
3(tan
2
u + 1)
_
3/2
= 3
3 sec
3
u.
Thus
I = 2
_
/6
0
3 sec
2
u
3
3 sec
3
u
du
=
2
3
_
/6
0
cos udu =
2
3
_
sin u
_
/6
0
.
Consequently
I =
1
3
.
keywords:
011 10.0 points
Evaluate the integral
I =
_
2
0
5x 7
x
2
2x 3
dx .
1. I = 5 ln3
2. I = ln 3 correct
3. I = 5 ln4
4. I = ln 4
5. I = ln 3
6. I = 5 ln 4
Explanation:
After factorization
x
2
2x 3 = (x + 1)(x 3) .
But then by partial fractions,
5x 7
x
2
2x 3
=
3
x + 1
+
2
x 3
.
Now
_
2
0
3
x + 1
dx =
_
3 ln|(x + 1)|
_
2
0
= 3 ln3 ,
while
_
2
0
2
x 3
dx =
_
2 ln|(x3)|
_
2
0
= 2 ln 3 .
Consequently,
I = ln3 .
012 10.0 points
Evaluate the denite integral
I =
_ 1
2
0
4x
2
1 x
2
dx .
1. I =
8
1
4
2. I =
4
1
2
Version 047 L EXAM 1 guntel (55200) 7
3. I =
2
1
4
4. I =
1
2
5. I =
4
1
8
6. I =
2
1 correct
Explanation:
Set x = sin u. Then
dx = cos udu,
_
1 x
2
= cos u,
while
x = 0 = u = 0,
x =
1
2
= u =
4
.
In this case
I =
_
/4
0
4 sin
2
ucos u
cos u
du
= 4
_
/4
0
sin
2
udu
= 2
_
/4
0
_
1 cos 2u
_
du.
Thus
I = 2
_
u
1
2
sin 2u
_
/4
0
.
Consequently,
I =
1
2
1 .
013 10.0 points
Evaluate the integral
I =
_
/4
0
3 + 3 tan
2
x
cos
2
x
dx .
1. I = 7
2. I = 5
3. I = 6
4. I = 3
5. I = 4 correct
Explanation:
Since
1
cos
2
x
= sec
2
x ,
we see that
3 + 3 tan
2
x
cos
2
x
= (3 + 3 tan
2
x)sec
2
x .
On the other hand,
d
dx
tan x = sec
2
x .
So if we set u = tan x, then
du = sec
2
x dx
while
x = 0 = u = 0 ,
x =
4
= u = 1 .
In this case,
I =
_
1
0
(3 + 3u
2
) du =
_
3u +u
3
_
1
0
.
Consequently,
I = 4 .
014 10.0 points
Evaluate the integral
I =
_
ln 3
0
x e
x
2
e
x
2
+ 4
dx .
1. I = 3
6
2. I = 2
_
3
6
_
Version 047 L EXAM 1 guntel (55200) 8
3. I =
1
2
_
3
6
_
4. I =
5 correct
5. I = 2
_
5
_
6. I =
1
2
_
5
_
Explanation:
The presence of the term xe
x
2
in the nu-
merator suggests the substitution
u = e
x
2
+ 4 ,
for then
du = 2xe
x
2
dx .
In this case
I =
_
7
5
1
2u
1/2
du =
_
u
1/2
_
7
5
.
Consequently,
I =
5 .
015 10.0 points
A colony of feral cats is increasing at a rate
of 5 +2t cats per year (where t is measured in
years). By how much does the colony increase
increase in size between the fourth and tenth
years?
1. increases by 114 cats correct
2. increases by 119 cats
3. increases by 124 cats
4. increases by 134 cats
5. increases by 129 cats
Explanation:
Since the rate of change in the size of the
feral cat population is
dN
dt
= 5 + 2t ,
the change in size from year 4 to year 10 is
given by the integral
_
10
4
dN
dt
dt =
_
10
4
(5 + 2t) dt .
Consequently, the population increases by
_
5t +t
2
_
10
4
= 114 cats .
016 10.0 points
The shaded region in the gure
x
y
is bounded by the graphs of
f(x) = x
3
x
2
x + 1 , g(x) = x + 1 .
Find the area of this region.
1. area =
97
8
sq. units
2. area =
49
12
sq. units
3. area =
5
4
sq. units
4. area =
25
12
sq. units
5. area =
37
12
sq. units correct
Explanation:
Version 047 L EXAM 1 guntel (55200) 9
To set up the denite integrals determing
the shaded region we need to nd the x-
coordinates of the points of intersection of
the two graphs. Now
f(x) g(x) = x
3
x
2
2x
= x(x 2)(x + 1).
Thus the graphs intersect when x = 1, 0, 2,
and so the required area is given by
_
0
1
(f(x) g(x)) dx +
_
2
0
(g(x) f(x)) dx.
But
_
0
1
(x
3
x
2
2x) dx
=
_
1
4
x
4
1
3
x
3
x
2
_
0
1
=
5
12
.
On the other hand,
_
2
0
(x
3
+x
2
+ 2x) dx
=
_
1
4
x
4
+
1
3
x
3
+x
2
_
2
0
=
8
3
.
Consequently,the shaded region has
area =
37
12
sq. units .
017 10.0 points
Find the volume, V , of the solid generated
by rotating about the x-axis the region en-
closed by the graphs of
y = sec x, x = 0, y = 0, x =
3
.
1. V = cu. units
2. V =
3
cu. units
3. V = ln
_
1
2
+
3
_
cu. units
4. V =
8
3
cu. units
5. V =
3 cu. units correct
Explanation:
The solid is generated by rotating the re-
gion
/3
about the x-axis. The cross-section perpen-
dicular to the x-axis has area
A(x) = y
2
= sec
2
x .
Consequently,
V =
_
3
0
sec
2
x dx =
_
tan x
_
3
0
= tan
3
=
3 cu. units
.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- M408L Exam 1Document9 pagesM408L Exam 1Nathan ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Shreve I I Solutions Chapter 07Document8 pagesShreve I I Solutions Chapter 07Anirudh KodaliPas encore d'évaluation
- De ShawDocument10 pagesDe ShawNishant GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Finance Formula SheetDocument2 pagesFinance Formula SheetBrandon RaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Ibig 04 08Document45 pagesIbig 04 08Russell KimPas encore d'évaluation
- ESPM 50ac MIDTERM Exam Study Guide K WorthyDocument3 pagesESPM 50ac MIDTERM Exam Study Guide K WorthyClaire YoonPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam P Formula SheetDocument14 pagesExam P Formula SheetToni Thompson100% (4)
- CPP For Financial Mathematics Cpp-Book-SolutionsDocument11 pagesCPP For Financial Mathematics Cpp-Book-SolutionsEmmanuelDasiPas encore d'évaluation
- Investment Banking GuideDocument3 pagesInvestment Banking GuidezzzzzzPas encore d'évaluation
- M&a Interview QuestionsDocument1 pageM&a Interview QuestionsJack JacintoPas encore d'évaluation
- CQF January 2014 Maths Primer Calculus ExercisesDocument2 pagesCQF January 2014 Maths Primer Calculus ExercisesShravan VenkataramanPas encore d'évaluation
- IBIG 02 01 Walk Through Resume GuideDocument24 pagesIBIG 02 01 Walk Through Resume GuideSuhasPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution Manual For Shreve 2Document84 pagesSolution Manual For Shreve 2sss1192Pas encore d'évaluation
- IB Total Interview GuideDocument82 pagesIB Total Interview GuideNicole GiacalonePas encore d'évaluation
- Solow Growth ModelDocument30 pagesSolow Growth ModelNadeem RaoPas encore d'évaluation
- BBG Ticker List - 2017Document1 475 pagesBBG Ticker List - 2017Rahul PatelPas encore d'évaluation
- (WSO) Behavioral Interview Guide 3eDocument107 pages(WSO) Behavioral Interview Guide 3egreenpostitPas encore d'évaluation
- Bank Modelling ValuationDocument4 pagesBank Modelling ValuationQuofi SeliPas encore d'évaluation
- Merger Model Sample BIWS JobSearchDigestDocument7 pagesMerger Model Sample BIWS JobSearchDigestCCerberus24Pas encore d'évaluation
- Manual To ShreveDocument64 pagesManual To ShreveIvan Tay100% (1)
- M408L 2 S09-SachseDocument8 pagesM408L 2 S09-SachseNathan ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- M408L Exam 2Document9 pagesM408L Exam 2Nathan ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- BCA SEM 3 Computer Oriented Numerical Methods BC0043Document10 pagesBCA SEM 3 Computer Oriented Numerical Methods BC0043Sreejithe Thummarukudy75% (4)
- S2 NRSm3 PDFDocument26 pagesS2 NRSm3 PDFbomtozorPas encore d'évaluation
- Quest HW1 SolutionsDocument6 pagesQuest HW1 Solutionsellie<3Pas encore d'évaluation
- 175 Fall2009 Final SolDocument6 pages175 Fall2009 Final Solnurullah_bulutPas encore d'évaluation
- 2010 Maths Advanced Higher Finalised Marking InstructionsDocument9 pages2010 Maths Advanced Higher Finalised Marking InstructionsQwaAlmanlawiPas encore d'évaluation
- MA1521 Solution3Document5 pagesMA1521 Solution3Ray TanPas encore d'évaluation
- First Year Calculus: WwlchenDocument21 pagesFirst Year Calculus: WwlchenGanesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 105 Practice Exam 3 SolutionsDocument3 pagesMath 105 Practice Exam 3 SolutionsexamkillerPas encore d'évaluation
- Ass Dca2101Document10 pagesAss Dca2101tera baapPas encore d'évaluation
- Solutions To Exercises 7.1: X Has Period TDocument16 pagesSolutions To Exercises 7.1: X Has Period TTri Phương NguyễnPas encore d'évaluation
- HW 2 Solutions For CalculusDocument9 pagesHW 2 Solutions For CalculusNguyen PhamPas encore d'évaluation
- Number of Movies RentedDocument11 pagesNumber of Movies RentedDaniela BerenicePas encore d'évaluation
- Jan98 MA1002 CalculusDocument6 pagesJan98 MA1002 CalculusZama MakhathiniPas encore d'évaluation
- h1 205Document13 pagesh1 205lowgangstaPas encore d'évaluation
- HW2 ProblemsDocument5 pagesHW2 ProblemsWilliam RodzewichPas encore d'évaluation
- Soln1 PsDocument6 pagesSoln1 PsRafran Rosly100% (1)
- HW 01 SolutionsDocument11 pagesHW 01 Solutionsellie<3Pas encore d'évaluation
- AY14-15 Sem2 M63 LE5 AnsDocument5 pagesAY14-15 Sem2 M63 LE5 AnsNo OnePas encore d'évaluation
- Numerical DifferentiationDocument11 pagesNumerical DifferentiationtsamuelsPas encore d'évaluation
- BINOMIAL SeriesDocument25 pagesBINOMIAL SeriesBench AminPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematical Methods For Physics 2Document62 pagesMathematical Methods For Physics 2horvath346Pas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Algeb ProjectDocument17 pagesAdvanced Algeb ProjectdiomPas encore d'évaluation
- Tanydy: Arctan X DXDocument9 pagesTanydy: Arctan X DXartecmkPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 16 Exponential Functions: EXERCISE 64 Page 136Document23 pagesChapter 16 Exponential Functions: EXERCISE 64 Page 136Hugo QuispePas encore d'évaluation
- Integration 110304071651 Phpapp01Document19 pagesIntegration 110304071651 Phpapp01Maan UsmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Midterm 100 SolDocument6 pagesMidterm 100 Solsfluk2Pas encore d'évaluation
- Techniques of IntegrationDocument61 pagesTechniques of IntegrationAma PredaPas encore d'évaluation
- MA1505 Tutorial Solution 1Document6 pagesMA1505 Tutorial Solution 1Bilguun BatboldPas encore d'évaluation
- 3 MethodsofintegrationDocument8 pages3 Methodsofintegrationapi-268267969Pas encore d'évaluation
- TFY4305 Solutions Exercise Set 1 2014: Problem 2.2.3Document4 pagesTFY4305 Solutions Exercise Set 1 2014: Problem 2.2.3Abu Bakar SiddiquePas encore d'évaluation
- m820 Sol 2011Document234 pagesm820 Sol 2011Tom DavisPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculus Late 10 Techniques of Integration PDFDocument20 pagesCalculus Late 10 Techniques of Integration PDFEatingbananaPas encore d'évaluation
- Final CribDocument10 pagesFinal CribAmber LucasPas encore d'évaluation
- Integral Calculus Module 2Document3 pagesIntegral Calculus Module 2AldzPas encore d'évaluation
- Pgdca-123 ConamDocument10 pagesPgdca-123 Conamrajendrarajpurohit19Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lagrange Multivariate InterpolationDocument9 pagesLagrange Multivariate InterpolationDeewakar SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- MCSE004 Dec2013 SolutionDocument14 pagesMCSE004 Dec2013 SolutionajayPas encore d'évaluation
- Muller's Method: Numerical Analysis - MTH603Document7 pagesMuller's Method: Numerical Analysis - MTH603Sandesh AhirPas encore d'évaluation
- Med. Term. 2aDocument27 pagesMed. Term. 2aNathan ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- cc306 1aDocument41 pagescc306 1aNathan ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Chemistry 1 OverallDocument18 pagesOrganic Chemistry 1 OverallNathan ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Med. Term. 2aDocument27 pagesMed. Term. 2aNathan ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- cc306 1bDocument26 pagescc306 1bNathan ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- cc306 0Document39 pagescc306 0Nathan ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- cc306 1bDocument26 pagescc306 1bNathan ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Med. Term. 1aDocument41 pagesMed. Term. 1aNathan ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- MIT Electric Field Notes, Electric Fields and Discrete Charge DistributionsDocument32 pagesMIT Electric Field Notes, Electric Fields and Discrete Charge DistributionsNathan ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- MIT Electric Field Notes, Electric Fields and Discrete Charge DistributionsDocument32 pagesMIT Electric Field Notes, Electric Fields and Discrete Charge DistributionsNathan ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- MIT Electric Field Notes, Electric PotentialDocument29 pagesMIT Electric Field Notes, Electric PotentialNathan ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- MIT Electric Field Notes, Gauss's LawDocument39 pagesMIT Electric Field Notes, Gauss's LawNathan ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- MIT Electric Field Notes, CapacitanceDocument44 pagesMIT Electric Field Notes, CapacitanceNathan ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- MIT Electric Field Notes, Columb's LawDocument41 pagesMIT Electric Field Notes, Columb's LawNathan ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Phy317l 5Document15 pagesPhy317l 5Nathan ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Phy317l 8Document12 pagesPhy317l 8Nathan ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Phy317l 3Document9 pagesPhy317l 3Nathan ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Phy317l 1Document4 pagesPhy317l 1Nathan ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Phy317l 2Document5 pagesPhy317l 2Nathan ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Phy317l 4Document19 pagesPhy317l 4Nathan ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- M408L - 2 - S09 (Makeup) - SachseDocument8 pagesM408L - 2 - S09 (Makeup) - SachseNathan ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Phy317l 9Document11 pagesPhy317l 9Nathan ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- Phy317l 10Document7 pagesPhy317l 10Nathan ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- M408L Exam 3Document9 pagesM408L Exam 3Nathan ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- M408L 1 S09-SachseDocument10 pagesM408L 1 S09-SachseNathan ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- M408L 2 S09-SachseDocument8 pagesM408L 2 S09-SachseNathan ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- M408L Exam 3Document5 pagesM408L Exam 3Nathan ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- M408L - 1 - S09 (Makeup) - SachseDocument11 pagesM408L - 1 - S09 (Makeup) - SachseNathan ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- M408L Exam 3Document11 pagesM408L Exam 3Nathan ThaiPas encore d'évaluation
- RATIODocument54 pagesRATIOShubham TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- FP1 Revision SheetDocument3 pagesFP1 Revision SheetKeshan Asbury100% (1)
- Math 9 Q4 Week 1Document10 pagesMath 9 Q4 Week 1Rocky Parinas DuquePas encore d'évaluation
- 11 Business Math Vol 1 EM PDFDocument232 pages11 Business Math Vol 1 EM PDFpradheepmsc2010Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chap 7Document11 pagesChap 7Nicoleta StPas encore d'évaluation
- Portfolio Maths TuftsDocument2 pagesPortfolio Maths Tuftsapi-370405606Pas encore d'évaluation
- TOS (First Summative)Document5 pagesTOS (First Summative)Mary Cris GoPas encore d'évaluation
- Residues and PolesDocument6 pagesResidues and PolesMuzna ZainabPas encore d'évaluation
- MEEM 3700 Mechanical VibrationsDocument11 pagesMEEM 3700 Mechanical VibrationsGOUAL SaraPas encore d'évaluation
- K03052 - 20200424155139 - 7.1 Integration - Integration by Parts MethodDocument19 pagesK03052 - 20200424155139 - 7.1 Integration - Integration by Parts Methodhariz syazwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Intervention Plan MATHEMATICSDocument8 pagesIntervention Plan MATHEMATICSLily CruzPas encore d'évaluation
- System of Linear EquationsDocument145 pagesSystem of Linear EquationsAhmed YasserPas encore d'évaluation
- Anees Hussain: Xi Mathematics FormulaeDocument33 pagesAnees Hussain: Xi Mathematics FormulaeRida TayyabPas encore d'évaluation
- JEE Adv. PYQsDocument58 pagesJEE Adv. PYQspardhan jiPas encore d'évaluation
- Computational Seismology: A Practical Introduction: October 2016Document8 pagesComputational Seismology: A Practical Introduction: October 2016Vladimir BratovPas encore d'évaluation
- Errata Alexander Sadiku 3rdedition Chris MackDocument3 pagesErrata Alexander Sadiku 3rdedition Chris MackDr-Jihad BaghdadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Jyoti Shukla (SME)Document14 pagesJyoti Shukla (SME)dhirajkapilaPas encore d'évaluation
- AMC8 Selected Problems (Mean, Median, Mode)Document2 pagesAMC8 Selected Problems (Mean, Median, Mode)spellscroll.comPas encore d'évaluation
- Target 1 - Level 1 - Chapter 1Document20 pagesTarget 1 - Level 1 - Chapter 1vishalPas encore d'évaluation
- Ujian Math Form 1 2020Document8 pagesUjian Math Form 1 2020Alf SheryPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4.7 Solutions of Triangles PDFDocument5 pagesChapter 4.7 Solutions of Triangles PDFjiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic: Coordinate Systems and TransformationDocument33 pagesTopic: Coordinate Systems and TransformationSri DharanPas encore d'évaluation
- SATmathwk03 (5e)Document14 pagesSATmathwk03 (5e)Hoàng HảiPas encore d'évaluation
- IMO Level1 Mock5 Class6Document17 pagesIMO Level1 Mock5 Class6Saket KhuranaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nonlinear Functional Analysis and Its ApplicationsDocument148 pagesNonlinear Functional Analysis and Its ApplicationsAntonio avilaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sets and Set Operations DalesandroDocument13 pagesSets and Set Operations DalesandroKhairy IsmailPas encore d'évaluation
- 30 IntegrationDocument3 pages30 IntegrationimaniceguyPas encore d'évaluation
- BaCal LAS-1 MELCs1-2Document4 pagesBaCal LAS-1 MELCs1-2Maria Angelica SandoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Jinivefsiti: Sultan LorisDocument13 pagesJinivefsiti: Sultan LorisSITI HAJAR BINTI MOHD LATEPIPas encore d'évaluation
- 2020 1 Me Munsyi Abdullah ADocument7 pages2020 1 Me Munsyi Abdullah ALIANG HUI YI MoePas encore d'évaluation