Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
SOM3601 Assignment 2
Transféré par
Elendu Emmanuel ChigozieDescription originale:
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
SOM3601 Assignment 2
Transféré par
Elendu Emmanuel ChigozieDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
18
12.2 Assignment 02
Question 1: Temperature Stresses
1.1 The steel rails of a railroad are 12 m with a clearance of 3 mm at 15
o
C. Calculate the
change in temperature that will cause the rails to touch. Calculate the stresses that would be
induced at this new temperature if there were no initial clearance (E = 200 GPa and = 12 10
-
6
/
o
C). [6]
1.2 A copper tube having a cross-sectional area of 2000 mm
2
and a length of 300 mm is palced
between to rigid caps. Four 22 mm diameter steel bolts are symmetrcally arranged parallel to
the axis of the tube and are lightly fastened.Find the stress in the tube if the temperature of the
assembly is raised by 70
o
C. What load will each bolt carry at the raised temperature? (E
st
= 200
GPa; E
cu
= 100 GPa;
st
= 12 10
-6
/
o
C). [14]
Question 2: Strain Energy
2.1 Two joules of strain energy is suddenly induced in a 300 mm long aluminium bar with a 40
mm square cross section, by a compressive load. Calculate the maximum instantaneous stress
induced in the bar and magnitude of the suddenly applied load (E = 70 GPa). [6]
2.2 A 160 mm long connecting link is 50 mm diameter for a length of 100 mm and 30 mm
diameter for the remaining length of 60 mm. The gradual application of the load P results in the
link storing a total of 10 J of energy. Calculate the magnitude of the applied load P, the value of
the stress induced in each section and the total extension. f this load had been applied
suddenly but without shock or impact, what maximum instantaneous stress would have been
induced in the link? (E = 200 GPa). [14]
Question 3: Second Moment of Area
Calculate the position of the centroids and the second moment of areas about the horizontal
and vertical axes through the centroid for the built-up section in Figure 1. Use the section tables
for standard sections (all dimensions are in mm). [20]
SOM3601/101
19
Figure 2
Question 4: Bending Stresses
4.1 A strip of steel 3 mm thick and 35 mm wide is bent round a cylindrical drum 4 mm in
diameter. Determine the maximum stress set up in the strip and the bending moment which has
to be applied to bend the strip to this curvature (E = 200 GPa) [5]
4.2 A hollow short cast iron column has outside and inside diameters of 250 mm and 150 mm
respectively. The column is subjected to an axial load applied at a distance of 60 mm from the
centre of the section. (a) Calculate the maximum safe load if the allowable stresses are 100
MPa compressive and 20 MPa tensile; (b) plot a stress distribution diagram and calculate the
position of the NA. [15]
Question 5: Shear Stress in Beams
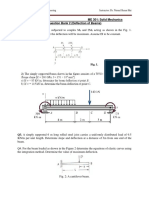
5.1 A built-up beam of box section (Figure 2) is simply supported over a span of 3 m and
carries a point load of 15 kN at 1 m from the end. The plate is attached to the channel by rivets
pitched at 100 mm intervals. f the shear stress in the rivets must not exceed 50 MPa, determine
a suitable rivet diameter (all dimensions in mm). [12]
20
Figure 3
5.2 Calculate the percentage of the shear force carried by the web of a T-section with a 142
mm x 11 mm flange and 360 mm x 7 mm web. [8]
Question 6: Shear Force and Bending Moment Diagrams
Draw the shear force and bending moment diagram for the built-in beam in Figure 3 and
calculate the point of contra-flexure(s). [20]
4 kN/m
5 kN
8 kN
8 kN
1m 1m 2m 2m 1m 1m
Figure 4
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Tutorial Questions 4523Document29 pagesTutorial Questions 4523Toby Joseph ThomasPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanical ScienceDocument12 pagesMechanical ScienceFernando EyzaguirrePas encore d'évaluation
- STRENGTH OF MATERIALS NOTESDocument16 pagesSTRENGTH OF MATERIALS NOTESSrini VasanPas encore d'évaluation
- 9A01302 Strength of Materials - IDocument8 pages9A01302 Strength of Materials - IsivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- 9A01501 Design & Drawing of Reinforced Concrete StructuresDocument7 pages9A01501 Design & Drawing of Reinforced Concrete Structuressietkcivil100% (1)
- Chapter 6 Assig PDFDocument15 pagesChapter 6 Assig PDFAnas Asif100% (1)
- rr310103 Structural Engineering Design and Drawing I (RCC)Document8 pagesrr310103 Structural Engineering Design and Drawing I (RCC)SRINIVASA RAO GANTAPas encore d'évaluation
- Comp BeamDocument9 pagesComp BeamYen CeynasPas encore d'évaluation
- Calculating tension resistance of members with holesDocument4 pagesCalculating tension resistance of members with holesNi MeshPas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture Static FailureDocument6 pagesLecture Static FailureKelly MooneyPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 3Document3 pagesTutorial 3Sothea ChimPas encore d'évaluation
- 2015 Assign-4 Fasteners & Joints SOLDocument12 pages2015 Assign-4 Fasteners & Joints SOLMohammad Tahir100% (1)
- Solved Problems Normal StressDocument3 pagesSolved Problems Normal StressA'TINSB19Pas encore d'évaluation
- DMM1 Important QuestionsDocument2 pagesDMM1 Important QuestionsChand Basha Shaik100% (1)
- Tension Member ExerciseDocument1 pageTension Member ExerciseBarnabas Udeh100% (1)
- Electrical Machine Tutorial 1Document3 pagesElectrical Machine Tutorial 1afiqPas encore d'évaluation
- Pre StressDocument9 pagesPre StressKevin John Ordoña EstillorePas encore d'évaluation
- CE5710 Assignment IDocument1 pageCE5710 Assignment INani RujaPas encore d'évaluation
- Design of Belt Drives ExamplesDocument3 pagesDesign of Belt Drives ExamplesAadrika UmashankarPas encore d'évaluation
- Problems CH-9 Thin Cylinders and Shells (Blank)Document13 pagesProblems CH-9 Thin Cylinders and Shells (Blank)محمد خريبطPas encore d'évaluation
- Strength of Materials Problem SolutionsDocument12 pagesStrength of Materials Problem SolutionssirwarameshPas encore d'évaluation
- 353 35435 ME357 2011 4 2 1 Sheet MD2Document10 pages353 35435 ME357 2011 4 2 1 Sheet MD2adel nabhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3Document30 pagesChapter 3Victoria JungPas encore d'évaluation
- Group Assignment On Reinforced Concrete Structures III (CEng554) ToDocument3 pagesGroup Assignment On Reinforced Concrete Structures III (CEng554) ToMPH SGSPas encore d'évaluation
- Oblique Shock WavesDocument10 pagesOblique Shock WavesJohn WickPas encore d'évaluation
- (WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - KPCL Civil Question Paper For Assistant and Junior EngineerDocument8 pages(WWW - Entrance-Exam - Net) - KPCL Civil Question Paper For Assistant and Junior EngineerRiski AnkitPas encore d'évaluation
- RCC Most Important Questions 3-1Document2 pagesRCC Most Important Questions 3-1Babu Sundararaman100% (1)
- Prestressed Concrete Structures - Design PDFDocument20 pagesPrestressed Concrete Structures - Design PDFyanickdouce1206Pas encore d'évaluation
- DMM 1 - 20 BitsDocument3 pagesDMM 1 - 20 BitsAnonymous YkDJkSqPas encore d'évaluation
- Question Bank HTDocument12 pagesQuestion Bank HTgreatrijuvanPas encore d'évaluation
- Mec 23Document2 pagesMec 23Hari PrasadPas encore d'évaluation
- E3-Bending TestDocument12 pagesE3-Bending TestLakshwanath Jaganath100% (1)
- Optimization of Piping Layout With Respect To Pressure and Temperature Using Caeser-IiDocument6 pagesOptimization of Piping Layout With Respect To Pressure and Temperature Using Caeser-IichabibPas encore d'évaluation
- FLEXURAL 12 (Autosaved)Document42 pagesFLEXURAL 12 (Autosaved)Ezen ChiPas encore d'évaluation
- Mech6441 Project eDocument6 pagesMech6441 Project eDaniel100% (1)
- The Behaviour of Composite BeamsDocument19 pagesThe Behaviour of Composite BeamssvnPas encore d'évaluation
- R7320103 Design of Steel StructuresDocument2 pagesR7320103 Design of Steel StructuressivabharathamurthyPas encore d'évaluation
- AM1.6 - Mechanical Testing (Tensile)Document6 pagesAM1.6 - Mechanical Testing (Tensile)Flying ThinPas encore d'évaluation
- AssignmentDocument2 pagesAssignmentWudu Mulat AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Quiz Model A Time 30 MinDocument4 pagesQuiz Model A Time 30 MinYahya Abdelhameed AamerPas encore d'évaluation
- Theory of Machines PDFDocument53 pagesTheory of Machines PDFShanmukha SundaramPas encore d'évaluation
- Mdid Lab ManualDocument48 pagesMdid Lab Manualjaimin777Pas encore d'évaluation
- Statics and Strength of Materials 7th Edition Ebook PDFDocument41 pagesStatics and Strength of Materials 7th Edition Ebook PDFwendy.ramos733Pas encore d'évaluation
- Stress Caused by Combined LoadingsDocument19 pagesStress Caused by Combined LoadingsRaja RosenaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Determination of Fragments of Multiaxial Service Loading Strongly Influencing The Fatigue of Machine ComponentsDocument10 pagesDetermination of Fragments of Multiaxial Service Loading Strongly Influencing The Fatigue of Machine Componentspaulocouceiro100% (1)
- 17me64 Dme-2 Module 1Document15 pages17me64 Dme-2 Module 1GgghhPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 6Document104 pagesModule 6rabih87Pas encore d'évaluation
- Strength of Materials - Stresses in Thin Walled Cylinder - Hani Aziz AmeenDocument13 pagesStrength of Materials - Stresses in Thin Walled Cylinder - Hani Aziz AmeenHani Aziz Ameen100% (1)
- Ass 1 Mech 6511 Mechanical Shaping of Metals and PlasticsDocument2 pagesAss 1 Mech 6511 Mechanical Shaping of Metals and PlasticsVarinder ThandiPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit-I Thin Plate Theory, Structural InstabilityDocument78 pagesUnit-I Thin Plate Theory, Structural InstabilityNirav LakhaniPas encore d'évaluation
- Department of Mechanical Engineering Instructor: Dr. Nirmal Baran HuiDocument3 pagesDepartment of Mechanical Engineering Instructor: Dr. Nirmal Baran HuiSatyajit SahuPas encore d'évaluation
- Ib RCC StructuresDocument12 pagesIb RCC StructuresRaj BakhtaniPas encore d'évaluation
- T.E Question Papers (2012 Pattern) May 2015Document297 pagesT.E Question Papers (2012 Pattern) May 2015Prof. Avinash MahalePas encore d'évaluation
- Ansys Analysis-Trolley Beam 3T1Document13 pagesAnsys Analysis-Trolley Beam 3T1Ye Wint ThuPas encore d'évaluation
- Coursework Structural Integrity 2017feedbackDocument10 pagesCoursework Structural Integrity 2017feedbackCarlosPas encore d'évaluation
- Questions On Advanced ConcreteDocument1 pageQuestions On Advanced ConcreteRatna Sai100% (1)
- Strength of Material 2Document6 pagesStrength of Material 2viv_1971Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mom AssignmentDocument8 pagesMom AssignmentfrogPas encore d'évaluation
- S. E. (Mechanical / Mechanical - SW / Automobile) 2012 CourseDocument3 pagesS. E. (Mechanical / Mechanical - SW / Automobile) 2012 CourseTejas AdakPas encore d'évaluation
- MOM Assignment IDocument3 pagesMOM Assignment IAll_regPas encore d'évaluation
- Book 1Document14 pagesBook 1Elendu Emmanuel ChigoziePas encore d'évaluation
- Pipeline Pig Trap DesignDocument1 pagePipeline Pig Trap DesignElendu Emmanuel ChigoziePas encore d'évaluation
- Pipe Flow Calculations PDFDocument12 pagesPipe Flow Calculations PDFharrypop418Pas encore d'évaluation
- Leadership Assessment QuestionnaireDocument8 pagesLeadership Assessment QuestionnaireElendu Emmanuel ChigoziePas encore d'évaluation
- WarningDocument1 pageWarningElendu Emmanuel ChigoziePas encore d'évaluation
- Asme 31 GDocument48 pagesAsme 31 GShriram Avasarkar100% (2)
- Pipeline Capacity IncreaseDocument8 pagesPipeline Capacity IncreaseElendu Emmanuel ChigoziePas encore d'évaluation
- Pipeline Pig TrapsDocument1 pagePipeline Pig TrapsElendu Emmanuel ChigoziePas encore d'évaluation
- Leadership Assessment SummaryDocument2 pagesLeadership Assessment SummaryElendu Emmanuel ChigoziePas encore d'évaluation
- 2003 SUT Effects of High Temperature On The Design of Deepwater Risers PDFDocument35 pages2003 SUT Effects of High Temperature On The Design of Deepwater Risers PDFvictor gerardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Leadership Assessment SummaryDocument2 pagesLeadership Assessment SummaryElendu Emmanuel ChigoziePas encore d'évaluation
- Riser DesignDocument1 pageRiser DesignElendu Emmanuel ChigoziePas encore d'évaluation
- Limit StatesDocument1 pageLimit StatesElendu Emmanuel ChigoziePas encore d'évaluation
- Pipeline Construction and Installation EngineeringDocument1 pagePipeline Construction and Installation EngineeringElendu Emmanuel ChigoziePas encore d'évaluation
- Tie inDocument1 pageTie inElendu Emmanuel ChigoziePas encore d'évaluation
- Limit States 1. Ultimate Limit States 2. Serviceability Limit States 3. Fatigue Limit States 4. Accidental Limit StatesDocument1 pageLimit States 1. Ultimate Limit States 2. Serviceability Limit States 3. Fatigue Limit States 4. Accidental Limit StatesElendu Emmanuel ChigoziePas encore d'évaluation
- 2010 OWA Risers and Mooring Lines Integrity Management Based On Real Time Integrity Monitoring PDFDocument19 pages2010 OWA Risers and Mooring Lines Integrity Management Based On Real Time Integrity Monitoring PDFElendu Emmanuel ChigoziePas encore d'évaluation
- Corrosion 1. Dents Are A Part of CorrosionDocument1 pageCorrosion 1. Dents Are A Part of CorrosionElendu Emmanuel ChigoziePas encore d'évaluation
- Method StatementDocument1 pageMethod StatementElendu Emmanuel ChigoziePas encore d'évaluation
- Shore PullingDocument1 pageShore PullingElendu Emmanuel ChigoziePas encore d'évaluation
- BuriedDocument1 pageBuriedElendu Emmanuel ChigoziePas encore d'évaluation
- Replacement For CodeDocument1 pageReplacement For CodeElendu Emmanuel ChigoziePas encore d'évaluation
- Plus OneDocument1 pagePlus OneElendu Emmanuel ChigoziePas encore d'évaluation
- SPanningDocument1 pageSPanningElendu Emmanuel ChigoziePas encore d'évaluation
- PVT Sim For OlgaDocument1 pagePVT Sim For OlgaElendu Emmanuel ChigoziePas encore d'évaluation
- ReferencesDocument1 pageReferencesElendu Emmanuel ChigoziePas encore d'évaluation
- StoriesDocument2 pagesStoriesElendu Emmanuel ChigoziePas encore d'évaluation
- Bottom StabilityDocument1 pageBottom StabilityElendu Emmanuel ChigoziePas encore d'évaluation
- Risers Are Vertical Sections of PipelinesDocument1 pageRisers Are Vertical Sections of PipelinesElendu Emmanuel ChigoziePas encore d'évaluation
- Are You Good To Be Able To Do A Riser AnalysisDocument1 pageAre You Good To Be Able To Do A Riser AnalysisElendu Emmanuel ChigoziePas encore d'évaluation
- Summary of Propeller Design Procedures and Data - Vol IIDocument379 pagesSummary of Propeller Design Procedures and Data - Vol IIasdalfPas encore d'évaluation
- SM - Sheet 2 - Questions PDFDocument3 pagesSM - Sheet 2 - Questions PDFlovely_mhmdPas encore d'évaluation
- Newton's Laws Infographics by SlidesgoDocument27 pagesNewton's Laws Infographics by SlidesgoFirdha TaniaPas encore d'évaluation
- Biconvex WinsDocument4 pagesBiconvex WinsSoorya PrashanthPas encore d'évaluation
- CH 5Document56 pagesCH 5Aldrin taduranPas encore d'évaluation
- HST9 05Document31 pagesHST9 05PedroMiguelCamizanVillegasPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanical PropertiesDocument65 pagesMechanical PropertiesAdamSyukurPas encore d'évaluation
- Forces QSDocument22 pagesForces QSaliza malikPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics Partial III - Dimensionless Groups for Flow ProblemsDocument1 pageFluid Mechanics Partial III - Dimensionless Groups for Flow ProblemsCristianSuarezPas encore d'évaluation
- Body Freedom Flutter of A Blended Wing Body ModelDocument5 pagesBody Freedom Flutter of A Blended Wing Body ModelFraPas encore d'évaluation
- Smith Ch01 8eDocument13 pagesSmith Ch01 8eBilal AhmedPas encore d'évaluation
- Dubai Towers Structural DesignDocument64 pagesDubai Towers Structural DesignKS LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Load Combo Sample As Per BNBCDocument2 pagesLoad Combo Sample As Per BNBCTanvir Hossain TuhinPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 PFE 201Document41 pagesChapter 1 PFE 201Preeti BirwalPas encore d'évaluation
- GDJP Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesGDJP Lesson Plansarathkumar sebastin0% (1)
- Project Summary Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) I17602: Baffle and Wall Feed PlatesDocument12 pagesProject Summary Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) I17602: Baffle and Wall Feed PlatesSteven MesaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid MechanicsDocument2 pagesFluid MechanicsMahesh B R MysorePas encore d'évaluation
- Tension Test of Ofhc CopperDocument7 pagesTension Test of Ofhc CopperUsman ishaqPas encore d'évaluation
- PE Cheat SheetDocument5 pagesPE Cheat Sheetdnl_vicars100% (1)
- Article 3 (2019) - Wang, Jing, Et Al.Document12 pagesArticle 3 (2019) - Wang, Jing, Et Al.Doom RefugePas encore d'évaluation
- Cement and Concrete Research: M.S. Abo Dhaheer, S. Kulasegaram, B.L. KarihalooDocument8 pagesCement and Concrete Research: M.S. Abo Dhaheer, S. Kulasegaram, B.L. KarihalooKhalid EL ABBAOUIPas encore d'évaluation
- 1D Kinematics Problems I SolutionsDocument4 pages1D Kinematics Problems I SolutionsYudhish PayagalaPas encore d'évaluation
- 52 TestBank Chap 1Document17 pages52 TestBank Chap 1Haridev RudrarajuPas encore d'évaluation
- Physics 111: Mechanics Lecture on Energy ConceptsDocument32 pagesPhysics 111: Mechanics Lecture on Energy ConceptsMuhammad Arif RachmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Whirling of Rotating ShaftsDocument11 pagesWhirling of Rotating ShaftsAldrich paul NiñalgaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 7.1 and 7.2 - Static Charge and Electric Force. Balloons & Static ElectricityDocument4 pagesChapter 7.1 and 7.2 - Static Charge and Electric Force. Balloons & Static Electricitymoni tranPas encore d'évaluation
- Waves, Sound and Optics: Team 8 20 May 2022Document5 pagesWaves, Sound and Optics: Team 8 20 May 2022mara gallardoPas encore d'évaluation
- SMK Mantin 2020 Physics Ques Sem 1Document12 pagesSMK Mantin 2020 Physics Ques Sem 1Keertana SubramaniamPas encore d'évaluation
- Ch.04 Force System ResultantsDocument16 pagesCh.04 Force System ResultantsCK_85_3Pas encore d'évaluation