Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Heap Sort - GeeksQuiz - GeeksQuiz
Transféré par
Ngô ĐạtTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Heap Sort - GeeksQuiz - GeeksQuiz
Transféré par
Ngô ĐạtDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
11/4/13
Heap Sort - GeeksQuiz | GeeksQuiz
GeeksQuiz
Computer science mock tests for geeks Home Latest Questions Articles Subscribe
Heap Sort
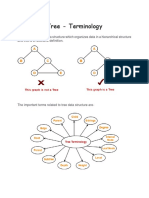
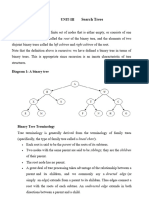
March 16, 2013 Heap sort is a comparison based sorting technique based on Binary Heap data structure. It is similar to selection sort where we first find the maximum element and place the maximum element at the end. We repeat the same process for remaining element. What is Binary Heap? Let us first define a Complete Binary Tree. A complete binary tree is a binary tree in which every level, except possibly the last, is completely filled, and all nodes are as far left as possible (Source Wikipedia) A Binary Heap is a Complete Binary Tree where items are stored in a special order such that value in a parent node is greater(or smaller) than the values in its two children nodes. The former is called as max heap and the latter is called min heap. The heap can be represented by binary tree or array. Why array based representation for Binary Heap? Since a Binary Heap is a Complete Binary Tree, it can be easily represented as array and array based representation is space efficient. If the parent node is stored at index I, the left child can be calculated by 2 * I + 1 and right child by 2 * I + 2. Heap Sort Algorithm for sorting in increasing order: 1. Build a max heap from the input data. 2. At this point, the largest item is stored at the root of the heap. Replace it with the last item of the heap followed by reducing the size of heap by 1. Finally, heapify the root of tree.
geeksquiz.com/heap-sort/ 1/8
11/4/13
Heap Sort - GeeksQuiz | GeeksQuiz
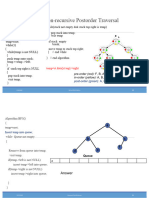
3. Repeat above steps until size of heap is greater than 1. How to build the heap? Heapify procedure can be applied to a node only if its children nodes are heapified. So the heapification must be performed in the bottom up order. Lets understand with the help of an example:
I n p u td a t a :4 ,1 0 ,3 ,5 ,1 4 ( 0 ) / \ 0 ( 1 ) 3 ( 2 ) / \ 5 ( 3 ) 1 ( 4 ) T h en u m b e r si nb r a c k e tr e p r e s e n tt h ei n d i c e si nt h ea r r a yr e p r e s e n t a t i o no fd a t a . A p p l y i n gh e a p i f yp r o c e d u r et oi n d e x1 : 4 ( 0 ) / \ 1 0 ( 1 ) 3 ( 2 ) / \ 5 ( 3 ) 1 ( 4 ) A p p l y i n gh e a p i f yp r o c e d u r et oi n d e x0 : 1 0 ( 0 ) / \ 5 ( 1 ) 3 ( 2 ) / \ 4 ( 3 ) 1 ( 4 ) T h eh e a p i f yp r o c e d u r ec a l l si t s e l fr e c u r s i v e l yt ob u i l dh e a pi nt o pd o w nm a n n e r .
/ /Ci m p l e m e n t a t i o no fH e a pS o r t # i n c l u d e< s t d i o . h > # i n c l u d e< s t d l i b . h > / /Ah e a ph a sc u r r e n ts i z ea n da r r a yo fe l e m e n t s s t r u c tM a x H e a p { i n ts i z e ; i n t *a r r a y ; } ; / /Au t i l i t yf u n c t i o nt os w a pt oi n t e g e r s
geeksquiz.com/heap-sort/ 2/8
11/4/13
Heap Sort - GeeksQuiz | GeeksQuiz
v o i ds w a p ( i n t *a ,i n t *b ){i n tt=* a ;* a=* b ; * b=t ;} / /T h em a i nf u n c t i o nt oh e a p i f yaM a xH e a p .T h ef u n c t i o na s s u m e st h a t / /e v e r y t h i n gu n d e rg i v e nr o o t( e l e m e n ta ti n d e xi d x )i sa l r e a d yh e a p i f i e d v o i dm a x H e a p i f y ( s t r u c tM a x H e a p *m a x H e a p ,i n ti d x ) { i n tl a r g e s t=i d x ; / /I n i t i a l i z el a r g e s ta sr o o t i n tl e f t=( i d x< <1 )+1 ; / /l e f t=2 * i d x+1 i n tr i g h t=( i d x+1 )< <1 ;/ /r i g h t=2 * i d x+2 / /S e ei fl e f tc h i l do fr o o te x i s t sa n di sg r e a t e rt h a nr o o t i f( l e f t<m a x H e a p > s i z e& &m a x H e a p > a r r a y [ l e f t ]>m a x H e a p > a r r a y [ l a r g e s t ] ) l a r g e s t=l e f t ; / /S e ei fr i g h tc h i l do fr o o te x i s t sa n di sg r e a t e rt h a nt h el a r g e s ts of a r i f( r i g h t<m a x H e a p > s i z e& &m a x H e a p > a r r a y [ r i g h t ]>m a x H e a p > a r r a y [ l a r g e s t ] ) l a r g e s t=r i g h t ; / /C h a n g er o o t ,i fn e e d e d i f( l a r g e s t! =i d x ) { s w a p ( & m a x H e a p > a r r a y [ l a r g e s t ] ,& m a x H e a p > a r r a y [ i d x ] ) ; m a x H e a p i f y ( m a x H e a p ,l a r g e s t ) ; }
/ /Au t i l i t yf u n c t i o nt oc r e a t eam a xh e a po fg i v e nc a p a c i t y s t r u c tM a x H e a p *c r e a t e A n d B u i l d H e a p ( i n t* a r r a y ,i n ts i z e ) { i n ti ; s t r u c tM a x H e a p *m a x H e a p=( s t r u c tM a x H e a p * )m a l l o c ( s i z e o f ( s t r u c tM a x H e a p ) ) ; m a x H e a p > s i z e=s i z e ; / /i n i t i a l i z es i z eo fh e a p m a x H e a p > a r r a y=a r r a y ;/ /A s s i g na d d r e s so ff i r s te l e m e n to fa r r a y / /S t a r tf r o mb o t t o m m o s ta n dr i g h t m o s ti n t e r n a lm o d ea n dh e a p i f ya l l / /i n t e r n a lm o d e si nb o t t o mu pw a y f o r( i=( m a x H e a p > s i z e-2 )/2 ;i> =0 ;i ) m a x H e a p i f y ( m a x H e a p ,i ) ; r e t u r nm a x H e a p ;
3/8
geeksquiz.com/heap-sort/
11/4/13
Heap Sort - GeeksQuiz | GeeksQuiz
/ /T h em a i nf u n c t i o nt os o r ta na r r a yo fg i v e ns i z e v o i dh e a p S o r t ( i n t *a r r a y ,i n ts i z e ) { / /B u i l dah e a pf r o mt h ei n p u td a t a . s t r u c tM a x H e a p *m a x H e a p=c r e a t e A n d B u i l d H e a p ( a r r a y ,s i z e ) ; / /R e p e a tf o l l o w i n gs t e p sw h i l eh e a ps i z ei sg r e a t e rt h a n1 .T h el a s t / /e l e m e n ti nm a xh e a pw i l lb et h em i n i m u me l e m e n t w h i l e( m a x H e a p > s i z e>1 ) { / /T h el a r g e s ti t e mi nH e a pi ss t o r e da tt h er o o t .R e p l a c ei tw i t ht h e / /l a s ti t e mo ft h eh e a pf o l l o w e db yr e d u c i n gt h es i z eo fh e a pb y1 . s w a p ( & m a x H e a p > a r r a y [ 0 ] ,& m a x H e a p > a r r a y [ m a x H e a p > s i z e-1 ] ) ; m a x H e a p > s i z e ; / /R e d u c eh e a ps i z e / /F i n a l l y ,h e a p i f yt h er o o to ft r e e . m a x H e a p i f y ( m a x H e a p ,0 ) ;
/ /Au t i l i t yf u n c t i o nt op r i n tag i v e na r r a yo fg i v e ns i z e v o i dp r i n t A r r a y ( i n t *a r r ,i n ts i z e ) { i n ti ; f o r( i=0 ;i<s i z e ;+ + i ) p r i n t f ( " % d" ,a r r [ i ] ) ; } / *D r i v e rp r o g r a mt ot e s ta b o v ef u n c t i o n s* / i n tm a i n ( ) { i n ta r r [ ]={ 1 2 ,1 1 ,1 3 ,5 ,6 ,7 } ; i n ts i z e=s i z e o f ( a r r ) / s i z e o f ( a r r [ 0 ] ) ; p r i n t f ( " G i v e na r r a yi s\ n " ) ; p r i n t A r r a y ( a r r ,s i z e ) ; h e a p S o r t ( a r r ,s i z e ) ;
geeksquiz.com/heap-sort/ 4/8
11/4/13
Heap Sort - GeeksQuiz | GeeksQuiz
p r i n t f ( " \ n S o r t e da r r a yi s\ n " ) ; p r i n t A r r a y ( a r r ,s i z e ) ; r e t u r n0 ;
Output:
G i v e na r r a yi s 1 21 11 3567 S o r t e da r r a yi s 5671 11 21 3
Notes: Heap sort is an in-place algorithm. Its typical implementation is not stable, but can be made stable (See this) Time Complexity: Time complexity of heapify is O(Logn). Time complexity of createAndBuildHeap() is O(n) and overall time complexity of Heap Sort is O(nLogn). Applications of HeapSort 1. Sort a nearly sorted (or K sorted) array 2. k largest(or smallest) elements in an array Heap sort algorithm has limited uses because Quicksort and Mergesort are better in practice. Nevertheless, the Heap data structure itself is enormously used. See Applications of Heap Data Structure Please write comments if you find anything incorrect, or you want to share more information about the topic discussed above.
Like
Tw eet
Writing code in comment? Please refer here for guidelines.
geeksquiz.com/heap-sort/
5/8
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Toefl iBT WritingDocument11 pagesToefl iBT WritingNgô ĐạtPas encore d'évaluation
- (EE332) (09ECE) (Group13) Report ProjectDocument23 pages(EE332) (09ECE) (Group13) Report ProjectNgô ĐạtPas encore d'évaluation
- Salvo RtosDocument30 pagesSalvo RtosNgô ĐạtPas encore d'évaluation
- Linux Cheat SheetDocument1 pageLinux Cheat SheetNgô ĐạtPas encore d'évaluation
- Bioelectronics & Biosciences-FULLDocument112 pagesBioelectronics & Biosciences-FULLNgô ĐạtPas encore d'évaluation
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceD'EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeD'EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeD'EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceD'EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)D'EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Évaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingD'EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItD'EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureD'EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryD'EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerD'EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaD'EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersD'EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealD'EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyD'EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyÉvaluation : 3.5 sur 5 étoiles3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnD'EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnÉvaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaD'EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreD'EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)D'EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Évaluation : 4.5 sur 5 étoiles4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesD'EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesÉvaluation : 4 sur 5 étoiles4/5 (821)
- Buet Admission About TreeDocument26 pagesBuet Admission About TreeOporajitaPas encore d'évaluation
- A Lion in The DesertDocument24 pagesA Lion in The DesertAlexander Choquenaira FlorezPas encore d'évaluation
- AVL TreeDocument43 pagesAVL TreeRajan JaiprakashPas encore d'évaluation
- Section 6 Objectives:: Data Structures & AlgorithmsDocument12 pagesSection 6 Objectives:: Data Structures & AlgorithmsYT PremonePas encore d'évaluation
- DS Module 3Document507 pagesDS Module 3m.bapardekarPas encore d'évaluation
- 16 Scapegoat and Splay Trees: 16.1 DefinitionsDocument15 pages16 Scapegoat and Splay Trees: 16.1 DefinitionsJanus Cesar Ruizan QuilenderinoPas encore d'évaluation
- LC QuestionsDocument2 pagesLC QuestionsKhalil IbrahimPas encore d'évaluation
- DSA Practical FinalDocument35 pagesDSA Practical FinalRiya GunjalPas encore d'évaluation
- Binary Search TreeDocument37 pagesBinary Search Treenehavj664Pas encore d'évaluation
- Arbore Binar MeDocument5 pagesArbore Binar MeCristina UngureanPas encore d'évaluation
- Optimal Merge PatternDocument5 pagesOptimal Merge Patternmansha99Pas encore d'évaluation
- General Tree: 1 Mitra Kabir, Dept. of CSE, DUDocument6 pagesGeneral Tree: 1 Mitra Kabir, Dept. of CSE, DUMD.ASHADUZZAMAN AyonPas encore d'évaluation
- Ds III Unit NotesDocument36 pagesDs III Unit NotesAlagandula KalyaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 06 - Binary Search Tree (BST) - Design Analysis of AlgorithmDocument30 pagesLecture 06 - Binary Search Tree (BST) - Design Analysis of AlgorithmMuhammad AfaqPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Structure PDFDocument1 pageData Structure PDFTHULASIPas encore d'évaluation
- CS2040S CheatSheetDocument2 pagesCS2040S CheatSheetPeter Joseph FungPas encore d'évaluation
- Binary Trees: What Is A Binary Tree?Document6 pagesBinary Trees: What Is A Binary Tree?Keith Tanaka MagakaPas encore d'évaluation
- Data Structures Lab ManualDocument73 pagesData Structures Lab ManualUdhaya SankarPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Algorithms AssignmentDocument17 pagesDesign of Algorithms AssignmentKudakwashePas encore d'évaluation
- BCA 3.3 Non Linear Data Structure Using C++Document18 pagesBCA 3.3 Non Linear Data Structure Using C++UMESH SIRMVPas encore d'évaluation
- Mcdermott 6014 Final Summer B 17Document14 pagesMcdermott 6014 Final Summer B 17api-373102817Pas encore d'évaluation
- MCS 021 Data and File StructuresDocument22 pagesMCS 021 Data and File StructuresSumit RanjanPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 3&5 TreesDocument54 pagesUnit 3&5 TreesrayedkhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Tree Material (3 Classes) PDFDocument23 pagesTree Material (3 Classes) PDFNaveen GowdruPas encore d'évaluation
- CS301 Lec15Document55 pagesCS301 Lec15Learn IslamPas encore d'évaluation
- CS225 - Midterm 2 Run-TimesDocument4 pagesCS225 - Midterm 2 Run-TimesMihir KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Discrete Maths TreesDocument12 pagesDiscrete Maths TreesOcira OyaroPas encore d'évaluation
- WEEK 10: Write A Java Program To Implement Dynamic Programming Algorithm For The Optimal Binary Search Tree ProblemDocument4 pagesWEEK 10: Write A Java Program To Implement Dynamic Programming Algorithm For The Optimal Binary Search Tree ProblemShanthan ReddyPas encore d'évaluation
- Implementation of Stack Using ArrayDocument4 pagesImplementation of Stack Using ArrayMeghna Raj CPas encore d'évaluation
- Programming Paradigms CSI2120: Jochen Lang EECS, University of Ottawa CanadaDocument27 pagesProgramming Paradigms CSI2120: Jochen Lang EECS, University of Ottawa Canadaaziz spamPas encore d'évaluation