Académique Documents
Professionnel Documents
Culture Documents
UNSCO 2014 Exam
Transféré par
wakuserCopyright
Formats disponibles
Partager ce document
Partager ou intégrer le document
Avez-vous trouvé ce document utile ?
Ce contenu est-il inapproprié ?
Signaler ce documentDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
UNSCO 2014 Exam
Transféré par
wakuserDroits d'auteur :
Formats disponibles
2014 U.S.
NATIONAL CHEMISTRY
OLYMPIAD
Local Section Exam
Using the Answer Panel
This "answer panel" at the bottom of the window is pre-set to show 10
answer boxes per page.
1. The current question has a black border.
2. Questions that have been answered will be tinted.
3. Click Submit to record your answer.
4. Any answer can be edited. Submit the correction.
5. > moves to the next set of questions ( < moves back )
6. Click on any number to answer that question.
Answers are saved and stored when Submit is used. When you have
completed the test, select Finished Test to return to your Test
Center and Log out.
Page 2 Property of ACS USNCO Not for use as a USNCO Local Section Exam after March 31, 2013
ABBREVIATIONS AND SYMBOLS CONSTANTS
amount of substance n
ampere A
atmosphere atm
atomic mass unit u
Avogadro constant N
A
Celsius temperature C
centi prefix c
coulomb C
density d
electromotive force E
energy of activation E
a
enthalpy H
entropy S
equilibrium constant K
Faraday constant F
free energy G
frequency v
gas constant R
gram g
hour h
joule J
kelvin K
kilo prefix k
liter L
measure of pressure mm Hg
milli prefix m
molal m
molar M
molar mass M
mole mol
Plancks constant h
pressure P
rate constant k
reaction quotient Q
second s
speed of light c
temperature, K T
time t
vapor pressure VP
volt V
volume V
R = 8.314 Jmol
1
K
1
R = 0.0821 Latmmol
1
K
1
1 F = 96,500 Cmol
1
1 F = 96,500 JV
1
mol
1
N
A
= 6.022 10
23
mol
1
h = 6.626 10
34
Js
c = 2.998 10
8
ms
1
0 C = 273.15 K
1 atm = 760 mm Hg
EQUATIONS
o
ln
RT
E E Q
nF
=
1
ln constant
H
K
R T
A | || |
= +
| |
\ .\ .
2
1 1 2
1 1
ln
a
E k
k R T T
| | | |
=
| |
\ . \ .
1 PERIODIC TABLE OF THE ELEMENTS 18
1A 8A
1
H
1.008
2 13 14 15 16 17
2A 3A 4A 5A 6A 7A
2
He
4.003
3
Li
6.941
4
Be
9.012
5
B
10.81
6
C
12.01
7
N
14.01
8
O
16.00
9
F
19.00
10
Ne
20.18
11
Na
22.99
12
Mg
24.31
3
3B
4
4B
5
5B
6
6B
7
7B
8
8B
9
8B
10
8B
11
1B
12
2B
13
Al
26.98
14
Si
28.09
15
P
30.97
16
S
32.07
17
Cl
35.45
18
Ar
39.95
19
K
39.10
20
Ca
40.08
21
Sc
44.96
22
Ti
47.88
23
V
50.94
24
Cr
52.00
25
Mn
54.94
26
Fe
55.85
27
Co
58.93
28
Ni
58.69
29
Cu
63.55
30
Zn
65.39
31
Ga
69.72
32
Ge
72.61
33
As
74.92
34
Se
78.96
35
Br
79.90
36
Kr
83.80
37
Rb
85.47
38
Sr
87.62
39
Y
88.91
40
Zr
91.22
41
Nb
92.91
42
Mo
95.94
43
Tc
(98)
44
Ru
101.1
45
Rh
102.9
46
Pd
106.4
47
Ag
107.9
48
Cd
112.4
49
In
114.8
50
Sn
118.7
51
Sb
121.8
52
Te
127.6
53
I
126.9
54
Xe
131.3
55
Cs
132.9
56
Ba
137.3
57
La
138.9
72
Hf
178.5
73
Ta
180.9
74
W
183.8
75
Re
186.2
76
Os
190.2
77
Ir
192.2
78
Pt
195.1
79
Au
197.0
80
Hg
200.6
81
Tl
204.4
82
Pb
207.2
83
Bi
209.0
84
Po
(209)
85
At
(210)
86
Rn
(222)
87
Fr
(223)
88
Ra
(226)
89
Ac
(227)
104
Rf
(261)
105
Db
(262)
106
Sg
(263)
107
Bh
(262)
108
Hs
(265)
109
Mt
(266)
110
Ds
(281)
111
Rg
(272)
112
Cn
(285)
113
(Uut)
(284)
114
(Uuq)
(289)
115
(Uup)
(288)
116
(Uuh)
(293)
117
(Uus)
(294)
118
(Uuo)
(294)
58
Ce
140.1
59
Pr
140.9
60
Nd
144.2
61
Pm
(145)
62
Sm
150.4
63
Eu
152.0
64
Gd
157.3
65
Tb
158.9
66
Dy
162.5
67
Ho
164.9
68
Er
167.3
69
Tm
168.9
70
Yb
173.0
71
Lu
175.0
90
Th
232.0
91
Pa
231.0
92
U
238.0
93
Np
(237)
94
Pu
(244)
95
Am
(243)
96
Cm
(247)
97
Bk
(247)
98
Cf
(251)
99
Es
(252)
100
Fm
(257)
101
Md
(258)
102
No
(259)
103
Lr
(262)
1) A 4.369 g sample of metal is placed in a f lask. Water is
added t o th e f lask a nd th e to tal v olume in t he f lask is
read t o be 126.4 ml. The mass of the water, flask, and
metal is 268. 5 g. If the mass of the flask is 139. 3 g and
the d ensity o f water is 1.000 g/ mL, t he d ensity o f t he
solid is ________ g/cm
3
.
(A) 2.78 (B) 3.21
(C) 0.366 (D) 0.641
2) A cube of an unknown metal measures 0.250 cm on one
side. T he mass o f the c ube is 0 .095 g. Which o f t he
following is most likely the unknown metal?
(A) niobium (B) copper
(C) zirconium (D) vanadium
3) Solids have a __________ shape and are not appreciably
__________.
(A) definite, compressible
(B) sharp, convertible
(C) indefinite, incompressible
(D) definite, incompressible
4) An atom of
118
Xe contains __________ neutrons.
(A) 54 (B) 172
(C) 118 (D) 64
5) A certain mass of carbon reacts with 23.3 g of oxygen to
form carbon monoxide. __________ grams of oxygen
would react with that same mass of carbon to form
carbon dioxide, according to the law of multiple
proportions?
(A) 11.7 (B) 23.3
(C) 233 (D) 46.6
6) A correct name for Fe(NO
3
)
2
is __________.
(A) ferric nitrate (B) ferrous nitrate
(C) ferric nitrite (D) iron nitrite
7) What is the empirical formula of a compound that
contains 27.0% S, 13.4% O, and 59.6% Cl by mass?
(A) SO
2
Cl (B) SOCl
(C) ClSO
4
(D) SOCl
2
8) One mole of __________ contains the largest number of
atoms.
(A) Na
3
PO
4
(B) S
8
(C) Cl
2
(D) C
10
H
8
9) The c ombustion o f pr opane ( C
3
H
8
) i n the p resence o f
excess oxygen yields CO
2
and H
2
O:
C
3
H
8
(g) + 5O
2
(g) 3CO
2
(g) + 4H
2
O (g)
When 2. 5 mol of O
2
are co nsumed i n t heir r eaction,
__________ mol of CO
2
are produced.
(A) 5.0 (B) 1.5
(C) 2.5 (D) 3.0
10) How many grams of NaOH (MW = 40.0) are there in
500.0 mL of a 0.225 M NaOH solution?
(A) 4.50 (B) 114
(C) 0.113 (D) 0.00219
11) A weak electrolyte exists predominantly as _________
in solution.
(A) molecules (B) an isotope
(C) ions (D) atoms
12) Which of the following are weak electrolytes?
HCl
HC
2
H
3
O
2
NH
3
KCl
(A) HCl, HC
2
H
3
O
2
, NH
3
, KCl
(B) HC
2
H
3
O
2
, NH
3
(C) HCl, HC2H3O2, KCl
(D) HCl, KCl
13) When a queous solutions o f A gNO
3
and N aCl ar e
mixed, A gCl p recipitates. The b alanced n et i onic
equation is __________.
(A) Ag
+
(aq) + Cl
-
(aq) AgCl (s)
(B) Ag
+
(aq) + NO
3
-
(aq) AgNO
3
(s)
(C) AgNO
3
(aq) + NaCl (aq) AgCl (s) + NaNO
3
(aq)
(D) AgNO
3
(aq) + NaCl (aq) AgCl (aq) + NaNO
3
(s)
14) The value of E for a system that performs 151 kJ of
work on i ts s urroundings a nd l oses 79 k J of h eat i s
________ kJ.
(A) +72 (B) -151
(C) -230 (D) -72
15) A s ample o f aluminum metal a bsorbs 11. 2 J of heat,
upon which the temperature of the sample increases from
23.2 C t o 3 0.5 C. Since t he s pecific heat cap acity o f
aluminum is 0. 90 J /g-K, the mass o f the s ample i s
________ g.
(A) 1.7 (B) 72
(C) 10. (D) 65
16) Which one of the following conditions would always
result in an increase in the internal energy of a system?
(A) The system gains heat and does work on the
surroundings.
(B) The system loses heat and does work on the
surroundings.
(C) The system gains heat and has work done on it by
the surroundings.
(D) The system loses heat and has work done on it by
the surroundings.
17) Identify the color that has a wavelength of 700 nm.
(A) blue (B) green
(C) red (D) yellow
18) Choose the transition (in a hydrogen atom) below that
represents the absorption of the shortest wavelength
photon.
(A) n = 1 to n = 2 (B) n = 6 to n = 5
(C) n = 3 to n = 1 (D) n = 4 to n = 6
19) Which one of the following represents an acceptable set
of quantum numbers for an electron in an atom?
(arranged as n, l, m
l
, and m
s
)
(A) 3, 3, -4, 1/2 (B) 3, 2, -2, -1/2
(C) 3, 4, 6, -1/2 (D) 3, 2, 0, 0
20) Which element would be expected to have chemical
and physical properties closest to those of rubidium?
(A) Fe (B) Cu
(C) K (D) Ca
21) 2F
2
(g) + 2H
2
O (l) ________
(A) 4HF (aq) + 2O
2-
(aq)
(B) 2F
-
(aq) + 2H
+
(aq) + H
2
O
2
(aq)
(C) 4HF (aq) + O
2
(g)
(D) 2HF
2
(aq) + 2OH
-
(aq)
22) The list that correctly indicates the order of metallic
character is ________.
(A) O > Se > S (B) Sr > Ca > Mg
(C) Li > Na > K (D) C > Ge > Si
23) Based on the octet rule, boron will most likely form a
__________ ion.
(A) B3+ (B) B1+
(C) B3- (D) B2-
24) A valid Lewis structure of __________ cannot be
drawn without violating the octet rule.
(A) SeF
4
(B) PO
4
3-
(C) SiF
4
(D) CF
4
25) The oxidation number of iron in Fe2O3 is __________.
(A) +2 (B) +1
(C) -2 (D) +3
26) Of the atoms below, __________ is the least
electronegative.
(A) Ca (B) Ba
(C) Sr (D) Be
27) Of the following, __________ cannot accommodate
more than an octet of electrons.
(A) Y (B) Ni
(C) C (D) As
28) Using the table of average bond energies below, the H
for the reaction is __________ kJ.
CO (g) + 2H
2
(g) H
3
C-O-H (g)
Bond: C-O C=O CO C-H H-H O-H
D (kJ/mol): 358 799 1072 413 436 463
(A) +735 (B) +276
(C) -735 (D) -116
29) The molecular geometry of t he l eft-most car bon at om
in the molecule below is __________.
(A) T-shaped (B) octahedral
(C) trigonal bipyramidal (D) tetrahedral
30) According to VSEPR theory, if there are s ix el ectron
domains i n t he valence shell o f a n a tom, t hey will b e
arranged in a(n) __________ geometry.
(A) octahedral
(B) tetrahedral
(C) linear
(D) trigonal bipyramidal
31) The L ewis s tructure o f c arbon m onoxide i s gi ven
below. T he hybridizations o f t he c arbon a nd o xygen
atoms i n c arbon monoxide a re ___ _______ a nd
__________, respectively.
: C O :
(A) sp
2
, sp
3
(B) sp
2
, sp
2
(C) sp
3
, sp
2
(D) sp, sp
32) There is/are __________ bond(s) in the molecule
below.
(A) 1 (B) 2
(C) 12 (D) 13
33) A balloon originally had a volume of 4.39 L at 44 C
and a pressure of 729 torr. The balloon must be cooled to
________ C to reduce its volume to 3.99 L (at constant
pressure).
(A) 0.00 (B) 15.1
(C) 546 (D) 288
34) A gas mixture of Ne and Ar has a total pressure of 4.00
atm and contains 16.0 mol of gas. If t he partial pressure
of Ne i s 2. 75 a tm, how many moles of Ar a re i n t he
mixture?
(A) 5.00 (B) 11.0
(C) 12.0 (D) 9.25
35) One significant difference between gases and l iquids i s
that ________.
(A) a gas is made up of molecules
(B) a gas may consist of both elements and compounds
(C) gases are always mixtures
(D) a gas expands to fill its container
36) In liquids, the attractive intermolecular forces are
________.
(A) very weak compared with kinetic energies of the
molecules
(B) strong enough to hold molecules relatively close
together but not strong enough to keep molecules from
moving past each other
(C) strong enough to hold molecules relatively close
together
(D) strong enough to keep the molecules confined to
vibrating about their fixed lattice points
37) Which of the following has dispersion forces as its only
intermolecular force?
(A) C
6
H
13
NH
2
(B) CH
3
Cl
(C) NaCl (D) CH
4
38) What intermolecular force is responsible for the fact
that ice is less dense than liquid water?
(A) hydrogen bonding
(B) dipole-dipole forces
(C) London dispersion forces
(D) ionic bonding
39) In a saturated solution of a salt in water, ________.
(A) the rate of dissolution > the rate of crystallization
(B) the rate of crystallization = the rate of dissolution
(C) seed crystal addition may cause massive
crystallization
(D) the rate of crystallization > the rate of dissolution
40) Which one of the following is most soluble in hexane
(C
6
H
14
)?
(A) CH
3
CH
2
CH
2
CH
2
CH
2
OH
(B) CH
3
CH
2
CH
2
OH
(C) CH
3
CH
2
OH
(D) CH
3
CH
2
CH
2
CH
2
OH
41) As the concentration of a solute in a solution increases,
the freezing point of the solution ________ and the
vapor pressure of the solution ________.
(A) decreases, increases
(B) decreases, decreases
(C) increases, decreases
(D) decreases, is unaffected
42) Nitrogen dioxide decomposes to nitric oxide and oxygen
via the reaction:
2NO
2
(g) 2NO (g) + O
2
(g)
In a particular experiment at 300 C, [NO
2
] drops from
0.0100 to 0.00800 M in The rate of appearance of O
2
for
this period is ________ M/s.
(A) 2.0 10-3 (B) 1.0 10-5
(C) 4.0 10-5 (D) 4.0 10-3
43) The graph shown below depicts the relationship
between concentration and time for the following
chemical reaction.
The slope of this line is equal to __________.
(A) -k (B) ln[A]
o
(C) -1/k (D) k
44) A r eaction was f ound t o be zer o order i n A. I ncreasing t he
concentration o f A b y a f actor o f 3 will cau se t he r eaction
rate to __________.
(A) increase by a factor of 27
(B) decrease by a factor of the cube root of 3
(C) triple
(D) remain constant
45) According to the Arrhenius concept, an acid is a substance
that __________.
(A) tastes bitter
(B) is capable of donating one or more H
+
(C) causes an increase in the concentration of H
+
in
aqueous solutions
(D) reacts with the solvent to form the cation formed by
autoionization of that solvent
46) The conjugate base of H
2
PO
4
-
is __________.
(A) HPO
4
-2
(B) H
2
PO
4
(C) PO
4
-3
(D) H
3
PO
4
47) What is the pOH of an aqueous solution at 25.0
C that contains 3.98 10
-9
M hydronium ion?
(A) 5.600 (B) 7.000
(C) 9.000 (D) 3.980
48) Which one of the following pairs cannot be
mixed together to form a buffer solution?
(A) KOH, HNO
2
(B) H
2
SO
3
, KHSO
3
(C) NaCl, HCl (D) RbOH, HF
49) S is positive for the reaction ________.
(A) 2NO
2
(g) N
2
O
4
(g)
(B) BaF
2
(s) Ba
2+
(aq) + 2F
-
(aq)
(C) 2H
2
(g) + O
2
(g) 2H
2
O (g)
(D) 2Hg (l) + O
2
(g) 2HgO (s)
50) For the reaction
C
2
H
6
(g) C
2
H
4
(g) + H
2
(g)
H is +137 kJ/mol and S is +120 J/K mol.
This reaction is ________.
(A) spontaneous only at high temperature
(B) nonspontaneous at all temperatures
(C) spontaneous only at low temperature
(D) spontaneous at all temperatures
51) Which one of the following processes produces a
decrease in the entropy of the system?
(A) dissolution of LiOH(s) in water
(B) freezing of Fe(l) into Fe(s)
(C) melting ice to form water
(D) evaporation of liquid ethanol into gaseous ethanol
52) Which element is reduced in the reaction below?
Fe(CO)
5
(l) + 2HI (g) Fe(CO)
4
I
2
(s) + CO (g) + H
2
(g)
(A) I (B) O
(C) Fe (D) H
53) What is the coefficient of the permanganate ion when
the following equation is balanced?
MnO
4
-
+ Br
-
Mn
2+
+ Br
2
(acidic solution)
(A) 2 (B) 1
(C) 3 (D) 4
54) Which one of the following reactions is a redox
reaction?
(A) Pb
2+
+ 2Cl
-
PbCl
2
(B) NaOH + HCl NaCl + H
2
O
(C) AgNO
3
+ HCl HNO
3
+ AgCl
(D) None of the above is a redox reaction.
55) Isotopes of hydrogen ________.
(A) have different atomic numbers and different mass
numbers
(B) have the same atomic number and different mass
numbers
(C) are exactly alike
(D) have the same atomic number and the same mass number
56) Which halogen is the most easily oxidized?
(A) Cl (B) Br
(C) I (D) F
57) Which condensed structure below representing an
alkane is not correct?
(A) CH
3
CH
2
CH
3
(B)
(C) CH
3
CH
2
CH
2
CH
3
(D)
58) Give the number of covalent bonds that a carbon
atom can form.
(A) 2 (B) 1
(C) 4 (D) 3
59) Identify the formula for an alkyne.
(A) C
n
H
2n
(B) C
n
H
2n+4
(C) C
n
H
2n+2
(D) C
n
H
2n-2
60) Molecules with the same formula but different
structures are called.
(A) achiral. (B) diastereomers.
(C) structural isomers. (D) enantiomers.
END OF TEST
Vous aimerez peut-être aussi
- 2003 Local Chemistry Olympiads Exam Question PapersDocument7 pages2003 Local Chemistry Olympiads Exam Question PapersRSLPas encore d'évaluation
- General Chemistry Exam with 30 Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument4 pagesGeneral Chemistry Exam with 30 Multiple Choice QuestionsAbdelfattah Mohamed OufPas encore d'évaluation
- Bcfnl08ans Space 3Document26 pagesBcfnl08ans Space 3Martin LeePas encore d'évaluation
- Chem 1100 and 1110 Exam 2 October 28 2009 Answer KeyDocument8 pagesChem 1100 and 1110 Exam 2 October 28 2009 Answer KeyElizabeth McKennaPas encore d'évaluation
- PRACTICE FINALDocument14 pagesPRACTICE FINALLakeshia AlvaradoPas encore d'évaluation
- Exam t2 2011.12 Chemistry f6 p1Document10 pagesExam t2 2011.12 Chemistry f6 p1asjawolverinePas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry 151 Final Exam ReviewDocument9 pagesChemistry 151 Final Exam ReviewNesrine LaradjiPas encore d'évaluation
- Cnhemistry 11 em Book Back One Mark Reduced SyllabusDocument14 pagesCnhemistry 11 em Book Back One Mark Reduced Syllabuselavarasannatesan0Pas encore d'évaluation
- CHEM101 172 Final SolvedDocument12 pagesCHEM101 172 Final SolvedTorong VPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Exam 1st Tri Multiple Choice 2016-2017 - KeyDocument7 pagesPractice Exam 1st Tri Multiple Choice 2016-2017 - KeyJohn YuanPas encore d'évaluation
- Acs Local Exam 1990Document10 pagesAcs Local Exam 1990kateexdPas encore d'évaluation
- chemistry practise questionDocument12 pageschemistry practise questiong24n3950Pas encore d'évaluation
- Narayana... Iit Jee PaperDocument26 pagesNarayana... Iit Jee PaperAbhishek KumarPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry Question Bank For HiighschoolDocument221 pagesChemistry Question Bank For HiighschoolsakuraleeshaoranPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry 151 Study Session For Exam 3 KeyDocument5 pagesChemistry 151 Study Session For Exam 3 KeymiketolPas encore d'évaluation
- Unofficial Acs Practice Test 01 ADocument11 pagesUnofficial Acs Practice Test 01 AMaggie Zhang100% (1)
- Review Exam 2Document9 pagesReview Exam 2justinsong213Pas encore d'évaluation
- All India Test Series For Iit-JeeDocument16 pagesAll India Test Series For Iit-JeeApex Institute100% (1)
- IE Review Chemistry TrackDocument3 pagesIE Review Chemistry TrackRugi Vicente RubiPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Questions For Chemistry EdexcelDocument7 pagesPractice Questions For Chemistry EdexcelPrinceIbz100% (1)
- Periodic Classification and PropertiesDocument10 pagesPeriodic Classification and PropertiesDhruv KuchhalPas encore d'évaluation
- Aieee 2009 Model Paper 1Document7 pagesAieee 2009 Model Paper 1Vicky_Munnetul_7889Pas encore d'évaluation
- Midterm Preparation DocumentDocument15 pagesMidterm Preparation DocumentbettieboomPas encore d'évaluation
- AP Chemistry Electrochemistry MCQsDocument5 pagesAP Chemistry Electrochemistry MCQsMohammed AbdelhakeemPas encore d'évaluation
- Quice Review Center: C) The Total Mass of The Atom A) RBDocument5 pagesQuice Review Center: C) The Total Mass of The Atom A) RBMary Francia RicoPas encore d'évaluation
- 2008 EXAM 2 For PRACTICE With Answers HighlightedDocument6 pages2008 EXAM 2 For PRACTICE With Answers HighlightedTricia Lee CairnsPas encore d'évaluation
- UPSEE Sample Papers 2 (UPSEE Chemistry Questions Paper 2)Document6 pagesUPSEE Sample Papers 2 (UPSEE Chemistry Questions Paper 2)Firdosh KhanPas encore d'évaluation
- 218 FinalDocument17 pages218 FinalmhaymourPas encore d'évaluation
- JEE Main Chemistry Model Paper 5Document6 pagesJEE Main Chemistry Model Paper 5PremKumarKalikiriPas encore d'évaluation
- Summative Exams For General and Analytical ChemistryFOR STUDENTDocument5 pagesSummative Exams For General and Analytical ChemistryFOR STUDENTsantos earlPas encore d'évaluation
- Tutorial 4 - ElectrochemistryDocument3 pagesTutorial 4 - ElectrochemistryAnis IssabellaPas encore d'évaluation
- CHEMISTRY BAMISE SS3 Mock EXAMDocument6 pagesCHEMISTRY BAMISE SS3 Mock EXAMPAUL VICTOR100% (2)
- RT Solutions-30!01!2012 XII ABCD Part Test IIDocument12 pagesRT Solutions-30!01!2012 XII ABCD Part Test IIvishal27042233Pas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry MockDocument4 pagesChemistry MockfaithPas encore d'évaluation
- Monica Bedi: 12+ Years of Teaching Experience Trained Million+ Students - Top Ranker's Series (TRS)Document65 pagesMonica Bedi: 12+ Years of Teaching Experience Trained Million+ Students - Top Ranker's Series (TRS)Alkash BaigPas encore d'évaluation
- AP 02 Multiple ChoiceDocument16 pagesAP 02 Multiple ChoiceKat TomasPas encore d'évaluation
- Question Bank Chemistry-2Document40 pagesQuestion Bank Chemistry-2Karanam.Ramakumar100% (1)
- Aieee 2012 Chem Sit yDocument4 pagesAieee 2012 Chem Sit yVaibhav SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- JEE Main Sample PaperDocument15 pagesJEE Main Sample PaperAnweshaBose100% (1)
- Diagnostic ExamDocument12 pagesDiagnostic ExamAnabel AbulenciaPas encore d'évaluation
- ch021 Us HistoryDocument27 pagesch021 Us Historyphdf5s2p5gPas encore d'évaluation
- JEE Main Chemistry Model Paper 4Document7 pagesJEE Main Chemistry Model Paper 4PremKumarKalikiriPas encore d'évaluation
- CHM1102Document10 pagesCHM1102AliPas encore d'évaluation
- F18 1040 MT - wScanTronDocument8 pagesF18 1040 MT - wScanTronAhmed OsmanPas encore d'évaluation
- Berg Fall 2008 T1-4Document70 pagesBerg Fall 2008 T1-4Jules BrunoPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemistry 101 Final Exam-B Fall 2014Document13 pagesChemistry 101 Final Exam-B Fall 2014Kristopher Park SolivenPas encore d'évaluation
- AP Summer Assignment 2012 #1 Answer KeyDocument5 pagesAP Summer Assignment 2012 #1 Answer KeyTanveer SinghPas encore d'évaluation
- 2009 Practice Exam 2 With Answers HighlightedDocument6 pages2009 Practice Exam 2 With Answers HighlightedTricia Lee CairnsPas encore d'évaluation
- Practice Test 4Document14 pagesPractice Test 4shreyshreyPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem 126 Common 3 Part I Summer 2014Document6 pagesChem 126 Common 3 Part I Summer 2014jnv jnecionwPas encore d'évaluation
- Half Yearly Exam 2021-22 Class XI ChemistryDocument9 pagesHalf Yearly Exam 2021-22 Class XI ChemistryAbhinandan KatochPas encore d'évaluation
- Olympiad Model Paper 2018Document9 pagesOlympiad Model Paper 2018deeyamullaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chapter 4 ElectrolysisDocument8 pagesChapter 4 ElectrolysisPremPas encore d'évaluation
- Single Choice Type Questions on Crystal Structure and ColloidsDocument188 pagesSingle Choice Type Questions on Crystal Structure and ColloidsGadde Gopala Krishna100% (2)
- Practice Exam 2Document9 pagesPractice Exam 2N193746Pas encore d'évaluation
- 11U Chemistry Exam Review Questions (Part 1) Units 1 - 3Document9 pages11U Chemistry Exam Review Questions (Part 1) Units 1 - 3tareqrxPas encore d'évaluation
- PoopDocument11 pagesPoopkurt2011100% (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionD'EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionÉvaluation : 5 sur 5 étoiles5/5 (1)
- Some Rules or Hints For Writing Lab ReportsDocument3 pagesSome Rules or Hints For Writing Lab ReportswakuserPas encore d'évaluation
- Dollhouse MurdersDocument1 pageDollhouse MurderswakuserPas encore d'évaluation
- Current Syl Lab UsDocument5 pagesCurrent Syl Lab UswakuserPas encore d'évaluation
- Quick Study For Computer Keyboard Short CutsDocument2 pagesQuick Study For Computer Keyboard Short Cutsmahazari100% (3)
- AgricultureDocument3 pagesAgriculturewakuserPas encore d'évaluation
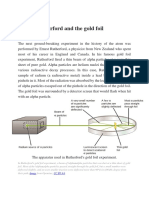
- Rutherford's gold foil experiment reveals the nuclear model of the atomDocument25 pagesRutherford's gold foil experiment reveals the nuclear model of the atomsohaib389892Pas encore d'évaluation
- Kinetic Molecular Theory of SolidDocument2 pagesKinetic Molecular Theory of SolidJasmine DelasasPas encore d'évaluation
- Chemical Bonds and Molecular Shape Summary PDFDocument4 pagesChemical Bonds and Molecular Shape Summary PDFSukfcPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 1.1 Kinetic Molecular Theory (Study Guide)Document12 pagesLesson 1.1 Kinetic Molecular Theory (Study Guide)Wilmark Rivera OfficialPas encore d'évaluation
- Grade 12 Quiz Bee2Document5 pagesGrade 12 Quiz Bee2Oliric FabiolasPas encore d'évaluation
- TPJC Prelim Exam 2009 H2 Chemistry Paper 1 QuestionsDocument14 pagesTPJC Prelim Exam 2009 H2 Chemistry Paper 1 QuestionsAmos YapPas encore d'évaluation
- Water PDFDocument60 pagesWater PDFWillGeePas encore d'évaluation
- States of Matter: Condensed PhasesDocument35 pagesStates of Matter: Condensed PhasesJr ParaynoPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 4 Bonding 4.1to 4.5 14.1to 14.2Document156 pagesTopic 4 Bonding 4.1to 4.5 14.1to 14.2SujithPas encore d'évaluation
- CHEM 15 Fundamentals of Chemistry Course Objectives, Outline and Grading SystemDocument2 pagesCHEM 15 Fundamentals of Chemistry Course Objectives, Outline and Grading SystemPaul Jeremiah Serrano NarvaezPas encore d'évaluation
- Attractive Forces Myers Chapter 4Document39 pagesAttractive Forces Myers Chapter 4Damian ezequiel BenitoPas encore d'évaluation
- Solid State Puc II 1Document41 pagesSolid State Puc II 1Rimmy AugustinePas encore d'évaluation
- FullDocument350 pagesFullgeorgePas encore d'évaluation
- CH 2 WaterDocument52 pagesCH 2 WaterahmedaznjadatPas encore d'évaluation
- Investigating Solubility and Acid-Base ReactionsDocument11 pagesInvestigating Solubility and Acid-Base ReactionsJackie MolstadPas encore d'évaluation
- ABM HUMMS Physical Science EM5 - Intermolecular ForcesDocument4 pagesABM HUMMS Physical Science EM5 - Intermolecular ForcesThe Lone WolfPas encore d'évaluation
- Gases Lecture4 NotesDocument5 pagesGases Lecture4 Notesro.ramji1Pas encore d'évaluation
- (Lecture 1) Molecular StructureDocument32 pages(Lecture 1) Molecular StructureKasraSrPas encore d'évaluation
- Physical Science: Quarter 1 - Module 4: Polarity of Molecules and Its PropertiesDocument23 pagesPhysical Science: Quarter 1 - Module 4: Polarity of Molecules and Its PropertiesNihara SultanPas encore d'évaluation
- Supramolecular Ordering in Oligothiophene-Fullerene MonolayersDocument7 pagesSupramolecular Ordering in Oligothiophene-Fullerene MonolayersNadia WilsonPas encore d'évaluation
- Revision Notes AS ChemistryDocument44 pagesRevision Notes AS ChemistryzaheeraPas encore d'évaluation
- Emt 2132 Introduction To Material Science PDFDocument52 pagesEmt 2132 Introduction To Material Science PDFStephanie MirañyiPas encore d'évaluation
- Organic Chemistry DK024Document19 pagesOrganic Chemistry DK024RosdianaPas encore d'évaluation
- 3rd-Quarter Midterm in Physical Science12Document7 pages3rd-Quarter Midterm in Physical Science12Gerry Chel-Nunez Awa-Laurente AgaPas encore d'évaluation
- Lesson 1 Student Handout 1Document3 pagesLesson 1 Student Handout 1Brion ReynosoPas encore d'évaluation
- Module 4 - Physical Science PDFDocument10 pagesModule 4 - Physical Science PDFDarry Blancia100% (1)
- ChemistryDocument10 pagesChemistryAman PDPas encore d'évaluation
- BSC I Sem SyllabusDocument29 pagesBSC I Sem SyllabuspdarshiPas encore d'évaluation
- Topic 7 Unit 07 Lp01ps - Van Der Waal Forces OkkkkaaaaayyyyyyyyDocument26 pagesTopic 7 Unit 07 Lp01ps - Van Der Waal Forces OkkkkaaaaayyyyyyyyRodjhen Anne P. BarquillaPas encore d'évaluation
- Chem 12Document15 pagesChem 12Glenn ClementePas encore d'évaluation