Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
Trusts Flowchart - Victorian Property Law
Transféré par
Luke McMahonCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
Trusts Flowchart - Victorian Property Law
Transféré par
Luke McMahonDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
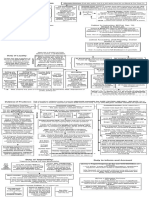
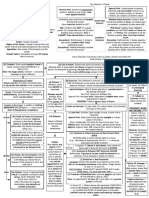
TRUSTS FLOW CHART
1.
ET? s.53(1)(b) PLA must be in writing, signed by Trustee. Must be a clear intention to create a trust. NB: s.53(2) PLA: RTs and CTS do not have to be in writing
2.
RT? Did one party acquire property at the others expense? There must have been a direct financial contribution to the purchase of the property (Calverley v Green); Does the presumption of advancement apply?; OR Is there a contrary intention
3. CT? There are 4 possible types (i) CT from specifically enforceable contract (specific performance) (ii) Common intention CT (iii) Unconscionability CT
(i) Specific performance 1. Contract needs to have been valid and enforceable: a. Be in writing (s53(1) PLA); b. There is sufficient writing (ANZ v Windin): i. The relevant piece of land; ii. The parties who are part of the contract; iii. The relevant amount; and iv. It must be signed by the parties 2. The contract must have been breach (and unenforceable); and 3. There must be no bar to remedy
(i) Common intention CT? Did the parties have a common intention about the beneficial ownership of the property (Rasmussen); and The party claiming the beneficial interest acted to their detriment on the basis of the common intention (Rasmussen; Ogilive); and It would be unconscionable for the legal title holder to deny the interest (Ogilvie) Was there a reasonable expectation?
(ii) Unconscionability CT? 1. Is there a joint venture or polling of resources (Baumgartner); 2. The contributions must be made for the purpose of the joint venture; 3. The property was acquired for the purposes of the joint venture; and 4. It would be unconscionable for the legal owner to deny the beneficial interest of the other party May be difficult to establish if only non-financial contributions made
Is there an oral contract? Part Performance 1. Oral agreement or insufficient writing (ANZ v Windin); 2. Acts done in part performance must be in reliance of the contract or consistent with the contract or on encouragement of the grantor; 3. Unequivocal acts performed for the purpose of carrying out the agreement (Ogilvie); and 4. Other than the writing requirement the agreement is capable of specific performance (Mason v Clarke)
4.
Estoppel Did other party make a representation on which claimant relied to her detriment? Failure to inform claimant of situation where other person knows or ought to know there is reliance is enough (Waltons Stores) Object: to heal detriment, not to make good representation (Verwayen) Court should award minimum equity to do justice (Giumelli)
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Wills, Estates and Trusts TermsDocument20 pagesWills, Estates and Trusts Termsseabreeze100% (1)
- Intestacy, Wills, and Trusts OutlineDocument59 pagesIntestacy, Wills, and Trusts OutlineMissy MeyerPas encore d'évaluation
- Contracts - Breach & RemediesDocument10 pagesContracts - Breach & RemediesDavidPlumpling100% (2)
- Contracts UCCDocument10 pagesContracts UCCTim McDevittPas encore d'évaluation
- Business Associations - Template 4 (Australia)Document7 pagesBusiness Associations - Template 4 (Australia)Marten NguyenPas encore d'évaluation
- Pleading Foreign Law Under Traditional and Modern ApproachesDocument9 pagesPleading Foreign Law Under Traditional and Modern ApproachesLaura C100% (2)
- UCC Article 2 Goods and Merchant RulesDocument5 pagesUCC Article 2 Goods and Merchant Rulesnkolder84100% (1)
- Best - Wills & Trust OutlineDocument68 pagesBest - Wills & Trust OutlineBilly Alvarenga GuzmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Secured Transations OutlineDocument153 pagesSecured Transations OutlineTara Patton100% (1)
- Corps Secret WeaponDocument4 pagesCorps Secret WeaponKeith DyerPas encore d'évaluation
- Bankruptcy OutlineDocument44 pagesBankruptcy Outlinevigilmat100% (1)
- Trusteeship - Fiduciary Obligations ChartDocument1 pageTrusteeship - Fiduciary Obligations Chartseabreeze0% (1)
- Wills & Trusts Bar Checklist OverviewDocument7 pagesWills & Trusts Bar Checklist OverviewroruangPas encore d'évaluation
- Flowchart For UCC 2-207Document1 pageFlowchart For UCC 2-207Matthew LeaperPas encore d'évaluation
- Trusts and Estates Outline Spring 2012 - Professor SterkDocument86 pagesTrusts and Estates Outline Spring 2012 - Professor SterkKeith Dyer100% (4)
- Delaware Wills and TrustsDocument13 pagesDelaware Wills and TrustscaribelitaPas encore d'évaluation
- Non-Probate Assets ChartDocument1 pageNon-Probate Assets ChartseabreezePas encore d'évaluation
- Corporations Outline Provides Overview of Key ConceptsDocument48 pagesCorporations Outline Provides Overview of Key ConceptsNegotiator101Pas encore d'évaluation
- Commerce NotesDocument73 pagesCommerce NotesAgrippa MungaziPas encore d'évaluation
- ENFORCEMENT DEFENSESDocument25 pagesENFORCEMENT DEFENSESalexoganesyan100% (1)
- Introduction To Estate Planning: Wills, Trusts & Estates Professor Catania Fall 2012Document35 pagesIntroduction To Estate Planning: Wills, Trusts & Estates Professor Catania Fall 2012Alex GarrigaPas encore d'évaluation
- Two Types of Power of AppointmentDocument1 pageTwo Types of Power of AppointmentseabreezePas encore d'évaluation
- Property Outline Exam Will Consist of 1 Issue Spotter, 2 or 3 Short Questions Requiring Refined Analysis, andDocument40 pagesProperty Outline Exam Will Consist of 1 Issue Spotter, 2 or 3 Short Questions Requiring Refined Analysis, andddonnik17Pas encore d'évaluation
- Attack Outline - Criminal ProDocument20 pagesAttack Outline - Criminal ProKeiara Pather100% (1)
- Governing Contract Law PrinciplesDocument24 pagesGoverning Contract Law PrinciplesBeth BrashearsPas encore d'évaluation
- Sales Final OutlineDocument44 pagesSales Final OutlineCole Hoffmeister75% (8)
- Property Exam LayoutDocument2 pagesProperty Exam Layoutkzmorg27Pas encore d'évaluation
- Property 2 Notes&BriefsDocument48 pagesProperty 2 Notes&BriefsHaifaPas encore d'évaluation
- Decedents' Estates Flashcards - QuizletDocument19 pagesDecedents' Estates Flashcards - QuizletseabreezePas encore d'évaluation
- Passing Wealth at Death: Wills, Trusts, Estates, and Intestacy RulesDocument16 pagesPassing Wealth at Death: Wills, Trusts, Estates, and Intestacy Rulesjarabbo50% (2)
- Intestate Disposition ChartDocument1 pageIntestate Disposition ChartseabreezePas encore d'évaluation
- Public Policy Considerations in Estate PlanningDocument79 pagesPublic Policy Considerations in Estate Planningkathmk7100% (1)
- Bankruptcy Outline Spring 2012Document66 pagesBankruptcy Outline Spring 2012DLR100% (5)
- Social Media Planning GuideDocument112 pagesSocial Media Planning GuideCristian Ticu100% (4)
- Conflict of Laws OutlineDocument32 pagesConflict of Laws OutlineseabreezePas encore d'évaluation
- UCC 2-207 Flow ChartDocument1 pageUCC 2-207 Flow Charttipo_de_incognitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Debtor-Creditor Outline FinalDocument22 pagesDebtor-Creditor Outline FinalJefff Petty100% (3)
- Contracts Issue ChecklistDocument7 pagesContracts Issue ChecklistKatie CrawfordPas encore d'évaluation
- Corps - Clarke - Short OutlineDocument14 pagesCorps - Clarke - Short OutlineLal LegalPas encore d'évaluation
- Guide to CA Community Property LawDocument18 pagesGuide to CA Community Property LawGPas encore d'évaluation
- Chart of Entity ComparisonDocument4 pagesChart of Entity ComparisonDee BeldPas encore d'évaluation
- Property Law Outline EDITDocument17 pagesProperty Law Outline EDITChris BurgePas encore d'évaluation
- Community Property - Lois SchwartzDocument33 pagesCommunity Property - Lois SchwartzMcApeG3Pas encore d'évaluation
- Agency Contract EssentialsDocument15 pagesAgency Contract EssentialsHer StorePas encore d'évaluation
- Amapofthelaw: Adapted From Managing The Law: The Legal Aspects of DoingDocument1 pageAmapofthelaw: Adapted From Managing The Law: The Legal Aspects of DoingHamraj SidhuPas encore d'évaluation
- For Upload Parol Evidence UCC 2-202Document1 pageFor Upload Parol Evidence UCC 2-202Inez Petersen100% (2)
- Remedies Checklist: Compensation, Debt, Coercion & MoreDocument1 pageRemedies Checklist: Compensation, Debt, Coercion & Moreyoung4180% (1)
- RhinoCAM2020 PPG Decoded GuideDocument55 pagesRhinoCAM2020 PPG Decoded GuideMileta SindjelicPas encore d'évaluation
- Civil Procedure OutlineDocument59 pagesCivil Procedure OutlineThomas JeffersonPas encore d'évaluation
- Bentley AECOsim Building Designer V8i (SELECTseries 4) 08.11.09Document8 pagesBentley AECOsim Building Designer V8i (SELECTseries 4) 08.11.09smartcad60Pas encore d'évaluation
- Final Contracts OutlineDocument29 pagesFinal Contracts Outlineblondimofo100% (1)
- Midterm Q and ADocument33 pagesMidterm Q and ACloieRjPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 4 - Housekeeping (Occupational Safety)Document20 pagesModule 4 - Housekeeping (Occupational Safety)Sam100% (1)
- CIPS L4M1.3.3 Procurement StructureDocument26 pagesCIPS L4M1.3.3 Procurement Structuresami mohmed ali100% (2)
- ICT BlocksDocument16 pagesICT Blocksnextlink80Pas encore d'évaluation
- L01-Project Quality ManagementDocument29 pagesL01-Project Quality ManagementMUHAMMAD AZEEM Khan100% (1)
- Executive Power and The Theory of Its Limits 2011Document20 pagesExecutive Power and The Theory of Its Limits 2011Luke McMahonPas encore d'évaluation
- Torts Outline Fall 2011Document31 pagesTorts Outline Fall 2011Steven Seigel100% (1)
- Trusts and Estates Outline HighlightsDocument182 pagesTrusts and Estates Outline HighlightshelennPas encore d'évaluation
- Contracts Outline-UCC R2kDocument13 pagesContracts Outline-UCC R2kmbeneshPas encore d'évaluation
- UCC 2 207 Flow ChartDocument1 pageUCC 2 207 Flow ChartJojuan GrossPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 1 Section 1 Slides AgencyDocument27 pagesChapter 1 Section 1 Slides AgencyShawn AcostaPas encore d'évaluation
- PJ Flow ChartDocument1 pagePJ Flow ChartMalik DeanPas encore d'évaluation
- CA Bar Property OutlineDocument10 pagesCA Bar Property OutlinechrisngoxPas encore d'évaluation
- OutlineDocument48 pagesOutlinebarg1113100% (1)
- Outline Laura Civil Procedure.Document97 pagesOutline Laura Civil Procedure.Mike Binka KusiPas encore d'évaluation
- Fedincometaxoutline 19Document17 pagesFedincometaxoutline 19ashajimerPas encore d'évaluation
- W&T Good OUTLINEDocument111 pagesW&T Good OUTLINElawstudent10Pas encore d'évaluation
- Torts Fall 2019 OutlineDocument64 pagesTorts Fall 2019 OutlineAmelia Poore100% (1)
- Step Three: Contract Enforceability: Paralegal ChecklistDocument2 pagesStep Three: Contract Enforceability: Paralegal ChecklistDjuna AdamsPas encore d'évaluation
- Crimes Act 1958 - As of July 2013Document561 pagesCrimes Act 1958 - As of July 2013Luke McMahonPas encore d'évaluation
- COURTROOM LEVEL 17 305 William Street, Melbourne WEDNESDAY, 10 JULY 2013Document1 pageCOURTROOM LEVEL 17 305 William Street, Melbourne WEDNESDAY, 10 JULY 2013Luke McMahonPas encore d'évaluation
- Writ of Mandamus - JUDICIARY ACT 1903 - SECT 39B Original Jurisdiction of Federal Court of AustraliaDocument3 pagesWrit of Mandamus - JUDICIARY ACT 1903 - SECT 39B Original Jurisdiction of Federal Court of AustraliaLuke McMahonPas encore d'évaluation
- Principles of Public Law Semester 1 730112Document3 pagesPrinciples of Public Law Semester 1 730112Luke McMahonPas encore d'évaluation
- Bar Dinner SpeechDocument10 pagesBar Dinner SpeechLuke McMahonPas encore d'évaluation
- Administrative Law: Overview of Judicial ReviewDocument4 pagesAdministrative Law: Overview of Judicial ReviewLuke McMahonPas encore d'évaluation
- Options For The Doctrine of Crown ImmunityDocument11 pagesOptions For The Doctrine of Crown ImmunityLuke McMahonPas encore d'évaluation
- C2011A00148Document111 pagesC2011A00148Luke McMahonPas encore d'évaluation
- Resume FinalDocument2 pagesResume Finalapi-507705451Pas encore d'évaluation
- About ASCM - ASCMDocument4 pagesAbout ASCM - ASCMSintoGPas encore d'évaluation
- Decision Tree 1Document9 pagesDecision Tree 1Vanessa FajardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Facebook Marketing Course OverviewDocument3 pagesFacebook Marketing Course OverviewIrfan BhattiPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Incentives Practice Closure or Withdrawal: When To Use This Form Filling in This FormDocument3 pagesPractice Incentives Practice Closure or Withdrawal: When To Use This Form Filling in This Formshaka biasaPas encore d'évaluation
- FlipHTML5, A Fantastic Tool For Converting PDF To Flipbook For FreeDocument2 pagesFlipHTML5, A Fantastic Tool For Converting PDF To Flipbook For FreeHasan TareqPas encore d'évaluation
- Employee Job Order TemplateDocument3 pagesEmployee Job Order TemplateNelson ColoPas encore d'évaluation
- Online Summer ReportDocument13 pagesOnline Summer ReportDevender DhakaPas encore d'évaluation
- Sla PS1 11.16.21 - 2.15.22Document7 pagesSla PS1 11.16.21 - 2.15.22kelly resurreccionPas encore d'évaluation
- Englisch PräsentationDocument10 pagesEnglisch PräsentationAlissa StrandPas encore d'évaluation
- Ifrs Edition: Prepared by Coby Harmon University of California, Santa Barbara Westmont CollegeDocument79 pagesIfrs Edition: Prepared by Coby Harmon University of California, Santa Barbara Westmont CollegeJhoni LiePas encore d'évaluation
- Financial Management in Public Service Delivery in Zambia A Brief Literature ReviewDocument4 pagesFinancial Management in Public Service Delivery in Zambia A Brief Literature ReviewInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyPas encore d'évaluation
- CWC Application FormDocument3 pagesCWC Application FormNiteshPas encore d'évaluation
- Bull Final Q223Document99 pagesBull Final Q223Elijah CherubPas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 CH 1 & 2 SAHAS Pamphlet EditedDocument39 pagesUnit 1 CH 1 & 2 SAHAS Pamphlet EditedDhrumil DesaiPas encore d'évaluation
- SAP Interview QuestionsDocument4 pagesSAP Interview QuestionsAmaranathreddy YgPas encore d'évaluation
- 3.WTO & Implications For Indian EconomyDocument10 pages3.WTO & Implications For Indian EconomyAvanish_Singh_2288Pas encore d'évaluation
- Integrated Farm Training Center Business PlanDocument5 pagesIntegrated Farm Training Center Business PlanWynona Samuelle Fontanilla PingoyPas encore d'évaluation
- Pt. Global Investasindo Indonesia: Success, Safe and ComfortableDocument23 pagesPt. Global Investasindo Indonesia: Success, Safe and Comfortableilhamrabbani8Pas encore d'évaluation
- IC LENDING INVESTORS CORPORATION SUPPLEMENTARY SCHEDULEDocument3 pagesIC LENDING INVESTORS CORPORATION SUPPLEMENTARY SCHEDULEjonely kantimPas encore d'évaluation
- Machine Shop GuideDocument6 pagesMachine Shop GuideZain MirzaPas encore d'évaluation