Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Svprecis 9th Maths Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles
Transféré par
api-252136290Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Svprecis 9th Maths Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles
Transféré par
api-252136290Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
SVPrecis_9th_Maths_Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles Key Points 1.
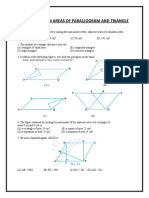
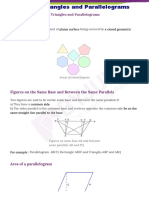
Two figures are said to be on the same base and between the same parallels, if they have a common side and the vertices opposite to the common base of each figure lie on a line parallel to the base. 2. Area of a figure is a number associated with the part of the plane enclosed by that figure. 3. Two congruent figures have equal areas but the converse need not be true. 4. If a planer region formed by a figure R is made up two non-overlapping planer region formed by figures R1 and R2, then ar (R) =ar (R1) + ar (R2) 5. A diagonal of a parallelogram divides it into two triangles of equal area. 6. Parallelograms on the same base and between same parallels are equal in area. 7. The area of a parallelogram is the product of its base and the corresponding altitude. 8. Parallelograms on equal bases and between the same parallels are equal in area. 9. Triangles on the same bases and between the same parallels are equal in area. 10. The area of a triangle is half the product of any of its sides and the corresponding altitude. 11. If a triangle and a parallelogram are on the same base and between same parallels, then the area of the triangle is equal to the half of the parallelogram. 12. The area of a trapezium is half the product of its height and the sum of parallel sides. 13. Triangles having equal areas and having one side of one of the triangles, equal to one side of the other, have their corresponding altitudes equal. 14. If each diagonal of a quadrilateral separates it into two triangles of equal area, then the quadrilateral is a parallelogram. 15. The area of a rhombus is half the product of the lengths of its diagonals. 16. Diagonals of a parallelogram divide it into four triangles of equal area. 17. A median of a triangle divides it into two triangles of equal area. Questions for practice 1. In triangle ABC, D is the midpoint of AB. P is any point of BC. CQ||PD meets AB in Q. Show that ( ) ( ). ) 2. In a parallelogram ABCD, E,F are any two points on the sides AB and BC respectively. Show that ( ( ) 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Prove that the area of an equilateral triangle is equal to , where a is the side of the triangle. ( ) ( ). BC||XY, BX||CA and AB||YC. Prove that: ) ( ). ABCD is a parallelogram. Prove that: ( ABC is a triangle in which D is the mid-point of BC and E is the midpoint of AD. Prove that area of BED = area of ABC. ) ABCD is a parallelogram X and Y are the mid points of BC and CD respectively. Prove that ar( ( ) The diagonals of a parallelogram ABCD intersect at a point O. through O; a line is drawn to intersect AD at P and BC at Q. show that PQ divides the parallelogram into two parts of equal area. The medians BE and CF of a triangle ABC intersect at G. prove that area of GBC = area of quadrilateral AFGE The side AB of a parallelogram ABCD is produced to any point P. A line through A parallel to CP meets CB ) ( ) produced in Q and the parallelogram PBQR completed. Show that ar(
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
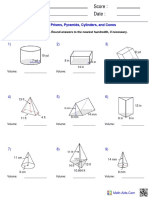
- Name: Teacher: Date: Score:: Volume of Prisms, Pyramids, Cylinders, and ConesDocument2 pagesName: Teacher: Date: Score:: Volume of Prisms, Pyramids, Cylinders, and ConesMark Christian Dimson GalangPas encore d'évaluation
- #Foundation All Test Bites (Single Sheets) AnswersDocument35 pages#Foundation All Test Bites (Single Sheets) AnswersjazibzpsPas encore d'évaluation
- Post Test-Algebra, Trigo and GeomDocument9 pagesPost Test-Algebra, Trigo and GeomRichard TandaguenPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 15 I Trigonometry II StudentDocument41 pagesChapter 15 I Trigonometry II StudentAngie Kong Su MeiPas encore d'évaluation
- Adobe Scan 01-Feb-2021Document4 pagesAdobe Scan 01-Feb-2021Shyam Shankar DasPas encore d'évaluation
- Area of Figure: What Are Congruents FiguresDocument5 pagesArea of Figure: What Are Congruents FiguresTIMEOFFICE KHARAGPURWORKSHOPPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 9 - Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles Revision NotesDocument8 pagesChapter 9 - Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles Revision NotesHariom SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- Gemh 109Document16 pagesGemh 109Aditya SharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Question Bank in Mathematics Class IX (Term II) : Areas of Parallelograms and TrianglesDocument34 pagesQuestion Bank in Mathematics Class IX (Term II) : Areas of Parallelograms and TrianglesAnonymous 8OXMQJQqxPas encore d'évaluation
- DownloadedDocument15 pagesDownloadedKRISHNA KUTADIPas encore d'évaluation
- concept Area TheoremsDocument23 pagesconcept Area TheoremsPartha MajumderPas encore d'évaluation
- Eucledan GeometryDocument39 pagesEucledan GeometryUrsula VersterPas encore d'évaluation
- Area SamralaB LDHDocument10 pagesArea SamralaB LDHapi-3731257Pas encore d'évaluation
- NCERT Exemplar Class 9 Maths: Chapter-9Document18 pagesNCERT Exemplar Class 9 Maths: Chapter-9funson123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Areas of Parallogram and TriangleDocument2 pagesAreas of Parallogram and TriangleVACHAN L APas encore d'évaluation
- 9maths 9 Areas of Parallelograms and TrianglesDocument44 pages9maths 9 Areas of Parallelograms and TrianglesHitesh TiwariPas encore d'évaluation
- Areas Parallelograms Triangles Grade 9Document2 pagesAreas Parallelograms Triangles Grade 9Katrina Kaif0% (1)
- 9 Maths Exemplar Chapter 9Document13 pages9 Maths Exemplar Chapter 9Sarthak RajPas encore d'évaluation
- Impquestionclass 9Document22 pagesImpquestionclass 9andrewmanshionPas encore d'évaluation
- Euclid 01Document45 pagesEuclid 01mach20_aardvark8064Pas encore d'évaluation
- Geometry Capsule For SSC Railway Exams Watermark - PDF 70Document13 pagesGeometry Capsule For SSC Railway Exams Watermark - PDF 70Tapas SwainPas encore d'évaluation
- Geom FinalDocument6 pagesGeom FinalDwight Seth LumantaPas encore d'évaluation
- TrapeziumDocument4 pagesTrapeziumPAWAN NAGALPas encore d'évaluation
- ParallelogramDocument5 pagesParallelogramanug singhPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculating Areas of Triangles and ParallelogramsDocument4 pagesCalculating Areas of Triangles and ParallelogramsAYUSH KUMAR JHA 9BPas encore d'évaluation
- Areas of Triangles and ParallelogramsDocument4 pagesAreas of Triangles and Parallelogramsdattatray deshmukhPas encore d'évaluation
- Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles NotesDocument2 pagesAreas of Parallelograms and Triangles NotesLatoyaWatkinsPas encore d'évaluation
- Asm 17861Document3 pagesAsm 17861dishadagar11Pas encore d'évaluation
- Properties of Parallelograms, Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Their RelationshipsDocument4 pagesProperties of Parallelograms, Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Their Relationshipsanushika sharmaPas encore d'évaluation
- Area of Parallelogram and Its TrianglesDocument3 pagesArea of Parallelogram and Its Trianglesaman5hazarikaPas encore d'évaluation
- Yr12 Maths in Focus 2U HSCDocument412 pagesYr12 Maths in Focus 2U HSCRichard Yang93% (14)
- L-9 Areas of Parallelograms and TrianglesDocument37 pagesL-9 Areas of Parallelograms and TrianglesferozamedPas encore d'évaluation
- Viktor v. Prasolov - Problems in Plane and Solid Geometry (Vol. 2, Solid Geometry) - 239pDocument239 pagesViktor v. Prasolov - Problems in Plane and Solid Geometry (Vol. 2, Solid Geometry) - 239pvitorres100% (4)
- My Honeybunchsugarplumplumwalangmakakapantaysayosweetiecutiepie NotebookDocument18 pagesMy Honeybunchsugarplumplumwalangmakakapantaysayosweetiecutiepie NotebookJhayPas encore d'évaluation
- GeometryDocument10 pagesGeometryPatrick Erwin Teñido AmbrosioPas encore d'évaluation
- Synopsis - Grade 9 Math Term II: Chapter 4: Linear Equations in Two VariablesDocument15 pagesSynopsis - Grade 9 Math Term II: Chapter 4: Linear Equations in Two VariablesMayank SainiPas encore d'évaluation
- Quadrilateral Formed by Joining Mid 9th ActivityDocument8 pagesQuadrilateral Formed by Joining Mid 9th ActivitypiyushPas encore d'évaluation
- CatiaDocument16 pagesCatiaD.n.PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles FormulasDocument13 pagesAreas of Parallelograms and Triangles FormulasnPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 05 - Congruence of Triangles (Mathematics Worksheet)Document1 pageUnit 05 - Congruence of Triangles (Mathematics Worksheet)Xiao ShadowlordPas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE Class 9 Mathematics Revision AssignmentsDocument17 pagesCBSE Class 9 Mathematics Revision AssignmentslauranistPas encore d'évaluation
- Properties of Lines: - GeometryDocument12 pagesProperties of Lines: - GeometrysanjeevPas encore d'évaluation
- Geometry - For Maths Olympiad MaterialDocument89 pagesGeometry - For Maths Olympiad Materialdrssagrawal100% (6)
- Geometry - Olympiad Material BY DR SHYAM SUNDAR AGRAWALDocument67 pagesGeometry - Olympiad Material BY DR SHYAM SUNDAR AGRAWALdrssagrawalPas encore d'évaluation
- Quadrilateral Worksheet For Class 9Document1 pageQuadrilateral Worksheet For Class 9Suman joonPas encore d'évaluation
- Geometry of ShapesDocument19 pagesGeometry of ShapesIstván MolnárPas encore d'évaluation
- Proportions and Similarity in Polygons and TrianglesDocument43 pagesProportions and Similarity in Polygons and TrianglesJeanelyn LegsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Maths Chp09Document66 pagesMaths Chp09bidyut naskarPas encore d'évaluation
- Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles FormulasDocument16 pagesAreas of Parallelograms and Triangles FormulasSyed Shoeb100% (1)
- Area Theorem Triangles and QuadrilateralsDocument5 pagesArea Theorem Triangles and QuadrilateralssabirafrinPas encore d'évaluation
- Pagpili NG Pang Abay Na Pamanahon 11Document29 pagesPagpili NG Pang Abay Na Pamanahon 11Joshua BoncodinPas encore d'évaluation
- Mensuration of Plane Figures (Quadrilateral)Document10 pagesMensuration of Plane Figures (Quadrilateral)Danica AguilarPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 1 Notes: Distance, Midpoint, & Slope Formulas Textbook 1.3Document8 pagesLesson 1 Notes: Distance, Midpoint, & Slope Formulas Textbook 1.3Laiba zzstu BukhariPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 9 (Areas of Parallelograms & Triangles) : Exercise 9.1: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS)Document18 pagesUnit 9 (Areas of Parallelograms & Triangles) : Exercise 9.1: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS)renu tomarPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 16Document29 pagesCH 16Ankita KumariPas encore d'évaluation
- Trapezium ABCD with diagonals AC and BD intersecting at PDocument8 pagesTrapezium ABCD with diagonals AC and BD intersecting at PUnniePas encore d'évaluation
- Quadrilateral SDocument13 pagesQuadrilateral SBiplabPas encore d'évaluation
- GR IXMCh 8 PPT1Document32 pagesGR IXMCh 8 PPT1Purple DasherPas encore d'évaluation
- Projective Geometry 2Document53 pagesProjective Geometry 2pipul36Pas encore d'évaluation
- Review Part II - Geom 2012Document3 pagesReview Part II - Geom 2012A BPas encore d'évaluation
- Quadrilaterals Class 9 Notes CBSE Maths Chapter 8 (PDF)Document19 pagesQuadrilaterals Class 9 Notes CBSE Maths Chapter 8 (PDF)SurbhiPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch-4 RD MathsDocument140 pagesCh-4 RD MathsThe VRAJ GAMESPas encore d'évaluation
- Quadrilaterals: HapterDocument12 pagesQuadrilaterals: HapterSangeeta BansalPas encore d'évaluation
- The Elements of Euclid for the Use of Schools and Colleges (Illustrated)D'EverandThe Elements of Euclid for the Use of Schools and Colleges (Illustrated)Pas encore d'évaluation
- Svpre Board 12th Physics Code 05Document5 pagesSvpre Board 12th Physics Code 05api-252136290Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sgoi Precis 10th Maths Linear Equations in Two VariablesDocument1 pageSgoi Precis 10th Maths Linear Equations in Two Variablesapi-252136290Pas encore d'évaluation
- Svpre Broad 12th ChemistryDocument3 pagesSvpre Broad 12th Chemistryapi-252136290Pas encore d'évaluation
- Svpre Board 01 12th MathDocument2 pagesSvpre Board 01 12th Mathapi-252136290Pas encore d'évaluation
- Svprecis 10th Maths PolynomialsDocument1 pageSvprecis 10th Maths Polynomialsapi-252136290Pas encore d'évaluation
- Svprecis 11th Maths Permutation and CombinationDocument3 pagesSvprecis 11th Maths Permutation and Combinationapi-252136290Pas encore d'évaluation
- SV Precise 12th Chemistry Chapter 1 Solid StatesDocument15 pagesSV Precise 12th Chemistry Chapter 1 Solid Statesapi-252136290100% (1)
- Svprecis 12 Maths Module 2 NewDocument16 pagesSvprecis 12 Maths Module 2 Newapi-252136290Pas encore d'évaluation
- Svprecis 12 Maths Module 1 NewDocument20 pagesSvprecis 12 Maths Module 1 Newapi-252136290Pas encore d'évaluation
- Svprecise 11th Maths SetsDocument1 pageSvprecise 11th Maths Setsapi-252136290Pas encore d'évaluation
- Svprecis 11th Eco Chapter - 1 Indian Economy On The Eve of IndependenceDocument4 pagesSvprecis 11th Eco Chapter - 1 Indian Economy On The Eve of Independenceapi-252136290Pas encore d'évaluation
- Svprecis 12th Physics Electrostatic Potential and CapacitanceDocument5 pagesSvprecis 12th Physics Electrostatic Potential and Capacitanceapi-252136290Pas encore d'évaluation
- Sgoi Notes Chap 1 Consumers EquilibriumDocument1 pageSgoi Notes Chap 1 Consumers Equilibriumapi-252136290Pas encore d'évaluation
- Svprecis 12th Physics Electrostatic Potential and CapacitanceDocument4 pagesSvprecis 12th Physics Electrostatic Potential and Capacitanceapi-252136290Pas encore d'évaluation
- Svprecis 10th Maths Some Applications of TrigonometryDocument1 pageSvprecis 10th Maths Some Applications of Trigonometryapi-252136290Pas encore d'évaluation
- Svprecis 10th Maths TrigonometryDocument2 pagesSvprecis 10th Maths Trigonometryapi-252136290Pas encore d'évaluation
- Svprecis Book Num 01 Micro Macro Economics NumericalDocument25 pagesSvprecis Book Num 01 Micro Macro Economics Numericalapi-252136290Pas encore d'évaluation
- Svprecis 12th Physics Electromagnetic WavesDocument1 pageSvprecis 12th Physics Electromagnetic Wavesapi-252136290Pas encore d'évaluation
- Svprecis Book Num 2 Macro Economics NumericalDocument62 pagesSvprecis Book Num 2 Macro Economics Numericalapi-252136290Pas encore d'évaluation
- Notes Chap 1 Introduction Central Problems of An EconomyDocument2 pagesNotes Chap 1 Introduction Central Problems of An Economyapi-252136290100% (2)
- Svprecis 12th Physics Wave OpticsDocument1 pageSvprecis 12th Physics Wave Opticsapi-252136290Pas encore d'évaluation
- Svprecis 12th Physics Electrostatic Force Electrostatic Field and Gauss TheoremDocument2 pagesSvprecis 12th Physics Electrostatic Force Electrostatic Field and Gauss Theoremapi-252136290Pas encore d'évaluation
- Svprecis 12th Chemistry Unit No 1 The Solid StateDocument11 pagesSvprecis 12th Chemistry Unit No 1 The Solid Stateapi-252136290Pas encore d'évaluation
- Svpreis 9th PolynomialsDocument1 pageSvpreis 9th Polynomialsapi-252136290Pas encore d'évaluation
- Svprecis 9th Surface Area VolumeDocument2 pagesSvprecis 9th Surface Area Volumeapi-252136290Pas encore d'évaluation
- Svprecis 9th Fa3 Linear EquationsDocument2 pagesSvprecis 9th Fa3 Linear Equationsapi-252136290Pas encore d'évaluation
- Svprogress Scrutiny 9th GravitationDocument1 pageSvprogress Scrutiny 9th Gravitationapi-252136290Pas encore d'évaluation
- Svprogress Scrutiny 9th Science Chem-Matter in Our SurroundingsDocument1 pageSvprogress Scrutiny 9th Science Chem-Matter in Our Surroundingsapi-252136290Pas encore d'évaluation
- Arya TexDocument58 pagesArya TexArya Krishnan IPas encore d'évaluation
- Cross SectionsDocument17 pagesCross Sectionsapi-294079637Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pentaksiran Year 1 March 2020Document12 pagesPentaksiran Year 1 March 2020Nor FarehaPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics For Grade 6 TeachersDocument15 pagesMathematics For Grade 6 TeachersJonas Reduta CabacunganPas encore d'évaluation
- Complex Number DPPDocument2 pagesComplex Number DPP1 AashuPas encore d'évaluation
- Demystifying The Natural LogarithmDocument3 pagesDemystifying The Natural LogarithmRajvi SampatPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics Kangaroo 2011 Group Kadett (Grades 7 and 8Document4 pagesMathematics Kangaroo 2011 Group Kadett (Grades 7 and 8jnPas encore d'évaluation
- Add Maths Form 3: Tutorial: Simultaneous EquationsDocument2 pagesAdd Maths Form 3: Tutorial: Simultaneous EquationsMuhaiminPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 3 End-of-Month Math Test Under 40 CharactersDocument8 pagesGrade 3 End-of-Month Math Test Under 40 Characterslife at Russian cultural centrePas encore d'évaluation
- t2 M 4412 Drawing Translated 2d Shapes Differentiated Activity SheetsDocument6 pagest2 M 4412 Drawing Translated 2d Shapes Differentiated Activity SheetsNguyen Thu TrangPas encore d'évaluation
- BCS 012 Previous Year Question Papers by IgnouassignmentguruDocument79 pagesBCS 012 Previous Year Question Papers by IgnouassignmentguruJapani TutorPas encore d'évaluation
- Units-Digits and DivisiblityDocument13 pagesUnits-Digits and DivisiblitymodestorosPas encore d'évaluation
- Differential Calculus Das MukherjeeDocument224 pagesDifferential Calculus Das MukherjeeYousuf AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Holy Cross College Sta. Lucia, Sta. Ana, Pampanga College of Arts Sciences and EducationDocument13 pagesHoly Cross College Sta. Lucia, Sta. Ana, Pampanga College of Arts Sciences and EducationangelPas encore d'évaluation
- CBSE - MATHS - PRE - FINAL - II - EXAM (Standard) - SET - 2 (BNG, TN, KA) - FINALDocument6 pagesCBSE - MATHS - PRE - FINAL - II - EXAM (Standard) - SET - 2 (BNG, TN, KA) - FINALbdsouza899Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 5: Trigonometric Functions of AnglesDocument54 pagesChapter 5: Trigonometric Functions of AnglesJames LangPas encore d'évaluation
- INFINITY Individual Round Practice PaperDocument7 pagesINFINITY Individual Round Practice PaperRudresh Kumar DubeyPas encore d'évaluation
- November 7, 2019 (Thursday) : ObjectiveDocument2 pagesNovember 7, 2019 (Thursday) : ObjectiveAndrei Sy JaviertoPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Drawing Book 2022 2023 1st Term 2 1 80Document80 pagesEngineering Drawing Book 2022 2023 1st Term 2 1 80Epimaque NkurunzizaPas encore d'évaluation
- Analytic GeometryDocument3 pagesAnalytic GeometryJennifer JumaquioPas encore d'évaluation
- Tobago Condary Entrance Assessment: AprilDocument23 pagesTobago Condary Entrance Assessment: AprilAnna Del Rey ValtersenPas encore d'évaluation
- Liu Po Shan Memorial College (2007 - 2008) Final Examination Secondary Four Mathematics Paper IDocument18 pagesLiu Po Shan Memorial College (2007 - 2008) Final Examination Secondary Four Mathematics Paper IKILLUASOPas encore d'évaluation
- The Elemnts of EuclidDocument107 pagesThe Elemnts of EuclidAngelica MontezonPas encore d'évaluation
- Mathematics Tracker Atp Grade 6 Term 3 of 2021Document37 pagesMathematics Tracker Atp Grade 6 Term 3 of 2021Emily MahlanguPas encore d'évaluation
- Maths Paper - I - Question PaperDocument4 pagesMaths Paper - I - Question PaperPrajwal SolankiPas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction To Conics: ParabolasDocument9 pagesIntroduction To Conics: Parabolaschen18111004 KFUEITPas encore d'évaluation