Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Anticipation Guide Rob Woller
Transféré par
Rob WollerDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Anticipation Guide Rob Woller
Transféré par
Rob WollerDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
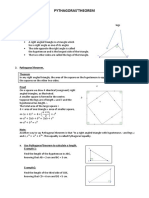
Anticipation Guide The Pythagorean Theorem
We have just learned about different types of triangles and their angle measures. The next topic to explore is the Pythagorean Theorem. You encountered the Pythagorean Theorem in Algebra, and possibly before that. Before reading section 4.4, carefully read each of the statements below and mark either an A for Agree or a D for Disagree in the Before column. Then, read the text and the examples in section 4.4. Once you have finished reading the section, review each statement. Do you still agree or disagree with each statement? Mark your opinion now in the After column. Correct the statements with which you disagree.
Before After
Statement The Pythagorean Theorem is named after a Greek philosopher and mathematician. The Pythagorean Theorem relates the side lengths of any triangle. In a right triangle, the right angle is formed by the legs. The formula for the Pythagorean Theorem is: 2 + 2 = 2 , where a and b are the legs and c is the hypotenuse of a right triangle. A right triangle with legs of 6m and 8m has a hypotenuse of 14 m. In the third picture above, the Pythagorean Theorem can be used to find the length of the ladder needed to reach a certain height on the house. A Pythagorean triple is a group of three numbers that could be the lengths of the sides of a right triangle. The Pythagorean Theorem can be interpreted as: the sum of the areas of the two squares created from the legs of a right triangle is equal to the area of the square created from the hypotenuse of the right triangle. Hint: Look at the second picture above.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- The Not-So-Scary Guide to Basic TrigonometryD'EverandThe Not-So-Scary Guide to Basic TrigonometryÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Three-Dimensional Figures with AnswersD'EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Geometry: Three-Dimensional Figures with AnswersPas encore d'évaluation
- Research Paper On Pythagorean TheoremDocument6 pagesResearch Paper On Pythagorean Theoremtdqmodcnd100% (1)
- Essay Outline - The Process of Phytagoras TheoremDocument2 pagesEssay Outline - The Process of Phytagoras TheoremAmar SafwanPas encore d'évaluation
- Applications of The Pythagorean TheoremDocument7 pagesApplications of The Pythagorean Theoremapi-290938633Pas encore d'évaluation
- Explore: Lesson 4: Pythagorean Theorem and Special Right TrianglesDocument53 pagesExplore: Lesson 4: Pythagorean Theorem and Special Right TrianglesKristabel Jullia ReyesPas encore d'évaluation
- ProjectDocument2 pagesProjectHiman ChauhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Pythagoras TheoremDocument29 pagesPythagoras TheoremSahil JindalPas encore d'évaluation
- Pythagoras Theorem LessonDocument3 pagesPythagoras Theorem LessonCruashai GTAPas encore d'évaluation
- Pythagorean TheoremDocument2 pagesPythagorean TheoremStephenPas encore d'évaluation
- Literature Review On Pythagoras TheoremDocument8 pagesLiterature Review On Pythagoras Theoremc5khavcy100% (1)
- Unit 5 SLMDocument2 pagesUnit 5 SLMapi-327041524Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pythagorean Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesPythagorean Lesson PlanLinda SchweitzerPas encore d'évaluation
- Section 7 Independent PracticeDocument18 pagesSection 7 Independent PracticejazzyPas encore d'évaluation
- GR09 Q3W08D00 H Mat 00 SLM GRDocument10 pagesGR09 Q3W08D00 H Mat 00 SLM GRAddy LovePas encore d'évaluation
- Verifying Pythagorn TheoremDocument6 pagesVerifying Pythagorn TheoremSanifer PlayzPas encore d'évaluation
- The Pythagorean TheoremDocument1 pageThe Pythagorean TheoremAbdulrahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics AssignmentDocument5 pagesMathematics AssignmentMishal HossainPas encore d'évaluation
- 17 Pythagoren TheoremDocument17 pages17 Pythagoren TheoremKristian MagsalinPas encore d'évaluation
- Research Paper On Pythagoras TheoremDocument6 pagesResearch Paper On Pythagoras Theoremxdhuvjrif100% (1)
- Grade 8-Term 3-Week 2-Day1Document20 pagesGrade 8-Term 3-Week 2-Day1Sabahath KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- First World WarDocument2 pagesFirst World WardefaultPas encore d'évaluation
- Solution: Solution:: 8-2 The Pythagorean Theorem and Its ConverseDocument31 pagesSolution: Solution:: 8-2 The Pythagorean Theorem and Its ConverseGERRYPas encore d'évaluation
- Pythagpras TheoremDocument1 pagePythagpras TheoremYoussef AmrPas encore d'évaluation
- DG TE Ch09Document42 pagesDG TE Ch09Florecita RiosPas encore d'évaluation
- MathDocument1 pageMathhk kwanPas encore d'évaluation
- MathsDocument1 pageMathsWilfred NnadiPas encore d'évaluation
- Pythagoras TheoremDocument1 pagePythagoras TheoremAlia KiranPas encore d'évaluation
- Using The Pythagorean Theorem in 3-Dimensional ShapesDocument7 pagesUsing The Pythagorean Theorem in 3-Dimensional ShapesFaiq Ali SutionoPas encore d'évaluation
- 12.4 Converse On TrianglesDocument12 pages12.4 Converse On TrianglesTonet Salago CanterePas encore d'évaluation
- The Six Trigonometric Functions and Reciprocals FunctionsDocument4 pagesThe Six Trigonometric Functions and Reciprocals FunctionsalvinPas encore d'évaluation
- Pythagoras Theorem PixiPPtDocument17 pagesPythagoras Theorem PixiPPtAmmaar Syed Year 9Pas encore d'évaluation
- L2-Apply P. T.: 8th Grade Unit 3: Geometric Applications of ExponentsDocument10 pagesL2-Apply P. T.: 8th Grade Unit 3: Geometric Applications of Exponentsapi-295961633Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pythagoras TheoremDocument2 pagesPythagoras TheoremMaria BeatriksPas encore d'évaluation
- Phytagorean TheoremDocument14 pagesPhytagorean TheoremyetriPas encore d'évaluation
- Env68 8 07 02 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 8 07 02 KCapi-367296283Pas encore d'évaluation
- FL G8 M07 Family+LetterDocument2 pagesFL G8 M07 Family+Letterahmed5030 ahmed5030Pas encore d'évaluation
- Putri Fitriyah Salsabila - B - Narasi Bhs InggrisDocument3 pagesPutri Fitriyah Salsabila - B - Narasi Bhs InggrisGenerasi BerkisahPas encore d'évaluation
- Pythagaros ThheroemDocument1 pagePythagaros ThheroemvinayakPas encore d'évaluation
- Colorful Playful Illustrative Pythagorean Theorem Education Presentation - 20240225 - 114846 - 0000Document13 pagesColorful Playful Illustrative Pythagorean Theorem Education Presentation - 20240225 - 114846 - 0000Xyn CelesPas encore d'évaluation
- c06PythagorasAndTrigonometry PDFDocument55 pagesc06PythagorasAndTrigonometry PDFmeenu100% (1)
- 8-2 The Pythagorean Theorem and Its ConverseDocument42 pages8-2 The Pythagorean Theorem and Its ConverseReeja Mathew0% (1)
- The Pythagorean TheoremDocument2 pagesThe Pythagorean Theoremjeehoonkim78Pas encore d'évaluation
- A LESSON PLAN For "Pythagorean Theorem" By: February 2019Document10 pagesA LESSON PLAN For "Pythagorean Theorem" By: February 2019Fave Chlair Misha FloresPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapt7 Pythagoras Thereom PDFDocument13 pagesChapt7 Pythagoras Thereom PDFMcNemarPas encore d'évaluation
- Math NotesDocument1 pageMath Notesthe wolf gaming JDBPas encore d'évaluation
- Env68 8 07 01 KCDocument1 pageEnv68 8 07 01 KCapi-367296283Pas encore d'évaluation
- Reciprocal Functions Also ImportantDocument4 pagesReciprocal Functions Also ImportantDivineJusticePas encore d'évaluation
- The Pythagoras TheoremDocument6 pagesThe Pythagoras TheoremNatthaphat SubphachaisirikulPas encore d'évaluation
- Pythagorean Theorem in BusinessDocument4 pagesPythagorean Theorem in BusinessDeelanshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Right TrianglesDocument13 pagesRight TrianglesMHARLOU TORINGPas encore d'évaluation
- Netright Triangle TheoremsDocument29 pagesNetright Triangle TheoremsFynn NiallPas encore d'évaluation
- Trignometry Presentation .Document13 pagesTrignometry Presentation .AYUSHPas encore d'évaluation
- Pythagoras ProjectDocument14 pagesPythagoras ProjectPriscylia KirojanPas encore d'évaluation
- 5 DaylessonDocument7 pages5 Daylessonapi-527940676Pas encore d'évaluation
- The Pythagorean Theorem Concept and ProofDocument1 pageThe Pythagorean Theorem Concept and ProofJejomar MotolPas encore d'évaluation
- Math 8 q3 Isosceles TriangleDocument21 pagesMath 8 q3 Isosceles Triangleallejahregala11Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pythagorean Theorem and PiDocument1 pagePythagorean Theorem and PishashwatsinhaPas encore d'évaluation
- Trigonometry - PresentationDocument99 pagesTrigonometry - PresentationsaifullahPas encore d'évaluation
- Colorful Playful Illustrative Pythagorean Theorem Education PresentationDocument13 pagesColorful Playful Illustrative Pythagorean Theorem Education Presentationbrandy57279Pas encore d'évaluation
- Math Module Quarter 4 L1Document5 pagesMath Module Quarter 4 L1Alex TutorPas encore d'évaluation
- MC Maths - Lesson Plans - Stage 6 - C03Document13 pagesMC Maths - Lesson Plans - Stage 6 - C03syasmiitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Evaluation ExamDocument3 pagesEvaluation ExamEmileandro Perito QuindiaganPas encore d'évaluation
- Circle and Rectangle Sum From P2 (R) Jan 21Document1 pageCircle and Rectangle Sum From P2 (R) Jan 21Aariyan K. ArkoPas encore d'évaluation
- Composition of ForceDocument14 pagesComposition of ForcePari GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Properties of Triangle Solved QuestionsDocument38 pagesProperties of Triangle Solved QuestionsKaran DoshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Geometry: Volume of Rectangular and Triangular PrismsDocument19 pagesGeometry: Volume of Rectangular and Triangular PrismsMedina WuistonPas encore d'évaluation
- The Symmetry of Things PDFDocument9 pagesThe Symmetry of Things PDFPrayag GowgiPas encore d'évaluation
- NetsDocument4 pagesNetsDtdc SenthlPas encore d'évaluation
- Rotational Symmetry Power PointDocument24 pagesRotational Symmetry Power Pointhmahlhubbs0% (1)
- 10th - Coordinate Geometry PDFDocument5 pages10th - Coordinate Geometry PDFhaloPas encore d'évaluation
- Tech. Draw. Module 12 Q4 WK 5 8 Jaa JCR 1Document28 pagesTech. Draw. Module 12 Q4 WK 5 8 Jaa JCR 1Genevieve Agno CaladPas encore d'évaluation
- SymmetryDocument43 pagesSymmetryDeepa Kapadia0% (1)
- Problems and Solutions IntermediateDocument6 pagesProblems and Solutions IntermediateGulit Radian WiyarnoPas encore d'évaluation
- Projection - Parallel and PerspectiveDocument26 pagesProjection - Parallel and PerspectiveGauravJainPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.2 NotesDocument8 pages3.2 NotesMrs. HedrickPas encore d'évaluation
- Trial Assessment For Geometry: Answer The Following Questions: 1-Complete The FollowingDocument3 pagesTrial Assessment For Geometry: Answer The Following Questions: 1-Complete The Followingmido titoPas encore d'évaluation
- 520386Document3 pages520386MuraliPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 13 - Pythagoras TheoremDocument2 pagesChapter 13 - Pythagoras TheoremJu WenPas encore d'évaluation
- SolidWorks Sketch Relations SummaryDocument2 pagesSolidWorks Sketch Relations Summaryxitta00Pas encore d'évaluation
- ETC ExtraDocument11 pagesETC Extraobelix2Pas encore d'évaluation
- MSE2183 Tutorial Letter 102Document17 pagesMSE2183 Tutorial Letter 102Markus100% (1)
- Chapter 6 - ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTIONDocument35 pagesChapter 6 - ORTHOGRAPHIC PROJECTIONHumberto AnguloPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 6 2 Law of CosinesDocument25 pagesChapter 6 2 Law of CosinesJamie JimenezPas encore d'évaluation
- Vector Algebra - JEE Main 2024 January Question Bank - MathonGoDocument4 pagesVector Algebra - JEE Main 2024 January Question Bank - MathonGoGaurav YadavPas encore d'évaluation
- Spherical Trigonometry: Reuleaux TriangleDocument3 pagesSpherical Trigonometry: Reuleaux TriangleAchandraPas encore d'évaluation
- Third Round 1997 - 2010Document49 pagesThird Round 1997 - 2010Cristian MateiPas encore d'évaluation
- Igo 2016 - Problems & Solutions - EnglishDocument29 pagesIgo 2016 - Problems & Solutions - Englishhaivan850557350% (1)
- TKSSDocument22 pagesTKSSsignboonsgslPas encore d'évaluation
- 9th Geometrial Construction Study Guide SolvedDocument53 pages9th Geometrial Construction Study Guide SolvedauroraepiclolPas encore d'évaluation