Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Extracorporial Circulation (Ecc) Heart Lung Machine Cardio-Pulmonary Bypass (CPB)
Transféré par
ameerabestTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Extracorporial Circulation (Ecc) Heart Lung Machine Cardio-Pulmonary Bypass (CPB)
Transféré par
ameerabestDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
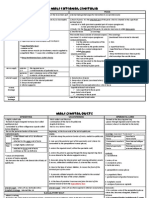
Heart operations, may be; CLOSED heart surgery - while the heart is beating - CMC - OPCAB - closure PDA
- coarctation of aorta OPEN heart surgery - non beating heart - valve replacement - repair of congenital defects (ASD, VSD) - coronary surgery (ON-PUMP)
Myocardial preservation = hypothermia MR & oxygen demand 1. Coronary perfusion hypothermia - cardioplegic solution (cold, 4oC, KCl) i) infused into aortic arch ii) direct into coronary ostia in aortic regurge iii) retrograde thru coronary sinus in LMCA disease 2. Local hypothermia - ice / cold saline on the heart 3. Systemic hypothermia Mild Moderate Severe Profound (total circulatory arrest) * in case of extensive aortic aneurysm
EXTRACORPORIAL CIRCULATION (ECC) HEART LUNG MACHINE CARDIO-PULMONARY BYPASS (CPB) Definition: a machine that replaces the function of the heart (pumping) & lung (oxygenation) during cardiac surgery Target: 1. Bloodless field 2. Motionless heart 3. Protection of vitas organ 4. Myocardial protection 5. Preservation of blood Components: 1. Reservoir 2. Oxygenator 3. Roller pump 4. Heater-cooler Steps of procedure 1. Mid sternotomy 2. Heparin 3. Cannulation - SVC + IVC - aortic arch 4. Deox. blood reservoir oxygenator 5. Oxygenated blood roller pump ascending aorta 6. Filter 7. Cooling 8. Aortic cross clamp @ ascending aorta 9. Cardioplegia @ aortic root 10. Protamine sulphate (neutralize heparin)
32 oC 25 oC 20 oC 16-18 oC
Complications of ECC 1. Cerebral stroke & neurocognitive defect 2. Psychological changes - psychosis - depression 3. Bleeding - 2ry to platelet dysfx 4. Renal insufficiency 5. Pulmonary insufficiency, lung atelectasis, ARDS, post perfusion lung 6. Cardiac complications - peri-operative MI - low COP syndrome - stone heart syndrome 7. Immunosupression 8. GIT complications - ileus - stress ulcer - acute pancreatitis
ISCHAEMIC HEART DISEASE Anatomy of coronary artery RIGHT CORONARY LEFT MAIN CORONARY ARTERY ARTERY PDA LAD Cx Diagonal OM branch branch
CORONARY ARTERY BYPASS GRAFT SURGERY (CABG) Indications 1. Left main stem coronary stenosis 2. 3 vessels disease 3. IHD in diabetic pt 4. Combined CABG & valvular surgery Approach = median sternotomy Grafts (conduits) Arterial Free arterial graft: - radial artery - right gastroepiploic artery Pedicle graft: - internal mammary artery
Venous Reversed long saphenous vein
*most commonly used graft = saphenous vein graft (lengthy, can be used for revascularization of many diseased vessels) *best graft used = internal mammary artery (long term patency) OFF-PUMP CABG (beating heart) - bleeding intracoronary shunt - conserve blood cell saver - heart movement stabilizer Complications 1. Peri-operative infarction 2. Low COP state 3. Arrythmias 4. Bleeding 5. Non-cardiac complications of other organs (brain, lung, kidney)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Acute Circulatory FailureDocument29 pagesAcute Circulatory FailureSanthoshi Sadhanaa SankarPas encore d'évaluation
- Heart FailureDocument4 pagesHeart FailurersheedmahdiiPas encore d'évaluation
- Heart FailureDocument1 pageHeart FailureDarell M. BookPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardio and Hema - DR PueyoDocument161 pagesCardio and Hema - DR Pueyoapi-3735995100% (2)
- Congestive Heart FailureDocument4 pagesCongestive Heart FailureZosmita Shane GalgaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Disease of Myocardium and PericardiumiDocument49 pagesDisease of Myocardium and PericardiumiDeepika LamichhanePas encore d'évaluation
- Drugs Used in The Treatment of Congestive Heart FailureDocument18 pagesDrugs Used in The Treatment of Congestive Heart Failurekarina azlia amandaPas encore d'évaluation
- CardiologyDocument52 pagesCardiologyDexzal100% (2)
- Cardiopulmonary BypassDocument62 pagesCardiopulmonary BypassNidya Putri100% (1)
- Chapter 41. Nursing Care of The Child With A Cardiovascular Disorder TermDocument11 pagesChapter 41. Nursing Care of The Child With A Cardiovascular Disorder TermJœnríčk AzueloPas encore d'évaluation
- Management of ShockDocument18 pagesManagement of ShockObongsamuel IdiongPas encore d'évaluation
- CardiovascularDocument155 pagesCardiovascularEric VeranoPas encore d'évaluation
- MEDICAL PATHOLOGIES - CardiovascularDocument6 pagesMEDICAL PATHOLOGIES - Cardiovascularngachangong victorinePas encore d'évaluation
- Lec 4 A - StrokeDocument9 pagesLec 4 A - StrokeEmily MurrayPas encore d'évaluation
- Intracranial Hypertension: Miroslav GajdošDocument30 pagesIntracranial Hypertension: Miroslav GajdošKobi DabushPas encore d'évaluation
- Congenital Heart Disease (CHD) : Kussia Ayano (MD)Document54 pagesCongenital Heart Disease (CHD) : Kussia Ayano (MD)Yemata HailuPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiology DR Osama MahmoudDocument138 pagesCardiology DR Osama MahmoudIsmail Habib100% (4)
- Ipd - KardiologiDocument116 pagesIpd - KardiologiWynda MuljonoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiology HFDocument11 pagesCardiology HFdhayemaruPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiology-6 CADDocument20 pagesCardiology-6 CADMahmoud RamadanPas encore d'évaluation
- ER & CCU ProtocolDocument14 pagesER & CCU ProtocolatinafansifPas encore d'évaluation
- Med Surg Cardiovascular SystemDocument154 pagesMed Surg Cardiovascular SystembamfalconPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiovascular FunctionDocument5 pagesCardiovascular FunctionJohn Fritz Gerald BascoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac FailureDocument63 pagesCardiac FailureNina OaipPas encore d'évaluation
- Heart Failure by IvsDocument66 pagesHeart Failure by IvsArianne LasamPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiology-3 HFDocument17 pagesCardiology-3 HFMahmoud RamadanPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiovascular Nursing: Study Online atDocument7 pagesCardiovascular Nursing: Study Online atLilly DayePas encore d'évaluation
- CCRN-PCCN-CMC Review Cardiac Part 3Document18 pagesCCRN-PCCN-CMC Review Cardiac Part 3Giovanni MictilPas encore d'évaluation
- CLASS 2 Low Cardiac Output Syndrome in Cardiac SurgeryDocument53 pagesCLASS 2 Low Cardiac Output Syndrome in Cardiac SurgeryjuanolivelloPas encore d'évaluation
- Increased Intracranial Pressure: DR - Muhammad Yusuf, Sps FinsDocument61 pagesIncreased Intracranial Pressure: DR - Muhammad Yusuf, Sps FinsFidhiyahR100% (1)
- MTE Diagnosis and Manag ShockDocument52 pagesMTE Diagnosis and Manag ShockGarbha JmrsPas encore d'évaluation
- DR Dhiman BanikCariogenic Shock Final 2022 DDDocument59 pagesDR Dhiman BanikCariogenic Shock Final 2022 DDCloudySkyPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiogenic Shock - SWDocument41 pagesCardiogenic Shock - SWAyu LuthfiyahPas encore d'évaluation
- CardiovascularDocument155 pagesCardiovascularWilliam Franz SyPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiopulmonary BypassDocument40 pagesCardiopulmonary BypassParvathy R NairPas encore d'évaluation
- CardiologyDocument52 pagesCardiologyusmani_nida1Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiomyopathy - PericarditisDocument16 pagesCardiomyopathy - PericarditismalekPas encore d'évaluation
- Rutherford CH96 - Unusual Conditions of The Carotid ArteryDocument3 pagesRutherford CH96 - Unusual Conditions of The Carotid Arteryomamah.almousaPas encore d'évaluation
- Heart Failure and ShockDocument34 pagesHeart Failure and Shockfrenee aradanasPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac EmergencyDocument56 pagesCardiac Emergency21rayhanf100% (1)
- Mitral RegurgitationDocument43 pagesMitral Regurgitationraissasafitry100% (1)
- Anesthesia For Neurosurg2Document42 pagesAnesthesia For Neurosurg2Praveen RamasamyPas encore d'évaluation
- Heart FaiilureDocument8 pagesHeart Faiilureagar agarPas encore d'évaluation
- 9, CHF BestDocument43 pages9, CHF BestauPas encore d'évaluation
- CardioDocument46 pagesCardiodinglasanerica57Pas encore d'évaluation
- Zhao Mingyao BMC - Zzu. 2004-3-8Document30 pagesZhao Mingyao BMC - Zzu. 2004-3-8api-19916399Pas encore d'évaluation
- Systolic Dysfunction:: Types of Heart FailureDocument13 pagesSystolic Dysfunction:: Types of Heart FailureElisabeth F. OjhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Congenital Heart Disease (CHD)Document89 pagesCongenital Heart Disease (CHD)jefferyPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiology Ebook Notes PDFDocument59 pagesCardiology Ebook Notes PDFsugiswePas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac Care and COVID-19: Perspectives in Medical PracticeD'EverandCardiac Care and COVID-19: Perspectives in Medical PracticePas encore d'évaluation
- Perfusion for Congenital Heart Surgery: Notes on Cardiopulmonary Bypass for a Complex Patient PopulationD'EverandPerfusion for Congenital Heart Surgery: Notes on Cardiopulmonary Bypass for a Complex Patient PopulationÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (2)
- Internal Medicine: Over 200 Case StudiesD'EverandInternal Medicine: Over 200 Case StudiesÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (17)
- Immediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuideD'EverandImmediate Life Support for healthcare Practitioners: A Step-By-Step GuidePas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac MappingD'EverandCardiac MappingMohammad ShenasaPas encore d'évaluation
- Guide to Canine and Feline ElectrocardiographyD'EverandGuide to Canine and Feline ElectrocardiographyRuth WillisPas encore d'évaluation
- Critical Decisions in Emergency and Acute Care ElectrocardiographyD'EverandCritical Decisions in Emergency and Acute Care ElectrocardiographyPas encore d'évaluation
- E.coli, Klebsiella, Proteus EtcDocument3 pagesE.coli, Klebsiella, Proteus EtcameerabestPas encore d'évaluation
- Cme Bronchial AsthmaDocument28 pagesCme Bronchial AsthmaameerabestPas encore d'évaluation
- @acute Nephritic SyndromeDocument3 pages@acute Nephritic Syndromeameerabest100% (1)
- @acute Nephrotic SyndromeDocument1 page@acute Nephrotic SyndromeameerabestPas encore d'évaluation
- @ductal CarcinomaDocument1 page@ductal CarcinomaameerabestPas encore d'évaluation
- Burn LectureDocument53 pagesBurn LectureHusna NadiaPas encore d'évaluation
- @sex SteroidsDocument2 pages@sex SteroidsameerabestPas encore d'évaluation
- @hypothalamic HormonesDocument1 page@hypothalamic HormonesameerabestPas encore d'évaluation
- @contraceptives DrugsDocument1 page@contraceptives DrugsameerabestPas encore d'évaluation
- @drugs Acting On Uterus and Erectile DysfunctionDocument2 pages@drugs Acting On Uterus and Erectile DysfunctionameerabestPas encore d'évaluation
- @histology of Male Genital SystemDocument6 pages@histology of Male Genital SystemameerabestPas encore d'évaluation
- Genital EmbryologyDocument6 pagesGenital EmbryologyameerabestPas encore d'évaluation
- @ovary Cyst ComparisonDocument2 pages@ovary Cyst ComparisonameerabestPas encore d'évaluation
- @tumors of The Breast 1Document2 pages@tumors of The Breast 1ameerabestPas encore d'évaluation
- Anatomy of Male GenitaliaDocument4 pagesAnatomy of Male GenitaliaameerabestPas encore d'évaluation
- @ovarian Tumors ComparisonDocument6 pages@ovarian Tumors ComparisonameerabestPas encore d'évaluation
- @ovary Cyst ComparisonDocument2 pages@ovary Cyst ComparisonameerabestPas encore d'évaluation
- Semen AnalysisDocument3 pagesSemen Analysisameerabest80% (5)
- @male PathoDocument8 pages@male Pathoameerabest100% (2)
- Genitourinarybacteria Comparisons PDFDocument7 pagesGenitourinarybacteria Comparisons PDFameerabest100% (1)
- Patho Male BreastDocument1 pagePatho Male BreastameerabestPas encore d'évaluation
- Histology Female PDFDocument5 pagesHistology Female PDFameerabestPas encore d'évaluation
- Genitourinarybacteria Comparisons PDFDocument7 pagesGenitourinarybacteria Comparisons PDFameerabest100% (1)
- @non Neoplastic Non Inflammatory Lesions of The BreastDocument2 pages@non Neoplastic Non Inflammatory Lesions of The BreastameerabestPas encore d'évaluation
- Nota Patho PDFDocument8 pagesNota Patho PDFameerabestPas encore d'évaluation
- OSCE DermaDocument8 pagesOSCE DermaameerabestPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac ExamDocument7 pagesCardiac ExamameerabestPas encore d'évaluation
- #Chest TraumasDocument4 pages#Chest Traumasameerabest100% (3)
- Virology of Hepatitis ADocument33 pagesVirology of Hepatitis AameerabestPas encore d'évaluation
- PleuraDocument6 pagesPleuraameerabest100% (1)
- Neuromuscular Cardiovascular Hypocalcemia: Hypermagnesemia (Symptoms)Document2 pagesNeuromuscular Cardiovascular Hypocalcemia: Hypermagnesemia (Symptoms)Glormina Asprec AvenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Concept PaperDocument14 pagesConcept PaperRyan Maghanoy100% (3)
- Anatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive SystemDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Male Reproductive SystemAdor AbuanPas encore d'évaluation
- September 26, 2018 by Sagar Aryal: Antigen-Properties, Types and Determinants of AntigenicityDocument23 pagesSeptember 26, 2018 by Sagar Aryal: Antigen-Properties, Types and Determinants of AntigenicityEzekiel GantiedPas encore d'évaluation
- Conversion of ASTM To TBP and EFVDocument111 pagesConversion of ASTM To TBP and EFVsyedmuhammadtariquePas encore d'évaluation
- Veterinary Internal Medicne - 2008 - Bruchim - Heat Stroke in Dogs A Retrospective Study of 54 Cases 1999 2004 andDocument9 pagesVeterinary Internal Medicne - 2008 - Bruchim - Heat Stroke in Dogs A Retrospective Study of 54 Cases 1999 2004 andGuillermo MuzasPas encore d'évaluation
- Patients' Perceptions of Barriers To Self-Managing Bipolar DisorderDocument10 pagesPatients' Perceptions of Barriers To Self-Managing Bipolar DisorderMilton MurilloPas encore d'évaluation
- Sop Icu H & FW 12725 28.04.2018Document20 pagesSop Icu H & FW 12725 28.04.2018shah007zaadPas encore d'évaluation
- Palmer Et Al v. Amazon - Com Inc Et AlDocument41 pagesPalmer Et Al v. Amazon - Com Inc Et AlGeekWirePas encore d'évaluation
- Ent AssessmentDocument23 pagesEnt AssessmentPdianghunPas encore d'évaluation
- Pyometra in A Cat: A Clinical Case Report: November 2021Document7 pagesPyometra in A Cat: A Clinical Case Report: November 2021Ronny Alberto GallegoPas encore d'évaluation
- ISC Class 12 Biology Syllabus: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 18Document18 pagesISC Class 12 Biology Syllabus: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 18HemantPas encore d'évaluation
- RRL Local and ForeignDocument2 pagesRRL Local and ForeignArjelyn Loquisan MonsalesPas encore d'évaluation
- Hospital IndustryDocument30 pagesHospital IndustryArun.RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Efficacy of Doctorvox On Mutational FalsettoDocument8 pagesEfficacy of Doctorvox On Mutational FalsettoANA CRISTINA MENDEZ DIAZPas encore d'évaluation
- Clandestine Sorbolene !!: Sorbolene Cream, What Is It & What Is It Made From ?Document6 pagesClandestine Sorbolene !!: Sorbolene Cream, What Is It & What Is It Made From ?Indika Lakshmana PathirathnePas encore d'évaluation
- Fidelis Drug List 2018Document80 pagesFidelis Drug List 2018Annie AnnaPas encore d'évaluation
- Apollo Excellence Report 2019 e VersionDocument289 pagesApollo Excellence Report 2019 e VersionrajPas encore d'évaluation
- English: Quarter 4 - Module 7 Making GeneralizationsDocument16 pagesEnglish: Quarter 4 - Module 7 Making Generalizationslenra esoj lasorPas encore d'évaluation
- Demography Using Cemetery DataDocument5 pagesDemography Using Cemetery DatamjbdobleuPas encore d'évaluation
- Surgery MCQDocument24 pagesSurgery MCQMoiz Khan88% (8)
- Community Radio Script - Why We Have COVID Vaccines NowDocument2 pagesCommunity Radio Script - Why We Have COVID Vaccines NowBenBuilds PHPas encore d'évaluation
- Spontaneous Pneumothorax - Management Feb15Document12 pagesSpontaneous Pneumothorax - Management Feb15samuelPas encore d'évaluation
- Effect of Nasapana in The Management of Avabahuka A Case StudyDocument5 pagesEffect of Nasapana in The Management of Avabahuka A Case StudyEditor IJTSRDPas encore d'évaluation
- Cosmetology Library ResourcesDocument40 pagesCosmetology Library Resourcesemiliana magerusanPas encore d'évaluation
- Do No Harm by Henry Marsh ExtractDocument15 pagesDo No Harm by Henry Marsh ExtractAyu Hutami SyarifPas encore d'évaluation
- Traditional Indian MedicineDocument3 pagesTraditional Indian MedicineShashvita RatraPas encore d'évaluation
- Assessment Dianosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Dianosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationkyaw100% (1)
- 3.ALS Algorithms Advanced Life SupportDocument1 page3.ALS Algorithms Advanced Life SupportLucian Alin DinuPas encore d'évaluation
- Ôn Nư C Rút 2023Document49 pagesÔn Nư C Rút 2023Miss'a HeyllaPas encore d'évaluation