Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Mauche CW 4 7
Transféré par
api-236168782Titre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Mauche CW 4 7
Transféré par
api-236168782Droits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
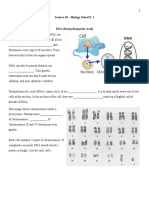
Replication of DNA
The process of copying DNA in a cell is called _____________________. During replication the two ____________________ chains separate by unwinding, each chain serves as a ___________________ for a new nucleotide chain. The first step is the separation of the two __________________ chains. The point at which two chains separate is called the ___________________. The chains are separated by ________________ called ___________________. As the helicase enzymes move along the DNA molecule, they break hydrogen _______________ between complementary bases, and the chain separates. Enzymes called DNA _______________________ bind (or attach) the separated chains of DNA. As DNA ______________________ move along the separated chains, new chains of DNA are __________________________ (or put together) using nucleotides in the surround medium that are complementary to the existing DNA chains (T needs an A, A needs a T, C needs a G, and G needs a C). Nucleotides are joined to the new chains by covalent ________________ between deoxyribose _________________ and __________________ groups. They are joined to the original nucleotide chain by hydrogen ______________. The complementary nature of the two chains of DNA is the foundation for _________________ DNA replication. Suppose that a sequence of nucleotides in one chain of the original DNA molecule is A-T-TC-C-G. DNA __________________ would produce a new nucleotide chain with the sequence T-A-A-G-G-C. DNA replication does not begin at one end of the molecule and proceed to the other. Rather, DNA ___________________ begin replication simultaneously (at the same time) at many points along the separated nucleotide chains. Replication occurring simultaneously (at the same time) at different sites permits ___________ DNA replication. When replication is completed, _______ new copies of the original DNA molecule are produced and the cell is ready to undergo cell _______________ (or to make a copy of itself MITOSIS). Each new DNA molecule consists of one new nucleotide chain joined by hydrogen ___________ to a _________________ chain from the original DNA molecule.
Guided Notes DNA Replication
Name: ______________________________________________ Period: _______________
1. The goal of DNA replication is to make ______
____________________________________ copies.
2. In the cell cycle, DNA is __________________ in S phase of Interphase. 3. Your cells do this so that after Mitosis the two new cells have DNA that is _________________________.
DNA Structure
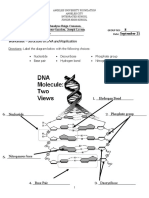
4. What three things make one nucleotide? Label where they are in this picture. ___________________. How many? _______ ___________________. How many? _______ ___________________. How many? _______
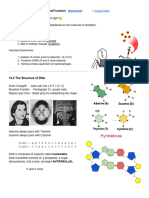
5. A (adenine) and G (guanine) are _________________________. They have __________ rings. 6. C (cytosine) and T (thymine) are _________________________. They have __________ ring. 7. 5 (five prime) end has the ______________________ on top. 8. 3 (three prime) end has the ____________________ on top. 9. ______ is like the beginning of a book and ______ prime is like the end of a book. ALWAYS read from _____ to _____.
S Sugar P - Phosphate
Base Pairs
S Sugar P - Phosphate
DNA Replication Steps
Now the cool stuff happens!! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dKubyIRiN84 DNA strands are unzipped by the enzyme _________________________. ________________________strand forms from the 5 to the 3 end using DNA __________________________. The leading strand is continuous (just keeps going with no breaks). No problem! ________________________ strand has some problems. It has to form from 5 to 3 too! If forms in pieces called Okazaki ________________________. First RNA primase lays down an RNA primer. Then DNA ______________________ lays down the DNA. The process repeats itself again and again. Next DNA polymerase replaces the RNA primers with ______. DNA _______________ links the Okazaki fragments together. At the end of DNA replication the one strand of DNA what we stared with (parent strand) becomes _____ daughter strands of DNA that are ____________________ to the parent strand.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Dna Replication WorksheetDocument3 pagesDna Replication WorksheetSakina İmanovaPas encore d'évaluation
- DNA - Student NotesDocument23 pagesDNA - Student NotesCola ChauPas encore d'évaluation
- DNA Replication WorksheetDocument2 pagesDNA Replication WorksheetMaktoumPas encore d'évaluation
- DNA Replication WorksheetDocument2 pagesDNA Replication WorksheetStrawberry RoPas encore d'évaluation
- DNA RNA WorksheetDocument5 pagesDNA RNA WorksheetKathleen FrancoPas encore d'évaluation
- 7.1 - Nucleic Acids, Ahl: (Adapted From)Document5 pages7.1 - Nucleic Acids, Ahl: (Adapted From)Big CinemaPas encore d'évaluation
- Protein-Synthesis WorksheetDocument5 pagesProtein-Synthesis WorksheetAme RealPas encore d'évaluation
- Science 10 Bio Notes Student VersionDocument29 pagesScience 10 Bio Notes Student VersionEvan HuangPas encore d'évaluation
- Kami Export - Luuk Van Meurs - DNA Replication WorksheetDocument2 pagesKami Export - Luuk Van Meurs - DNA Replication WorksheetLuuk Van MeursPas encore d'évaluation
- DNA Replication Worksheet 2-16-2023 2Document2 pagesDNA Replication Worksheet 2-16-2023 2dfvccfPas encore d'évaluation
- Dna WorksheetDocument8 pagesDna WorksheetLuis100% (6)
- PDFDocument4 pagesPDFYordan Gomez Capellan0% (1)
- FGIKReplicationTeacherKey6!18!15 CompressedDocument16 pagesFGIKReplicationTeacherKey6!18!15 CompressedSantiago Teixeira100% (1)
- Key Key Key Key Key KeyDocument12 pagesKey Key Key Key Key KeyArsalan RabbanianPas encore d'évaluation
- DNA Replication WorksheetDocument1 pageDNA Replication WorksheetBio_Joe100% (2)
- DNA Notes - Student1Document5 pagesDNA Notes - Student1ElPas encore d'évaluation
- Modeling Mitosis ActivityDocument4 pagesModeling Mitosis ActivityJobanie AmadhayPas encore d'évaluation
- Transcription and Translation VIrtual Lab Worksheet-1Document2 pagesTranscription and Translation VIrtual Lab Worksheet-1Jael Oliva EscobarPas encore d'évaluation
- Docsity Cell Division 29Document5 pagesDocsity Cell Division 29Jake KreidelPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 5 Lesson 2 AssignmentDocument4 pagesModule 5 Lesson 2 AssignmentFelix BrockmanPas encore d'évaluation
- The Cell Cycle WorksheetDocument3 pagesThe Cell Cycle WorksheetSelina LiPas encore d'évaluation
- PART 3 DNA SYNTHESIS (REPLICATION) With Test ReviewerDocument5 pagesPART 3 DNA SYNTHESIS (REPLICATION) With Test ReviewerIslam SamirPas encore d'évaluation
- Ds80-Dna Laboratory Formative AssessmentDocument6 pagesDs80-Dna Laboratory Formative Assessmentapi-110789702Pas encore d'évaluation
- Gene Expression – The 40-Character TitleDocument4 pagesGene Expression – The 40-Character TitlepinkPas encore d'évaluation
- DNA replication and the importance of copying DNADocument5 pagesDNA replication and the importance of copying DNAGGPas encore d'évaluation
- Mitosis Teacher NoteDocument4 pagesMitosis Teacher NoteJonathan JayakrishnanPas encore d'évaluation
- Student Exploration: Cell Division: Isabella Jacquin Rivas November 24, 2022Document5 pagesStudent Exploration: Cell Division: Isabella Jacquin Rivas November 24, 2022。Poki 。Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tori Daniel - DNA & RNA Notes - Student PDFDocument4 pagesTori Daniel - DNA & RNA Notes - Student PDFTori DanielPas encore d'évaluation
- Study Guide Dna Rna No VirusDocument4 pagesStudy Guide Dna Rna No VirusLara AlbeeshyPas encore d'évaluation
- DNA Replication: Name: Section: ScoreDocument2 pagesDNA Replication: Name: Section: ScoreashPas encore d'évaluation
- Dna, Rna & Proteins: The Molecules of LifeDocument32 pagesDna, Rna & Proteins: The Molecules of LifeMeri hardinaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Virtual Cell WorksheetDocument2 pagesThe Virtual Cell WorksheetRafael CunetaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 11 - DNA-2021Document42 pagesChapter 11 - DNA-2021thesoccerprince.10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Kami Export - Cell Cycle Notes and VocabDocument5 pagesKami Export - Cell Cycle Notes and VocabVALERIA ACUNA VILLEGASPas encore d'évaluation
- WORKBOOK - Cell DivisionDocument9 pagesWORKBOOK - Cell DivisionAsad AbbasPas encore d'évaluation
- MitosisLabWorksheet 06Document2 pagesMitosisLabWorksheet 06dadangsutisna196195Pas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 5B Notes OutlineDocument19 pagesTopic 5B Notes OutlinehamoudyelmouallemPas encore d'évaluation
- General Biology Quiz Cell CycleDocument2 pagesGeneral Biology Quiz Cell CycleQueng ElediaPas encore d'évaluation
- SNC2D Cell Cycle and Mitosis WorksheetDocument1 pageSNC2D Cell Cycle and Mitosis WorksheetKristin 123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Cycle Worksheet 2Document4 pagesCell Cycle Worksheet 2Rodolf Jones RaboPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Cycle and MitosisDocument4 pagesCell Cycle and MitosisJudy TanPas encore d'évaluation
- 3:5 BioDocument4 pages3:5 BioMaya FinklePas encore d'évaluation
- DNA Guided NotesDocument4 pagesDNA Guided Noteschatnoirsgirlfriend123Pas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Division Pipe Cleaner ActivityDocument3 pagesCell Division Pipe Cleaner Activityanon_374314835Pas encore d'évaluation
- DNA WorksheetDocument2 pagesDNA WorksheetH DPas encore d'évaluation
- Rna and Protein Synthesis Guided NotesDocument6 pagesRna and Protein Synthesis Guided NotesqzweqwPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Transport and Cycle NotesDocument4 pagesCell Transport and Cycle NotesJustin TisPas encore d'évaluation
- DNA Replication Worksheet 1 GROUP 8Document3 pagesDNA Replication Worksheet 1 GROUP 8FINMARPas encore d'évaluation
- DNA and RNA WorksheetsDocument6 pagesDNA and RNA WorksheetsA. Nurul Virninda YusufPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Cycle - Mitosis - Meiosis - STUDENT VERSIONDocument51 pagesCell Cycle - Mitosis - Meiosis - STUDENT VERSIONStacy TroupePas encore d'évaluation
- Key Point - Cell Cycle 2005Document2 pagesKey Point - Cell Cycle 2005Elizabeth GentryPas encore d'évaluation
- Cell Division Worksheet Chapter SummaryDocument18 pagesCell Division Worksheet Chapter SummaryEma Fatimah0% (1)
- A1.2 NotesDocument16 pagesA1.2 NotesteddyenPas encore d'évaluation
- VC 1-Q&A - Cell Cycle & Cell DivisionDocument8 pagesVC 1-Q&A - Cell Cycle & Cell DivisionAnubhab DasPas encore d'évaluation
- Mitosis Song Paired Activity Sheet: Name - DateDocument2 pagesMitosis Song Paired Activity Sheet: Name - Datepurplepink 127Pas encore d'évaluation
- Rna Protein SynthesisDocument6 pagesRna Protein SynthesisDaniel Hanna86% (7)
- Dna WorksheetDocument5 pagesDna Worksheetapi-233187566Pas encore d'évaluation
- DNA Replication Study GuideDocument3 pagesDNA Replication Study Guide黄诗雨Pas encore d'évaluation
- Las in Science 12Document3 pagesLas in Science 12Richez VillaranPas encore d'évaluation
- Mauche Test Survey 4 8 14Document2 pagesMauche Test Survey 4 8 14api-236168782Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Reaction Lab Conclusions 2Document7 pagesChemical Reaction Lab Conclusions 2api-236168782Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Reaction Project Rubric-2Document3 pagesChemical Reaction Project Rubric-2api-236168782100% (1)
- Chemical Reaction Project-3Document3 pagesChemical Reaction Project-3api-236168782Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Reaction LabDocument6 pagesChemical Reaction Labapi-236168782Pas encore d'évaluation
- Meeting 2 12 14Document2 pagesMeeting 2 12 14api-236168782Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mauche CW 3 11 14 ActivityDocument2 pagesMauche CW 3 11 14 Activityapi-236168782Pas encore d'évaluation
- InquriyunitplanDocument18 pagesInquriyunitplanapi-236168782Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mauche HW 3 31 14Document2 pagesMauche HW 3 31 14api-236168782Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mauche Obs 3 19 14 CompleteDocument4 pagesMauche Obs 3 19 14 Completeapi-236168782Pas encore d'évaluation
- Survey1 2Document1 pageSurvey1 2api-236168782Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chemreact Presentation2Document9 pagesChemreact Presentation2api-236168782Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dna ReadingDocument2 pagesDna Readingapi-236168782Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mauche Oct 16 ElementprojectDocument4 pagesMauche Oct 16 Elementprojectapi-236168782Pas encore d'évaluation
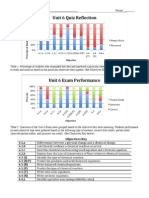
- Unit 6 Quiz Exam ReflectionDocument1 pageUnit 6 Quiz Exam Reflectionapi-236168782Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 6 Quiz-Exam ReflectionDocument7 pagesUnit 6 Quiz-Exam Reflectionapi-236168782Pas encore d'évaluation
- Individ Chemreac Project2Document2 pagesIndivid Chemreac Project2api-236168782Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chemreact PresentationDocument7 pagesChemreact Presentationapi-236168782Pas encore d'évaluation
- Individ Chemreact Project3Document16 pagesIndivid Chemreact Project3api-236168782Pas encore d'évaluation
- Individ Chemreac ProjectDocument2 pagesIndivid Chemreac Projectapi-236168782Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Reaction Lab ConclusionsDocument8 pagesChemical Reaction Lab Conclusionsapi-236168782Pas encore d'évaluation
- Individ Chemreact Project4Document11 pagesIndivid Chemreact Project4api-236168782Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Reaction Project RubricDocument2 pagesChemical Reaction Project Rubricapi-236168782Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Reaction ProjectDocument2 pagesChemical Reaction Projectapi-236168782Pas encore d'évaluation
- News Article 2Document4 pagesNews Article 2api-236168782Pas encore d'évaluation
- Mauche Dec 9 HWDocument2 pagesMauche Dec 9 HWapi-236168782Pas encore d'évaluation
- News Artcle 1 U3 Test AnswersDocument1 pageNews Artcle 1 U3 Test Answersapi-236168782Pas encore d'évaluation
- News Article 1Document2 pagesNews Article 1api-236168782Pas encore d'évaluation
- News Article 1 HWDocument1 pageNews Article 1 HWapi-236168782Pas encore d'évaluation
- Invernol 2021Document18 pagesInvernol 2021Victor JustinianoPas encore d'évaluation
- HW6 Nucleic AcidDocument2 pagesHW6 Nucleic AcidLylePas encore d'évaluation
- 18 DNA Structure and Replication-S 1 PDFDocument5 pages18 DNA Structure and Replication-S 1 PDFZoe101Pas encore d'évaluation
- This Study Resource Was: Complete The Following TasksDocument4 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Complete The Following TasksKathy60% (5)
- Lecture 4 (Cell Mol Biology - Biological Molecules - Gene Structure Function)Document41 pagesLecture 4 (Cell Mol Biology - Biological Molecules - Gene Structure Function)BakalJenazahPas encore d'évaluation
- Biology Chapter 20 Full (47 S.Q'S)Document11 pagesBiology Chapter 20 Full (47 S.Q'S)ranajawad579Pas encore d'évaluation
- Lecture 2Document19 pagesLecture 2MuhammadFakhriAimi100% (1)
- Dna Profiling STR AnalysisDocument1 pageDna Profiling STR Analysisapi-290865873Pas encore d'évaluation
- DNA - The Double Helix, Coloring WorksheetDocument4 pagesDNA - The Double Helix, Coloring WorksheetRob MullerPas encore d'évaluation
- Differences between D- and L-amino acids and their biological rolesDocument5 pagesDifferences between D- and L-amino acids and their biological rolesKrizzi Dizon GarciaPas encore d'évaluation
- DNA Modeling Objectives:: ProcedureDocument5 pagesDNA Modeling Objectives:: ProcedureAyesha MhallawiPas encore d'évaluation
- Fats and OilsDocument36 pagesFats and Oilstafer692002100% (1)
- KORONADAL NATIONAL COMPREHENSIVE HIGH SCHOOL SCIENCE 10 QUARTER 3 TESTDocument3 pagesKORONADAL NATIONAL COMPREHENSIVE HIGH SCHOOL SCIENCE 10 QUARTER 3 TESTRowena Nim100% (2)
- Transcription: From DNA To RNADocument74 pagesTranscription: From DNA To RNAmd habibur rahmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Prodew 400: Amino Acid Based Humectant For Skin CareDocument26 pagesProdew 400: Amino Acid Based Humectant For Skin CareKlara Miliktrisa KirbitievnaPas encore d'évaluation
- 5f9387df86519729ccfa86b7-1603504549-Rey Intro Nucleic-Acids PDFDocument115 pages5f9387df86519729ccfa86b7-1603504549-Rey Intro Nucleic-Acids PDFAriston Blaise Sarte RualesPas encore d'évaluation
- MLS117-Pipetting-Exercises-to-DNA-isolation-NotesDocument4 pagesMLS117-Pipetting-Exercises-to-DNA-isolation-NotesJohanna Marie To-osPas encore d'évaluation
- 2 6 Repair 2002Document26 pages2 6 Repair 2002KhushbuPas encore d'évaluation
- DnareplicationvideonotesamoebasistersDocument2 pagesDnareplicationvideonotesamoebasistersapi-323720899Pas encore d'évaluation
- (Chem 102.2) Polymerase Chain ReactionDocument19 pages(Chem 102.2) Polymerase Chain ReactionRalph John UgalinoPas encore d'évaluation
- DNA Structure and Replication Online Classes I 1 2 3 MYPDocument36 pagesDNA Structure and Replication Online Classes I 1 2 3 MYPMedinaPas encore d'évaluation
- Dna Replication-9Document3 pagesDna Replication-9api-281171147100% (1)
- Biology-ModuleSixLessonThreePathwayThreeActivity RedoDocument7 pagesBiology-ModuleSixLessonThreePathwayThreeActivity Redomiranda50% (4)
- PROTEIN (Polypeptide) : Protein: Senyawa Organik Yang Merupakan Polimer Asam Amino Penyusun ProteinDocument79 pagesPROTEIN (Polypeptide) : Protein: Senyawa Organik Yang Merupakan Polimer Asam Amino Penyusun ProteinDwinur ChasanahPas encore d'évaluation
- Performance Task #1 - Aceron, Barrina, VelasDocument6 pagesPerformance Task #1 - Aceron, Barrina, VelasCalil AceronPas encore d'évaluation
- Activities To Develop Pre-TaskDocument6 pagesActivities To Develop Pre-Taskeduardo arenasPas encore d'évaluation
- ESP Soy Protein Powder Talk Sheet - EnGDocument15 pagesESP Soy Protein Powder Talk Sheet - EnGVanessa VivPas encore d'évaluation
- Formula of The 20 Common Amino AcidsDocument11 pagesFormula of The 20 Common Amino AcidsAngelica AngelesPas encore d'évaluation
- Microbial GeneticsDocument17 pagesMicrobial Geneticsزين العابدين محمد عويش مشريPas encore d'évaluation
- Bds Protein Chemistry 1Document53 pagesBds Protein Chemistry 1Isaiah Johnson100% (1)