Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Rods and Cables Design Problems
Transféré par
lewisbardsonTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Rods and Cables Design Problems
Transféré par
lewisbardsonDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
ASSIGNMENT 1 (INDIVIDUAL)
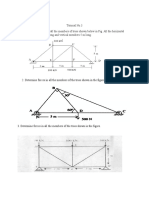
1. Two solid cylindrical rods AB and BC are welded together at B and loaded as shown in Figure 1. Knowing that the average normal stress must not exceed 175 MPa in rod AB and 150 MPa in rod BC, determine the smallest allowable values of d1 and d2.
Figure 1
2.
Member ABC is supported by a pin and bracket at C and a cable BD, was designed to support the 16kN load P as shown. a. Knowing that the ultimate load for cable BD is 100kN, determine the factor of safety with respect to cable failure. b. Knowing that the ultimate load for cable BD is 100kN and that a factor of safety of 3.2 with respect to cable failure is required, determine the magnitude of the largest force P that can be safely applied as shown to member ABC.
Figure 2
3.
Knowing that = 40 and P = 9 kN as shown in Figure 2, determine: (a) the smallest allowable diameter of the pin at B if the average shearing stress in the pin is not to exceed 120 MPa, (b) the corresponding average bearing stress in member AB at B, (c) the corresponding average bearing stress in each of the support brackets at B.
Figure 3.
4.
The 4-mm diameter cable BC is made of a steel with E=200 GPa. Knowing that the maximum stress in the cable must not exceed 190 MPa and that the elongation of the cable must not exceed 6 mm, find the maximum load P that can be applied as shown.
Figure 4
5.
Link BD is made of brass (E =105 GPa) and has a cross-sectional area of 240 mm2. Link CE is made of aluminum (E =72 GPa) and has a cross-sectional area of 300 mm2. Knowing that they support rigid member ABC, determine the maximum force P that can be applied vertically at point A if the deflection of A is not to exceed 0.35 mm.
Figure 5
6.
An axial force of 200 kN is applied to the assembly as shown in Figure 4 by means of rigid end plates. Determine: (a) the normal stress in the aluminum shell, (b) the corresponding deformation of the assembly.
Figure 6
7.
A rod consisting of 2 cylindrical portions AB and BC is restrained at both ends. Portion AB is made of steel (Es=200GPa, s = 11.7 x 10-6/C) and portion BC is made of brass (Eb=105GPa, b = 20.9 x 10-6/C). Knowing that the rod is initially unstressed, determine the compressive force induced in ABC when there is a temperature rise of 50C.
Figure 7 8. A torque of magnitude T = 4 kN-m is applied at end A of the composite shaft shown in Figure 5. Knowing that the modulus of rigidity is 77 GPa for the steel and 27 GPa for the aluminum, determine: (a) the maximum shearing stress in the steel core, (b) the maximum shearing stress in the aluminum jacket, (c) the angle of twist at A.
Figure 8
9.
Under normal operating conditions, the electric motor exerts a torque of 2.8 kN-m on shaft AB. Knowing that each shaft is solid, determine the maximum shearing stress in (a) shaft AB, (b) shaft BC, (c) shaft CD.
Figure 9
10.
A 38-mm-diameter steel shaft of length 1.2 m will be used to trasmitt 45 kW between a motor and a pump. Knowing that G = 77 GPa, determine the lowest speed of rotation at which the stress does not exceed 60 MPa and the angle of twist does not exceed 2.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Statics and Strength of Materials 7th Edition Ebook PDFDocument41 pagesStatics and Strength of Materials 7th Edition Ebook PDFwendy.ramos733Pas encore d'évaluation
- Solution Manual Mechanical Engineering Principles John Bird 1Document24 pagesSolution Manual Mechanical Engineering Principles John Bird 1ridwansadelyPas encore d'évaluation
- Handbook of Physics in Medicine and Biology PDFDocument521 pagesHandbook of Physics in Medicine and Biology PDFYudi TrigunaPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Mechanics Equation SheetDocument11 pagesFluid Mechanics Equation SheetJerone Manley0% (1)
- Physics Test Assignment: Section 1-NumericalDocument2 pagesPhysics Test Assignment: Section 1-Numericalfuny poy0% (2)
- Workbook FMDocument66 pagesWorkbook FMSubhash JhurawatPas encore d'évaluation
- Measuring Speed of Light ExperimentallyDocument2 pagesMeasuring Speed of Light ExperimentallybrettPas encore d'évaluation
- Written Exam, Interaction Design, 7,5 ECTS: Good Luck! Malin Nilsson - 14Document12 pagesWritten Exam, Interaction Design, 7,5 ECTS: Good Luck! Malin Nilsson - 14Stephen MensahPas encore d'évaluation
- UrooewoDocument16 pagesUrooewoRao IndiaPas encore d'évaluation
- NAAC SSR Vol IIDocument407 pagesNAAC SSR Vol IIsummerstoryPas encore d'évaluation
- HCIDocument2 pagesHCIlenciadonickaPas encore d'évaluation
- Writing Papers 3Document4 pagesWriting Papers 3Marin NicolaePas encore d'évaluation
- Group 5: Glendell Atesora Estelle Nica Marie Dunlao Johny Sevilla Jeoffrey Casipong Elny Rose Vio Zweetsel SeñeresDocument45 pagesGroup 5: Glendell Atesora Estelle Nica Marie Dunlao Johny Sevilla Jeoffrey Casipong Elny Rose Vio Zweetsel SeñeresEstelle Nica Marie DunlaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Truss Lecture6xDocument28 pagesTruss Lecture6xJoe JoePas encore d'évaluation
- Som Prob SetDocument50 pagesSom Prob SetAnonymous mXicTi8hBPas encore d'évaluation
- 3-Dimensional Drawings, or Photographic or Pictorial Drawings. Isometric DrawingDocument12 pages3-Dimensional Drawings, or Photographic or Pictorial Drawings. Isometric DrawingHarshit SolankiPas encore d'évaluation
- ENGINEERING MECHANICS Assignment WorkDocument14 pagesENGINEERING MECHANICS Assignment WorkAchyut MorangPas encore d'évaluation
- Kavita Thesis PDFDocument139 pagesKavita Thesis PDFnavpreet bhullarPas encore d'évaluation
- Raja DharmaDocument277 pagesRaja DharmaMahesh KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- TrussDocument5 pagesTrussChaubey AjayPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 3: Structures: TrussesDocument19 pagesChapter 3: Structures: TrussesBadar Sharif100% (1)
- System of CoPlanar Forces Notes Engineering MechanicsDocument7 pagesSystem of CoPlanar Forces Notes Engineering MechanicsKiran BeldarPas encore d'évaluation
- E.M 1Document5 pagesE.M 1Syed Shaul100% (1)
- B.Sc. Software Engineering Project Proposal TemplateDocument7 pagesB.Sc. Software Engineering Project Proposal TemplateengineerPas encore d'évaluation
- CPW Characteristic Impedance FormulaDocument1 pageCPW Characteristic Impedance FormulaAshraff AliPas encore d'évaluation
- KinemaTics Extra Study QuestionsDocument165 pagesKinemaTics Extra Study Questions10chirag10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Introduction to Mechanical Engineering Bridge CourseDocument45 pagesIntroduction to Mechanical Engineering Bridge Coursekrunal07786Pas encore d'évaluation
- Kinematic Analysis MethodsDocument43 pagesKinematic Analysis MethodsSAMRUDDHI SARDARPas encore d'évaluation
- Bandwidth Limitations of Log-Periodic Microstrip Patch Antenna ArraysDocument2 pagesBandwidth Limitations of Log-Periodic Microstrip Patch Antenna ArraysJorge MitrionePas encore d'évaluation
- Footing DETAILDocument1 pageFooting DETAILjeff alcazarPas encore d'évaluation
- Fracture of Cracked MembersDocument21 pagesFracture of Cracked MembersZach DeLukePas encore d'évaluation
- Solved Problems Normal StressDocument3 pagesSolved Problems Normal StressA'TINSB19Pas encore d'évaluation
- Seminar Virtual Reality: Presented By: Dingku Singh Oinam (M.tech CSE, 1 Semester, 20210)Document22 pagesSeminar Virtual Reality: Presented By: Dingku Singh Oinam (M.tech CSE, 1 Semester, 20210)Dingku OinamPas encore d'évaluation
- Free Body DiagramsDocument10 pagesFree Body Diagramsatif irshadPas encore d'évaluation
- CAD Mechanical All TheoriesDocument165 pagesCAD Mechanical All TheoriesMohammedSafuvanKazhungilPas encore d'évaluation
- EM & SOMDocument8 pagesEM & SOMVikram RaoPas encore d'évaluation
- Cadcam Geometric ModelingDocument31 pagesCadcam Geometric ModelingPankaj ChhabraPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter FourDocument65 pagesChapter FourKhanPas encore d'évaluation
- First Semester Engineering Graphics Two Marks With Answers Regulation 2013Document26 pagesFirst Semester Engineering Graphics Two Marks With Answers Regulation 2013PRIYA RAJIPas encore d'évaluation
- Study Problems PDFDocument33 pagesStudy Problems PDFAbdul Hai MohammedPas encore d'évaluation
- Math Ebook CombineDocument653 pagesMath Ebook CombineSantiago KeLvin60% (5)
- Research Into Design For Communities, Volume 2 - Proceedings of ICoRD 2017 (PDFDrive)Document1 036 pagesResearch Into Design For Communities, Volume 2 - Proceedings of ICoRD 2017 (PDFDrive)Aesthetic Arch100% (1)
- MFG Eng HW 10 PDFDocument5 pagesMFG Eng HW 10 PDFVinith PachiappanPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced SurveyingDocument176 pagesAdvanced SurveyingSelvakumarPas encore d'évaluation
- How to Construct Regular PolygonsDocument4 pagesHow to Construct Regular PolygonsMuhammad Nadeem KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- Vedic Mathematics - RajendranDocument3 pagesVedic Mathematics - RajendranAmit Kumar GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Orthographic, Oblique - UnknownDocument37 pagesOrthographic, Oblique - UnknownCHakyeonPas encore d'évaluation
- Approved Calendar of Events 2023-2024 (AB) 1Document3 pagesApproved Calendar of Events 2023-2024 (AB) 1hw hwngethe100% (1)
- Finite Element Model Question PaperDocument4 pagesFinite Element Model Question PaperSrinivasan SriniPas encore d'évaluation
- Principle of Minimum Potential EnergyDocument5 pagesPrinciple of Minimum Potential EnergySaran Jl100% (1)
- Theory of Machines PDFDocument53 pagesTheory of Machines PDFShanmukha SundaramPas encore d'évaluation
- Production Process of Monolithic ICDocument5 pagesProduction Process of Monolithic ICAmanda Spence100% (2)
- 2 - Kinematic Diagrams & Degrees of FreedomDocument21 pages2 - Kinematic Diagrams & Degrees of FreedomSachin Giroh100% (1)
- PDFDocument3 pagesPDFShehena fernando50% (2)
- Building Planning and DrawingDocument203 pagesBuilding Planning and DrawingSelvakumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Engineering Drawing Form 4 (Quadrilaterals)Document14 pagesEngineering Drawing Form 4 (Quadrilaterals)farah sakinah100% (1)
- Engineering DrawingDocument3 pagesEngineering DrawingLeonel ZurbitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Building ConstructionDocument225 pagesBuilding ConstructionSelvakumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Prob SheetDocument20 pagesProb SheetAditya ShuklaPas encore d'évaluation
- TutorialDocument4 pagesTutorialvarjith007Pas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 2 Chapter 2: Axial Load: (Ans 73.7 Gpa)Document12 pagesTutorial 2 Chapter 2: Axial Load: (Ans 73.7 Gpa)ha haPas encore d'évaluation
- How Two Boys Made Their Own Electrical Apparatus Containing Complete Directions for Making All Kinds of Simple Apparatus for the Study of Elementary ElectricityD'EverandHow Two Boys Made Their Own Electrical Apparatus Containing Complete Directions for Making All Kinds of Simple Apparatus for the Study of Elementary ElectricityPas encore d'évaluation
- Doppler EffectDocument38 pagesDoppler EffectIhtisham Ahmad ButtPas encore d'évaluation
- Https Courses Lumenlearning Com Precalctwo Chapter Testing-polar-equations-For-symmetryDocument6 pagesHttps Courses Lumenlearning Com Precalctwo Chapter Testing-polar-equations-For-symmetryAkash TutiPas encore d'évaluation
- Mechanical Design of Overhead LinesDocument9 pagesMechanical Design of Overhead Linesmuhammad_sarwar_27Pas encore d'évaluation
- Pro Olayanju AssDocument3 pagesPro Olayanju AssOladoyin AyodejiPas encore d'évaluation
- CFTSDocument4 pagesCFTSStefan NaricPas encore d'évaluation
- MOHR'S CIRCLE ANALYSISDocument26 pagesMOHR'S CIRCLE ANALYSISMuthoka VincentPas encore d'évaluation
- Ebbing 12Document20 pagesEbbing 12Ra MilPas encore d'évaluation
- Uit RGPV First Year SyllabusDocument19 pagesUit RGPV First Year SyllabusYasir MujtabaPas encore d'évaluation
- FM End-Sem Question Paper - 2021Document1 pageFM End-Sem Question Paper - 2021Anshu MeenaPas encore d'évaluation
- Analytical DynamicsDocument731 pagesAnalytical DynamicsCeleste Romero LongarPas encore d'évaluation
- Magnetic InteractionsDocument13 pagesMagnetic InteractionsZsuzsa BorsayPas encore d'évaluation
- Modal Analysis of Rotating Machinery Structures PDFDocument170 pagesModal Analysis of Rotating Machinery Structures PDFAhmed MohammedPas encore d'évaluation
- CCHE4271: Preliminary Examination in ChemistryDocument8 pagesCCHE4271: Preliminary Examination in ChemistryEkanisaKurniawatiPas encore d'évaluation
- 05-Dinamika Fluida Lanjut - Turbulent FlowDocument17 pages05-Dinamika Fluida Lanjut - Turbulent FlowSri Peni WijayantiPas encore d'évaluation
- Einsteins RefrigeratorDocument2 pagesEinsteins RefrigeratorHua Hidari YangPas encore d'évaluation
- Radiation Safety For Baggage X-Ray Inspection Systems: CanadaDocument83 pagesRadiation Safety For Baggage X-Ray Inspection Systems: CanadaLinssen KongPas encore d'évaluation
- Shell and Tube Heat ExchangerDocument31 pagesShell and Tube Heat ExchangerDhiyyah Mardhiyyah100% (1)
- Bag Bcs Primus t5 Data SheetDocument4 pagesBag Bcs Primus t5 Data SheetAyman ZarefyPas encore d'évaluation
- 7 - GravitationDocument5 pages7 - GravitationAvik DasPas encore d'évaluation
- MELCOR Computer Code Manuals Vol. 2: Reference ManualDocument897 pagesMELCOR Computer Code Manuals Vol. 2: Reference ManualJack CavaluzziPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Chemistry Homework AssignmentDocument3 pagesPhysical Chemistry Homework AssignmentJosef CatiggayPas encore d'évaluation
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science 8: ProceduresDocument8 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in Science 8: ProceduresMc Laurence Marquez SaligumbaPas encore d'évaluation
- Charles' Law AttachmentsDocument4 pagesCharles' Law AttachmentsSherwin UbandoPas encore d'évaluation
- Phy Proj Clas 12 CbseDocument16 pagesPhy Proj Clas 12 CbseNarmadha RameshPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 2 - Waveguide PDFDocument38 pagesChapter 2 - Waveguide PDFHiroshi RayPas encore d'évaluation
- Appendix For GlassDocument2 pagesAppendix For GlassGian ClimacoPas encore d'évaluation
- Entropy Tutorial + SolutionsDocument2 pagesEntropy Tutorial + SolutionsAnonymous 8SemaIglBvPas encore d'évaluation
- Andrianov 2012 Composites Part B EngineeringDocument5 pagesAndrianov 2012 Composites Part B EngineeringKancharla KiranPas encore d'évaluation