Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
NCP FORM For Tetralogy
Transféré par
GraceMelendresTitre original
Copyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
NCP FORM For Tetralogy
Transféré par
GraceMelendresDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
NURSING CARE PLAN Tetralogy of Fallot
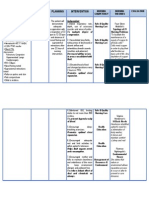
Cues Objective: -V/S: BP:80/50 mmHg PR: 124 bpm RR: 28 cpm Temp: 37.1 C -with O2 inhalation @ 2lpm via nasal cannula as ordered -circumoral cyanosis noted Need Activity and exercise pattern Nursing Diagnosis Impaired gas exchange related to altered oxygen supply as evidenced by dyspnea, tachypnea, tachycardia, and fatigue secondary to Congenital Heart Disease t/c Tetralogy of fallot. Congenital Heart Disease refers to a problem with the hearts structure and function due to abnormal heart development Before birth. It can disrupt the normal flow of blood to the different parts of the body thus affecting the exchange of gasses. Objective of care That within 8 hr span of care the patient will be able to demonstrate improving ventilation as evidenced by: a. Respiratory rate within normal limits b. Absence of cyanosis c. Clear breath sounds on both lung fields d. ABG test result within normal range Interventions and Rationale 1. Establish good trusting relationship with the patient and significant others To gain both trust and cooperation 2. Monitor respiratory rate/depth, use of accessory muscles, areas of cyanosis. Indicators of adequacy of respiratory function or degree of compromise and therapy needs/effectiveness. 3. Auscultate breath sounds, noting presence or absence and adventitious sounds. Development of atelectasis and stasis of secretion can impair gas exchange. 4. Monitor vital signs; note changes in cardiac rhythm. Compensatory. Compensatory changes in vital signs and development of dysrhythmias reflect effects of impaired gas exchange. 5. Help with breathing exercises. Pursed lip breathing. Helps improve oxygen inspiration of the lungs. 6. Elevate head of bed to moderate or high back rest. Helps the lung expand and aids in the relaxation of the muscles decreasing the oxygen demand of the body. Evaluation
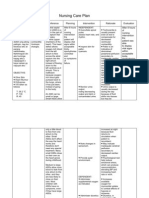
Cues Objectives: -bluish discoloration on lips noted -clubbing of finger noted -nasal flaring -use of accessory muscle noted -with capillary refill time of 3 seconds -with O2 of 2 lpm via nasal cannula as ordered -body weakness noted(allways on bed)
Need Activity and exercise pattern
Nursing Diagnosis Ineffective tissue perfusion (cardiopulmonary) Related to decrease oxygen cellular exchange secondary to congenital heart disease t/c tetralogy of fallot
Objective of care That within 8hours span of care, the patient will be able to have adequate tissue perfusion as evidenced by: a) Absence or decrease bluish discoloration of lips; 1. Due to narrowing of b) Decrease respiratory the artery which rate within normal small amount of range; and oxygenated blood can c) Learn techniques to pass through the minimize or lessen systemic circulation the risk of decrease Which the patient tissue perfusion experience difficulty in breathing.
Interventions and Rationale 1. Monitored skin colour and temp. every 2hours. Assess for signs of skin breakdown. Cool, blanched, mottled skin and cyanosis may indicate tissue perfusion. 2. Monitored and documented patients vital signs every hour. Decrease heart rate and blood pressure may indicate increased arteriovenous exchange,which leads to decrease tissue perfusion. 3. Keep patient warm Warmth aids vasodilation, which improve tissue perfusion. 4. Elevate lower extremities. To increase arterial blood supply and improve tissue perfusion. 5. Change position regularly and inspect skin every shift. To avoid decrease in tissue perfusion and risk of skin breakdown.
Evaluation
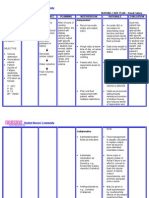
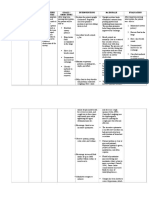
ASSESSMENT
NURSING DIAGNOSES SCIENTIFIC ANALYSIS
PLANNING
NURSING INTERVENTION
RATIONALE
EVALUA-TION
Cyanosis dyspnea delay in growth and development blue anoxia attacks
Risk for Decreased cardiac output related to structural abnormalities of the heart.
Tetralogy fallot results in low oxygenation of blood due to mixing of oxygenated and de oxygenated blood in the left ventricle through the VSD and preferential low of both oxygenated and deoxgenated blood from the ventricles through the aorta because of obstruction to flow through the pulmonary valve.
After 4 hours of nursing intervention the pt, will have adequate cardiac output as evidenced by cardiac rate within normal range.
Assess and record the vital sign. Administer cardiac drugs as ordered. Assess dypsnea,exertion skin color during rest and when active. Avoid allowing the infant to cry for a long period of time,use soft nipple when feeding.
If the patient experience cardiac output he cardiac and respiratory rate will increase and bp will decrease. Cardiac drugs are given to increase the strength of cardiac contractions. Indicates hypoxia and increase oxygen need. Conserves energy,cross cut nipple requires less energy for infant to feed.
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- Improving Neonatal Tissue Perfusion for SepsisDocument2 pagesImproving Neonatal Tissue Perfusion for SepsisNiña Montejo Ealdama100% (1)
- Tof Care PlanDocument4 pagesTof Care Plankayal67% (12)
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosis Pathophysiolog Y Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosis Pathophysiolog Y Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationCharina Aubrey100% (3)
- Tetralogy of Fallot NCPDocument6 pagesTetralogy of Fallot NCPHarlene Joyce ReyPas encore d'évaluation
- Bronchopneumonia Care PlanDocument6 pagesBronchopneumonia Care PlanAbhijit Soundade0% (1)
- Case NCPDocument25 pagesCase NCPJoher Bolante Mendez100% (1)
- Hydrocephalus PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesHydrocephalus Pathophysiologyjon.lag87% (23)
- Bacterial MeningitisDocument2 pagesBacterial MeningitisChristine V. Fernandez100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan Renal FailureDocument11 pagesNursing Care Plan Renal Failurenosevad88850% (2)
- Baby fever nursing careDocument6 pagesBaby fever nursing caregopscharanPas encore d'évaluation
- (NCP) Risk For Decreased Cardiac Output Related To Tetralogy of FallotDocument2 pages(NCP) Risk For Decreased Cardiac Output Related To Tetralogy of FallotSam Alipio0% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of LeukemiaDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of LeukemiaJamaica Aurelio75% (4)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanBhie DizonPas encore d'évaluation
- Imbalance Nutrition Lass Than Body Requirements Related To Loss of Appetite Due To Aging 2Document2 pagesImbalance Nutrition Lass Than Body Requirements Related To Loss of Appetite Due To Aging 2Senyorita KHaye100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Renal FailureDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Renal FailureMark Jason Rabadan100% (1)
- NCP - EdemaDocument1 pageNCP - Edemavipncpusers100% (1)
- NCP Hydrocephalus-Delayed Growth and DevelopmentDocument4 pagesNCP Hydrocephalus-Delayed Growth and DevelopmentCazze Sunio100% (3)
- Care Plan Prep May 13 Rheumatic FeverDocument16 pagesCare Plan Prep May 13 Rheumatic Feverapi-256360167Pas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan For Anaphylactic Shockwith A Primary NursingDocument11 pagesNursing Care Plan For Anaphylactic Shockwith A Primary NursingKenn Harl CieloPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP HydrocephalusDocument3 pagesNCP HydrocephalusCazze SunioPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Near DrowningDocument1 pageNCP Near Drowningchristine louise bernardoPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care Plan 1Document4 pagesNursing Care Plan 1Johndelle Banlasan Hernan100% (1)
- Nursing Interventions for Fever Management: Assessment, Diagnosis, Planning, and EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Interventions for Fever Management: Assessment, Diagnosis, Planning, and EvaluationChristine Esguerra OrozcoPas encore d'évaluation
- Tetralogy of Fallot OverviewDocument12 pagesTetralogy of Fallot OverviewMaricel Agcaoili GallatoPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP - Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisDocument12 pagesNCP - Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisAya BolinasPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBMack Jhed AnarconPas encore d'évaluation
- Buergers Disease NCPDocument5 pagesBuergers Disease NCPNikko Dela Cruz100% (2)
- NCP Increased IcpDocument2 pagesNCP Increased IcphelloaPas encore d'évaluation
- Appendicitis Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramDocument1 pageAppendicitis Pathophysiology - Schematic Diagrambayu jaya adigunaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale: Prioritized Nursing Problem For AtelectasisDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis Nursing Intervention Rationale: Prioritized Nursing Problem For AtelectasisFatima Zainab Matlih IdjiraniPas encore d'évaluation
- CAD NCP Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument3 pagesCAD NCP Decreased Cardiac OutputLeizel Apolonio100% (3)
- Tetanus Case StudyDocument41 pagesTetanus Case StudyFAt Ty100% (1)
- Myocardial Infarction Pathophysiology ExplainedDocument3 pagesMyocardial Infarction Pathophysiology ExplainedAbi Habiling100% (3)
- Course in The WardDocument12 pagesCourse in The WardBunzay GelinePas encore d'évaluation
- NCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument4 pagesNCP - Ineffective Airway ClearanceKim Gabrielle Exene LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Fluid Volume Deficient Patient with Diabetes MellitusDocument2 pagesFluid Volume Deficient Patient with Diabetes MellitusMarlon AnryPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP - Excess Fluid Volume (Aortic Stenosis)Document3 pagesNCP - Excess Fluid Volume (Aortic Stenosis)Daniel Vergara Arce100% (3)
- NURSING CARE PLAN Decreased Cardiac Output FnaDocument2 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN Decreased Cardiac Output FnaAce Dioso Tubasco100% (1)
- NCP - LeprosyDocument3 pagesNCP - LeprosyKevin DarePas encore d'évaluation
- NCP BleedingDocument3 pagesNCP Bleedingapi-316491996Pas encore d'évaluation
- NCP - TBDocument2 pagesNCP - TBPahw BaluisPas encore d'évaluation
- Rheumatic Heart Disease PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesRheumatic Heart Disease Pathophysiologyjethro sanchez100% (1)
- NCP NicuDocument3 pagesNCP NicuNoel Telosa100% (1)
- Assess and Care for Impaired Oral Mucous MembranesDocument2 pagesAssess and Care for Impaired Oral Mucous MembranesNolan Cabral100% (1)
- NCP For CTTDocument1 pageNCP For CTTJen Rhae LimPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocument1 pageNCP Risk For InfectionFielMendozaPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 pagesNursing Care PlanJoshua Pascasio100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for Activity Intolerance and Nutrition ImbalanceDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan for Activity Intolerance and Nutrition ImbalanceEjie Boy Isaga100% (1)
- NCP PTBDocument2 pagesNCP PTBKath TalubanPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Hyperbilirubinemia Staff NursingDocument3 pagesNCP Hyperbilirubinemia Staff NursingVerajoy DaanPas encore d'évaluation
- Oxy Act 2Document5 pagesOxy Act 2Joshua DauzPas encore d'évaluation
- Nursing Care PlanDocument26 pagesNursing Care PlanPrincessLienMondejarPas encore d'évaluation
- Interventions For Critically Ill Patients With Respiratory Problems HandoutsDocument115 pagesInterventions For Critically Ill Patients With Respiratory Problems HandoutsDemuel Dee L. BertoPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP PleuralDocument5 pagesNCP Pleuraljanine_valdezPas encore d'évaluation
- NCPDocument15 pagesNCPCamille PinedaPas encore d'évaluation
- CHRONIC HEART FAILURE CASE STUDYDocument12 pagesCHRONIC HEART FAILURE CASE STUDYMary Cris CanonPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardiac Tamponade Aortic DissectionDocument3 pagesCardiac Tamponade Aortic DissectionJhoeverly TebrioPas encore d'évaluation
- Diseases ConditionDocument8 pagesDiseases ConditionNur faizah bt azmiPas encore d'évaluation
- 1 Cardiac FailureDocument18 pages1 Cardiac FailurepauchanmnlPas encore d'évaluation
- NCP Cardio PrintDocument7 pagesNCP Cardio PrintNicole MapiliPas encore d'évaluation
- Pathophysiology and Treatment of Tetralogy of FallotDocument2 pagesPathophysiology and Treatment of Tetralogy of FallotMark James Melendres100% (12)
- ReAction 3Document1 pageReAction 3GraceMelendresPas encore d'évaluation
- CHN Reaction PaperDocument1 pageCHN Reaction PaperGraceMelendresPas encore d'évaluation
- Abstract 2003 FinalDocument1 pageAbstract 2003 FinalGraceMelendresPas encore d'évaluation
- Maquet - Training - Respiratory - Crash CourseDocument25 pagesMaquet - Training - Respiratory - Crash Coursejolujan6258Pas encore d'évaluation
- Unit 1 Embryo Q and A ModuleDocument76 pagesUnit 1 Embryo Q and A ModuleBAYAN NADER YOSRI JABARI 22010404Pas encore d'évaluation
- Basics of Nursing Care: Human Dignity, Ethics and SafetyDocument108 pagesBasics of Nursing Care: Human Dignity, Ethics and SafetyYsmech SalazarPas encore d'évaluation
- Polycythemia VeraDocument22 pagesPolycythemia VeraMelisande Rae CiruelaPas encore d'évaluation
- EXAM-Medical - CANJA NR42Document11 pagesEXAM-Medical - CANJA NR42joshua canjaPas encore d'évaluation
- OJT Application Form TitleDocument8 pagesOJT Application Form TitleTagreed MeshrefPas encore d'évaluation
- Pharmacology II Lab Manual New - Updated2.0Document70 pagesPharmacology II Lab Manual New - Updated2.0Bella AstilahPas encore d'évaluation
- Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDocument4 pagesPregnancy Induced HypertensionFatmah Sarah CornellPas encore d'évaluation
- Pulmonary Vascular DiseaseDocument4 pagesPulmonary Vascular DiseaseSaima JabbarPas encore d'évaluation
- Understanding CHF and Monitoring Fluid StatusDocument4 pagesUnderstanding CHF and Monitoring Fluid StatusWeng RamojalPas encore d'évaluation
- HyperlipidemiaDocument22 pagesHyperlipidemiamaritzaPas encore d'évaluation
- Level 3 Anatomy and Physiology 50 Mock Questions + AnswersDocument16 pagesLevel 3 Anatomy and Physiology 50 Mock Questions + AnswersMultifurious TechPas encore d'évaluation
- PHENYLEPHRINEDocument3 pagesPHENYLEPHRINERoger Jr PumarenPas encore d'évaluation
- Advanced Proteomics and Cluster Analysis For Identifying Novel Obstructive Sleep Apnea Subtypes Before and After CPAP TherapyDocument34 pagesAdvanced Proteomics and Cluster Analysis For Identifying Novel Obstructive Sleep Apnea Subtypes Before and After CPAP Therapy马三强Pas encore d'évaluation
- Dr Ashish Jha's CVDocument3 pagesDr Ashish Jha's CVVaishnavi GuptaPas encore d'évaluation
- Differential Diagnosis of The Diseases With Systolic MurmursDocument2 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of The Diseases With Systolic MurmursXiang Yun TanPas encore d'évaluation
- Cardio conditions management guideDocument6 pagesCardio conditions management guideLaura Lopez RocaPas encore d'évaluation
- Aortic AneurysmDocument20 pagesAortic AneurysmMargaretta LimawanPas encore d'évaluation
- Jfo14261 AmDocument18 pagesJfo14261 AmLunaPas encore d'évaluation
- The Muscular System ExplainedDocument22 pagesThe Muscular System ExplainedFiraol DiribaPas encore d'évaluation
- Calcium channel blocker and antacid drug studiesDocument28 pagesCalcium channel blocker and antacid drug studiessfkjalkhsafgPas encore d'évaluation
- Fluids and ElectrolytesDocument6 pagesFluids and Electrolytessabrina AliPas encore d'évaluation
- Chest Trauma - PIBDocument21 pagesChest Trauma - PIBJayarasti KusumanegaraPas encore d'évaluation
- The Urinary System: Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical CollegeDocument91 pagesThe Urinary System: Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical CollegeNicole NipasPas encore d'évaluation
- 1st Prof + Supl Questions Aio 2010-21Document87 pages1st Prof + Supl Questions Aio 2010-21Kashif GhazaliPas encore d'évaluation
- Chronic Kidney Disease ManagementDocument3 pagesChronic Kidney Disease ManagementAngie MandeoyaPas encore d'évaluation
- Cholestest LDLDocument3 pagesCholestest LDLAntz GrownesiaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chest Pain FinalDocument17 pagesChest Pain FinalVarun R'MenonPas encore d'évaluation
- NeoplasiaDocument45 pagesNeoplasiaQanita RehmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Meckel's Diverticulum: I. EpidemiologyDocument6 pagesMeckel's Diverticulum: I. EpidemiologyAlessandra EndozoPas encore d'évaluation